Figure 4.
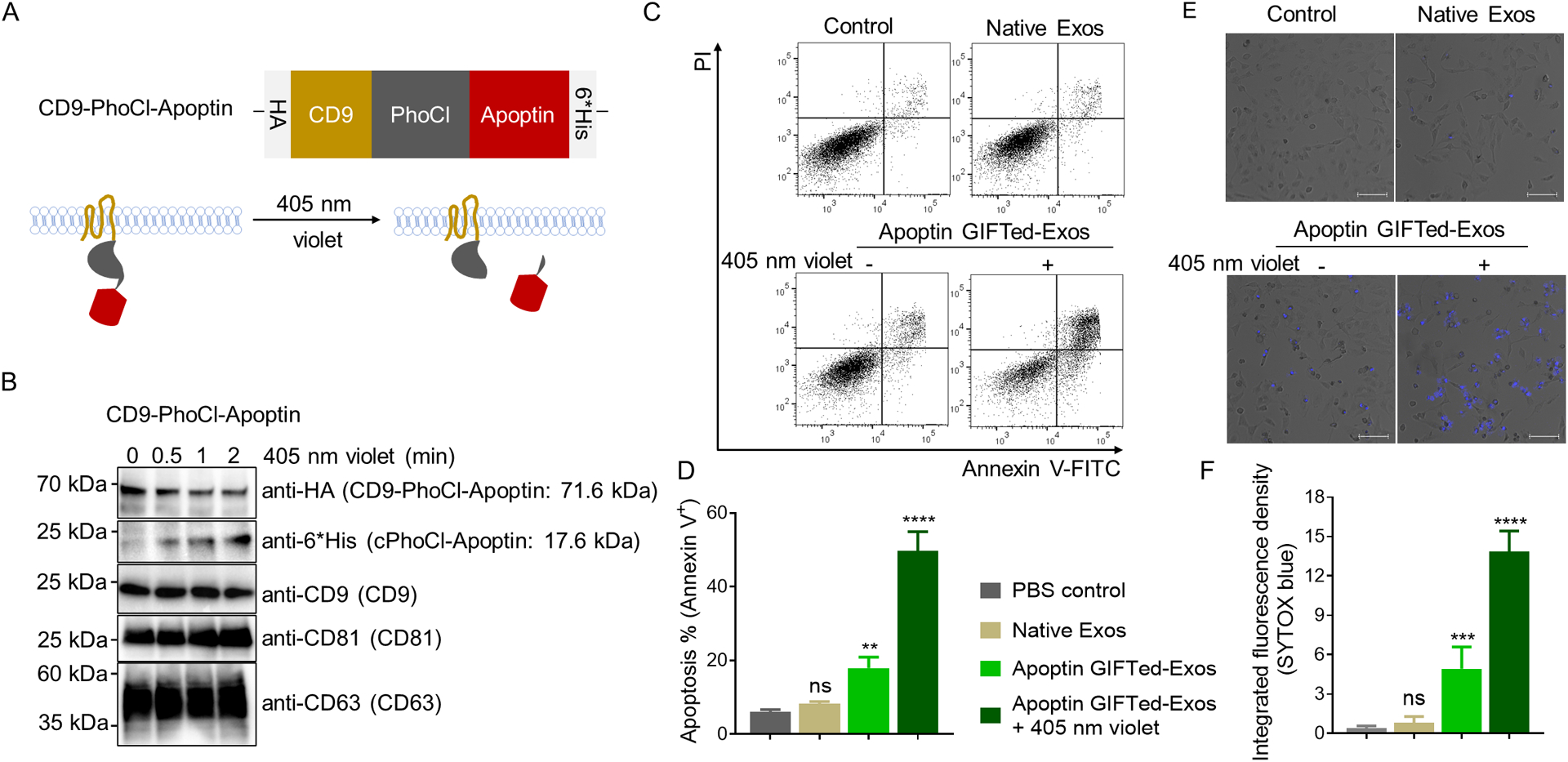
Generation and analysis of apoptin GIFTed-Exos. (A) Schematic of the design of apoptin GIFTed-Exos. (B) Immunoblot analysis of the apoptin GIFTed-Exos and violet light-induced release of apoptin. Theoretical molecular weights of fusion proteins are shown. (C) Representative flow cytometry analysis of cell apoptosis induced by apoptin GIFTed-Exos. HeLa cells were incubated in the absence or presence of native exosomes or apoptin GIFTed-Exos (500 μg mL−1) for 24 hours at 37°C, followed by apoptosis analysis through annexin V-FITC/PI staining. (D) Quantitative representation of the percentages of annexin V-positive apoptotic cells for each group of (C). Data are shown as mean ± SD of triplicates. ns, not significant; ** p < 0.01; **** p < 0.0001. (E) Representative confocal images of cell apoptosis induced by apoptin GIFTed-Exos. Following treatment without and with native or apoptin GIFTed-Exos (500 μg mL−1) for 24 hours at 37°C, HeLa cells were analyzed for apoptosis through SYTOX blue staining. Scale bars: 100 μm (F) Quantitative representation of the percentage of SYTOX blue-positive apoptotic cells for each group of (E) (6 fields of view per region). Data are shown as mean ± SD. ns, not significant; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.
