Abstract
The COVID-19 disease has forced countries to make a considerable collaborative effort between scientists and governments to provide indicators to suitable follow-up the pandemic’s consequences. Mathematical modeling plays a crucial role in quantifying indicators describing diverse aspects of the pandemic. Consequently, this work aims to develop a clear, efficient, and reproducible methodology for parameter optimization, whose implementation is illustrated using data from three representative regions from Chile and a suitable generalized SIR model together with a fitted positivity rate. Our results reproduce the general trend of the infected’s curve, distinguishing the reported and real cases. Finally, our methodology is robust, and it allows us to forecast a second outbreak of COVID-19 and the infection fatality rate of COVID-19 qualitatively according to the reported dead cases.
Keywords: Mathematical modeling, Parameter estimation method, Predictive modeling, Computational model, Epidemiological modeling
1. Introduction
From the early stage of the pandemic, the Chilean government has strengthened the health system by increasing the number of intensive care unit beds and mechanical ventilation devices for critically ill patients. Currently, the government is enhancing tools for tracing capture on cases and contacts of confirmed COVID-19 patients. A collaborative effort among the main universities, the ministries of health and science, technology, knowledge, and innovation produced a web platform for data analysis. The site provides key indicators to represent the state and evolution of the pandemic. These indicators are meant to provide timely and clear information to the authorities, communication media, citizenship, and the scientific community to understand the pandemic evolution and improve decision-making.
Mathematical modeling plays a crucial role in quantifying indicators describing diverse aspects of the pandemic. Many research groups in Chile have developed mathematical models, and providing a comprehensive review would ask for much unnecessary effort. Therefore, we selected some that have produced periodic reports on COVID-19, which we comment on next and partly use ideas. It is worth noting that, in general, these works do not provide details on the methodology, which would be desirable to reproduce results scientifically.
The Center for Mathematical Modeling (CMM) group provided mainly simulations, not predictions. Their results aimed to estimate the maximum capacity required for intensive care unit beds and simulate different opening scenarios (for teaching and economic activities). They developed complex modeling based on a generalization of the SEIR compartmental model, including variables for hospitalized, separating those requiring critical services, and even age structures, and containing several parameters making it difficult to deal with in the sense of forecasting; see the website. [7].
The COVID-19 University of Concepción (UdeC) group provided simulations and predictions. Their results aim to predict the curve of real infected for different datasets encompassing the Ñuble, Bío-Bío regions, and the entire country and simulate different scenarios with or without confinements. They developed a variant of the SEIR compartmental model, adding a fraction to account for the proportion of real infected observed by the RT-PCR tests and carrying out parameter estimation to calibrate each dataset. In our work, we used some of their ideas and compared some of our results of calibration for the Ñuble Region; see the website [6].
We want to note that the research group of the previous paragraph and other manuscripts [8] support their ideas in the fact that there are unreported cases or that only a fraction of the real infected is observed. Indeed, data is measured with great uncertainty, as we explain in Section 2, and consequently has been reviewed and changed retrospectively. In this sense, we aim to obtain a suitable model that fits the data and forecast the general trend of the real infected’ curve, despite the uncertainty in data. We believe that the way is not constructing a complex model. In that case, the parameter estimation required to make the model calibration becomes very difficult or even impossible to do in real-time or does not necessarily provide suitable results. Concerning this, we cite the work [14] that used a complex generalization of the SEIR model proposed in [21], and applied it Chilean data until April 14, 2020, obtained that the peak of infected would occur between April and May, an unsuitable prediction that may be explained because data were near to its zero equilibrium, as we will discuss in Section 4.
Parameter estimation involves solving an inverse problem: given a model and measurements of some state or output variables, the parameters that characterize the system, i.e., those producing a good fit of the model with the data, need to be identified [1], [11]. This problem is difficult since no unique analytical or numerical solution is usually available [1], [11]. Even if a unique solution was available, suitable initial guesses are required by optimization solvers to compute suitable parameter estimates [1], [11]. From the previous discussion, the main goal of the present study was to describe a hybrid approach [10], i.e., a methodology that holistically mixes mathematical modeling and experimental design, which is required, as shown in the literature, for better understanding the studied system by fitting parameters of a given model with a specific scenario and for obtaining models with predictive capability. In particular, we aim to develop a clear, efficient, and reproducible methodology for optimization parameters, whose implementation is illustrated by using data from three representative regions from Chile and a suitable generalized SIR model. The methodology relies on a numeric procedure called the Trust-Region-Reflective optimization algorithm. Simultaneously, we computed the model’s predictive power using goodness-of-fit criteria and assessed parameter uncertainty through sensitivities that yield the standard errors.
2. A generalized SIR model with constant time delays and fitted positivity rate
The classical SIR model’s main assumptions are that the mean infection and recovery rates are positive constants over time, which is not necessarily realistic for a given disease. In COVID-19, when a susceptible has just been infected does not instantaneously show symptoms. There should be a time-delay period due to the SARS-CoV-2 incubation. Similarly, the infected subjects are not recovered or dead instantaneously, but this would occur within a time-delay period. Indeed, these time-delay periods for both phenomena, incubation, and removed (by recovery or dead), are well documented and reported, e.g., in [23].
In this work, we consider the following generalization of the classical SIR model (adapted from the model from Book by Hairer et al. [15] p. 295; [19]), which we will call generalized SIR model with constant time delays:
The parameters of the model (1) are that corresponds to the average number of contacts per person per time, multiplied by the probability of disease transmission in exposure between a susceptible and an infectious subject (see first report at the web site [7]), or more simply, is the mean rate of disease transmission; is the mean removal rate, which in the classical SIR model represents the average time of infection duration; is the mean incubation time of disease; is the median time from onset to clinical recovery or death caused by disease, or the duration time of disease until recovery or death.
Parameter depends essentially on two factors: the disease characteristics and the contact rate within the population [12]. Since we cannot modify the disease characteristics, authorities can foster or even impose incentives to each individual to reduce his/her contact rate with other individuals in the population, causing a decrease in . Consequently, we consider variable in time to consider mitigation strategies dynamics of COVID-19 such as scenarios confinement and opening at different periods.
The variables of model (1) are:
-
1.
, the number of susceptible individuals;
-
2.
, the number of infectious individuals;
-
3.
, the number of removed (and immune), or deceased individuals.
The initial conditions have to satisfy , where is the size of the population under study for a closed system and taking into account that for all , and where is a day chosen suitably after the pandemic began, and which varies for every studied population (in Chile, the first infected subject was detected on March 02, 2020). We remark that the model (1) considers the symptomatic and presymptomatic subjects since the term at the right-hand side of Eq. (1a) represents the number of infected cases that do not manifest symptoms yet since the infection is under incubation.
The solution of model (1) will be defined in , where is defined as the first time at which the infected number becomes zero, i.e., . From Eq. (1b), we have that for every , if and only if
or equivalently
| (2) |
In Eq. (2), is the effective reproductive number of the generalized SIR model with constant time delays (1), is the effective reproductive number in the classical SIR model, and is the ratio of the latent over the removed infected.
It is worth to note that the generalized SIR model with constant time delays can generate a complex dynamics since, as we will see in Section 4, by contrast to the classical SIR model, it can simulate more than one local maximum, providing thus a way to explain a COVID-19 second-outbreak, as already observed in some European countries.
We assume that infectious subjects are detected only when RT-PCR tests are applied to them, and their results are positive. Therefore the observation of this variable is equivalent to the number of positive RT-PCR tests. In this sense, the number of asymptomatic subjects in the population is underestimated, given that they are difficult to detect since they do not manifest any symptoms. Therefore this variable is difficult to observe with accuracy, so we did not consider it in our modeling directly.
Remark
The generalized SIR model with constant time delays would produce better prediction results than the classical SEIR model since no observation of the exposed population is available. This is because, similarly to the asymptomatic population, the exposed are difficult to observe. Indeed, the Chilean government database [16], [17], apart from the symptomatic cases, counts the asymptomatic cases, and there is no way to know how many become symptomatic ones.
By contrast, the symptomatic cases are detected as symptoms manifest themselves, and the RT-PCR test confirms the infection. Therefore, this variable is relatively well-observed, provided that the RT-PCR tests are reliable and enough are available. Taking this into account, we assume that the daily number of infected with symptoms reported by the ministry of health, denoted by , is underestimated since it depends on the availability and proper application of RT-PCR tests; see the presentation on COVID-19 in Chile in [2]. Consequently, we assume that is a fraction of the actual number of infected cases , i.e.,
| (3) |
In Eq. (3), is the ratio between positive RT-PCR tests number and the real infected cases for day , which accounts for the real positivity rate. It is worth noting that is related to the positivity rate of detected cases, denoted by , reported by the Ministry of Health, and defined as the proportion of tests that result positive to the total number of applied tests for day , denoted by . Let us denote by the ratio of actual infected cases to the total number of applied tests, and by the proportion of asymptomatic infected subjects to the actual infected ones, where stands for the asymptomatic infected reported for day . Since the number of positive detected cases corresponds to the total number of confirmed infected reported with and without symptoms, , then it easily follows that
| (4a) |
| (4b) |
From (4b), one has that if then . In addition, assuming that for some constant satisfying that where is the maximum of , which can be determined from data, from (4a) it can be proven that .
We modeled in the same way as Cabrera-Vives et al.; see the first report in [6]. That is to say, is an inverted Sigmoid-type function such that if is small enough, which occurred during the beginning of the outbreak, then an important fraction of the real infected cases are detected (). On the contrary, when is large enough, which occurred just before the quarantines were imposed, then only a small fraction of the real infected cases are detected (). Precisely, is defined as
| (5) |
whose parameters are and , where and represent the minimum and the decay rate of , respectively. On the other hand, the measure of how large/small is is given by a threshold such that implies , and implies .
3. Material and methods
This section describes the data and the methodology used for estimating the optimal parameters that produce the model’ fit to the data.
The data corresponds to the reported Chilean government’s daily official cases at the regional level in the current year, which we used to predict the COVID-19 spreading. We chose data from some representative regions of the north, south, and central zones. Specifically, we worked with the Antofagasta, the Metropolitan, and the Ñuble regions, where the Metropolitan Region is the most populous and which capital is Santiago of Chile, the country’s capital. The data we used is available from the web site [17]; also, the countrywide level data is at [16]. The data in [17] contains not only the number of confirmed cases but also the size of targeted populations () and the periods of quarantines per commune.
3.1. Scenarios for the fittings and forecastings
We fitted the model (1) to each dataset by taking into account different scenarios that encompass, at least, three phases of the pandemic spreading: an early stage characterized by low dissemination and levels of daily new infected cases relatively low, followed by a fast-propagation under quarantine, a measure taken by the Ministry of Health as a reaction to the first phase in a selective way by sectors that may encompass several communes of the region at different periods, characterized by a fast increasing of daily new infected cases and finally, a spreading slowdown stage where the quarantine is relaxed. In a general way, to account for the phases described, we modeled the mean rate of COVID-19 transmission by a piecewise constant function as
| (6) |
In Eq. (6), denotes the mean rate of transmission for every scenario , is the number of scenarios, stands for the indicator (or characteristic) function of the time interval that corresponds to the th scenario, is the initial time, and is the maximal time of existence of model solutions, defined in Section 2. For the three datasets considered, the initial condition was imposed at a day chosen with respect to day 1 that corresponds to March 03, 2020, when it began to measure the infected in the three targeted regions.
From the definition (6), we denote the model parameters as the vector
, where is the minimum of scenarios to calibrate the model (1) to the data. In our computations, for the Antofagasta Region dataset, we split the second phase into two to capture the real behavior of COVID-19 expansion more accurately due to two differentiated periods of quarantine in that region, taking in that case.
Finally, we simulated a possible change of scenario, which was evaluated by computing the relative errors predicting data after the final calibration time. To do that, we solved the model (1) by taking a mean rate of transmission , as in (6), adding one more scenario to the computed from the calibration, and letting vary to verify the value that forecasts the best possible the data after the calibration. To be precise, we solved the model (1) by redefining as
| (7) |
where denotes the parameters estimated for the fitting of every dataset (computed together with ), the time represents a new change of scenario, extends until the last predicted datum, and describes the value of the mean rate of transmission after the time ( means no change of scenario).
3.2. Identifiability analysis of model’ parameters
In this section, we explain in detail the methodology to conduct the identifiability analysis of model’ parameters, i.e., finding the parameters of the generalized SIR model with constant time delays (1) that best fit to the every dataset.
3.2.1. Direct and inverse problem
Given a parameters vector , the direct problem consists of finding the (unique) solution of model (1) with initial condition imposed at a suitable initial time, after the pandemic began. The solution to the direct problem is required to solve the inverse problem. The present study aimed to forecast and simulate different scenarios of COVID-19 expansion in Chile, for which we developed a clear, efficient, and reproducible methodology to solve the parameter identification problem. This procedure is referred to as the inverse problem, i.e., given data that provides observations of the variable , namely , for some time points to identify the parameters vector such that the mathematical model (1) fits the data in the sense of the least-squares. More precisely, to solve the inverse problem of parameter estimation, we have to find the vector that minimizes the sum of squares
| (8) |
The objective function defined in (8) corresponds to the sum of squares of the absolute errors relative to the size of the targeted population , i.e., of the differences between the daily number of infected reported with symptoms, , and the theoretical daily symptomatic infected , which is a fraction of the real symptomatic infected , corresponding to the model solution evaluated at at days , for a given value of the parameters vector , and where is the size of each dataset. The variable depends on and , while the fraction depends on and , with .
The minimum of the sum of squares is designated as for every dataset. The vector is called the nonlinear least-squares estimator denoted as nonlinear LSE hereafter. To minimize , we applied the Trust-Region Interior Reflective (TIR) method implemented in Matlab© as the subroutine lsqnonlin, specially adapted for solving nonlinear least-squares minimization problems.
Below, we describe the entire methodology extensively. In Section 3.2.2, we provide details on the implementation of the lsqnonlin solver, specifically on the procedure to assess the quality of the optimal solution , and on the stopping criterion associated with the algorithm, both concerning the convergence. Also, we computed the fit performance by some goodness-of-fit criteria and represented graphically the traditional sensitivity functions associated with the nonlinear LSE to assess parameter uncertainty, as explained in Section 3.2.3.
3.2.2. Parameter estimation
Convergence of TIR method, as described in [9], is theoretically achieved under general conditions. However, in practice, the convergence depends strongly on the initial parameter estimations, which has to be relatively close to the optimal solution. We were able to efficiently minimize the objective function by a trial and error process, by executing the codes hundreds of times, to guess the suitable initial parameters vector that is different for every dataset [1], [11]. It is worth noting that the initial parameters that mostly influence the fitting results are that describe the mean rate of COVID-19 transmission, according to the scenarios of expansion. As usual, there is a tradeoff among how well the model outputs fit the empirical data, the number of parameters (increasing ), and the risk of overfitting. Moreover, there is the human factor involved in selecting the time intervals associated with each parameter , although changes in lockdown policies determine reasonable interval boundaries. We will estimate parameters using hand-picked intervals to address this issue, justifying our choices in Section 4. In Section 4.4, we will explore our results’ robustness using equal length intervals and varying values of .
To evaluate the objective function , we numerically solved the model (1) at days for different parameters vectors depending on every dataset by applying a Runge–Kutta type formulae [22]. We invoked the subroutine dde23 implemented in Matlab© , designed for solving delay differential equations (DDE) systems with constant time delays. In addition, we had to reconstruct the function of history for the model (1) by interpolating the daily reported data of infected with symptoms, recovered and dead considered for every dataset. The interpolation used is a shape-preserving piecewise cubic as devised by the interp1 Matlab subroutine with the option pchip.
As for the options chosen for the lsqnonlin solver, we first choose the TIR method as the optimization algorithm, which is the default. Secondly, the maximum number of iterations was set at 1,000, while the maximum number of function evaluations was set at 20,000. Finally, the function tolerance was set at , whereas the norm of step tolerance, denoted by , was set variable between and , depending on the targeted dataset. The norm of the step measures the change between two successive iterates and , which is defined as:
| (9) |
On the other hand,
| (10) |
is the relative change in the sum of squares. The stopping criterion for our algorithm is defined as:
| (11) |
When the previous condition is met, the algorithm stops at iteration and returns an approximation of the nonlinear LSE , as well as an approximation of the Jacobian matrix evaluated at for every dataset; see Section 3.2.3 for details. To check the convergence of the algorithm, we also provided the first-order optimality measure, which measures how close the approximation is to the actual minimum of the sum of squares under the criterion of first-order partial derivatives. The first-order optimality measure is defined as the infinity norm of the gradient of the objective function evaluated at the nonlinear LSE , i.e., the maximum absolute value of the partial derivatives of the objective function with respect to the variables:
| (12) |
Other metrics that quantify convergence are the norm of the step , the relative change in the sum of squares (see Eqs. (9)–(10)), and the number of iterations . Optionally, lsqnonlin displays the metrics of convergence at the end of its execution.
We computed the model parameters within the following bounds: , days (the average for the time of incubation and removal, by recovery or death, is 5 and 14 days respectively; see [23]), , in the time interval considered, and all the rest of parameters are positive (i.e., between and ).
3.2.3. Goodness-of-fit criteria and parameter uncertainty
We used statistical methods (from the context of nonlinear least-squares regression) to quantify the fit performance of the model to the data. More precisely, once estimating the nonlinear LSE , one may compute several goodness-of-fit criteria, which evaluate how well the model (1) fits each dataset. We calculated and , the unbiased variance of the residuals, and the root mean square error (RMSE) defined respectively in [3], [13] as
| (13) |
If the residuals were normally distributed or if the datasets sizes were sufficiently large, then the estimated covariance matrix, and the sensitivities associated with the nonlinear LSE would be expressed as
| (14) |
| (15) |
| (16) |
The matrix is called the traditional sensitivity function, and it quantifies the variation of the state variable with respect to changes in the parameters vector components . Sensitivity analysis can provide information about the relevance of data measurements to identify parameters; it then yields the basis for new tools to design inverse problem studies; see [4] for details. By using the covariance matrix given in (14), we can compute the standard errors, , and the normalized standard errors, , associated to the nonlinear LSE from which we could quantify the accuracy of the parameter estimate. Both quantities are defined by
| (17) |
The quantities defined by (14)–(17) are asymptotic, i.e., they are valid only if each dataset size is sufficiently large because the nonlinear least-squares estimators are asymptotically normally distributed [3], [13]. We computed the and the sensitivities of parameters , , with a larger than 100%; see (16). Also, we plotted to justify why some parameters were estimated relatively reliably even if their were larger than 100%.
4. Results and discussion
In this section, we show and discuss the numerical results obtained according to the generalized SIR model with constant time delays (1), for each dataset corresponding to the selected regions of Chile for performing the calibration and prediction. We start by describing how we chose the different scenarios, followed by the fitting and prediction by using a figure that depicts the actual and calibrated infected, and , respectively, computed according to our model. Next, we discuss parameter estimation’s reliability by depicting the traditional sensitivity functions for those parameters having a larger than 100% if it applies; see (16)–(17). A table follows that shows quantitative measures to verify the convergence of the optimization algorithm. Concretely, the table shows the number of iterations made by the optimization solver to meet the stopping criterion, the sum of squares’ optimal value, the RMSE, the first-order optimality measure, the norm of step, and the estimated parameters’ values. Finally, we show numerical results to simulate an eventual change of scenario, which effect we measured by computing the relative errors for predicted data after the final time of calibration and discussing the number of infected’ curve’s long-time behavior.
We should warn that the actual values would depend on people behavior and of the measures taken by sanitary authorities of the state. Therefore, the results of the article should consider as a general trend on curves’ behavior at simulation’ conditions.
4.1. Results for the Antofagasta Region
Next, we show and discuss fitting and forecasting results for the Antofagasta Region, whose capital is Antofagasta, located 1093 km to the North of Santiago of Chile straight line. The region has inhabitants, and it is representative of the country by its important ore activity. We fitted data starting from day 36 up to day 201, corresponding to April 7 and September 19, respectively (dataset size ). We chose April 7 as the initial time because the number of active accumulated cases was 69.
The region had four of nine communes under confinement (Antofagasta, Mejillones, Calama, and Tocopilla) in the following periods. Antofagasta and Mejillones from May 5 to May 29, and from June 23 to September 28; Calama from June 9 to September 21, and Tocopilla from June 23 to August 9. On average and taking into account the population density, we defined four scenarios for Antofagasta Region as follows: for the early expansion free of quarantine (between April 7 and May 5); for the phase of fast propagation under the first quarantine (between May 5 and May 29); for a phase of quarantine’ relaxation with relatively fast propagation (between May 29 and June 23); and for a phase of slowdown expansion under the second quarantine (between June 23 and September 19).
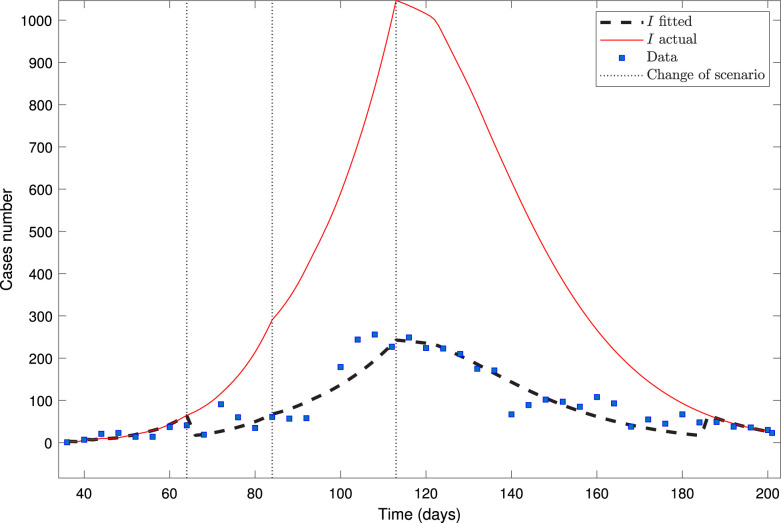
Fig. 1 depicts the model fitted to the Antofagasta Region dataset, plotting them each four-time points.
Fig. 1.
Calibration for the Antofagasta Region dataset from April 7 up to September 19.
Fig. 1 shows that the calibrated and actual curves of infected are very different from each other, except in scenario 1 and near the end of scenario 4 of the pandemic. We expected this result since a few infected people would be almost all detected, so the calibrated and actual curves would coincide. On the other hand, we observe that the calibrated curve of infected fits quite well the data (infected reported ). Indeed, since the dataset is large enough and encompasses the four stages of the pandemic, we estimated the parameters reliably. Only parameter , corresponding to the decay rate of fraction (see (5)), has a larger than 100%; see Table 1. Its sensitivity function, , varies in the interval for all within the time interval of calibration; therefore, its estimate is unreliable. However, all the rest of the parameters have a less than 100%, so fitting is relatively reliable. Indeed, from Table 1, one can observe that the overall fitting is suitable since the error is quite low (sum of squares and RMSE).
Table 1.
Fit performance for the Antofagasta Region dataset from April 7 up to September 19 .
| Quantity | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Iterations | 37 | |
| Sum of squares | ||
| RMSE | 31.0148 | |
| First-order optimality | ||
| Norm of step | ||
| Mean transmission rate | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Mean removal rate | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Mean time delays | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Parameters of fraction | ||
| Normalized standard errors |
The trend for the mean transmission rates is realistic. Indeed, is the largest for scenario 1 (free of quarantine), followed by for scenario 2 (with quarantine), followed by for scenario 3 (free of quarantine), and finally is the least of the four for scenario 4 (with quarantine). The same trend is observed for the fittings of the other datasets.
As explained in Section 3.1, we will show different predictions assuming that may vary after September 19. Concretely, we run simulations by considering a mean transmission rate defined by (7) taking . The predicted data (not fitted) encompasses September 20 to October 05, that corresponds to this last date. Table 2 shows the range (minimum and maximum) and the average of the relative errors of the model’ forecasting for different values of , and where to try of capturing that none commune of the Antofagasta Region remained confined since September 28 (day 210).
Table 2.
Predictions of the infected curve under different scenarios for the Antofagasta Region .
| Value | Minimum | Maximum | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.3163 | |||
| 1.3163 | |||
| 1.3163 | |||
| 1.3163 | |||
| 1.3163 | |||
| 1.3163 | |||
| 1.3163 | |||
| 1.3163 | |||
| 1.3163 | |||
| 1.3163 | |||
| 1.3163 | |||
| 1.3827 |
From Table 2, we observe that yields the least relative error mean, which implies that after the quarantine finished on September 28, the mean rate of transmission doubled, producing a negative change of scenario. Our model forecasts that, if these conditions were kept, a COVID-19 second-outbreak would occur in the Antofagasta Region. The peak of this new outbreak would occur around January 24, 2021, with an estimate of 102,154 real infected and 23,703 daily reported infected.
4.2. Results for the Metropolitan Region
Next, we show and discuss the results of fitting and forecasting for the Metropolitan Region (RM), whose capital is Santiago of Chile, also the capital of Chile. We fitted data starting from day 15 until day 203 corresponding to March 17 and September 21, respectively (dataset size =189). We chose March 17 as the starting day because the number of newly infected with symptoms was 29, with 152 active accumulated cases.
The region has inhabitants (around 41.76% of the total inhabitants of Chile) and 52 communes. From these, 47 communes have been under selective quarantine at different periods (few of which are yet), the most of which on average between May 7 and June 30. Therefore, we defined the three scenarios for MR as follows: for the first stage that encompasses the period from March 17 to May 7 (early expansion free of quarantine on average); for the second phase that ranges from May 7 to June 30 (fast propagation under quarantine); and for the third step that goes from June 30 up to September 21 (slowdown expansion with relaxation of quarantine on average).
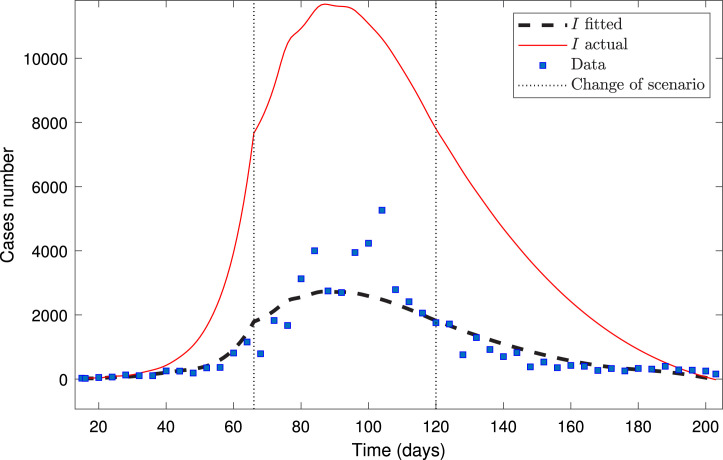
Fig. 2 depicts the model fitted to the MR dataset, plotting them each four-time points.
Fig. 2.
Calibration for MR dataset from March 17 up to September 21.
Fig. 2 shows that curves of calibrated and actual infected are very different from each other. On the other hand, we observe a good calibration of the model to the data since the computed curve of infected, , fits quite well the daily reported infected, . Indeed, since the dataset is large enough and encompasses the three stages of the pandemic, we estimated the parameters reliably, which is reinforced by the fact that the maximum is 89.39%, meaning accurate calibration results. To further appreciate the suitable fitting of the model, Table 3 presents its performance.
Table 3.
Fit performance for the MR dataset from March 17 up to September 21 .
| Quantity | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Iterations | 34 | |
| Sum of squares | ||
| RMSE | ||
| First-order optimality | ||
| Norm of step | ||
| Mean transmission rate | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Mean removal rate | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Mean time delays | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Parameters of fraction | ||
| Normalized standard errors |
As explained in Section 3.1, we will show different predictions assuming that may vary after September 21. Concretely, we run simulations by considering a mean rate of transmission defined by (7) for . The predicted data (not fitted) encompasses September 22 to 28, that corresponds to this last date. Table 4 shows the range (minimum and maximum) and the average of the relative errors of the model’ forecasting for different values of and for to try of capturing that almost none commune of the MR remained confined since August 31 (day 182).
Table 4.
Predictions of the infected curve under different scenarios for the MR .
| Value | Minimum | Maximum | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|
From Table 4, we observe that yields the least relative error (minimum and mean), which reinforces the assumption that the quarantine is valid for the MR between May 7 and June 30, on average, and that there was a little change of scenario from August 31 until September 28. Our model forecasts that, if these conditions were kept, a COVID-19 second-outbreak would occur in the MR. The peak of this new outbreak would occur around May 24, 2021, with an estimate of 70,937 real infected and 16,568 daily reported infected.
4.3. Results for the Ñuble Region
Next, we show and discuss fitting and forecasting results for the Ñuble Region, located 403.8 km to the south of Santiago of Chile, and whose capital city is Chillán (population ). On September 21, Chillán was the fourth city with more active infected per 100,000 inhabitants (407 cases). The three scenarios considered here are more easily identifiable than for the MR and the Antofagasta Region since the quarantines in the Ñuble Region were imposed mostly in Chillán at a single date within the time interval of calibration.
We split the results into two parts; first, we did the fitting for the data from March 21 to April 27 and next from March 21 to September 02. Therefore, the scenarios are the following: for the first stage that encompasses the period from March 21 up to March 30 (early expansion); for the second phase that ranges from March 30 up to April 23 (fast propagation under quarantine); and where and or for the third step that goes from April 23 to April 27 and to September 2 (slowdown expansion, free of quarantine), corresponding to the first and second results, respectively.
4.3.1. Results for fitting until April 27
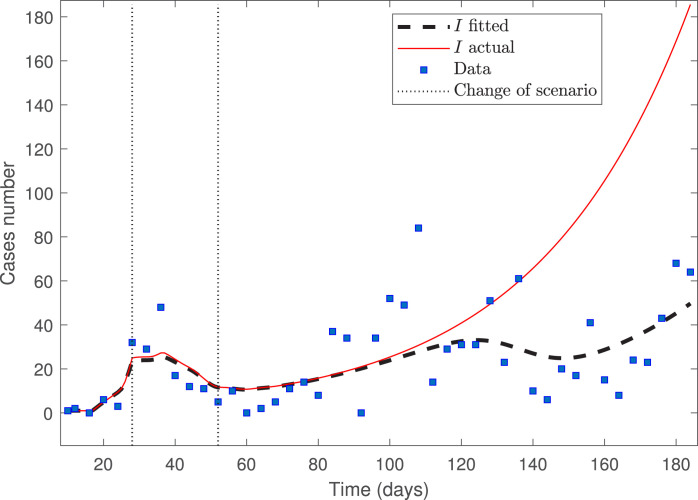
To compare with the only quantitative results we know of for the fitting of data from the Ñuble Region (see the first report by Cabrera-Vives et al. [6]), we did the fitting starting from day 19 (March 21) until day 57 (April 27) (dataset size ), when the accumulated infected at the Ñuble Region were 58. It is worth noting that, because of the small number of data points, the third scenario does not represent a spreading’s slowdown. We performed this fitting only to compare our results with that of Cabrera-Vives and collaborators’ first report.
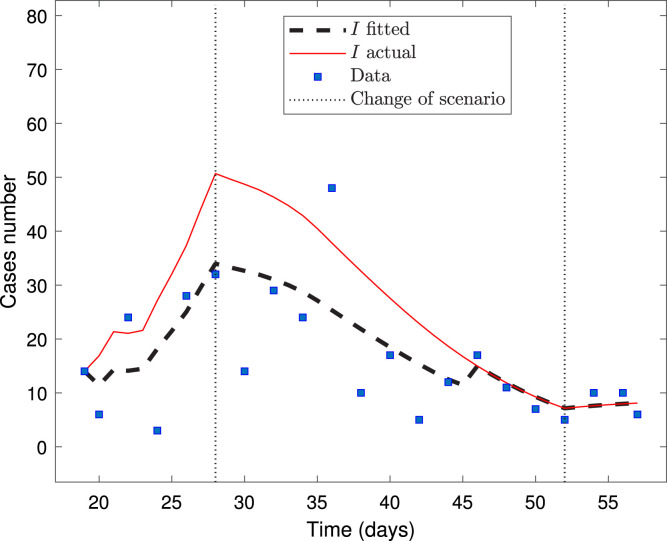
Fig. 3 depicts the model fitted to the dataset for the Ñuble Region, plotting the data each two-time points.
Fig. 3.
Calibration for the Ñuble Region dataset from March 21 up to April 27.
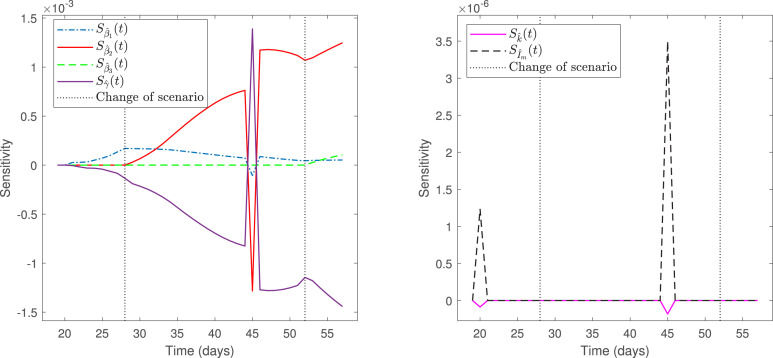
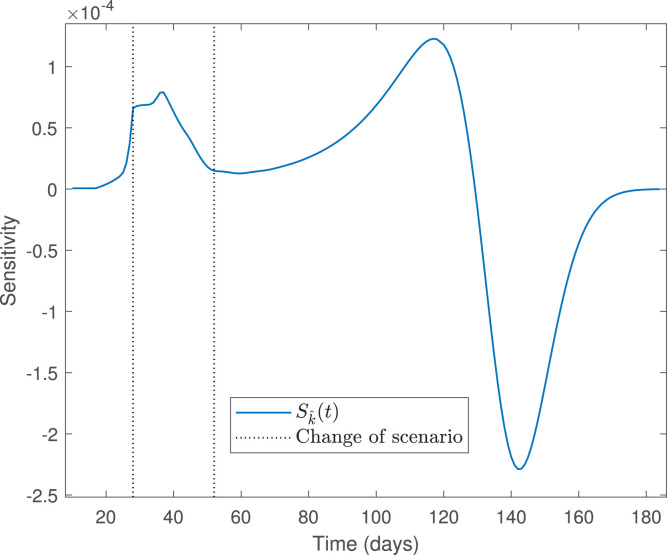
From Fig. 3, we observe that the calibrated curve of infected does not fit suitably the data, despite that the optimization solver converged (the last change in the relative sum of squares is less than the value of the function tolerance). Indeed, the calibrated curve does not represent the trend of not fitted data from April 28 to May 02 (not reported here). Following the findings in [4], the explanation is that the data used to make the fitting is close to the zero equilibrium (the early stage of the pandemic), suggesting limited ability to determine some parameters reliably. This is related to the traditional sensitivity functions, depicted in Fig. 4, for the parameters estimated with a larger than 100%; see Table 5.
Fig. 4.
Sensitivity functions for parameters estimated with a nse larger than 100%.
Table 5.
Fit performance for the Ñuble Region dataset from March 21 up to April 27 .
| Quantity | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Iterations | 41 | |
| Sum of squares | ||
| RMSE | 13.5179 | |
| First-order optimality | ||
| Norm of step | ||
| Mean transmission rate | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Mean removal rate | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Mean time delays | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Parameters of fraction | ||
| Normalized standard errors |
From Fig. 4(right), we observe that parameters and (see Eq. (5)) have the smallest sensitivities (very near to zero for every ), which implies that their estimations are not reliable. By contrast, Fig. 4(left) shows that parameter has the largest sensitivity, which means that its estimate is relatively better than the other parameters having a larger than 100%. In the case of parameters , and are small in the regions of scenarios 1 and 3, where and represent the mean rates of transmission, respectively; by contrast, is large enough in the region of scenario 2, where describes the mean rate of transmission. Consequently, the estimation of is relatively better than those of and . We will see that fitting the data in the three phases of the pandemic provides better results.
Table 5 shows the quantitative results of the fitting.
The results are comparable with that from the first report by Cabrera-Vives et al. [6] (a similar RMSE), although we did the fitting by using the real date at which the authorities imposed the quarantine. Our model also forecasts that, if the same conditions of the third scenario were kept, the outbreak’s peak would occur around February 20, 2021, that qualitatively coincides with the prediction obtained by Cabrera-Vives et al. [6]; see the bottom of Figure 1 from the first report. However, according to the previous discussion, the fitting obtained from data near an equilibrium point produces wrong prediction results [4], [5].
4.3.2. Results until September 2
Now, we show the results of fitting and predictions for the data from Ñuble Region, widening the time window from March 12 to September 02 (dataset size ), considering the same constraints as before (quarantine from March 30 to April 23), but now instead of 57 (day 184 corresponds to September 2). Fig. 5 depicts the model fitted to the dataset for the Ñuble Region, plotting the data at each four-time points
Fig. 5.
Calibration for the Ñuble Region dataset from March 21 up to September 2.
From Fig. 5, we observe that the calibrated curve of infected fits quite well the data. In this case, since the dataset is large enough and encompasses data from the three stages of the pandemic, this time, we estimated the parameters reliably, except maybe for that is the only with a larger than 100%; see Table 6. Fig. 6 depicts the sensitivity function of .
Table 6.
Fit performance for the Ñuble Region dataset from 12 March to 02 September .
| Quantity | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Iterations | 68 | |
| Sum of squares | ||
| RMSE | 14.4360 | |
| First-order optimality | ||
| Norm of step | ||
| Mean transmission rate | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Mean removal rate | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Mean time delays | ||
| Normalized standard errors | ||
| Parameters of fraction | ||
| Normalized standard errors |
Fig. 6.
Sensitivity function for parameter .
From Fig. 6, we observe that is relatively large in the region corresponding to scenario 3, and therefore estimate of is relatively reliable. The result is better than the last fitting (data until April 27); see Fig. 4 and the discussion below it.
Table 6 shows the corresponding quantitative results of the fitting.
Consistently with the results obtained fitting the dataset until April 27, our model forecasts that, if the same conditions of the third scenario were kept, the outbreak’s peak would occur around March 02, 2021. However, we would expect a change of scenario since September 2 because authorities re-imposed confinement in Chillán due to the high increase in daily new cases.
As explained in Section 3.1, we will show different predictions assuming that may vary after September 2 due to the confinement (helpful or counterproductive measure depending on people behavior). Concretely, we run simulations by defining as in (7) (with ) to predict the data (not fitted) between September 3 and September 22 (data number ), and putting and that correspond to September 2 and 22, respectively. Table 7 shows the range (minimum and maximum) and the average of the relative errors of the model’ forecasting for different values of .
Table 7.
Predictions of the infected curve under different scenarios for the Ñuble Region .
| Value | Minimum | Maximum | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0677 | |||
| 2.9773 | |||
| 2.8704 | |||
| 3.8428 | 1.1393 | ||
| 4.8728 | 1.2234 | ||
| 5.0685 | 1.5241 | ||
| 7.1286 | 2.0765 | ||
| 8.2770 | 2.3404 | ||
| 8.4642 | 2.7584 | ||
| 9.1426 |
From Table 7, we observe that yields the least relative error maximum and mean. The interpretation is that quarantine effectively reduced the transmission rate, and therefore there was a positive change of scenario since September 2. Our model forecasts that, if these conditions were kept, a COVID-19 second-outbreak would not occur in the Ñuble Region.
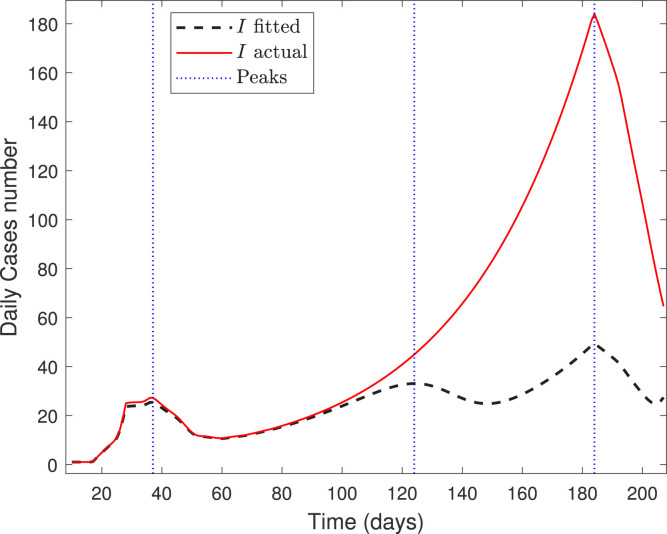
Finally, Fig. 7 depicts the calibrated and real curves of infected for the Ñuble Region until September 25, by taking as before. The third peak corresponds to September 2, the final calibration date.
Fig. 7.
Forecasted curve of infected for Ñuble Region from March 21 to September 25.
The result of Fig. 7 coincides with a report by the Chilean Society of Intensive Medicine, published on September 25, which pointed out that Chillán underwent the third peak of the COVID-19 outbreak by this date; see [20].
4.4. On the robustness of the optimization algorithm and the estimation of the infection fatality rate
To assess the robustness of the parameter estimations we repeated the fitting processed we described in Section 4.2 after modifying some assumptions. Instead of assuming that is piecewise constant and defining the three scenarios based on actual policy changes, here we considered to be piecewise linear with equal length time intervals. More formally we replaced Eq. (6) with
| (18) |
where is the tent function with value of one at and tapers off to zero at and . Thus, we determine values for the ’s. We tried 5 values for and we summarize the results in Table 8.
Table 8.
Estimators for using segments piecewise linear functions .
| 8 | ||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||
| 4 |
The results in Table 8 are, up to a point, compatible with the values shown in Table 3. For example, we can see that for values of the ’s are in the [0.13, 0.19] range consistently for from Table 3. Moreover, for and the same trend follows as in Table 3, i.e., the values for are relatively large for both small and large ’s (first and last scenario). We already stated in Section 4 that this was a consequence of the different scenarios considered for each dataset. The same trend is not seen if . This is natural, as having many time intervals, and therefore many ’s parameters to adjust will tend to cause overfitting. Indeed, we observe across rows of Table 8 a relatively large variability (range [0.13, 0.75]) among the ’s. The same can be said about the values for (range ). One consequence of this observation is that predictions are likely to be very inaccurate if we simply assume that will hold during an extrapolation beyond the last data point after trying the fitting with a single . Nonetheless, we can use the ranges the ’s lie on for a scenario analysis as we did in Section 4 (Table 2, Table 4, Table 7). Another consequence is the difficulty to estimate precisely the effectiveness of the quarantine procedures. This follows from the variability within each row of Table 8. In principle, quarantines should lower the values for . However, because of the inherent inaccuracy of the estimation during the initial disease propagation, and the enforcement of quarantines as soon as the cases multiply (and thus the estimation becomes reliable), computing the temporal changes in accurately is more than challenging. Yet, for small values of (say 4 or 5), the qualitative behavior of the ’s we expect is observed.
Furthermore, it is of practical interest to estimate the lethality of a disease. The infection fatality rate (IFR), the probability of dying for an infected person, is computed as the ratio of dead subjects to the number of infected people for the targeted population [18]. However, according to our model, there is a time delay between that an infected person recovers or dies (), and therefore to compute the IFR at a given day , we divided (the number of death at ) into the number of infected at time . To exemplify the model’s usefulness, we will show IFR estimations computed for each dataset by combining empirical data and model outputs. To do that, we will use from Table 1, Table 3, Table 6, the confirmed number of deaths for each region reported in [17], and the actual number of infected computed from the outputs of model (1). As usual, we divided the process into the scenarios, as described in Section 4, plus the pandemic’s entire period used in the calibration. Table 9 shows the IFR medians in percentage.
Table 9.
IFR median estimation for each dataset .
| Region | Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 | Scenario 4 | Entire |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antofagasta | 0 | 0 | |||
| Metropolitan | 1.1396 | 1.0444 | Does not apply | ||
| Ñuble | 0 | 0 | 0 | Does not apply | 0 |
We computed the median since it is more appropriate for skewed distribution, such as the confirmed number of deaths, , which are raw data. We did not plot the IFR since it presents many oscillations and a few outlier values because of uncertainty in data and the numerical error of calibration results. The values of Table 9 are consistent with the recent results in [18], where the author claims that , which implies that the curve of real infected provided by the model is accurate since it yields a realistic value for the IFR’s median in the case of MR. By contrast, for the Ñuble and Antofagasta Regions, the confirmed death cases are not large enough to yield an accurate IFR’s estimation (for neither mean nor median).
5. Conclusions
We described and successfully implemented a clear, efficient, and reproducible parameter estimation methodology to a generalized SIR model with constant time delays that can reproduce complex dynamics for COVID-19. We illustrated our methodology and modeling by carrying out parameter estimation for three datasets corresponding to Chile’s three representative regions, although this can be applied to any country. From a methodological viewpoint, we assessed the reliability of estimated parameters and showed that when the data are located in the transition from the zero to the non-zero equilibria (encompassing all the stages of pandemic spread), the parameters are reliably estimated. Also, we verified our optimization methodology’s robustness by considering an arbitrary number of scenarios.
The numerical results allow us to forecast the general trend of the infected’ curve, the calibrated and the real, and provide some predictions that allow us to prognosticate a possible COVID-19 second-outbreak. This prognosis is valid only if the conditions that allowed arrive at the estimated mean transmission rate are kept. In the absence of an effective vaccine or drug, these conditions are essentially translated into self-care. Finally, we showed that our model is precise enough to reproduce the infection fatality rate fairly accurately, according to the reported dead cases.
There are two lines of research that we would like to tackle. First, we expect to apply our model and methodology to other regions/communes in Chile. Because of the heterogeneity among their socio-economic conditions, the pandemic has affected them differently. On the other hand, we intend to calibrate our model to the reported dead to estimate more accurately and quantitatively the infection fatality rate of COVID-19, including structures of age and the dynamics of interactions among individuals of diverse age groups.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
Funding
The Centre for Biotechnology and Bioengineering (CeBiB), Chile supported this work under PIA grant FB-01 from ANID. P.C.’s work was also supported by DIUBB 2120432 IF/R regular research project from the University of Bío-Bío, Chile .
References
- 1.Badillo G., Cumsille P., Segura-Ponce L., Pataro G., Ferrari G. An efficient optimization methodology of respiration rate parameters coupled with transport properties in mass balances to describe modified atmosphere packaging systems. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 2020;28(10):1361–1383. doi: 10.1080/17415977.2020.1717488. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Baeza-Yates R. 2020. Work group of data sciences on Covid-19 in Chile.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T26vGwcbxH4&feature=share&fbclid= [Google Scholar]
- 3.Banks H.T., Davidian M., Samuels J.R., Sutton K.L. In: Mathematical and Statistical Estimation Approaches in Epidemiology. Chowell G., Hyman J.M., Bettencourt L.M.A., Castillo-Chavez C., editors. Springer Netherlands; Dordrecht: 2009. An inverse problem statistical methodology summary; pp. 249–302. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Banks H.T., Dediu S., Ernstberger S.L. Sensitivity functions and their uses in inverse problems. J. Inverse Ill-Posed Probl. 2008;15(7):683–708. doi: 10.1515/jiip.2007.038. doi: 10.1515/jiip.2007.038. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Banks H.T., Ernstberger S.L., Grove S.L. Standard errors and confidence intervals in inverse problems: sensitivity and associated pitfalls. J. Inverse Ill-Posed Probl. 2007;15(1):1–18. doi: 10.1515/JIIP.2007.001. doi: 10.1515/JIIP.2007.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cabrera-Vives G., Donoso-Oliva C., Martínez M., Molina R., Sánchez A. 2020. Informe proyecciones COVID-19 UdeC.https://github.com/guille-c/Covid-19/tree/master/Informes [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cancino A., Gajardo P., Lecaros R., Muñoz C., Ramírez H., Ortega J. 2020. COVID-19 en Chile.http://www.cmm.uchile.cl/?p=37663 [Google Scholar]
- 8.Candia Reyes M., Vergara-Hermosilla G. 2020. Estimación de casos no reportados de infectados de COVID-19 en Chile, el Maule y la Araucanía durante marzo de 2020: Working Paper or Preprint. URL https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02560526. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Coleman T.F., Li Y. An Interior Trust Region approach for nonlinear minimization subject to bounds. SIAM J. Optim. 1996;6(2):418–445. doi: 10.1137/0806023. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cumsille P., Coronel A., Conca C., Quiñinao C., Escudero C. Proposal of a hybrid approach for tumor progression and tumor-induced angiogenesis. Theoret. Biol. Med. Model. 2015;12(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12976-015-0009-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cumsille P., Godoy M., Gerdtzen Z.P., Conca C. Parameter estimation and mathematical modeling for the quantitative description of therapy failure due to drug resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumor metastasis to the liver. PLoS One. 2019;14(5):1–27. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Elie R., Hubert E., Turinici G. Contact rate epidemic control of COVID-19: an equilibrium view. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 2020;15:35. doi: 10.1051/mmnp/2020022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Greene W.H. seventh ed. Pearson Education; 2012. Econometric Analysis. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Guerrero-Nancuante C., Manríquez P. R. An epidemiological forecast of COVID-19 in Chile based on the generalized SEIR model and the concept of recovered. Medwave. 2020;20(04) doi: 10.5867/medwave.2020.04.7898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hairer E., Nørsett S.P., Wanner G. Springer Series in Computational Mathematics. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg; 1993. Solving Ordinary Differential Equations I: Nonstiff Problems. URL https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783540566700. [Google Scholar]
- 16.de Ciencia Tecnología Conocimiento e Innovación M. 2020. Datos-COVID19.https://github.com/MinCiencia/Datos-COVID19/blob/master/output/producto5/TotalesNacionales.csv [Google Scholar]
- 17.de Ciencia Tecnología Conocimiento e Innovación M. 2020. Datos-COVID19.https://github.com/MinCiencia/Datos-COVID19/blob/master/output/producto3/TotalesPorRegion.csv [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ioannidis J. Infection fatality rate of COVID-19 inferred from seroprevalence data. Bull. World Health Organ. 2020 doi: 10.2471/BLT.20.265892. arXiv:https://www.who.int/bulletin/online_first/BLT.20.265892.pdf?ua=1. URL https://www.who.int/bulletin/online_first/en/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Maleewong M. Time delay epidemic model for COVID-19. MedRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.05.23.20111500. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.S. Núñez, A. Meleán, They warn that Chillán is going through the third peak of infections by Covid-19 (Advierten que Chillán atraviesa el tercer peak de contagios por Covid-19), The discussion” Newspaper (Diario la Discusión). URL: http://www.ladiscusion.cl/advierten-que-chillan-atraviesa-el-tercer-peak-de-contagios-por-covid-19/.
- 21.Peng L., Yang W., Zhang D., Zhuge C., Hong L. Epidemic analysis of COVID-19 in China by dynamical modeling. MedRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.02.16.20023465. arXiv:https://www.medrxiv.org/content/early/2020/02/18/2020.02.16.20023465.full.pdf. URL https://www.medrxiv.org/content/early/2020/02/18/2020.02.16.20023465. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shampine L.F., Thompson S. Solving DDEs in MATLAB. Appl. Numer. Math. 2001;37:441–458. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9274(00)00055-6. URL http://gen.lib.rus.ec/scimag/index.php?s=10.1016/s0168-9274(00)00055-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.. WHO, Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/who-china-joint-mission-on-covid-19-final-report.pdf.