Extended Data Fig. 5. Brd4 suppression impairs regenerative and neoplastic fate outcomes of injury-driven pancreas plasticity.
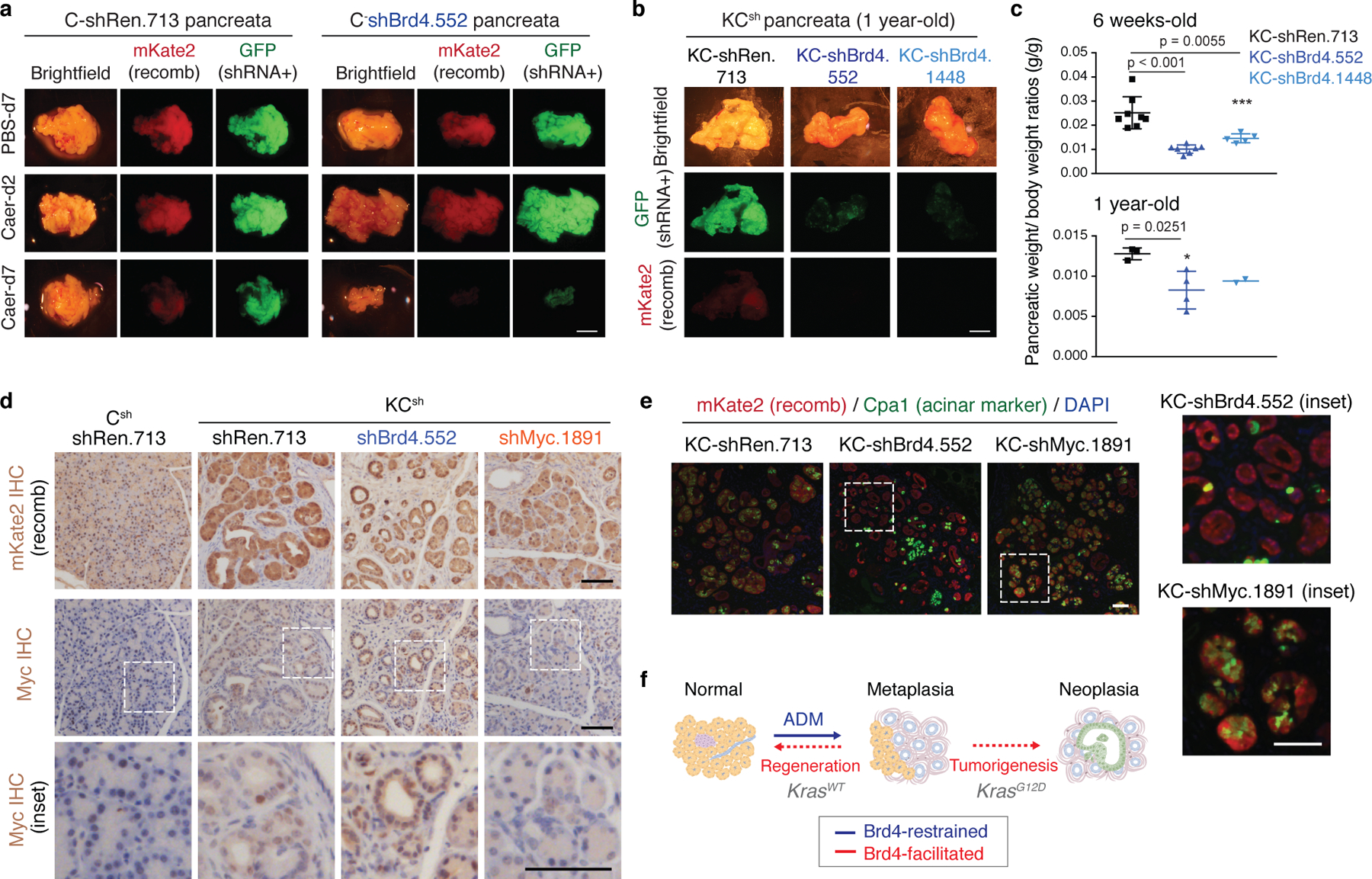
a Representative bright-field and fluorescence images showing gross morphology of pancreata of C-shRen and -shBrd4 mice treated with caerulein or PBS control and analyzed at the indicated time points in days (d). Lineage-traced pancreatic epithelial cells expressing shRNA are marked by the fluorescent reporters mKate2 and GFP. Reduced mKate2 and GFP signals denote loss of pancreatic tissue expressing shBrd4. Scale bar, 5 mm. b, Representative bright-field and fluorescence images showing gross morphology of pancreata of KC-shRen and -shBrd4 mice placed on dox since postnatal day 10 to induce shRNA expression and analyzed at 1-year of age. Reduced mKate2 and GFP signals denote loss of shBrd4-expressing mutant Kras pancreatic epithelial cells. Scale bar, 5 mm. c, Quantification of pancreatic weight normalized to animal body weight by genotype. Data are presented as means ± s.e.m; n=8, 7 or 5 (top, from left to right) mice, or n=3, 4 or 2 (bottom, from left to right) mice; unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. d, Representative immunohistochemistry stains of mKate2 (top) and Myc (bottom) in pancreata from 6 weeks old mice KCsh of the indicated genotypes and placed on dox fed at day 10 after birth (stochastic tumorigenesis setting). Lower panels show high magnification images of regions marked with dashed line boxes for visualization of Myc nuclear localization. While oncogenic Myc expression can require Brd4-associated enhancers in some settings35,83,84 and is suppressed by systemic BET inhibition in KC mice85, epithelial-specific Brd4 suppression did not reduce Myc protein in our model. Scale bar, 100 μm. e, Representative co-IF stains of mKate2 (red) and the acinar marker CPA1 (green) in pancreata from 6 weeks old mice KCsh mice of the indicated genotypes and placed on dox fed at day 10 after birth, as above. Right panels show high magnification images of regions marked with dashed line boxes. KCsh mice harboring a validated shRNA targeting Myc (instead of Brd4) exhibited impaired rather than accelerated ADM. The reduction of CPA1 observed in KC-shBrd4 mice is not phenocopied in KC-shMyc mice, which retain Cpa1 expression. Scale bar, 100 μm. f, Schematic representation of the phenotypic output of pancreas-specific suppression of Brd4 during mutant Kras-driven neoplasia and tissue injury-driven regeneration: Brd4 is dispensable for acinar-to-ductal metaplasia induction in both contexts but mediates subsequent neoplastic progression to PanIN or regenerative plasticity, respectively.
