Abstract
Rationale: Early empirical antimicrobial treatment is frequently prescribed to critically ill patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) based on Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines.
Objectives: We aimed to determine the prevalence of early bacterial identification in intubated patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pneumonia, as compared with influenza pneumonia, and to characterize its microbiology and impact on outcomes.
Methods: A multicenter retrospective European cohort was performed in 36 ICUs. All adult patients receiving invasive mechanical ventilation >48 hours were eligible if they had SARS-CoV-2 or influenza pneumonia at ICU admission. Bacterial identification was defined by a positive bacterial culture within 48 hours after intubation in endotracheal aspirates, BAL, blood cultures, or a positive pneumococcal or legionella urinary antigen test.
Measurements and Main Results: A total of 1,050 patients were included (568 in SARS-CoV-2 and 482 in influenza groups). The prevalence of bacterial identification was significantly lower in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia compared with patients with influenza pneumonia (9.7 vs. 33.6%; unadjusted odds ratio, 0.21; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.15–0.30; adjusted odds ratio, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.16–0.33; P < 0.0001). Gram-positive cocci were responsible for 58% and 72% of coinfection in patients with SARS-CoV-2 and influenza pneumonia, respectively. Bacterial identification was associated with increased adjusted hazard ratio for 28-day mortality in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia (1.57; 95% CI, 1.01–2.44; P = 0.043). However, no significant difference was found in the heterogeneity of outcomes related to bacterial identification between the two study groups, suggesting that the impact of coinfection on mortality was not different between patients with SARS-CoV-2 and influenza.
Conclusions: Bacterial identification within 48 hours after intubation is significantly less frequent in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia than patients with influenza pneumonia.Clinical trial registered with www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT 04359693).
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, influenza, bacterial, intensive care, mechanical ventilation
At a Glance Commentary
Scientific Knowledge on the Subject
Prevalence of early bacterial coinfection in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) seems low, but data regarding critically ill patients are lacking.
What This Study Adds to the Field
This multicenter retrospective cohort study reports 9.7% bacterial identification within 48 hours after intubation in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pneumonia, which is threefold lower than patients with influenza pneumonia. Our findings suggest that early empirical antimicrobial treatment should be carefully evaluated at ICU admission after respiratory secretions sampling. Further studies are needed to determine whether antibiotic treatment should be limited to the most severe patients.
By spring 2021, the ongoing coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has affected more than 130 million people, resulting in more than 2,800,000 deaths worldwide (1). Approximately 20% of hospitalized patients are admitted to the ICU because of acute respiratory failure (2). A large proportion of these critically ill patients require intubation, and among them, almost half will eventually die, with high variability depending on patients’ age and geographic location (2–4).
For the sickest patients (i.e., those invasively mechanically ventilated), the Surviving Sepsis Campaign COVID-19 panel suggested, in March 2020, the use of empirical antibiotic therapy to reduce the mortality associated with potential early bacterial coinfection, with necessary daily assessment for deescalation according to microbiology results and the patient’s clinical status (5). This recommendation was based on low-quality evidence upon extrapolation of data from other viral pneumonias, particularly influenza (6, 7). Indeed, bacterial coinfection is commonly reported in critically ill patients admitted for either seasonal or pandemic influenza (8–10). The copathogenesis of influenza viruses and bacteria in the lung is characterized by complex interactions between coinfecting pathogens and the host, leading to the disruption of physical barriers, dysregulation of immune responses, and, at last, bacteria adhesion, overgrowth, and additional immune-mediated host damage (11, 12). As a result, bacterial coinfection may promote a greater severity of viral infection, as supported by few autopsy series of fatal influenza cases during past pandemics (11, 13), and has been reported as a major cause of morbidity and mortality among critically ill patients (9).
However, data on the prevalence of early bacterial coinfection in critically ill patients with COVID-19 are limited. In the last update of the living meta-analysis from Langford and colleagues (14), including 7,107 patients with COVID-19, bacterial coinfection was identified in 4.9% of hospitalized patients on admission (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.6–7.1), although the reported rate was higher in ICU settings at 16.0% (95% CI, 11.6–20.4). However, few critically ill patients were included, illness severity was heterogeneous, and healthcare-associated infections were combined in the ICU subgroup analysis. Recently, two French cohorts including, respectively, 47 and 83 critically ill patients under invasive mechanical ventilation both reported a 28% rate of bacterial coinfection upon ICU admission (15, 16).
Given the scarce and conflicting available data, we conducted this study to compare the prevalence of bacterial identification within the first 2 days after intubation in patients with SARS-CoV-2 or influenza pneumonia and to characterize the microbiological findings and the impact on clinical outcomes of bacterial coinfection. Some of the results of this study have been previously reported in the form of an abstract (17).
Methods
Study Design and Population
This study is a preplanned ancillary analysis of the COVID-19 and ventilator-assocaited pneumonia (coVAPid) multicenter retrospective observational cohort study (18), conducted in 36 ICUs in Europe (28 centers in France, 3 in Spain, 3 in Greece, 1 in Portugal, and 1 in Ireland), selected by invitation. Eligibility criteria included age equal to or above 18 years, the need for invasive mechanical ventilation for more than 48 hours, and the presence at ICU admission of either SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia or influenza pneumonia. Patients were excluded if a viral respiratory infection other than SARS-CoV-2 or influenza was simultaneously diagnosed at ICU admission.
Participating centers retrospectively collected data from consecutive patients admitted to their ICU with SARS-CoV-2 (starting at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in each center) or influenza A or B pneumonia (starting from the last patients admitted with this diagnosis in 2020 and going back to previous seasons if necessary). Each center was asked to include the same number of patients (10–20) in each of the two study groups. Viral infections were confirmed by a positive result of PCR assay of nasopharyngeal or respiratory secretions samples.
The Ethics Committee and Institutional Review Board of the Lille University Hospital approved the study protocol (Comité de Protection des Personnes Ouest VI; approved by April 14, 2020; registration number RIPH:20.04.09.60039) as minimal-risk research using data collected for routine clinical practice and waived the need for informed consent from individual patients. Patients (or their proxies) received written information about the study and could refuse to participate. The study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT 04359693).
Definitions
Early bacterial identification was defined by a positive culture of one or more bacterial pathogens within 48 hours after intubation in a respiratory tract sample (endotracheal aspirate or BAL), blood, or a positive Streptococcus pneumoniae or Legionella pneumophila urinary antigen test. Microbiological identification and susceptibility tests were performed using standard culture-dependent methods. Multidrug-resistant isolates were defined as acquired nonsusceptibility to at least one agent in three or more antimicrobial categories (19). Initial antibiotic treatment was considered as appropriate when at least one antibiotic matching the in vitro susceptibility of the pathogen causing bacterial coinfection was given to treat this infection (20).
Outcomes
The primary outcome of our study was the prevalence of early bacterial identification among patients admitted to the ICU with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia compared with influenza pneumonia. The secondary endpoints included the etiology and outcomes of bacterial coinfection, including mechanical ventilation duration, ICU length of stay, and 28-day all-cause mortality.
Statistical Analysis
We compared the prevalence of early bacterial identification between the two study groups by using logistic regression analysis before and after adjustment for the following prespecified confounders: simplified acute physiology score (SAPS) II, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic respiratory failure, immunosuppression, recent hospitalization, and antibiotic treatment on ICU admission.
We assessed the association of early bacterial identification with the patient’s outcomes censored at 28 days (overall survival, mechanical ventilation duration, and length of ICU stay) using a Cox’s regression model performed on the whole population (study groups combined together). Cause-specific hazard was calculated for mechanical ventilation duration (considering extubation alive as event of interest and death under mechanical ventilation as competing event) and for length of ICU stay (considering ICU discharge alive as event of interest and death during ICU as competing event) (21), including study group, bacterial identification, and interaction between bacterial identification and study group. In each study group, hazard ratios (HRs) for association of bacterial identification with different outcomes were derived from this model as effect sizes using linear contrast. The associations were further adjusted for the following prespecified confounders: sex, SAPS II, body mass index, MacCabe classification, shock, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), cardiac arrest, antibiotic treatment at ICU admission, and ventilator-associated pneumonia (treated as a time-varying variable).
To avoid case deletion in multivariate analyses because of the presence of missing data in covariates, multivariable logistic and Cox’s regression models were performed after handling missing data on a patient’s characteristics at ICU admission by using a multiple imputation procedure (22).
In addition to the main analyses, we performed two post hoc sensitivity analyses to assess, according to study group, the prevalence of bacterial identification and association of coinfection with the patient’s outcomes in two more stringent subpopulations of interest. First, patients intubated more than 48 hours after hospital admission were excluded, focusing on the occurrence and prognosis of community-acquired bacterial coinfections only. Second, we excluded patients from whom no respiratory sample could be collected within 48 hours of intubation because of a lack of productive tracheal secretions for noninvasive sampling via endotracheal aspirate or unavailability of an invasive sampling method.
Statistical testing was performed at the two-tailed α level of 0.05. Data were analyzed using the SAS software package, release 9.4 (SAS Institute). The statistical analysis is fully detailed in the online supplement.
Results
A total of 1,050 patients (568 in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia group and 482 in influenza pneumonia group) admitted to ICU between March 2016 and May 2020 were included in the 36 participating centers (Figure 1). Influenza A and B were diagnosed in 421 (87.3%) and 61 (12.7%) of patients with influenza pneumonia, respectively.
Figure 1.
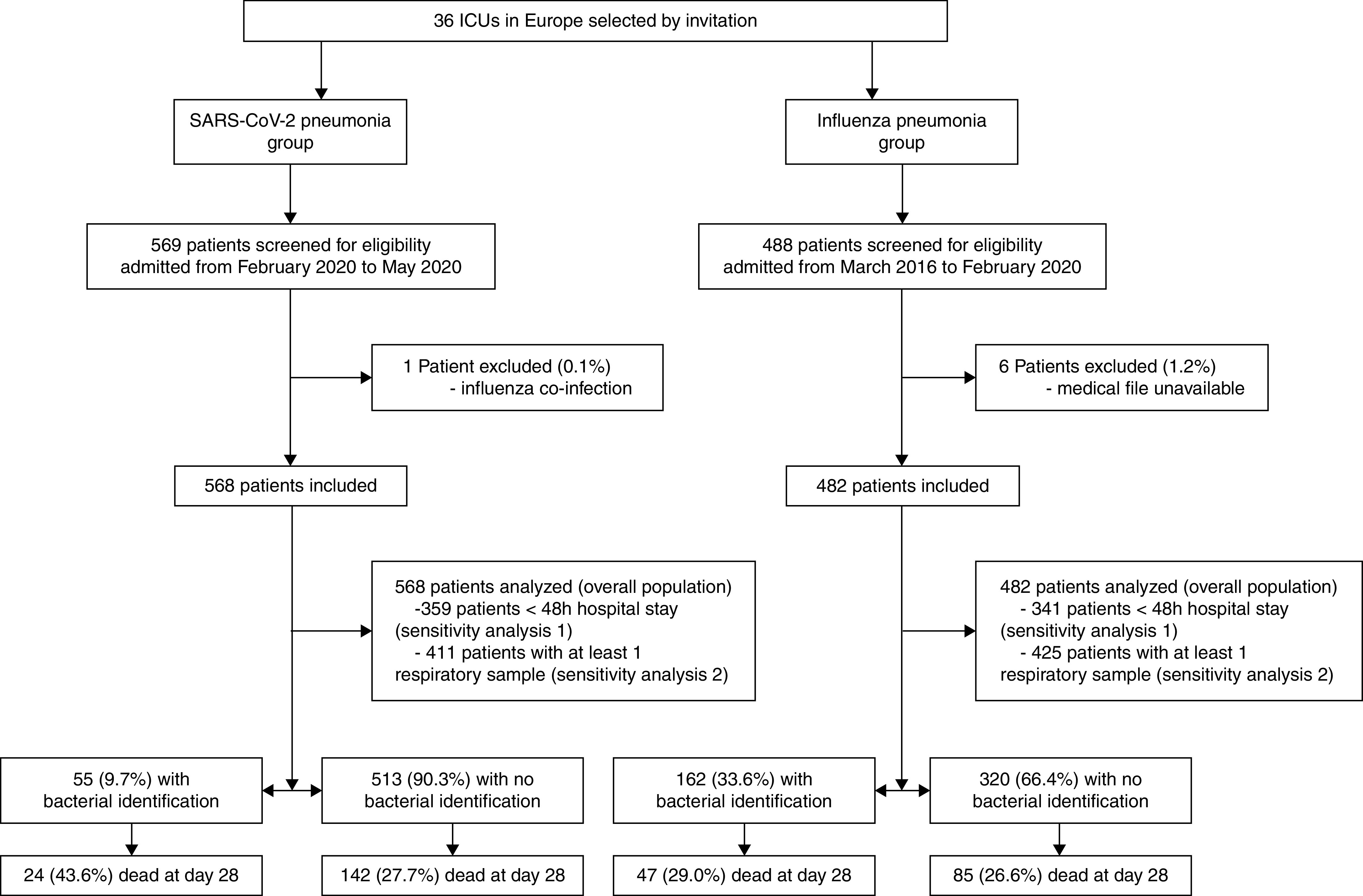
Patient flowchart. SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Patient Characteristics at ICU Admission
Percentage of men, body mass index, and percentage of ARDS as the cause for ICU admission were higher in the SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia group than in influenza pneumonia group. SAPS II, sequential organ failure assessment score, comorbidities scores, chronic diseases (COPD, chronic respiratory failure, immunosuppression, active smoking, and alcohol abuse), rate of recent hospitalization, and percentage of shock, cardiac arrest, neurological failure, or acute kidney injury as causes for ICU admission were lower in the SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia group than in the influenza pneumonia group. Intubation occurred in the first 48 hours after hospital admission in 68.4% of patients with SARS-CoV-2 and 76.0% of patients with influenza, respectively. Antibiotics on ICU admission were reported in 88.5% of patients in both groups (Table 1).
Table 1.
Patient Characteristics at ICU Admission
| SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia (n = 568) | Influenza Pneumonia (n = 482) | P Value | Absolute Standardized Difference, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yr | 64 (55–71) | 62 (53–71) | 0.044 | 12.7 |
| Men | 407/568 (71.7) | 298/482 (61.8) | <0.001 | 21.1 |
| Body mass index*, kg/m2 | 28.9 (25.8–33.3) | 27.5 (23.3–32.3) | <0.001 | 30.0 |
| Severity scores | ||||
| SAPS II† | 41 (32–55) | 50 (39–64) | <0.001 | 48.5 |
| SOFA score‡ | 6 (3–8) | 8 (6–11) | <0.001 | 56.0 |
| Comorbidities scores | ||||
| MacCabe classification, nonfatal | 475/543 (87.5) | 324/456 (71.1) | <0.001 | 40.1 |
| Fatal <5 yr | 62/543 (11.4) | 114/456 (25.0) | ||
| Fatal <1 yr | 6/543 (1.1) | 18/456 (3.9) | ||
| Charlson Comorbidity Index§ | 3 (1–4) | 3 (2–5) | <0.001 | 28.4 |
| Chronic diseases | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 168/565 (29.7) | 104/474 (21.9) | 0.004 | 17.9 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 33/559 (5.9) | 39/475 (8.2) | 0.15 | 9.0 |
| Heart disease | 103/560 (18.4) | 117/476 (24.6) | 0.015 | 15.1 |
| Chronic heart failure | 21/558 (3.8) | 37/475 (7.8) | 0.005 | 17.3 |
| COPD | 37/560 (6.6) | 129/475 (27.2) | <0.001 | 57.1 |
| Chronic respiratory failure | 20/558 (3.6) | 67/475 (14.1) | <0.001 | 37.7 |
| Cirrhosis | 8/559 (1.4) | 16/475 (3.4) | 0.039 | 12.7 |
| Immunosuppression | 52/559 (9.3) | 107/479 (22.3) | <0.001 | 36.3 |
| Active smoking | 29/560 (5.2) | 149/476 (31.3) | <0.001 | 71.9 |
| Alcohol abuse | 34/558 (6.1) | 85/475 (17.9) | <0.001 | 36.9 |
| Recent hospitalization (<3 mo) | 44/566 (7.8) | 72/479 (15.0) | <0.001 | 23.0 |
| Recent antibiotics (<3 mo) | 74/567 (13.1) | 95/477 (19.9) | 0.003 | 18.6 |
| Location before ICU admission | ||||
| Home | 271/568 (47.7) | 275/481 (57.2) | 0.006 | 19.0 |
| Hospital ward | 215/568 (37.9) | 157/481 (32.6) | ||
| Another ICU | 82/568 (14.4) | 49/481 (10.2) | ||
| Time from hospital to ICU admission, d | 1 (0–2) | 0 (0–2) | 0.015 | 15.5 |
| ⩽48 h | 425/537 (79.1) | 373/454 (82.2) | 0.23 | 7.6 |
| Time from hospital admission to intubation, d | 1 (0–3) | 1 (0–2) | <0.001 | 23.0 |
| ⩽48 h | 359/525 (68.4) | 341/449 (76.0) | 0.009 | 16.9 |
| Antibiotic treatment on ICU admission | 494/558 (88.5) | 417/471 (88.5) | 1.00 | 0.0 |
| Causes for ICU admission | ||||
| Shock | 102/557 (18.3) | 210/470 (44.7) | <0.001 | 59.2 |
| Acute respiratory failure | 521/567 (91.9) | 433/461 (90.2) | 0.34 | 5.9 |
| ARDS | 386/563 (68.6) | 220/469 (46.9) | <0.001 | 44.9 |
| Neurological failure | 26/548 (4.7) | 69/465 (14.8) | <0.001 | 34.5 |
| Cardiac arrest | 3/547 (0.6) | 25/465 (5.4) | <0.001 | 28.8 |
| Acute kidney injury | 96/567 (17.5) | 133/480 (28.9) | <0.001 | 27.1 |
Definition of abbreviations: ARDS = acute respiratory distress syndrome; COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; SAPS II = simplified acute physiology score II; SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; SOFA = sequential organ failure assessment.
Values are n/N (%) or median (interquartile range). McCabe classification of comorbidities and likelihood of survival: likely to survive >5 yr, 1–5 yr, or <1 yr; chronic kidney disease: National Kidney Foundation Kidney Disease Outcome Quality Initiative (KDOQI CKD) classification stage 4 or 5 (creatinine clearance <30 ml/mn); chronic heart failure: New York Heart Association class III or IV; heart disease: ischemic heart disease or atrial fibrillation; cirrhosis: Child-Pugh score B or C; immunosuppression: hematological malignancy, allogenic stem cell transplant, solid cancer, organ transplant, HIV, or immunosuppressive drugs; and antibiotic treatment on ICU admission: at least one dose of antibiotics in the first day of ICU stay. More than one cause for ICU admission is possible.
100 missing values (SARS-CoV-2, n = 32; influenza, n = 68).
66 missing values (SARS-CoV-2, n = 43; influenza, n = 21).
25 missing values (SARS-CoV-2, n = 21; influenza, n = 4).
30 missing values (SARS-CoV-2, n = 19; influenza, n = 11).
Prevalence of Early Bacterial Identification
The prevalence of bacterial identification was significantly lower in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia than in patients with influenza pneumonia (9.7% vs. 33.6%; unadjusted OR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.15–0.30; Table 2). This difference remained significant after adjustment for the aforementioned baseline relevant confounders (adjusted OR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.16–0.33; P < 0.0001). At least one respiratory sample could be collected within 48 hours after intubation in 73.5% of patients with SARS-CoV-2 and 89.5% of patients with influenza. Antibiotic treatment was reported at the time of sampling in 85.4% and 89.6% of cases. Bacteria were mostly isolated on endotracheal aspirate in coinfected patients (see Table E1 in online data supplement). Patient characteristics at ICU admission and at the time of bacterial identification according to study group and bacterial identification status are reported in Table E2. Coinfected patients in the SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia group had a higher sequential organ failure assessment score and higher rates of shock and ARDS on admission than noncoinfected patients. Furthermore, at the time of diagnosis, among patients with available data, coinfected patients showed higher levels of procalcitonin than noncoinfected patients (0.9 [0.3–4.3] vs. 0.5 [0.2–1.5] in the SARS-CoV-2 group and 6.4 [1.4–50.2] vs. 1.5 [0.5–9.8] in the influenza group). Sensitivity analyses regarding the prevalence of early bacterial identification across study groups were consistent with overall population results (Table 2).
Table 2.
Prevalence of Early Bacterial Identification
| SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia | Influenza Pneumonia | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) |
Adjusted OR* (95% CI) |
P Value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall population | 55/568 (9.7) | 162/482 (33.6) | 0.21 (0.15–0.30) | 0.23 (0.16–0.33) | <0.0001 |
| <48-h hospital stay† | 29/359 (8.1) | 129/341 (37.8) | 0.14 (0.09–0.23) | 0.15 (0.09–0.25) | <0.0001 |
| At least one respiratory sample† | 55/411 (13.4) | 162/425 (38.1) | 0.25 (0.17–0.36) | 0.26 (0.18–0.39) | <0.0001 |
Definition of abbreviations: CI = confidence interval; OR = odds ratio; SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Values are n/N (%).
Adjusted for prespecified confounders simplified acute physiology score II, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic respiratory failure, immunosuppression, recent hospitalization, and antibiotic treatment on ICU admission and calculated after handling missing values on covariates by multiple imputation.
Sensitivity analyses were performed among patients intubated in the first 48 hours after hospital admission (359/525 [68.4] in the SARS-CoV-2 group and 341/449 [76.0] in the influenza group) or in whom at least one respiratory sample could be collected within 48 hours of intubation (411/559 [73.5] in the SARS-CoV-2 group and 425/475 [89.5] in the influenza group).
Microbiological Results
The majority of early bacterial identification was related to gram-positive cocci (58% in the SARS-CoV-2 group and 72% in the influenza group), mostly Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Among gram-negative rods, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Haemophilus influenzae were, respectively, responsible for 11% and 9% of episodes in patients with SARS-CoV-2 and for 6% and 11% of episodes in patients with influenza. Early bacterial coinfection was polymicrobial in 9% and 7% of cases in the SARS-CoV-2 and influenza groups, respectively. The rate of patients with coinfection owing to multidrug-resistant bacteria was low (6% and 4%) in the two study groups (Table 3). Initial antibiotic treatment was appropriate in 38 of 54 (70.4%) and 125 of 158 (79.1%) coinfected patients in the SARS-CoV-2 and influenza groups, respectively.
Table 3.
Microbiological Data
| SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia (n = 55) | Influenza Pneumonia (n = 162) | |
|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive cocci | 32 (58.2) | 116 (71.6) |
| Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus | 13 (23.6) | 47 (29.0) |
| Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus | 1 (1.8) | 4 (2.5) |
| Staphylococcus other than aureus | 1 (1.8) | 2 (1.2) |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | 12 (21.8) | 52 (32.1) |
| Other Streptococcus spp | 4 (7.3) | 10 (6.2) |
| Enterococcus spp | 1 (1.8) | 1 (0.6) |
| Gram-negative bacilli | 23 (41.8) | 45 (27.8) |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 6 (10.9) | 10 (6.2) |
| Haemophilus influenzae | 5 (9.1) | 18 (11.1) |
| Moraxella catarrhalis | 3 (5.5) | 1 (0.6) |
| Enterobacter spp | 2 (3.6) | 1 (0.6) |
| Klebsiella pneumonia | 2 (3.6) | 3 (1.9) |
| Other Klebsiella spp | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.6) |
| Serratia marcescens | 2 (3.6) | 0 (0.0) |
| Citrobacter spp | 1 (1.8) | 0 (0.0) |
| Proteus mirabilis | 1 (1.8) | 0 (0.0) |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | 1 (1.8) | 2 (1.2) |
| Escherichia coli | 0 (0.0) | 5 (3.1) |
| Morganella morganii | 0 (0.0) | 3 (1.9) |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.6) |
| Other | 4 (7.3) | 9 (5.6) |
| Polymicrobial | 5 (9.1) | 11 (6.8) |
| Multidrug-resistant isolates | 3 (5.5) | 6 (3.7) |
Definition of abbreviation: SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Values are n (%). More than one bacteria can be identified for each patient.
Impact on Outcomes
The difference in 28-day mortality rates between patients with and without bacterial identification was 16.0% (95% CI, 2.2 to 29.7) in the SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia group and 2.5% (95% CI, −6.1 to 11.0) in the influenza pneumonia group (Figure 1). Additional patient characteristics during ICU stay, including 28-day outcomes, and cumulative incidence of 28-day mortality, extubation alive, and ICU discharge alive according to study group and bacterial identification status are reported in Table E3 and Figure 2.
Figure 2.
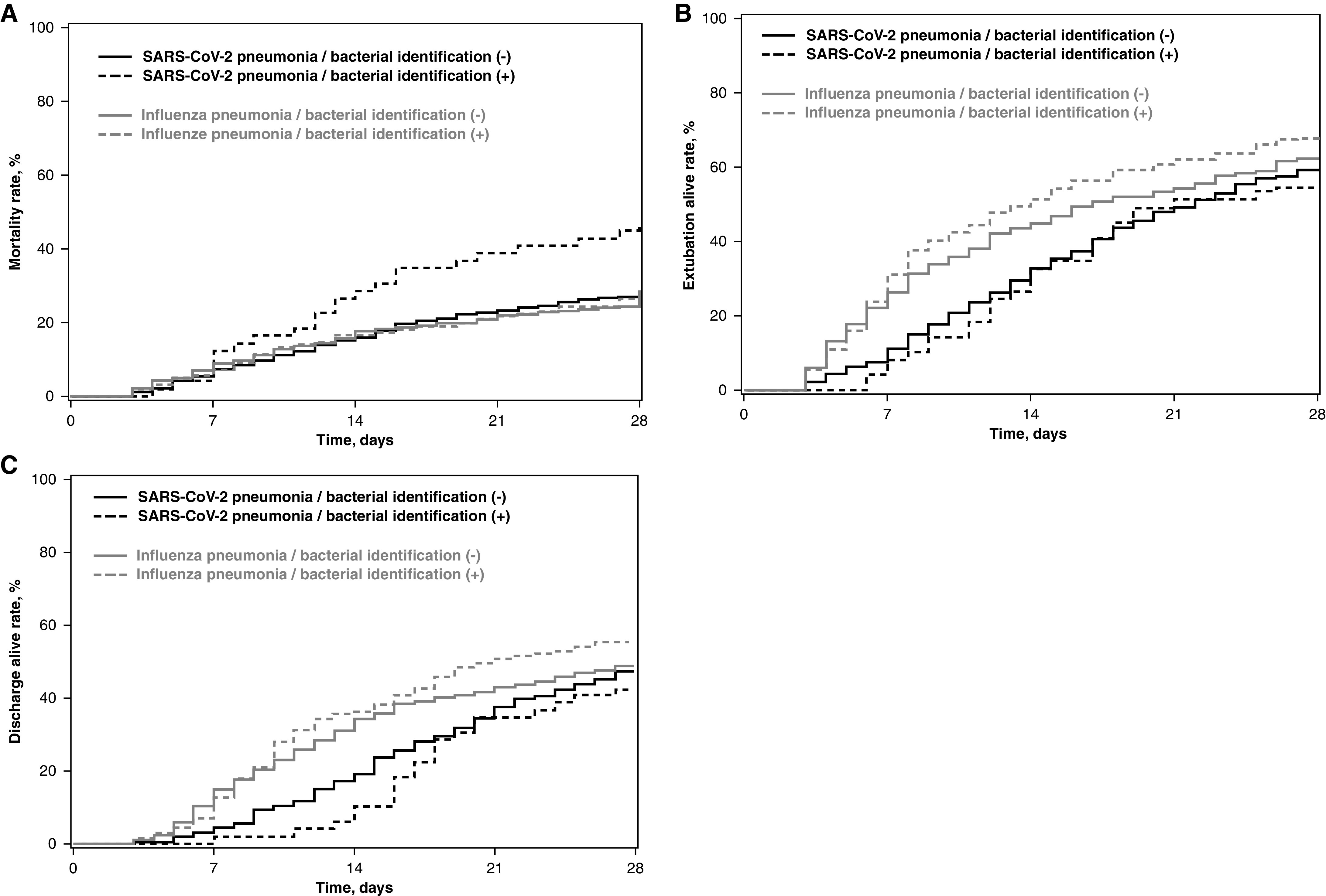
Cumulative incidence of (A) 28-day mortality, (B) extubation alive, and (C) and ICU discharge alive according to study groups (SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia vs. influenza pneumonia) and early bacterial identification. Time axis origin is the day of intubation. SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Early bacterial identification was associated with increased HR for 28-day mortality in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia (unadjusted HR, 1.72; 95% CI, 1.11–2.66) but not in patients with influenza pneumonia (unadjusted HR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.75–1.55) (Figure 3). This increased risk was still significant after adjustment for potential confounders (adjusted HR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.01–2.44; P = 0.043). However, the P value for heterogeneity with the influenza pneumonia group was not significant (PHet = 0.16). Furthermore, no significant association was found between bacterial identification and mechanical ventilation duration or length of ICU stay in patients with SARS-CoV-2 or influenza pneumonia.
Figure 3.
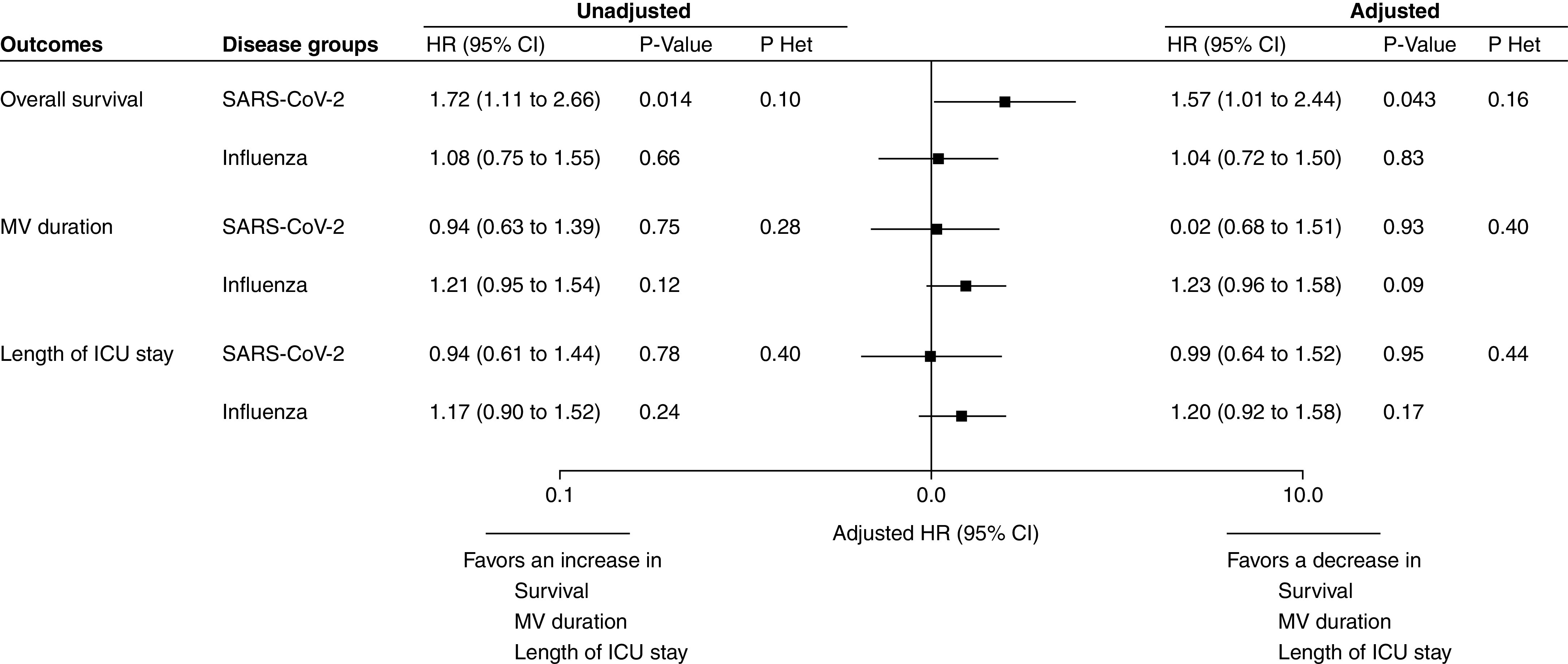
Association of early bacterial identification with 28-day outcomes according to study groups (SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia and influenza pneumonia). HRs were calculated using cause-specific proportional hazard models by considering mortality as a competing event for mechanical ventilation and length of ICU stay. Adjusted HRs were calculated by including sex, simplified acute physiology score II, body mass index, MacCabe classification, shock, acute respiratory distress syndrome, cardiac arrest, antibiotic treatment on ICU admission, and ventilator-associated pneumonia (treated as time-varying variable) as prespecified covariates in Cox’s models (after handling missing values by multiple imputation). An HR > 1 indicates a decrease in survival (i.e., an increased risk for mortality), MV duration (i.e., an increased risk for extubation alive), and ICU length of stay (i.e., an increased risk for discharge alive), and an HR < 1 indicates an increase in survival (i.e., a decreased risk for mortality), MV duration (i.e., a decreased risk for extubation alive), and ICU length of stay (i.e., a decreased risk for discharge alive). The event of interest for survival is a pejorative event (death), whereas for MV duration and ICU length of stay, the event of interest is a positive event (extubation or discharge alive). Consequently, the detrimental effect of bacterial identification on each outcome was associated with an HR > 1 for overall survival but with an HR < 1 for MV duration and ICU length of stay. P Het indicates the P value for heterogeneity in association of bacterial identification and 28-day outcomes across study groups (SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia vs. influenza pneumonia). CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; MV = mechanical ventilation; SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Similar results regarding early bacterial identification impact on outcomes according to study groups were observed across sensitivity analyses, although differences in the significance of size effects were observed (Figures E2 and E3). Antibiotic treatment on ICU admission had no significant impact on the association of bacterial identification with 28-day all-cause mortality in the two study groups (see Figure E4).
Discussion
Our study reports a threefold lower prevalence of bacterial identification among patients with SARS-CoV-2 within 48 hours after intubation compared with patients with influenza pneumonia. Gram-positive cocci, mostly S. aureus and S. pneumoniae, were responsible for the majority of bacterial coinfections. Early bacterial identification was associated with increased risk for 28-day mortality in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. However, no significant difference was found in heterogeneity of outcomes related to bacterial identification between the two study groups, suggesting that the impact of coinfection on mortality was not different between patients with SARS-CoV-2 and influenza.
To date, the absence of reliable estimates of the prevalence of early bacterial coinfection together with their challenging diagnosis, namely, the inability to formally exclude bacterial involvement, promoted a widespread prescribing of systematic empirical antimicrobial treatment in patients admitted to ICU for SARS-CoV-2 infection. The use of broad-spectrum antibiotics is reported in 72% of hospitalized patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 (23), and there are higher rates, close to 90%, among critically ill patients (2, 24) despite limited available microbiological data. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest study examining the prevalence of early bacterial identification in intubated patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia compared with influenza pneumonia. In addition, strengths of our study include the multicenter design, the choice of a relevant control group, the defined timing of bacterial isolation, and the robust adjustment for confounding factors.
The 34% rate of bacterial identification in patients with influenza pneumonia is roughly consistent with previous data from several ICU cohorts, reporting 17–30% of coinfected patients on admission, considering that all included patients were not intubated (8–10). Coinfection was unsurprisingly caused by S. pneumoniae, S. aureus, and H. influenzae, although the proportion of P. aeruginosa was lower than expected (8, 9). The lower rate of bacterial identification in patients admitted for COVID-19 could be explained by fewer underlying respiratory conditions, such as COPD and chronic respiratory failure, associated with a risk of prior bronchial colonization as well as less immunosuppression, healthcare exposure, and multiple organ failure at admission in the SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia group compared with the influenza pneumonia group. However, careful adjustment for these confounding factors was performed. Although both viral respiratory infections, COVID-19 differs from influenza in many ways by activating distinct immune-response pathways (25, 26) and having specific gut microbial signature (27) and specific pulmonary histopathology characterized by severe endothelial injury, thrombosis, and vascular angiogenesis (28, 29). Future research will undoubtedly shed light on SARS-CoV-2 and bacteria interactions and explain the resulting risk for bacterial coinfection.
The rate of early bacterial identification in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia is much lower than the reported prevalence of 28% at ICU admission in two recent cohorts (15, 16). These studies were monocentric and included a small number of patients with SARS-CoV-2 without a control group. Both respiratory multiplex PCR and culture were used, which could explain the higher rate of coinfection diagnosis. Furthermore, the absence of a standardized protocol for microbiological sampling after intubation and the exposure to antibiotics at the time of collection might have led to an underestimation of the rate of coinfected patients in our study, especially in patients with COVID-19. In the context of the heavy strain on healthcare systems, in overwhelmed ICUs, routine microbiological investigations might have been reduced because of extreme workloads or even constrained by the fear of exposure of caregivers to potential aerosolization of SARS-CoV-2. In our study, only 74% of patients with SARS-CoV-2 had at least one respiratory sample collected within 48 hours after intubation versus 90% of patients with influenza, whereas antibiotic exposure at the time of microbiological sampling was reported in 85% and 90% of cases, respectively. However, sensitivity analysis excluding patients without respiratory samples showed similar findings regarding the prevalence of bacterial identification across study groups. Furthermore, all analyses were adjusted on the presence of antibiotic treatment on ICU admission.
Time from hospital admission to bacterial isolation, allowing for the classification of documented early bacterial coinfection in community- or hospital-acquired infection, might have impacted the coinfection rate in our study, assuming the time-dependent process of bacterial airway colonization after severe viral infection. However, the majority of included patients were admitted to the ICU within 48 hours after hospital admission (79% in the SARS-CoV-2 and 82% in the influenza group). Data on bacterial identification prevalence in sensitivity analysis performed among patients intubated within 48 hours after hospital admission were also consistent with whole population findings.
The bacteria responsible for early coinfection in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia were the same as in patients with influenza pneumonia: S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, and H. influenzae, which is overall in line with previous observations (14–16). Appropriate early antibiotic treatment was reported in 70% and 79% of coinfection episodes among patients with SARS-CoV-2 and influenza pneumonia, respectively. However, early antibiotics on ICU admission did not significantly modify the impact of bacterial identification on 28-day mortality across study groups.
We found no impact of early bacterial identification on clinical outcomes among patients with influenza pneumonia, but the direct role played by bacterial coinfection on morbidity and mortality in these populations has been previously difficult to estimate (8, 10). Similarly, the increased mortality risk associated with bacterial identification among patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia could not be confirmed in sensitivity analyses. However, despite careful adjustments, our analyses might have missed some residual confounders. Furthermore, the number of patients with bacterial identification in the SARS-CoV-2 group was relatively small, and our study might have been underpowered to detect a significant difference in this subgroup regarding secondary outcomes. Larger studies are needed to explore the impact of early bacterial coinfection on clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19.
Our results have potentially important implications on the empirical antibiotic strategy of patients with COVID-19 in the first days after their intubation, as they suggest that the majority of these patients may not require antimicrobial treatment. Proactive respiratory microbiological investigations, before any antibiotic administration at best, are essential to accurately identify situations in which antimicrobial treatment can be promptly withdrawn. For this purpose, routine use of respiratory multiplex PCR could be a major asset, contributing to accelerate and possibly improve bacterial coinfection diagnosis during severe COVID-19 pneumonia (30). By reducing unnecessary antibiotic exposure and subsequent selection pressure, a restrictive prescription of early empirical antibiotic treatment could prevent the emergence of antimicrobial resistance within healthcare systems (31). This is of major importance because the incidence of ventilator-associated lower respiratory tract infections is particularly high in critically ill patients with COVID-19 (18, 32).
In addition to those previously mentioned, our study has some limitations. First, the study is retrospective, and our results may not be generalized to other parts of the world, as most participating centers were located in France. Second, a high percentage of patients were receiving antibiotic treatment when respiratory samples were collected in patients with SARS-Cov-2 and those with influenza pneumonia, which might have decreased the diagnostic yield and the number of reported positive bacterial cultures. Therefore, bacterial identification may not reflect the real rate of bacterial coinfection in both groups. Third, differentiating bacterial airway colonization from infection in patients with a positive microbiological specimen may be difficult in patients with SARS-CoV-2 or influenza pneumonia. Fourth, our definition of early bacterial identification did not include bacteria isolated before intubation. Fifth, numerous data regarding procalcitonin were missing, and no conclusion could be reached in our study on its usefulness in the diagnosis of bacterial coinfection among intubated patients with COVID-19 (33). Sixth, we did not collect data on the delay between the onset of symptoms and hospital admission as well as some potentially useful diagnostic tools for bacterial coinfection, such as leukocyte count, C-reactive protein, and chest computed tomographic scan findings in study patients. It would have been interesting to determine whether superimposed focal consolidation to the typical ground-glass opacities (34) could predict the presence of associated bacterial coinfection. Seventh, no data on antibiotic deescalation, after initial empirical antibiotic treatment, was collected in studied patients. Finally, based on inclusion criteria, only patients who received invasive mechanical ventilation for more than 48 hours were included. Therefore, an immortal time bias could not be excluded because of early mortality before 48 hours of mechanical ventilation. However, this bias would have occurred in the two study groups.
To conclude, we report a prevalence of bacterial identification of 9.7% within 48 hours after intubation in critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, which is threefold lower compared with patients with influenza pneumonia. Our findings encourage the careful evaluation of the indication of early empirical antimicrobial treatment in this population, necessarily guided by a proactive diagnostic strategy. A strategy limiting antibiotic treatment to most severe patients, with ARDS or shock, should also be evaluated. Further studies are needed to better predict early bacterial coinfection and to assess the feasibility and safety of antibiotic stewardship strategies in critically ill patients with COVID-19.
Acknowledgments
coVAPid Study Group members: Julien Poissy, CNRS, UMR 8576, CHU de Lille, Centre de Réanimation, Lille, France; Raphaël Favory, CHU de Lille, Centre de Réanimation, Lille, France; Sébastien Preau, CHU de Lille, Centre de Réanimation, Lille, France; Mercè Jourdain, CHU de Lille, Centre de Réanimation, Lille, France; Sean Boyd, Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Multidisciplinary Intensive Care Research Organization, St. James’s Hospital, Dublin, Ireland; Luis Coelho, Polyvalent Intensive Care Unit, Hospital de São Francisco Xavier, CHLO, Lisbon, Portugal, and NOVA Medical School, CHRC, New University of Lisbon, Portugal; Julien Maizel, Service de médecine intensive réanimation, CHU Amiens Picardie, Amiens, France; Pierre Cuchet, Department of Medical Intensive Care, Caen University Hospital, Caen, France; Wafa Zarrougui, Service de réanimation polyvalente, Centre Hospitalier de Valenciennes, Valenciennes, France; Déborah Boyer, Medical Intensive Care Unit, Rouen University Hospital, Rouen, France; Jean-Pierre Quenot, Department of Intensive Care, François Mitterrand University Hospital, Dijon, France; Mehdi Imouloudene, Service de réanimation et de soins intensifs, Centre Hospitalier de Douai, Douai, France; Charles-Edouard Luyt, Service de Médecine Intensive Réanimation, Institut de Cardiologie, Groupe Hospitalier Pitié-Salpêtrière, Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris, Paris, France; Thierry van der Linden, Service de médecine intensive réanimation, Hôpital Saint Philibert GHICL, Université Catholique, Lille, France; Justine Bardin, CHU de Poitiers, Médecine Intensive Réanimation, CIC 1402 ALIVE, Université de Poitiers, Poitiers, France; Sebastian Voicu, Department of Medical and Toxicological Critical Care, Lariboisière Hospital, INSERM UMRS-1144, Paris University, Paris, France; Elie Azoulay, Service de médecine intensive réanimation, Hôpital Saint-Louis, Paris, France; Gemma Goma, Critical Care Department, Hospital Universitari Parc Taulí, Sabadell, Spain; Frédéric Pene, Medical Intensive Care Unit, Cochin Hospital, Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris, Paris, France; Antoni Torres, Department of Pulmonology, Hospital Clinic of Barcelona, University of Barcelona, IDIBAPS, CIBERES, Barcelona, Spain; Didier Thevenin, Service de réanimation polyvalente, Centre Hospitalier de Lens, Lens, France; StéphanEhrmann, Service de Médecine Intensive Réanimation, CHU de Tours, Hôpital Bretonneau, Tours, France; Laurent Argaud, Service de Médecine Intensive Réanimation, Hôpital Edouard Herriot, Hospices Civils de Lyon, Lyon, France; Bertrand Guidet, Service de Médecine Intensive Réanimation, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris, Paris, France; Guillaume Voiriot, Sorbonne Université, Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris, Service de Médecine Intensive Réanimation, Hôpital Tenon, Paris, France; Damien Contou, Service de réanimation polyvalente, CH Victor Dupouy, Argenteuil, France; Julien Le Marec, Service de Médecine Intensive Réanimation et Pneumologie, Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière, Paris, France; Julien Demiselle, Département de Médecine Intensive Réanimation, CHU d'Angers, Angers, France; David Meguerditchian, Service de médecine intensive réanimation, CHU de Bordeaux, Bordeaux, France; Keyvan Razazi, Hôpitaux Universitaires Henri-Mondor, Service de Médecine Intensive Réanimation, Université Paris Est Créteil, CARMAS INSERM U955, Institut Mondor de recherche Biomédicale, Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris, Créteil, France; Vassiliki Tsolaki, Intensive Care Unit, University Hospital of Larissa, University of Thessaly, Biopolis Larissa, Greece; Caroline Sejourne, Intensive Care Unit, Hôpital de Béthune, Béthune, France; Guillaume Brunin, Service de réanimation, Hôpital Duchenne, Boulogne-sur-Mer, France; Loïc Le Guennec, Département de Neurologie, Unité de Médecine Intensive Réanimation Neurologique, Hôpital de la Pitié-Salpêtrière, Sorbonne Université, Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris, Paris, France; and Luis Morales, Intensive Care Unit, Hospital Universitari Sagrat Cor, Barcelona, Spain.
Footnotes
A complete list of coVAPid Study Group members may be found before the beginning of the References.
Supported in part by a grant from the French government through the Programme Investissement d’Avenir (I-SITE ULNE) managed by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (coVAPid project). I.M.-L. has been supported by Science Foundation Ireland grant number 20/COV/0038. The funders of the study had no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation, writing of the report, or decision to submit for publication.
Author contributions: Conception and design of the study: A.R., I.M.L., P.P., A.D., J.L., and S.N. Data acquisition: all authors. Data analysis and interpretation: A.R., I.M.L., P.P., M.F., D.M., A.A., A.D., J.L., and S.N. Manuscript drafting or critical revision for important intellectual content: all authors. Final approval of the submitted version: all authors.
This article has a related editorial.
This article has an online supplement, which is accessible from this issue’s table of contents at www.atsjournals.org.
Originally Published in Press as DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202101-0030OC on May 26, 2021
Author disclosures are available with the text of this article at www.atsjournals.org.
Contributor Information
Collaborators: for the coVAPid Study Group, Julien Poissy, Raphaël Favory, Sébastien Preau, Mercè Jourdain, Sean Boyd, Luis Coelho, Pierre Cuchet, Wafa Zarrougui, Déborah Boyer, Jean-Pierre Quenot, Mehdi Imouloudene, Charles-Edouard Luyt, Thierry van der Linden, Justine Bardin, Sebastian Voicu, Elie Azoulay, Gemma Goma, Frédéric Pene, Antoni Torres, Didier Thevenin, Stéphan Ehrmann, Laurent Argaud, Bertrand Guidet, Guillaume Voiriot, Damien Contou, Julien Le Marec, Julien Demiselle, David Meguerditchian, Keyvan Razazi, Vassiliki Tsolaki, Caroline Sejourne, Guillaume Brunin, Loïc Le Guennec, and Luis Morales
References
- 1.European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 2021. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/geographical-distribution-2019-ncov-cases
- 2. Argenziano MG, Bruce SL, Slater CL, Tiao JR, Baldwin MR, Barr RG, et al. Characterization and clinical course of 1000 patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York: retrospective case series. BMJ. 2020;369:m1996. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Lim ZJ, Subramaniam A, Ponnapa Reddy M, Blecher G, Kadam U, Afroz A, et al. Case fatality rates for patients with COVID-19 requiring invasive mechanical ventilation: a meta-analysis. JJ Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;203:54–66. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202006-2405OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Doidge JC, Gould DW, Ferrando-Vivas P, Mouncey PR, Thomas K, Shankar-Hari M, et al. Trends in intensive care for patients with COVID-19 in England, Wales, and northern Ireland. JJ Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;203:565–574. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202008-3212OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Alhazzani W, Møller MH, Arabi YM, Loeb M, Gong MN, Fan E, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: guidelines on the management of critically ill adults with Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Intensive Care Med. 2020;46:854–887. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06022-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Uyeki TM, Bernstein HH, Bradley JS, Englund JA, File TM, Fry AM, et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America: 2018 update on diagnosis, treatment, chemoprophylaxis, and institutional outbreak management of seasonal influenza. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;68:e1–e47. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, Anzueto A, Brozek J, Crothers K, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia: an official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. JJ Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200:e45–e67. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201908-1581ST. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Martín-Loeches I, Sanchez-Corral A, Diaz E, Granada RM, Zaragoza R, Villavicencio C, et al. H1N1 SEMICYUC Working Group. Community-acquired respiratory coinfection in critically ill patients with pandemic 2009 influenza A(H1N1) virus. Chest. 2011;139:555–562. doi: 10.1378/chest.10-1396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Martin-Loeches I, Schultz MJ, Vincent JL, Alvarez-Lerma F, Bos LD, Solé-Violán J, et al. Increased incidence of co-infection in critically ill patients with influenza. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43:48–58. doi: 10.1007/s00134-016-4578-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Rice TW, Rubinson L, Uyeki TM, Vaughn FL, John BB, Miller RR, III, et al. NHLBI ARDS Network. Critical illness from 2009 pandemic influenza A virus and bacterial coinfection in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2012;40:1487–1498. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182416f23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. McCullers JA. The co-pathogenesis of influenza viruses with bacteria in the lung. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014;12:252–262. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Martin-Loeches I, van Someren Gréve F, Schultz MJ. Bacterial pneumonia as an influenza complication. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017;30:201–207. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Morens DM, Taubenberger JK, Fauci AS. Predominant role of bacterial pneumonia as a cause of death in pandemic influenza: implications for pandemic influenza preparedness. J Infect Dis. 2008;198:962–970. doi: 10.1086/591708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Langford BJ, So M, Raybardhan S, Leung V, Westwood D, MacFadden DR, et al. Bacterial co-infection and secondary infection in patients with COVID-19: a living rapid review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26:1622–1629. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.07.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Kreitmann L, Monard C, Dauwalder O, Simon M, Argaud L. Early bacterial co-infection in ARDS related to COVID-19. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46:1787–1789. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06165-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Contou D, Claudinon A, Pajot O, Micaëlo M, Longuet Flandre P, Dubert M, et al. Bacterial and viral co-infections in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia admitted to a French ICU. Ann Intensive Care. 2020;10:119. doi: 10.1186/s13613-020-00736-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Proceedings of Réanimation 2021, the French Intensive Care Society International Congress [abstract] Ann Intensive Care 20211197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Rouzé A, Martin-Loeches I, Povoa P, Makris D, Artigas A, Bouchereau M, et al. coVAPid Study Group. Relationship between SARS-CoV-2 infection and the incidence of ventilator-associated lower respiratory tract infections: a European multicenter cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2021;47:188–198. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06323-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Magiorakos A-P, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18:268–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Paul M, Shani V, Muchtar E, Kariv G, Robenshtok E, Leibovici L. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of appropriate empiric antibiotic therapy for sepsis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:4851–4863. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00627-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Austin PC, Lee DS, Fine JP. Introduction to the analysis of survival data in the presence of competing risks. Circulation. 2016;133:601–609. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.017719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. van Buuren S, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K. mice: multivariate imputation by chained equations in R. J Stat Softw. 2011;45:1–67. [Google Scholar]
- 23. Rawson TM, Moore LSP, Zhu N, Ranganathan N, Skolimowska K, Gilchrist M, et al. Bacterial and fungal coinfection in individuals with coronavirus: a rapid review to support COVID-19 antimicrobial prescribing. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:2459–2468. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Cummings MJ, Baldwin MR, Abrams D, Jacobson SD, Meyer BJ, Balough EM, et al. Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1763–1770. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Zhu L, Yang P, Zhao Y, Zhuang Z, Wang Z, Song R, et al. Single-cell sequencing of peripheral mononuclear cells reveals distinct immune response landscapes of COVID-19 and influenza patients. Immunity. 2020;53:685–696.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.07.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. McElvaney OJ, McEvoy NL, McElvaney OF, Carroll TP, Murphy MP, Dunlea DM, et al. Characterization of the inflammatory response to severe COVID-19 illness. JJ Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;202:812–821. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202005-1583OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Gu S, Chen Y, Wu Z, Chen Y, Gao H, Lv L, et al. Alterations of the gut microbiota in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 or H1N1 influenza. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:2669–2678. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, Haverich A, Welte T, Laenger F, et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:120–128. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2015432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Patel BV, Arachchillage DJ, Ridge CA, Bianchi P, Doyle JF, Garfield B, et al. Pulmonary angiopathy in severe COVID-19: physiologic, imaging, and hematologic observations. JJ Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;202:690–699. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202004-1412OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris. 2020. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04334850
- 31. Holmes AH, Moore LSP, Sundsfjord A, Steinbakk M, Regmi S, Karkey A, et al. Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet. 2016;387:176–187. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Razazi K, Arrestier R, Haudebourg AF, Benelli B, Carteaux G, Decousser JW, et al. Risks of ventilator-associated pneumonia and invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with viral acute respiratory distress syndrome related or not to coronavirus 19 disease. Crit Care. 2020;24:699. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03417-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Gautam S, Cohen AJ, Stahl Y, Valda Toro P, Young GM, Datta R, et al. Severe respiratory viral infection induces procalcitonin in the absence of bacterial pneumonia. Thorax. 2020;75:974–981. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-214896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Kanne JP, Little BP, Chung JH, Elicker BM, Ketai LH. Essentials for radiologists on COVID-19: an update-Radiology scientific expert panel. Radiology. 2020;296:E113–E114. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020200527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


