Abstract
Objective:
We hypothesized that healthcare workers (HCWs) with high-risk exposures outside the healthcare system would have less asymptomatic coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) disease and more symptoms than those without such exposures.
Design:
A longitudinal point prevalence study was conducted during August 17–September 4, 2020 (period 1) and during December 2–23, 2020 (period 2).
Setting:
Community based teaching health system.
Participants:
All HCWs were invited to participate. Among HCWs who acquired COVID-19, logistic regression models were used to evaluate the adjusted odds of asymptomatic disease using high-risk exposure outside the healthcare system as the explanatory variable. The number of symptoms between exposure groups was evaluated with the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. The risk of seropositivity among all HCS by work exposure was evaluated during both periods.
Interventions:
Survey and serological testing.
Result:
Seroprevalence increased from 1.9% (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.2%–2.6%) to 13.7% (95% CI, 11.9%–15.5%) during the study. Only during period 2 did HCWs with the highest work exposure (versus low exposure) have an increased risk of seropositivity (risk difference [RD], 7%; 95% CI, 1%–13%). Participants who had a high-risk exposure outside of work (compared to those without) had a decreased probability of asymptomatic disease (odds ratio [OR], 0.38; 95% CI, 0.16–0.86) and demonstrated more symptoms (median 3 [IQR, 2–6] vs 1 [IQR, 0–4]; P = .001).
Conclusions:
Healthcare-acquired COVID-19 increases the probability of asymptomatic or mild COVID-19 disease compared to community-acquired disease. This finding suggests that infection prevention strategies (including masks and eye protection) may be mitigating inoculum and supports the variolation theory in COVID-19.
The risk of transmission of SARS and subsequent coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) appears to vary based on multiple factors: susceptibility of the individual, type and duration of exposure, and use of infection preventative measures.1–3 Except for individual susceptibility, these factors vary based on location of exposure to severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Exposures within the healthcare system may occur during times of high transmissibility or in the presence of aerosol-generating procedures. However, exposures are also more likely to occur in an environment requiring mandatory mask use and high compliance with other infection prevention measures (eg, disinfection, social distancing, personal protective equipment (PPE) use and 100% compliance with hand hygiene). Conversely, exposures in the community may occur in settings with lower compliance with public health recommendations or with prolonged in-home exposure. Hence, exposures in different environments may result in higher or lower viral inoculums and differences in epidemiology and disease severity.2 Limited data are available regarding the epidemiology and disease severity characteristics of COVID-19 when accounting for high-risk exposures outside the healthcare system.
Biological plausibility suggests some healthcare workers (HCWs) may be at an increased risk for infection with SARS-CoV-2 due to exposure to patients during stages of high transmissibility, exposure to family members or colleagues who may be infected, and exposure to work environments with heavy contamination. However, serological surveys have demonstrated inconsistent associations between HCW exposure risk at work and acquired COVID-19 diagnosed by seropositivity to SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.4–13 Although misclassification bias, infection prevention preparedness, and imprecision and diversity in testing methods likely explains some of this variation, the picture is incomplete high-risk exposures outside the healthcare system must still be considered.14–18
Accordingly, in this study, we evaluated the proportion of asymptomatic spread and the symptomology of COVID-19 among HCWs with and without high-risk exposure outside the healthcare system. We hypothesized that HCWs with high-risk exposure outside the healthcare system would have less asymptomatic COVID-19 disease and more symptoms than those without such exposures.
Methods
In this longitudinal point-prevalence study, we evaluated the seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in HCWs. The trial was conducted and reported in accordance with the (Strengthening the Reporting of Observational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement on reporting observational trials.19 The study was approved by the Metro-Health University of Michigan Health Institutional Review Board. Study consent was obtained electronically via response to the survey invitation. The survey invitations and data were managed using Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) tools hosted at the University of Michigan Health System. REDCap is a secure, web-based application designed to support data capture for research studies.
Setting
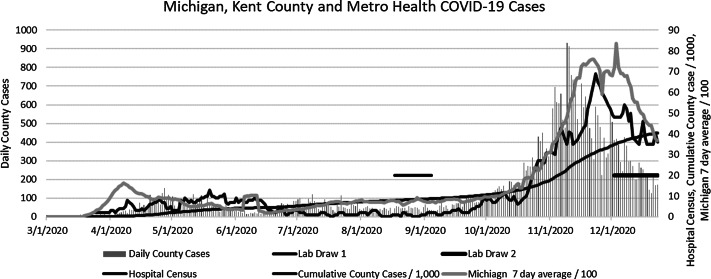
Metro Health–University of Michigan Health is composed of a 210-bed community-based teaching hospital with multiple outpatient, urgent care, and surgery centers. The system is located in the second largest county in Michigan (Kent County in west Michigan) and employs or contracts with ∼2,800 HCWs. Michigan emerged as an epicenter for COVID-19 in mid-April 2020 fueled by a surge of cases in heavily populated regions of southeastern Michigan. Kent County experienced a moderate surge in coronavirus cases during May with low community prevalence until October 2020, when cases exponentially increased, resulting in significant stress on the healthcare systems. Figure 1 depicts the epidemiology of COVID-19 in the state, county, and hospital during the study period.
Fig. 1.
Epidemiology of COVID-19 during the study periods. A surge of cases April was centered in southeastern Michigan with a later surge moderate surge in cases in Kent County, May–June 2020. A larger surge occurred in Michigan that disproportionately affected western Michigan.
Preparedness plan
On March 4, 2020, COVID-19 incident command was established for planning, communication, and implementation of pandemic policies. COVID-19 units were established within 1 week along with policies for extended N95 mask use, limited staff entrances, daily staff screening and testing measures, and restricted visitor policies. The PPE policy required all staff to wear surgical masks and eye protection for all suspected or known COVID-19 patients as well as enhanced respiratory protection (N95 masks or CAPRs) for patients in the ICU or undergoing aerosol-generating procedures. The first confirmed COVID-19 case occurred on March 22, 2020. On April 10, 2020, all emergency department (ED) staff were required staff to wear N95 masks. On April 20, 2020, in-house reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing was available. Universal mask use for all staff was implemented on May 4, 2020. On October 1, 2020, policies instructed all staff to wear enhanced respiratory protection when caring for all suspected or confirmed COVID-19 cases. Since July 10, Michigan has been operating under some form of mask mandate that requires residents to have face and nose coverings when in public.
Surveys
On August 3, 2020, all adult employed and contracted HCWs were sent survey invitations via e-mail inviting them to participate in a voluntary survey on risk of exposure to COVID-19 and antibody testing. The survey and invitations were also translated into Spanish, and paper surveys were available. Participants were excluded if they had not worked in the healthcare system since March 1, 2020. Patients with active COVID-19 at time of the invitation were offered participation 2 weeks following symptom onset. Survey participants received their antibody results via e-mail through the REDCap system. The current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidance on implications of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies were provided to participants before and after survey and with the test results. For this study, period 1 was August 17 through September 4, 2020, and period 2 was December 2 to 23, 2020 (the period of the COVID-19 vaccine roll out) (Fig. 1).
Antibody test
Consistent with CDC recommendations, we used an orthogonal testing algorithm in which persons who initially test positive were confirmed with a second test. All participants received a total antibody chemiluminescent immunoassay intended for qualitative detection of total IgG and IgM antibodies (Siemens Atellica IM SARS-CoV-2 Total [COV2T], which has 100% sensitivity and 99.82 specificity). All participants who tested positive underwent a confirmatory IgG antibody test (bioMerieux Vdas SARS-COV-2 IgG), an automated assay using the enzyme-linked fluorescent assay technique intended for qualitative detection of IgG antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, which has sensitivity of 96.6% and specificity >99.9% at >7 days from exposure.20
Data collection
A copy of the survey is presented in Appendix 1 (online) as well as laboratory results linked to the participant’s study ID.
Primary outcomes
We compared the risk of asymptomatic COVID-19 disease between HCWs with and without high-risk exposure outside the healthcare system. COVID-19 disease was diagnosed by either self-reported PCR or antigen test (diagnostic tests) or seropositivity for SARS-CoV-2 antispike protein IgG using the previously mentioned testing algorithm. High-risk exposures outside the healthcare system included exposures to someone with diagnosed COVID-19 living in the same household or exposure to someone outside a participant’s home within 2 m (6 feet) for >15 minutes. We also compared the median number of COVID-19 symptoms between HCWs with and without high-risk exposures outside the healthcare system. Only participants with jobs that involved at least some patient contacts were included in this analysis.
Secondary outcome
We evaluated the risk of seropositivity among HCW with the highest exposure, compared to moderate and low exposure, during period 1 (low community prevalence) and period 2 (high community prevalence). Reports have been conflicting regarding whether COVID-19 exposure within the healthcare system increases the risk of acquiring COVID-19 when evaluated by seropositivity to SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Definitions to assess risk have varied widely across studies such as clinical providers, job title, specialty, working in a COVID unit, subsets of staff (ie, nurses, respiratory therapists, and physicians), and perceived exposure. Hence, misclassification bias likely accounts for a large part of the conflicting literature.4–13 We assigned high exposure risk to HCWs taking care of hospitalized COVID-19 patients (ie, in a stage of highest stage of transmissibility).2,3 We classified other clinical providers as moderate exposure risk and nonclinical HCWs as low exposure risk. Participants who were seropositive during period 1 were excluded from period 2 analyses.
Exploratory analysis
We compared the seroprevalence in HCWs to that of the surrounding population using estimates from a large-scale CDC seroprevalence study.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were screened for normality using normality plots and histograms. Parametric data are expressed as mean (±SD) and nonparametric data as median (interquartile range [IQR]). Continuous variables were compared using seropositive status with 2-sample t tests or the Wilcoxon rank-sum test, as appropriate. Categorical variables were compared by seropositive status using the χ2 or Fisher exact test. The 95% confidence intervals for the seroprevalence were estimated using the asymptotic approximation method. We used logistic regression to estimate the adjusted odds of asymptomatic COVID-19 between HCWs with and without a high-risk exposure outside the healthcare system. The following variables were chosen for entry into the model based on biological plausibility: type of mask worn (N95/CAPR vs surgical mask), compliance with public health measures and hospital infection prevention policies (yes vs no/sometimes), high-risk patient exposures (caring for hospitalized COVID-19 patients versus no), gender (female vs male), and age (continuous; increasing year). Variables were chosen for entry into the final model using backward recursive selection based on a probability of 0.1 (Wald statistic). Goodness of fit was measured with the likelihood ratio and the Hosmer and Leseshow test. We used the Wilcoxon rank-sum test to evaluate the difference in number of symptoms of COVID-19 between HCWs with and without a high-risk exposure outside the healthcare system. We also calculated the risk difference (95% confidence interval) for seropositivity of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies among all HCWs during period 1 and period 2 based on risk of exposure (high, moderate, or low).
To compare the seroprevalence of HCWs to the general community, we used the seroprevalence for Michigan as determined by the CDC during study period 1 (4%; 95% CI 3-7%).21 For study period 2, following a surge of COVID-19 in the community, we estimated the community seroprevalence using the ratio of actual to reported infections (3.3; 95% CI, 2.2–4.3) determined for Michigan by the CDC.21 Recent data demonstrate a humoral response (antibody response) in 91% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 and that antibodies can persist for at least 4 months.22,23 Given that 26,623 new cases of COVID-19 were reported during the ∼4-month period from the start of period 1 until period 2, we estimated that 87,856 actual cases occurred. Hence, we conservatively estimated the seroprevalence in Kent County to be at least 12.3% ([87,856 × 0.91]/650,000). P values <.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Approximately 50% of HCWs participated in the survey and serological testing during each study period. The demographics and clinical characteristics of participants by seropositivity against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein can be seen in Table 1. As expected, during study period 2, a slightly higher percentage (3.5% vs 9%) of HCWs reported being exposed to someone with COVID-19 outside work. A higher proportion of HCWs reported a high perceived risk of COVID-19 exposure while at work (11.8% vs 23.1%); however, a high risk of perceived exposure did not predict seropositivity. We asked why providers perceived a high risk of exposure, and although most reported patient exposures, approximately two-thirds of respondents listed additional factors. Hence, it was not common for patient exposure alone to be the reason behind a high perceived risk of exposure. No evidence of pandemic “fatigue” was observed in HCWs who reported high compliance with public healthcare and infection prevention measures during both study periods.
Table 1.
Demographics and Clinical Characteristics of Participants by Seropositivity Against SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
| Variable | Study Period 1 (n=1,385) August 17–September 4, 2020, Seropositivity 1.9% |
Study Period 2 (n=1,445) December 2–23, 2020, Seropositivity 13.7% |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seropositive (N = 26) |
Seronegative (N = 1359) |
P Value | Seropositive (N =198) |
Seronegative (N = 1247) | P Value | |
| Age, y (SD) | 36 (±11.6) | 40 (±11.8) | .08 | 38.9 (±11.5) | 40.3 (±12) | .13 |
| Sex, no. (%) | .24 | .16 | ||||
| Male | 8 (30.8) | 271 (19.9) | 38 (19.2) | 250 (20.1) | ||
| Female | 18 (69.2) | 1,086 (79.9) | 159 (80.3) | 997 (79.9) | ||
| Other | 0 (0) | 2 (0.2) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0) | ||
| Race/Ethnicity, no. (%) | .008 | .30 | ||||
| Caucasian | 20 (76.9) | 1,254 (92.3) | 176 (88.9) | 1,127 (90.4) | ||
| Hispanic-Latino | 1 (3.9) | 33 (2.4) | 8 (4) | 31 (2.5) | ||
| Black-African American | 1 (3.9) | 20 (1.5) | 6 (3) | 17 (1.4) | ||
| Asian-Pacific Islander | 0 (0) | 22 (1.6) | 4 (2) | 29 (2.3) | ||
| Arabic-Middle Eastern | 1 (3.9) | 9 (0.7) | 1 (0.5) | 7 (0.6) | ||
| Other | 3 (11.5) | 21 (1.6) | 3 (1.5) | 36 (2.9) | ||
| COVID-19 diagnosis via PCR/antigen, no. (%) | 16 (61.5) | 7 (0.52) | <.001 | 102 (51.5) | 18 (1.4) | <.0001 |
| Symptoms, no. (%) | ||||||
| None | 8 (30.8) | 960 (70.6) | <.001 | 56 (28.3) | 901 (72.3) | <.0001 |
| Fever | 11 (42.3) | 131 (9.6) | <.001 | 44 (22.2) | 58 (4.7) | <.0001 |
| Myalgias | 10 (38.5) | 129 (9.5) | <.001 | 68 (34.4) | 100 (8) | <.0001 |
| Sore throat | 9 (34.6) | 215 (15.8) | .03 | 46 (23.2) | 187 (15) | .0034 |
| Runny nose | 8 (30.8) | 159 (11.7) | .009 | 67 (33.8) | 186 (14.9) | <.0001 |
| Loss of smell | 11 (42.3) | 34 (2.5) | <.001 | 88 (44.4) | 35 (2.8) | <.0001 |
| Cough | 9 (34.6) | 198 (14.6) | .01 | 73 (36.9) | 139 (11.2) | <.0001 |
| Shortness of breath | 7 (26.9) | 102 7.5) | .03 | 40 (20.2) | 58 (4.7) | <.0001 |
| Unusual headaches | 10 (38.5) | 112 (8.2) | <.001 | 66 (33.3) | 110 (8.9) | <.0001 |
| Diarrhea/Upset stomach | 7 (26.9) | 117 (8.6) | .06 | 40 (20.2) | 86 (6.9) | <.0001 |
| Full time (vs part time), no. (%) | 20 (76.9) | 1,059 (77.9) | .90 | 152 (76.8) | 967 (77.6) | .81 |
| Have you practiced public health measures as outlined by MDHHS? No. (%) | .21 | .97 | ||||
| Usually | 23 (88.5) | 1,291 (89.7) | 182 (91.9) | 1140 (91.4) | ||
| Sometimes | 2 (7.7) | 130 (9.6) | 15 (7.6) | 100 (8) | ||
| Rarely | 1 (3.8) | 10 (0.7) | 1 (0.5) | 7 (0.6) | ||
| Have you been exposed to someone with COVID-19? No. (%) | ||||||
| Outside of work but not in your household? | 7 (26.9) | 115 (8.5) | .006 | 48 (24.5) | 181 (14.5) | .0005 |
| Living in your household? | 5 (19.2) | 44 (3.2) | .002 | 43 (21.7) | 90 (7.2) | .0001 |
| Have you worn appropriate PPE at work (congruent with hospital policy)? No. (%) | .76 | .15 | ||||
| Yes | 26 (100) | 1277 (94) | 189 (95.5) | 1,193(95.7) | ||
| No | 0 (0) | 23 (1.7) | 4 (2.5) | 9 (0.7) | ||
| Sometimes | 0 (0) | 58 (4.3) | 5 (2.5) | 45 (3.6) | ||
| Enhanced respiratory protection, No. (%) | .897 | .34 | ||||
| N95 mask | 10 (38.5) | 443 (32.6) | 101 (51) | 594 (47.6) | ||
| CAPRs | 0 (0) | 41 (3) | 7 (3.5) | 24 (1.9) | ||
| Mix of N95/CAPRs | 2 (7.7) | 97 (7.1) | 10 (5.5) | 74 (5.9) | ||
| Not applicable to my role (surgical mask only) | 14 (53.9) | 778 (57.3) | 80 (40.4) | 555 (44.6) | ||
| Providers, no. (%) a | .59 | .73 | ||||
| 1) Clinical provider | 17 (65.4) | 691 (50.9) | 107 (54) | 693 (55.6) | ||
| 2) Interprofessional | 1 (3.9) | 131 (9.6) | 33 (16.7) | 189 (15.2) | ||
| 3) Ancillary | 1 (3.9) | 104 (7.7) | 10 (5.1) | 84 (6.7) | ||
| 4) Nonclinical | 7 (29.9) | 433 (31.9) | 48 (24.2) | 281 (22.5) | ||
| Perceived risk of work exposure, no. (%) | .008 | .26 | ||||
| High | 8 (30.8) | 156 (11.4) | 56 (28.3) | 288 (23.1) | ||
| Moderate | 5 (19.2) | 539 (39.7) | 82 (41.4) | 535 (42.9) | ||
| Low | 13 (50) | 664 (48.9) | 60 (30.3) | 424 (35) | ||
| If you perceived a high risk of exposure at work; why? No. (%) | ||||||
| (N=396). Only asked during study period 2 only patient exposures | 23 (41.1) | 98 (34) | .31 | |||
| Patient exposures + another risk factor | 55 (98.2) | 275 (95.5) | .34 | |||
| Colleague exposures | 24 (42.9) | 142 (49.3) | .38 | |||
| Visitor exposures | 21 (37.5) | 103 (35.8) | .80 | |||
| Perceived lack of PPE or IP policies | 8 (14.3) | 34 (11.8) | .60 | |||
Note. SD, standard deviation; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; MDHHS, Michigan Department of Health and Human Services; PPE, personal protective equipment; CAPR, controlled air purifying respirator; IQR, interquartile range; IP, infection prevention measures.
Providers (clinical providers with most patient exposure): physicians, residents, advanced practice providers (APPs), nurses, medical assistants (MAs), respiratory therapists. Interprofessional services: nutrition/registered dietician (RD), social work, case management, physical therapy (PT), occupational therapist (OT), speech-language pathologist (SLP), pharmacy. Ancillary services: radiology technicians, lab. Nonclinical: clerical, administrative, research, security, food services, maintenance, housekeeping, other.
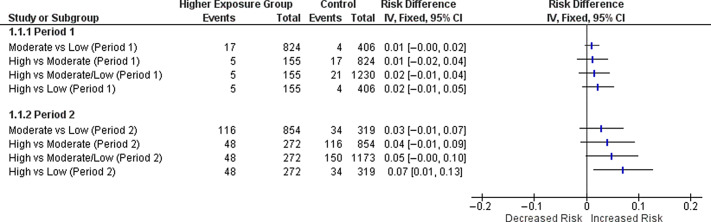
During study period 1, the seroprevalence was 1.9% (95% CI, 1.2%–2.6%), which increased to 13.7% (95% CI, 11.9%–15.5%) during study period 2. During period 2, but not period 1, HCWs with the highest exposure did have an increased risk of seropositivity compared to those with low exposure (risk difference, 7%; 95% CI, 1%–13%) (Fig. 2). Using the community seroprevalence for reported for Michigan by the CDC during period 1, HCWs demonstrated a significantly lower seroprevalence (1.9% vs 4%; one 1-sided P value < .0001). Using our conservative estimate of community seroprevalence during period 2, HCWs did not have a higher risk of seropositivity (13.7% vs 12.3%; 1-sided P value = .053).
Fig. 2.
The risk difference and 95% CI between higher and lower exposure groups during study periods 1 and 2. During period 2, healthcare workers at the highest exposure risk had an increased probability COVID-19 by seropositivity to SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
During period 1, 979 HCWs reported patient contact and 36 developed COVID-19. During period 2, 1,126 HCWs reported patient contact and 114 developed COVID-19 (Fig. 3). Participants who had a high-risk exposure outside of work (compared to those without) had a decreased probability of asymptomatic disease (aOR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.16–0.86). Similarly, participants with a high-risk outside work exposure also demonstrated more symptoms compared to participants without on a high-risk outside work exposure (median 3 [IQR, 5] vs median 1 [IQR, 2]; P = .0097) (Fig. 4). Type of mask use, compliance with public healthcare and infection prevention measures, highest work exposure risk, sex, and age did not confound this relationship.
Fig. 3.
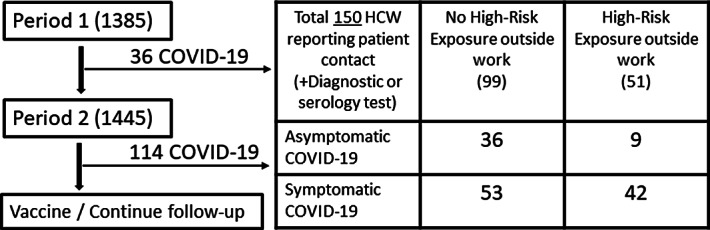
Cohort for the primary outcome.
Fig. 4.
High-risk exposure outside work and number of symptoms in participants who developed COVID-19.
Discussion
Over this study period, a significant change in seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies among HCWs was demonstrated, which likely mirrored the community disease spread. During a time of high community COVID-19 disease prevalence, HCWs with the highest exposure may be at an increased risk of acquiring COVID-19. However, when exposure to COVID-19 occurred only within the healthcare system, HCWs demonstrated a higher likelihood of mild and asymptomatic disease. This finding suggests that community and home exposures may be of greater significance than healthcare-system exposure, and it underscores the importance of public healthcare measures to mitigate viral transmission outside the healthcare system and to reduce disease severity.
Much of the literature on wearing masks has focused on the use of masks for the protection of others; however, protection for the mask wearer has also been observed.24 Following the initial surge of COVID-19 disease in southeastern Michigan, the largest healthcare system in the region reported that HCWs who wore masks during COVID-19 exposure had a lower seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. However, they did not ask whether the exposure occurred in the healthcare system or community, and they also found that those who reported using enhanced respiratory protection during exposure had more asymptomatic disease than others.4 Our finding that HCWs who avoided high risk outside hospital exposures had milder disease and a higher proportion of asymptomatic disease suggests that infection prevention measures may result in lower inoculum when exposed. This information supports the hypothesis that infection prevention measures, which are in high compliance within the healthcare system, may reduce the inoculum of the virus (blocking most but not all viral particles), leading to more mild or asymptomatic disease.18,25 In essence, this results in a variolation process in which individuals are exposure to low viral inoculum, resulting in mild or asymptomatic disease followed by immunity.
The strengths of our study include the prospective, longitudinal evaluation on risk of exposure within the home and community, adherence to PPE policies at work, and adherence to public healthcare interventions. Despite these strengths, our study was limited by the convenience sample, and ∼50% of our staff did not participate in either the survey or the antibody testing. Additionally, we did not obtain information about body mass index and other comorbid medical conditions, which may confound disease severity, given that little was known about these factors at inception of the survey.
Our data suggest that HCWs at the highest exposure to COVID-19 have a clinically significant increased risk of acquiring COVID-19, even after adjusting for exposures outside work and compliance with infection prevention measures. However, healthcare-acquired COVID-19 may be more likely to be asymptomatic or milder than community-acquired disease. These findings suggest that infection prevention strategies (including mask wearing) are mitigating inoculum and disease severity and that such strategies should be encouraged outside the healthcare system to mitigate disease severity.
Acknowledgments
Supplementary material
For supplementary material accompanying this paper visit http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/ice.2021.167.
click here to view supplementary material
Financial support
No financial support was received for this research project.
Conflicts of interest
No authors report any conflicts of interest relevant to this manuscript.
References
- 1.Bai Y, Yao L, Wei T, et al. Presumed asymptomatic carrier transmission of COVID-19. JAMA 2020;323:1406–1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cevik M, Marcus JL, Buckee C, Smith TC. SARS-CoV-2 transmission dynamics should inform policy. Clin Infect Dis 2020. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 3.Meyerowitz EA, Richterman A, Gandhi RT, Sax PE. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: a review of viral, host, and environmental factors. Ann Intern Med 2021;174:69–79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Sims MD, Maine GN, Childers KL, et al. COVID-19 seropositivity and asymptomatic rates in healthcare workers are associated with job function and masking. Clin Infect Dis 2020. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Jeremias A, Nguyen J, Levine J, et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among healthcare workers in a tertiary community hospital. JAMA Intern Med 2020. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.4214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Moscola J, Sembajwe G, Jarrett M, et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in health care personnel in the New York City area. JAMA 2020;324:893–895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Steensels D, Oris E, Coninx L, et al. Hospital-wide SARS-CoV-2 antibody screening in 3056 staff in a tertiary center in Belgium. JAMA 2020;324:195–197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Celebi G, Piskin N, Beklevic AC, et al. Specific risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 transmission among health care workers in a university hospital. Am J Infect Control 2020;48:1225–1230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Godbout EJ, Pryor R, Harmon M, et al. COVID-19 seroprevalence among healthcare workers in a low prevalence region. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2020. doi: 10.1017/ice.2020.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Iversen K, Bundgaard H, Hasselbalch RB, et al. Risk of COVID-19 in healthcare workers in Denmark: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis 2020;20:1401–1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Keeley AJ, Evans C, Colton H, et al. Roll-out of SARS-CoV-2 testing for healthcare workers at a large NHS Foundation Trust in the United Kingdom, March 2020. Euro Surveill 2020;25:2000433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yogo N, Greenwood KL, Thompson L, et al. Point-prevalence survey to evaluate the seropositivity for COVID-19 among high-risk healthcare workers. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2020. doi: 10.1017/ice.2020.1370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Self WH, Tenforde MW, Stubblefield WB, et al. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 among frontline healthcare personnel in a multistate hospital network—13 academic medical centers, April–June 2020. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:1221–1226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fung HF, Martinez L, Alarid-Escudero F, et al. The household secondary attack rate of SARS-CoV-2: a rapid review. Clin Infect Dis 2020. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Ghinai I, Woods S, Ritger KA, et al. Community transmission of SARS-CoV-2 at two family gatherings—Chicago, Illinois, February–March 2020. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:446–450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hamner L, Dubbel P, Capron I, et al. High SARS-CoV-2 attack rate following exposure at a choir practice—Skagit County, Washington, March 2020. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:606–610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Madewell ZJ, Yang Y, Longini IM Jr, Halloran ME, Dean NE.Household transmission of SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 2020;3:e2031756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mahale P, Rothfuss C, Bly S, et al. Multiple COVID-19 outbreaks linked to a wedding reception in rural Maine—August 7–September 14, 2020. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:1686–1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, et al. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007;370:1453–1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Trabaud MA, Icard V, Milon MP, Bal A, Lina B, Escuret V.Comparison of eight commercial, high-throughput, automated or ELISA assays detecting SARS-CoV-2 IgG or total antibody. J Clin Virol 2020;132:104613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bajema KL, Wiegand RE, Cuffe K, et al. Estimated SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in the US as of September 2020. JAMA Intern Med 2021;181:450–460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Patel MM, Thornburg NJ, Stubblefield WB, et al. Change in antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 over 60 days among healthcare personnel in Nashville, Tennessee. JAMA 2020;324:1781–1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Poland GA, Ovsyannikova IG, Kennedy RB.SARS-CoV-2 immunity: review and applications to phase 3 vaccine candidates. Lancet 2020;396:1595–1606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chu DK, Akl EA, Duda S, et al. Physical distancing, face masks, and eye protection to prevent person-to-person transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2020;395:1973–1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gandhi M, Rutherford GW.Facial masking for COVID-19—potential for “variolation” as we await a vaccine. N Engl J Med 2020;383:e101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
For supplementary material accompanying this paper visit http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/ice.2021.167.
click here to view supplementary material