SUMMARY
Agrochemical fungicidal leads have been prepared from photochemically derived 1-aminonorbornane building blocks. The unique 1-aminonorbornane core is generated via direct excitation of a Schiff base precursor, leveraging the N-centered radical character of the excited state species to facilitate a series of radical reactions that construct the norbornane core. This process requires no exogenous reagents, only solvent and photons; thus, it represents an exceptionally simple and efficient means of generating the key building blocks. These (hetero) arene-fused 1-aminonorbornanes are unprecedented in both the agrochemical and pharmaceutical discovery literature; therefore, photochemical advances have provided the unique opportunity to explore the functional utility of novel chemical space. Toward this end, the 1-aminonorbornanes were used to generate next-generation succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors. In vitro fungicidal activity is demonstrated against three fungal plant pathogens affecting field crops, specifically: Fusarium graminearum, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, and Macrophomina phaseolina. The in vitro performance against F. graminearum was shown to translate into a greenhouse setting. The discovery of in planta fungicidal activity illustrates the interdisciplinary value available via photochemical innovation.
Graphical Abstract
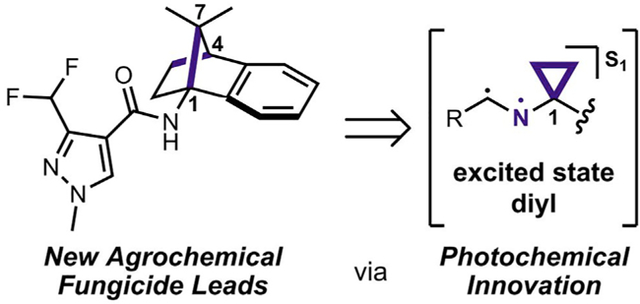
Advances in synthetic photochemistry can directly affect the world of agrochemical development. Staveness et al. report using photochemically derived 1-aminonorbornanes to produce and evaluate a series of fungicidal candidates in vitro and in the greenhouse and that offer fungicidal activity on par with commercial agents.
INTRODUCTION
Advances in synthetic photochemistry have disruptive potential to influence modern industrial chemistry.1,2 Excited state species offer reactivity modes that are fundamentally unique, in regard to both the reactive intermediates involved and the structural motifs that can be generated.3,4 In many cases, photochemical methodology offers the most efficient, if not the only, reliable means of preparing a given scaffold. Strained, saturated carbocycles and heterocycles are arguably the most prominent demonstration of this concept, evidenced by classic examples such as the synthesis of oxetanes via the Paterno-Buchi reaction or cyclobutanes via the De Mayo [2+2] photocycloaddition. This attribute of photochemistry is optimally aligned with the rising prominence of sp3-centric drug design5 and the pressing need for increased diversification of synthetically accessible chemical space.6,7 This alignment explicitly communicates the opportunity to affect the industrial sector via a concerted focus on photochemical reaction science.
Importantly, while most synthetic labs frame the applications of their work around pharmaceutical development, the opportunity to influence agrochemical development is equally advantageous. Agrochemistry faces many of the hallmark challenges of medicinal chemistry (e.g., target specificity, biodistribution, genetic variation in the target population),8 and the ability to explore new chemical space necessarily improves the likelihood of designing, identifying, and optimizing for new functions in either setting. One could argue that delivering efficient synthetic access to novel molecular frameworks is even more imperative for the agrochemical sector, given the exceedingly stringent cost-of-production restrictions (generally ≤$200/kg).
In regard to fungicidal development, the most pressing concern for the field is the rising resistance pressures.9 Fungal pathogens are developing resistance at alarming rates, and there is a clear need for next-generation fungicides with differentiated activity, as current commercial agents become less effective in the face of increasingly prominent resistant strains. Achieving highly effective control of fungal pathogens is of paramount importance to ensure prolonged food security.10 With the global population projected to reach 9 billion by 2050, food production must rise 60%–100% in that time frame.11 Fungal pathogens are already estimated to cause a 30% loss across the production chain (e.g., harvest, storage, distribution),12 which does not account for downstream effects of mycotoxin contamination in livestock, aquaculture, and dairy industries. The mid-1990s outbreak of Fusarium graminearum (wheat head blight) in North Dakota illustrates the economic impact that can result from uncontrolled fungal pathogens, eliciting estimated losses of $2.5 billion in the grain sector and $7.7 billion across the state economy after accounting for secondary market effects.13 Unsurprisingly, F. graminearum was recognized as one of the “top 10 most dangerous fungal pathogens” in modern agriculture.14,15 Furthermore, climate change is anticipated to exacerbate fungal diseases as well as change the geographic distribution of disease occurrence.10 While small-molecule fungicides clearly are not the only disease management options moving forward (genetically engineered crops, increased breeding efforts, biofungicides, improved crop rotation and cultural practices), they are assuredly a necessary component of the multifaceted solution that will be needed to achieve sustainable food security in this era of rapidly emerging challenges.
As mentioned above, new photochemical methodology is well suited to rapidly translate from academic lab benches to leading edge discovery and development efforts. Of the many potential interdisciplinary applications for this new reaction science, fungicidal agents (and other agrochemicals) should be a key focus; accessing new chemical space and generating novel fungicidal leads is an exceptionally facile means of influencing industrial chemistry and eliciting real-world impact. The effort reported herein is our preliminary progress toward this goal, detailing the synthesis and evaluation (both in vitro and in planta) of 1-aminonorbornane-based succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors (SDHIs) as novel fungicidal leads for the control of Ascomycete plant pathogens.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Preparation of SDHI candidates
The design and preparation of the fungicidal candidate library detailed herein was founded on an enabling photochemical methodology recently developed in the Stephenson lab.16 The unique (hetero)aryl-fused 1-aminonorbornane (1-aminoNB) scaffold was accessed through a masked N-centered radical strategy, in which direct irradiation of cyclopropylimine starting materials engaged in formal intramolecular [3+2] cycloadditions to forge the norbornane core (see Figure 1). More specifically, N-cyclopropyl 4-nitrobenzimines with an appropriately tethered styrene-like motif were irradiated with 390 nm light to facilitate an n→π* transition. From the S1(n,π*) state, the N-centered radical character drives the homolytic fragmentation of the cyclopropane to initiate the requisite 6-exo-trig, 5-exo-trig radical cyclizations, returning the radical character to the nitrogen and thus facilitating the termination of both radical intermediates through simple reformation of the imine motif. The operational simplicity of this photochemical method provides rapid entry to the protected 1-aminoNB scaffolds, and simple solvolysis of the Schiff base was shown to readily generate the free amine for N-derivatization.
Figure 1. Design of novel fungicidal candidates as enabled by photochemical innovation.
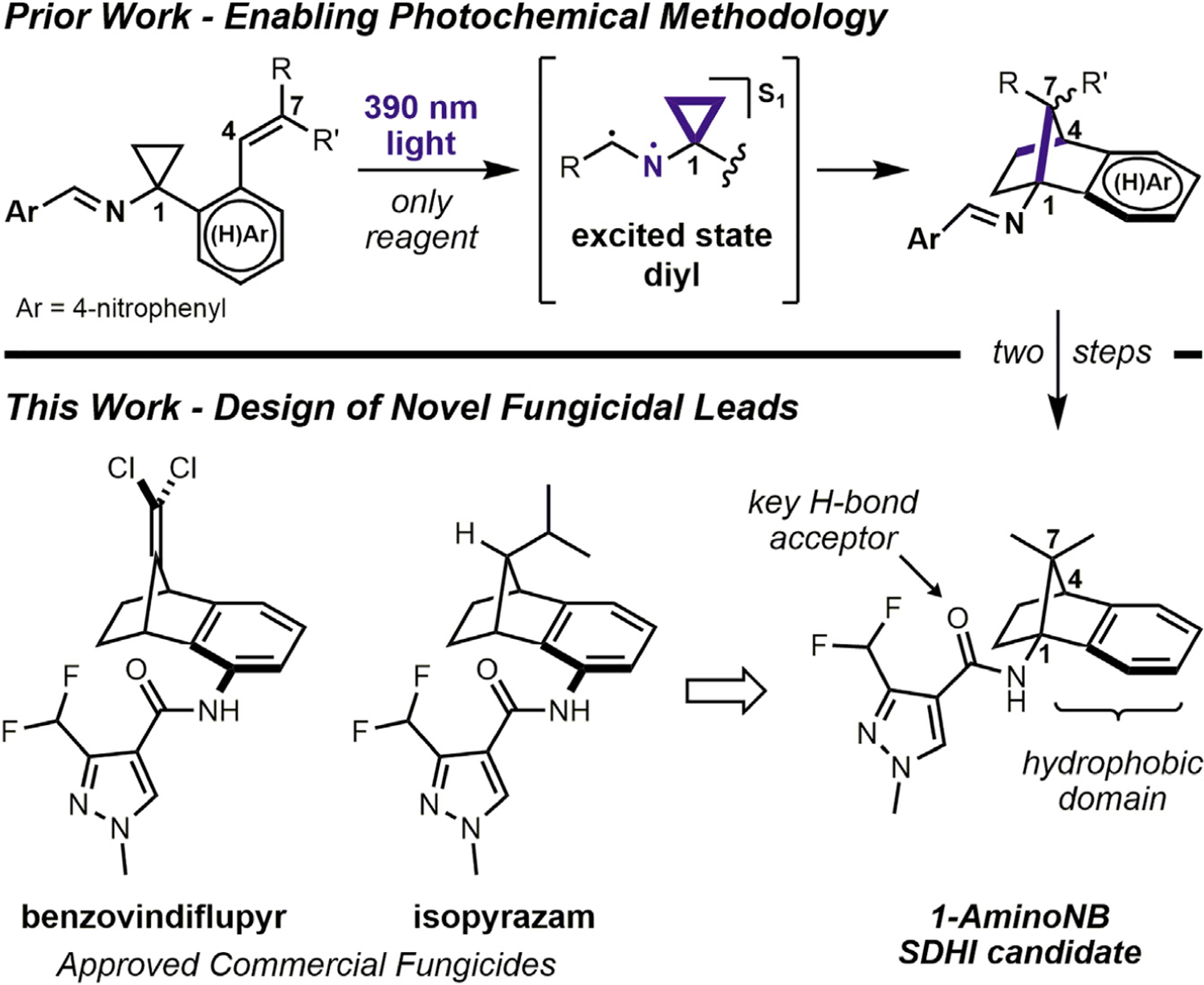
Generic synthetic approach to 1-aminonorbornanes is depicted, as is the basis for the design of the proposed SDHI candidate class.
These 1-aminoNB building blocks were directed toward the SDHI class of fungicides owing to the close analogy to design features within this class. Initially brought to market in 2003 with the introduction of boscalid, SDHIs are characterized by a carboxamide pharmacophore appended to a hydrophobic domain.17–19 The 3-difluoromethylpyrazole carboxamide motif has proven the most broadly applicable pharmacophore, while the hydrophobic domain is represented by a great deal more structural diversity. Two notable examples are the norbornane-fused anilines found in benzovindiflupyr and isopyrazam.17 These species possess unique three-dimensional structures and contain localized bulk near the pharmacophoric motif, two factors that communicated the potential for our 1-aminoNB substrates to serve as the basis of a new class of SDHI candidates.
To generate said SDHI candidates, the previously reported library of Schiff base-protected 1-aminoNBs were converted to the desired pyrazole carboxamides through a two-step solvolysis and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC)-coupling sequence; a general protocol and the yields for the individual sequences can be found in the supplemental information. The library is represented in Figure 2, predominantly comprising the 3-difluoromethyl-pyrazole carboxamide. The compounds were evaluated using a poison plate mycelial growth assay, in which an active mycelial culture is positioned in the center of a plate containing medium inoculated with the compound of interest; radial growth is measured and then compared to growth on an untreated control (data reported as percent relative growth). The three pathogens chosen for this initial evaluation were Fusariumgraminearum, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, and Macrophomina phaseolina, three agriculturally relevant fungal pathogens in the Ascomycota phylum for which there are currently a limited number of effective fungicides.
Figure 2. Fungicidal activity of 1-aminoNB SDHI candidates—percent radial mycelial growth.
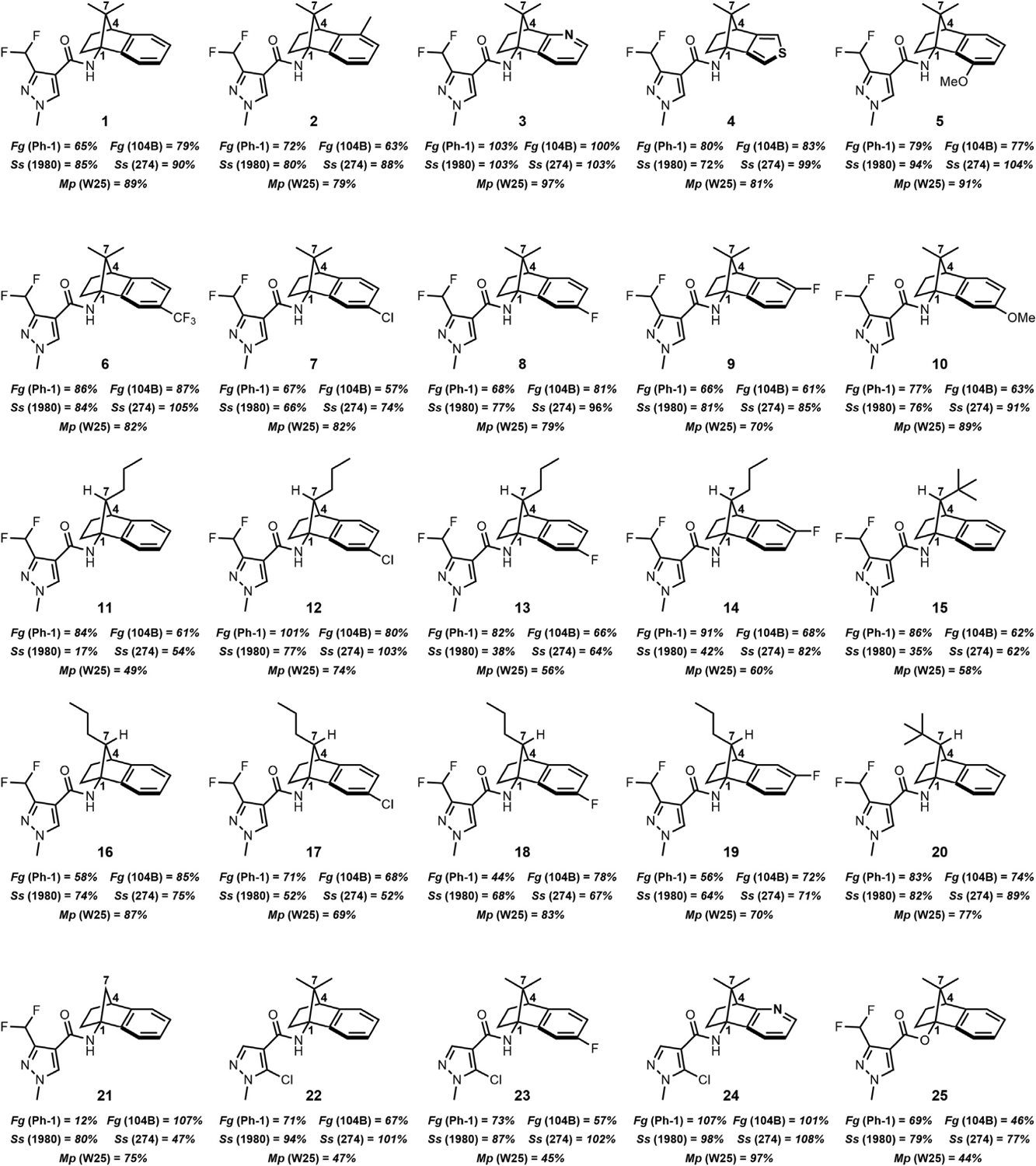
All values reported as the percent relative growth relative to an untreated control (untreated control set to 100% by convention; experimental details provided in the supplemental information); the fungi abbreviations are as follows: Fg, Fusarium graminearum; Ss, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum; Mp, Macrophomina phaseolina; the specific fungal isolate is provided in parentheses; the standard error for each value is provided in the supplemental information. Fluxapyroxad, a commercial SDHI (not shown), was used as a positive control; data provided in the supplemental information and reported in the text where applicable (“fluxa”). All compounds tested at 10 ppm concentration in agar growth medium (~30 μM for this class of compounds).
Gratifyingly, many of the 1-aminoNB carboxamides demonstrated fungicidal activity relative to untreated controls, at times matching the performance of the commercial fungicide fluxapyroxad. In general, S. sclerotiorum isolates were the most sensitive, with a few notable exceptions arising from F. graminearum and M. phaseolina; three isolates of each species were tested, although only five representative isolates are presented in Figure 2 for clarity (see Figure S1 and Table S1 for complete dataset).
Evaluation of 1-aminoNB-based fungicidal candidates
Certain structure-activity relationships can be inferred from the data presented below. Among the C7-dimethyl series (1–10), the in vitro performance proved to be most heavily influenced by the heteroarene-fused variations, while little influence was observed with substituents on the benzene ring. For instance, the C11-Me compound 2 was effectively indistinguishable from parent 1-aminoNB lead 1. However, the pyridine within compound 3 proved to be the most ineffective motif evaluated, leading to no observable fungicidal activity. The thiophene-fused system 4 and electron-rich C8-OMe system 5 showed mixed effects. Both modifications appeared to diminish activity in F. graminearum isolate Ph-1 (relative growth: 4 = 80% and 5 = 79% versus 1 = 65%), although the introduction of the thiophene motif in analog 4 may be somewhat beneficial against S. sclerotiorum isolate 1980 and M. phaseolina isolate W25 (relative growth: 4 = 72%/81% versus 1 = 85%/89%). Electron-withdrawing groups on the benzene ring showed little effect, as seen in the C9-substituted series −H (1), −CF3 (6), −Cl (7), −F (8), although the C9-CF3 compound 6 did appear to be the least active of the group. A pair of positional variants led to little influence on activity; the C9-F (8) versus C10-F (9) comparison and the C9-OMe (10) versus C8-OMe (5) provided nearly identical performances, reinforcing the notion that these motifs would simply lie in a large hydrophobic pocket and not directly influence binding.
The most influential alterations in the 1-aminoNB candidate library were the manipulations of the bridging carbon in the norbornane (C7) (see Figure 3). In general, both the C7-syn and C7-anti isomers of mono-substituted systems (11–20) were more active than the C7-dimethyl congeners (1, 7–9); the addition of halogenation at C9 or C10 again proved minimally effective (compare syn-C7-Pr analogs 13 and 14 as well as anti-C7-Pr analogs 18 and 19). The C7-methylene species 21, prepared via decarboxylation of a C7-CO2H (see supplemental information), also demonstrated improved performance. Interestingly, these C7 manipulations offered examples of isolate-specific performance against certain fungal species. The C7-methylene candidate 21 demonstrated excellent performance against F. graminearum isolate Ph-1 (relative growth: 11%), but little to no activity against the other isolates 104B (relative growth: 107%) or 66B (relative growth: 94%; data not shown), mirroring the activity profile of commercial fungicide fluxapyroxad. Alternatively, the addition of C7 substitution (syn-, anti-, or gem-dimethyl) led to diminished activity against isolate Ph-1 while slightly improving activity against isolate 104B. The latter activity is not sufficient to compete with modern commercial fungicides, but the presence of this apparent size exclusion-based inversion of isolate selectivity may prove informative for future development programs. A similar C7-mediated isolate specificity was seen in the performance against S. sclerotiorum. While the anti-mono-substituted systems 16 and 20 were only modestly active across all of the isolates, the syn C7-Pr isomers 11 and 15 were more active against isolate 1980 than isolate 274, even matching the performance of fluxapyroxad (relative growth against S. sclerotiorum isolate 1980: fluxa = 11%, 11 = 17%, 16 = 74%). C7-methylene compound 21, the least bulky of the series, reversed this profile, showing modest activity against S. sclerotiorum isolate 1980 (relative growth: 80%), yet good activity against S. sclerotiorum isolate 274 (relative growth: 47%). Further investigation of the connection between these substitution patterns and the genomic profile of the individual isolates will be explored in due course.
Figure 3. Isolate-specific fungicidal activity as a function of C7 substitution.
See Figure 2 for description of assay and data representation.
Lastly, a small series of alternative pyrazoles were prepared to assess the potential to improve the pharmacophore itself (see Figure 4). The C5′-Cl species was chosen as a potential covalent inhibitor and did appear to offer improved activity (e.g., relative growth against M. phaseolina isolate W25, C5′-Cl compounds 22, 23, 24 = 47%, 45%, 97%, respectively, versus C3′-difluoromethyl congeners 1, 8, 3 = 89%, 79%, 97%, respectively). Interestingly, the pyrazole ester, available from a bridgehead hydro-deamination of the corresponding 1-aminoNB, also offered a modest improvement in activity (relative growth against F. graminearum 104B and M. phaseolina isolate W25: 1 = 79%/89% versus 25 = 46%/44%). Whether or not these pyrazole variations would retain these benefits in a field setting relative to the proven 3-difluoromethylpyrazole carboxamide remains to be seen. Additional variants can be found in the supplemental information.
Figure 4. Comparison of analogs with alternative pyrazole motifs.
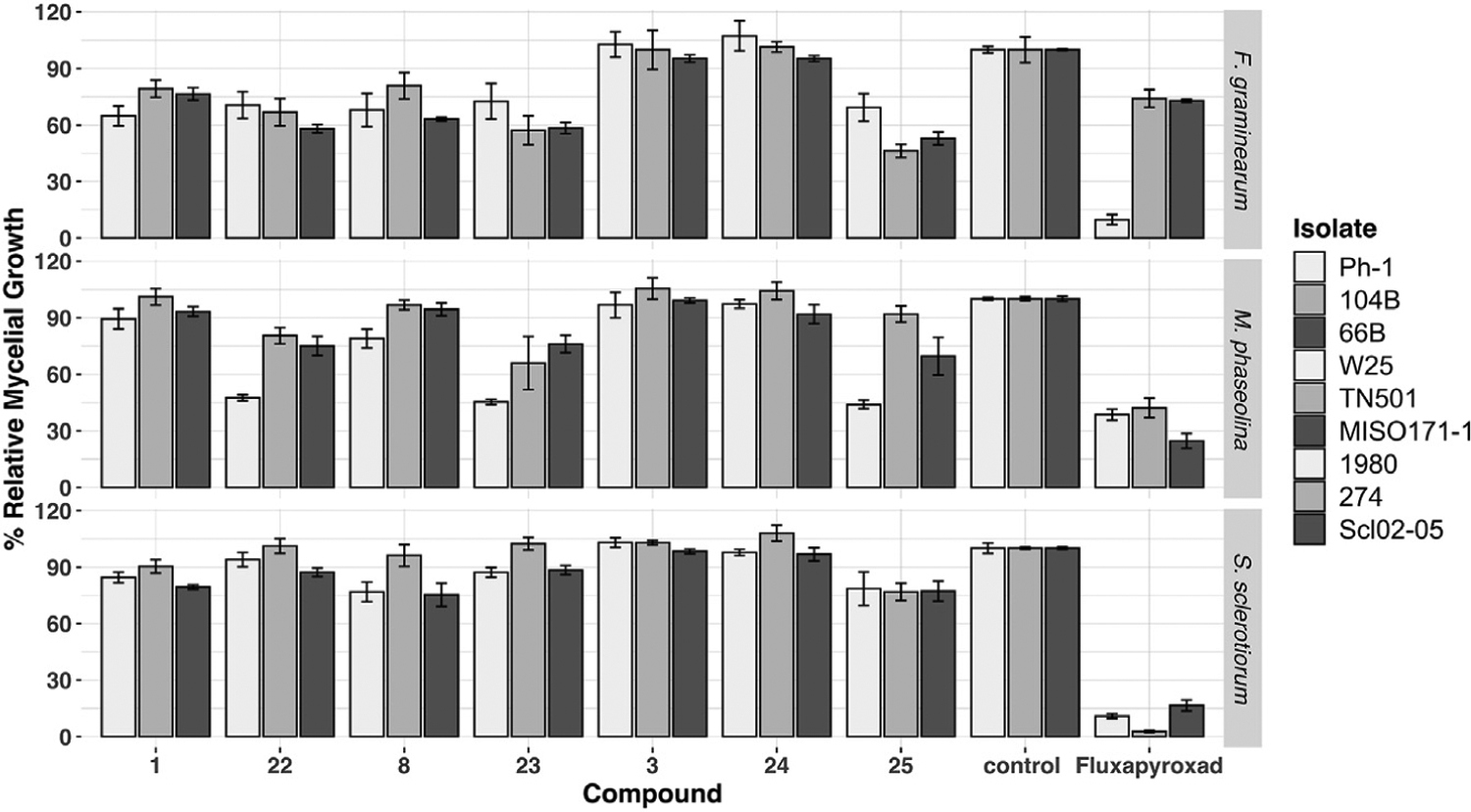
See Figure 2 for description of assay and data representation.
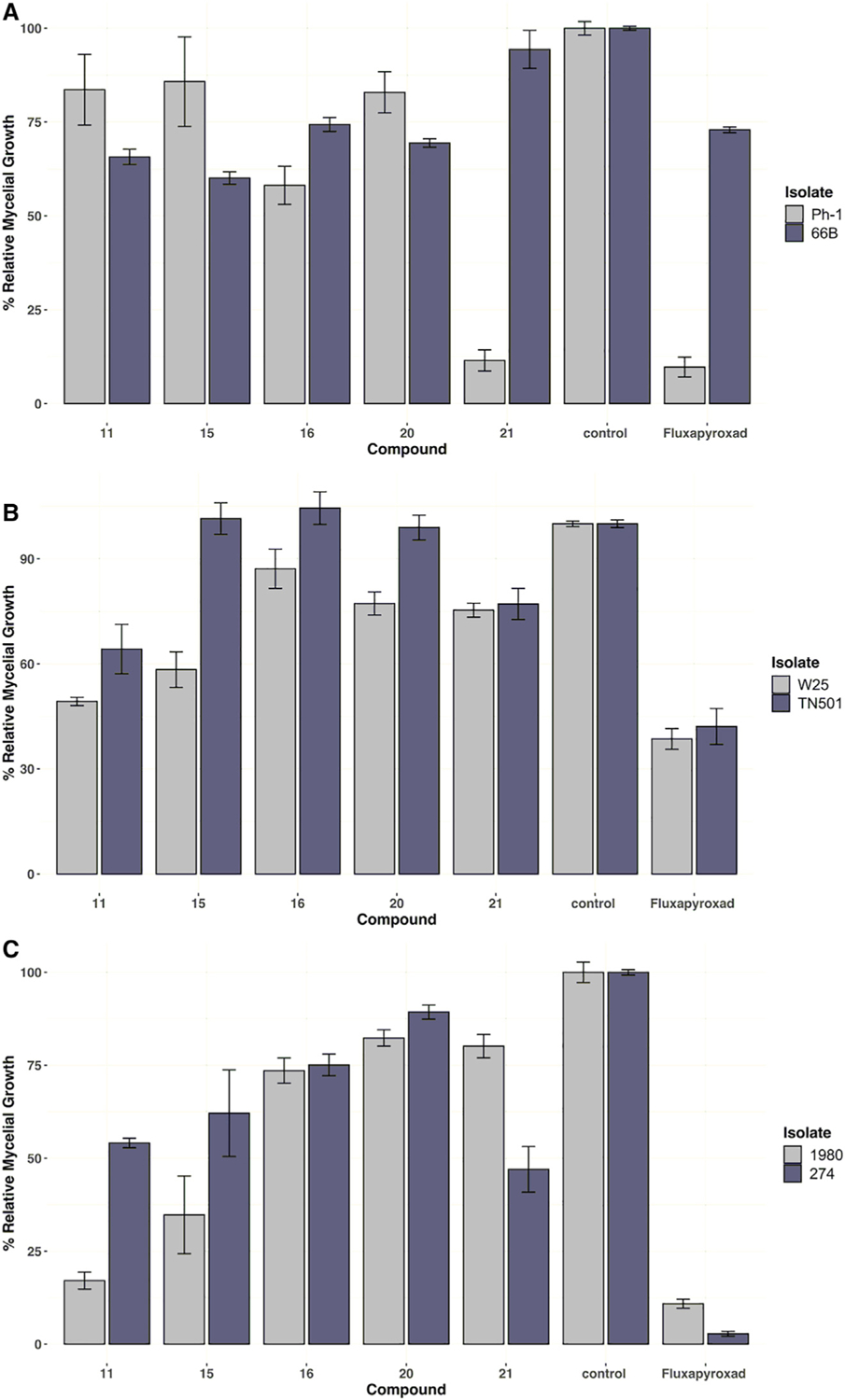
Significantly, the fungicidal activity described above was not limited to in vitro performance. A subset of compounds was tested against F. graminearum isolate Ph-1 in a greenhouse setting, evaluating preventive activity in spring wheat (cv. Wheaton). SDHI candidates were applied as 250 ppm stock solutions in acetone 24 h before inoculation with the F. graminearum isolate Ph-1, evaluating performance relative to commercial SDHI fungicide pydiflumetofen. Due to variation in a greenhouse setting, there were no statistically significant differences, but major trends align with in vitro data (see Figure 5). The C7-methylene compound 21 proved active, preventing disease progression at a level similar to the commercial control. While less active, the C7-mono-substituted systems 11 and 16 demonstrated performance that aligned with the radial mycelial growth assay, with the syn-substituted species 11 proving more effective than the corresponding anti-substituted isomer 16. These data suggest the functional predictive capabilites of the in vitro assay for this collection of SDHI candidates. More important, these data demonstrate that our 1-aminoNB-based leads do not suffer from any inherent or systematic pharmacokinetic barriers to in planta function, although the locale of fungicidal function cannot be determined from the data (residual activity versus distribution into the plant tissue). While additional replications and studies would be needed to fully characterize the fungicidal activity of these 1-aminoNB-based leads in vivo, the observed in planta performance indicates the potential for translational development.
Figure 5. In planta performance of 1-aminoNBs.
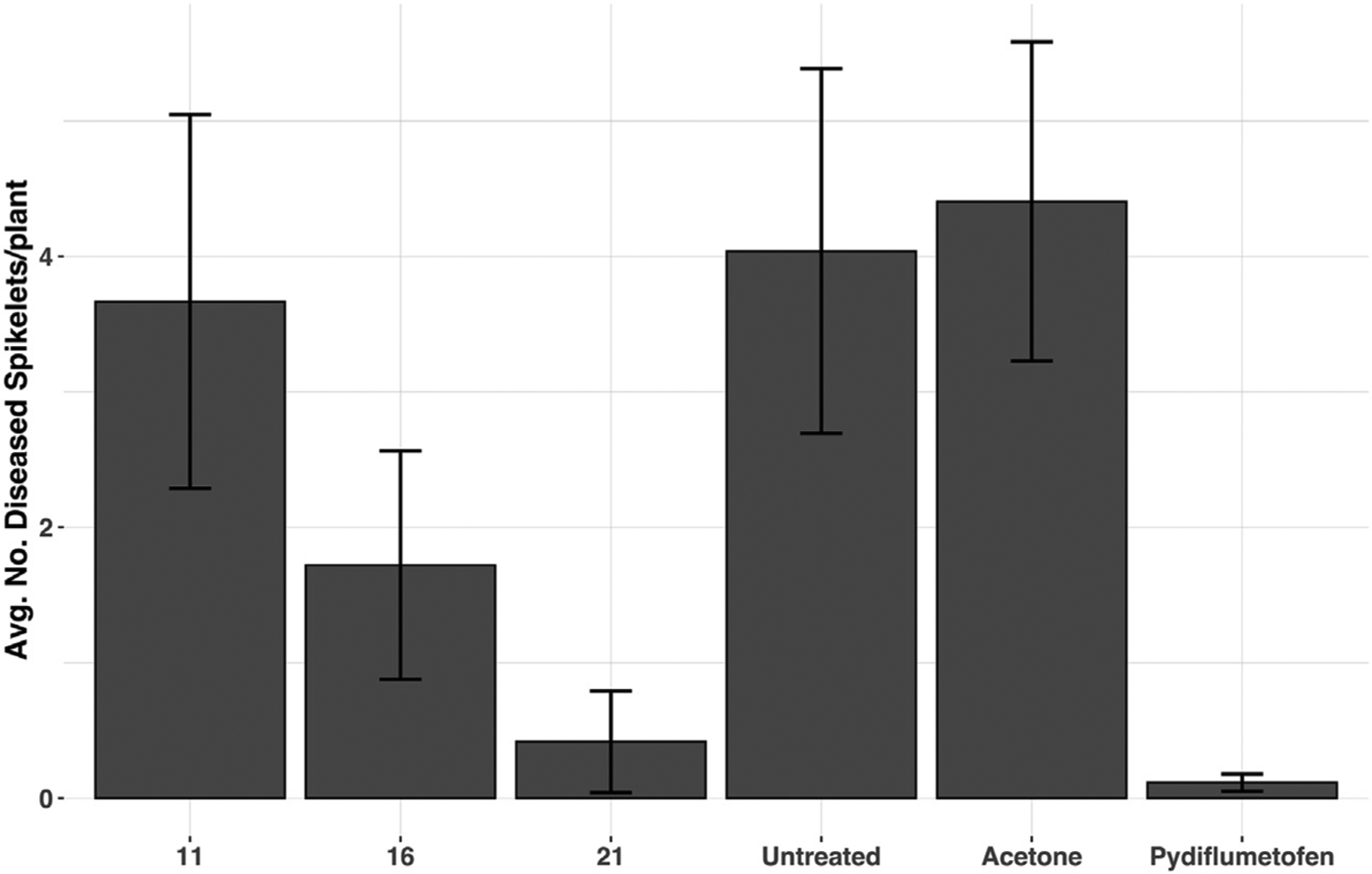
Results of in planta testing in a greenhouse setting, a 250-ppm solution in acetone (~750 μM for these compounds) was sprayed on wheat heads 24 h before spraying heads with F. graminearum conidia (isolate Ph-1) with surfactant tween at anthesis in a susceptible spring wheat variety. A maximum of 600 μL was applied to each head, leading to an estimated maximum dose of 0.15 mg per head. Approximately 21 days after inoculation, wheat heads were rated for necrosis (sign of infection) by counting the number of affected spikelets per head. Three pots with at least 3 plants per pot were used in each experiment, and 2 runs were completed, with the mean of both runs presented here, and error bars representing the standard error of the mean.
Structurally unique 1-aminoNB building blocks have been implemented in the design, synthesis, and evaluation of novel agrochemical fungicide candidates. These building blocks were only made available through photochemical innovation, showcasing the ability of synthetic discoveries to have immediate interdisciplinary impact. Certain 1-aminoNB SDHI leads showcased fungicidal activity that competed with commercial fungicidal agents in vitro, while also revealing isolate-specific activity profiles that can be used to inform next-generation design. Importantly, the 1-aminoNB compounds also demonstrated in planta activity against the prominent fungal pathogen Fusarium graminearum, highlighting the potential for this class of compounds (and thus the photochemical methodology) to influence industrial agrochemical development.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Resource availability
Lead contact
The lead contact is Corey R.J. Stephenson (crjsteph@umich.edu).
Materials availability
Detailed procedures to generate these unique analogs can be found in the supplemental information. A generic protocol and photochemical reaction setup are depicted in Scheme S1 and Figure S4, respectively. NMR and other characterization data are provided, including the NMR spectra (see Figures S5–S88). The compounds reported herein may be obtained and used for research purposes under the auspices of a material transfer agreement and/or related confidentiality agreements with the University of Michigan; requests and inquiries can be sent to Prof. Corey R.J. Stephenson (crjsteph@umich.edu).
Data and code availability
This study did not generate datasets or codes. Full experimental procedures and corresponding datasets are provided in the supplemental information (see Figures S1–S3 and Table S1).
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
Photochemical advances enable new design tactic in fungicidal development
In vitro and in planta fungicidal activity found with 1-aminonorbornane scaffold
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors acknowledge the financial support for this research from the NIH NIGMS (R01-GM127774) and the University of Michigan. D.S. was supported by a Postdoctoral Fellowship, PF-16-236-01-CDD, from the American Cancer Society. J.L.C. was supported by the University of Michigan’s Rackham Merit Fellowship. This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship (to R.C.M., grant no. DGE 1256260). This work was supported by the ADVANCE Grant Proof of Concept Fund, sponsored by the Michigan Economic Development Corportation (MEDC).
Footnotes
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrp.2021.100548.
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
Efforts related to this work are the subject of ongoing commercialization efforts, as supported by the University of Michigan Office of Technology Transfer. D.S. and C.R.J.S. are authors of provisional patent filings associated with this research.
REFERENCES
- 1.Douglas J, Sevrin M, and Stephenson CRJ (2016). Visible light photocatalysis: applications and new disconnections in the synthesis of pharmaceutical agents. Org. Process Res. Dev 20, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Blakemore DC, Castro L, Churcher I, Rees DC, Thomas AW, Wilson DM, and Wood A (2018). Organic synthesis provides opportunities to transform drug discovery. Nat. Chem 10, 383–394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schultz DM, and Yoon TP (2014). Solar synthesis: prospects in visible light photocatalysis. Science 343, 1239176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kärkäs MD, Porco JA Jr., and Stephenson CRJ (2016). Photochemical approaches to complex chemotypes: applications in natural product synthesis. Chem. Rev 116, 9683–9747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lovering F, Bikker J, and Humblet C (2009). Escape from flatland: increasing saturation as an approach to improving clinical success. J. Med. Chem 52, 6752–6756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ritchie TJ, and Macdonald SJ (2014). Physicochemical descriptors of aromatic character and their use in drug discovery. J. Med. Chem 57, 7206–7215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Brown DG, and Boström J (2016). Analysis of past and present synthetic methodologies on medicinal chemistry: where have all the new reactions gone? J. Med. Chem 59, 4443–4458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Leadbetter A (2015). Recent developments and challenges in chemical disease control. Plant Prot. Sci 51, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hawkins NJ, and Fraaije BA (2018). Fitness penalties in the evolution of fungicide resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol 56, 339–360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kettles GJ, and Luna E (2019). Food security in 2044: How do we control the fungal threat? Fungal Biol. 123, 558–564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Alexandratos N, and Bruinsma J (2012). World Agriculture Towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision. ESA Working Paper no. 12–03 (Food and Agriculture Organization; ). [Google Scholar]
- 12.Avery SV, Singleton I, Magan N, and Goldman GH (2019). The fungal threat to global food security. Fungal Biol. 123, 555–557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nganje W, Kaitibie S, Wilson W, Leistritz L, and Bangsund D (2004). Economic Impacts of Fusarium Head Blight in Wheat and Barley: 1993–2001. Agribusiness Applied Economics Report No. 538 (Department of Agribusiness and Applied Economics, Agricultural Experiment Station, North Dakota State University; ). [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dean R, Van Kan JA, Pretorius ZA, Hammond-Kosack KE, Di Pietro A, Spanu PD, Rudd JJ, Dickman M, Kahmann R, Ellis J, and Foster GD (2012). The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol 13, 414–430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dweba C, Figlan S, Shimelis H, Motaung T, Sydenham S, Mwadzingeni L, and Tsilo T (2017). Fusarium head blight of wheat: pathogenesis and control strategies. Crop Prot. 91, 114–122. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Staveness D, Collins JL 3rd, McAtee RC, and Stephenson CRJ (2019). Exploiting Imine Photochemistry for Masked N-Centered Radical Reactivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 58, 19000–19006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Walter H, Tobler H, Gribkov D, and Corsi C (2015). Sedaxane, isopyrazam and Solatenol: novel broad-spectrum fungicides inhibiting succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) - synthesis challenges and biological aspects. Chimia (Aarau) 69, 425–434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sierotzki H, and Scalliet G (2013). A review of current knowledge of resistance aspects for the next-generation succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor fungicides. Phytopathology 103, 880–887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wei G, Huang MW, Wang WJ, Wu Y, Mei SF, Zhou LM, Mei LC, Zhu XL, and Yang GF (2021). Expanding the chemical space of succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors via the carbon-silicon switch strategy. J. Agric. Food Chem 69, 3965–3971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
This study did not generate datasets or codes. Full experimental procedures and corresponding datasets are provided in the supplemental information (see Figures S1–S3 and Table S1).


