Abstract
Cells must replicate and segregate their DNA to daughter cells accurately to maintain genome stability and prevent cancer. DNA replication is usually fast and accurate, with intrinsic (proofreading) and extrinsic (mismatch repair) error-correction systems. However, replication forks slow or stop when they encounter DNA lesions, natural pause sites, and difficult-to-replicate sequences, or when cells are treated with DNA polymerase inhibitors or hydroxyurea, which depletes nucleotide pools. These challenges are termed replication stress, to which cells respond by activating DNA damage response signaling pathways that delay cell cycle progression, stimulate repair and replication fork restart, or induce apoptosis. Stressed forks are managed by rescue from adjacent forks, repriming, translesion synthesis, template switching, and fork reversal which produces a single-ended double-strand break (seDSB). Stressed forks also collapse to seDSBs when they encounter single-strand nicks or are cleaved by structure-specific nucleases. Reversed and cleaved forks can be restarted by homologous recombination (HR), but seDSBs pose risks of mis-rejoining by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) to other DSBs, causing genome rearrangements. HR requires resection of broken ends to create 3’ single-stranded DNA for RAD51 recombinase loading, and resected ends are refractory to repair by NHEJ. This Mini Review highlights mechanisms that help maintain genome stability by promoting resection of seDSBs and accurate fork restart by HR.
Keywords: genome instability, DNA damage, DNA double-strand breaks, structure-specific nucleases, replication stress
Introduction
Cells maintain relatively stable genomes during cell division to prevent accumulation of potentially oncogenic mutations. Cells proliferate despite copious DNA damage caused by endogenous and exogenous agents. Endogenous agents include reactive oxygen species (ROS) from oxidative metabolism, nucleases and other enzymes such as members of the AID/APOBEC DNA deaminase family, mis-incorporated ribonucleotides, and DNA chemical lability (Gates, 2009; Ciccia and Elledge, 2010; Nick Mcelhinny et al., 2010; Williams et al., 2013; Petljak and Maciejowski, 2020; Juan et al., 2021). DNA damage is induced directly or indirectly by exogenous chemical agents including alkylating agents and other DNA-reactive chemicals including cancer chemotherapeutics, and pollutants in food, water and air. Physical agents that damage DNA include ultraviolet light and ionizing radiation (Friedberg et al., 2014; Nickoloff et al., 2020a). DNA damage comprises chemical changes to bases and the sugar-phosphate backbone, base loss, single-strand breaks, double-strand breaks (DSBs), and intra- and interstrand crosslinks. Protein-DNA crosslinks arise when topoisomerases are trapped in covalent linkages to DNA by topoisomerase poisons, commonly used in cancer therapy (Pommier et al., 2006; Deweese and Osheroff, 2009; Friedberg et al., 2014; Thomas and Pommier, 2019; Riccio et al., 2020). DNA damage detection, signaling and repair systems evolved to manage these threats, termed the DNA damage response (DDR). Nearly all DNA lesions block replicative polymerases (Pol ε, Pol δ), causing fork stalling and fork collapse, and cells manage this replication stress by activating S phase-specific DDR pathways. Replication stress is also caused by depletion of nucleotide pools by hydroxyurea, and DNA polymerase inhibitors (Vesela et al., 2017).
Unstressed cells suffer > 100,000 DNA lesions per day, with a steady state of ∼10,000 lesions per cell (Tubbs and Nussenzweig, 2017). Thus, human cells manage an average of ∼2000 DNA lesions per day in each chromosome, or roughly one lesion per 30 kbp per day. Given that typical human replicons are 75–175 kbp (ranging from 30–450 kbp) (Ligasova et al., 2009) and S phase comprises ∼30% of a 24 h cell cycle, each active replicon will harbor > 2 DNA lesions (assuming lesions arise at similar rates throughout the cell cycle). The DNA replication machinery faces many other challenges in addition to DNA damage. The replisome helicase complex (CDC45, MCM2-7 and GINS), or more often replicative polymerases, slow or stall at unusual structures such as G-rich sequences that form G-quadraplexes, common fragile sites, and hairpins at inverted repeats and CAG/CTG triplet repeats (Bochman et al., 2012; Barlow et al., 2013; Zeman and Cimprich, 2014; Gadaleta and Noguchi, 2017; Kaushal and Freudenreich, 2019; Spiegel et al., 2020; Poggi and Richard, 2021). Replication stress is also caused by conflicts with R-loops formed during transcription, particularly at fragile sites, telomeres, and ribosomal DNA, and by proteins that bind tightly to DNA (Ivessa et al., 2003; Bermejo et al., 2012; Kotsantis et al., 2016; Billard and Poncet, 2019; Gomez-Gonzalez and Aguilera, 2019). These so-called ‘difficult-to-replicate’ sequences are encountered by replisomes in every S phase. Activated oncogenes in cancer cells also increase replication stress through de-regulated replication origin firing (Hills and Diffley, 2014). Persistent fork stalling can cause replisome dissociation, or forks may be cleaved by nucleases to yield seDSBs, both of which have been termed ‘fork collapse’ (Cortez, 2015). We discuss the distinct challenges associated with repair of frank, two-ended DSBs vs replication-associated seDSBs, and recent studies that illuminate mechanisms that ensure accurate, timely repair and restart of stressed replication forks.
Double-Strand Break Repair: A Double-Edged Sword
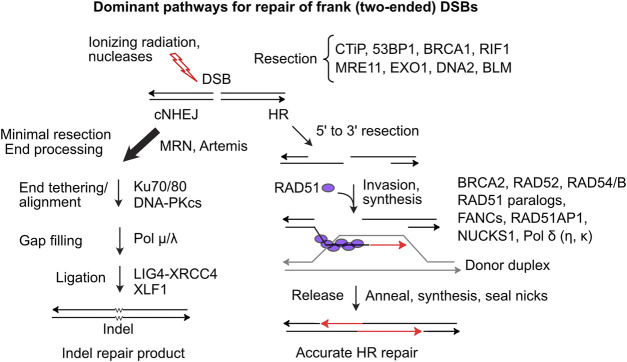
DSBs are dangerous DNA lesions that can cause genome instability and cell death. These threats are mitigated by several DSB repair pathways with different levels of accuracy. In mammalian cells, classical non-homologous end-joining (cNHEJ) is the dominant DSB repair pathway (Figure 1). An early cNHEJ step involves Ku70/Ku80 binding to broken ends. Ku protects ends from degradation and recruits DNA-PKcs, activating the DNA-PK holoenzyme, which promotes end-alignment and rejoining by LIG4-XRCC4 and other factors (Chang et al., 2017). cNHEJ operates on blunt or short overhanging ends and is error-prone, typically producing small insertion/deletion (indel) mutations that may be deleterious, but in certain contexts are quite beneficial, as in the generation of diverse antibody receptor genes (Arya and Bassing, 2017). Alternative NHEJ (aNHEJ) is a backup NHEJ pathway mediated by DNA ligase III when ends anneal at microhomologies. aNHEJ is more error-prone than cNHEJ, producing larger deletion mutations and translocations (Simsek et al., 2011; Iliakis et al., 2015; Sallmyr and Tomkinson, 2018). HR repair of DSBs is generally error-free as it employs an undamaged homologous sequence as repair template. HR initiates when broken ends are resected by > 50 nt, exposing long 3’ ssDNA extensions initially bound by RPA that is exchanged with RAD51 which catalyzes strand invasion into homologous duplex DNA (Figure 1). End resection is regulated and mediated by many factors. CtIP, phosphorylated by CDK, ATM and ATR (limiting resection to S/G2 phases), activates MRE11 nuclease (in complex with RAD50-NBS1) to effect limited end resection (Anand et al., 2016). BRCA1-BARD1 promotes end resection in part by ubiquitination of H2A and by blocking the anti-resection factors 53BP1-RIF1/Shieldin (Mirman et al., 2018; Densham and Morris, 2019). Extensive resection is effected by EXO1 and by DNA2-BLM (Zhao et al., 2020).
FIGURE 1.
Dominant two-ended DSB repair pathways. (Left) cNHEJ is the dominant pathway for repairing two-ended DSBs. cNHEJ acts on blunt or minimally processed ends bound by Ku70/Ku80 and DNA-PKcs. Short gaps are filled and ends are ligated to complete repair, typically with small insertions or deletions at the repair junction (Right) HR initiates with 5′-3′ resection and binding of ssDNA by RPA, which is replaced by RAD51 in a reaction mediated by BRCA2 and RAD51 paralogs. The RAD51 nucleoprotein filament invades homologous duplex DNA, assisted by RAD54, RAD54B and other factors. RAD51 dissociates and the invading end is extended and then released allowing pairing to ssDNA on the opposite side of the DSB. Gaps are filled and ends ligated to complete accurate DSB repair.
Limiting HR largely to S/G2 phases promotes sister chromatid use as HR templates. RAD51 loading and strand invasion are mediated by many factors including BRCA1, BRCA2, five RAD51 paralogs (RAD51B/C/D, XRCC2/3), members of the Fanconi’s anemia (FANC) protein family, RAD54/B, and RAD51AP1 and its paralog NUCKS1 (Pires et al., 2017; Wright et al., 2018; Niraj et al., 2019; Maranon et al., 2020). After repair synthesis, the extended strand reanneals with the resected end on the other side of the DSB, and gaps are filled and ligated to complete repair. Alternative HR pathways yield double Holliday junctions that can be resolved with or without crossovers (Piazza and Heyer, 2019). Single-strand annealing (SSA) is a RAD51-independent HR pathway that requires RAD52 and is observed, for example, in BRCA2-mutated breast cancer cells (Tutt et al., 2001). SSA is error-prone as resected ends anneal at complementary sequences, either between repeats flanking a DSB deleting one repeat and intervening sequences, or between repeats on different chromosomes causing translocations (Weinstock et al., 2006; Nickoloff et al., 2008; Bhargava et al., 2016). Failure to repair DSBs can cause chromosome loss and cell death, but it’s clear that DSB repair also poses significant risks to genome integrity, including genome rearrangements, lethal dicentric chromosomes, and bridge-breakage-fusion cycles (Fenech et al., 2011; Murnane, 2012; Feijoo et al., 2014).
DNA Damage and Replication Stress Responses
The DDR elicits checkpoint responses that arrest or slow cell cycle progression and stimulate DNA repair. Checkpoints arrest or slow cell cycle progression at the G1/S transition, within S phase (intra-S checkpoint) and the G2/M transition. The DDR also promotes programmed cell death if damage is excessive (Roos and Kaina, 2013; Tian et al., 2015; Mladenov et al., 2016; Blackford and Jackson, 2017). Cells initially respond to replication stress by protecting stalled forks and maintaining replisomes until the stress is resolved, otherwise various mechanisms are employed to restart or rescue the fork to ensure timely completion of DNA replication before mitosis. The DDR is important because defects in DDR proteins typically cause genome instability that can drive carcinogenesis (Tubbs and Nussenzweig, 2017), and because DDR proteins are important targets to augment cancer therapy (Nickoloff et al., 2017; Desai et al., 2018; Pilie et al., 2019; Nickoloff et al., 2020b; Baillie and Stirling, 2021). Central to the DDR are three members of the phosphatidyl inositol 3′ kinase-related kinase (PIKK) family, DNA-PKcs, ATM, and ATR, all of which play important roles in DSB repair. These PIKKs are structurally related and phosphorylate target proteins at canonical serine/threonine-glutamine (S/T-Q) sites, as well as non-canonical sites. PIKKs auto- and cross-phosphorylate each other and other DDR proteins to regulate checkpoints and repair (Liu et al., 2012; Marechal and Zou, 2013; Ashley et al., 2014; Boohaker and Xu, 2014; Blackford and Jackson, 2017). Although PIKKs phosphorylate overlapping targets, they have distinct roles in specific DSB repair contexts.
DNA-PKcs plays a critical role in cNHEJ repair of two-ended DSBs induced, for example, by ionizing radiation or nucleases (Chang et al., 2017). The catalytic subunit of DNA-dependent protein kinase, DNA-PKcs, is activated when complexed with Ku70/Ku80-bound DSB ends. DNA-PKcs mediates cNHEJ and checkpoint responses by phosphorylating itself, Ku, MRE11, RAD50, XRCC4-6, XLF, artemis, and histone H2AX, as well as proteins involved in transcription, cell growth, heat shock responses, and viral DNA integration (Anisenko et al., 2020). ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated) is also activated by DSBs, mediated by the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex. ATM promotes frank DSB repair by HR, phosphorylating hundreds of targets including itself, BRCA1, NBS1, H2AX, p53, MDC1, and Chk2 kinase (Blackford and Jackson, 2017). Phosphorylated/activated Chk2 phosphorylates effector proteins that mediate HR and cell cycle arrest (among other processes), including BRCA1, BRCA2, p53, CDC25A, and RB (Marechal and Zou, 2013; Zannini et al., 2014). ATM autophosphorylation promotes ATM binding to MDC1 which binds to phospho-S139 S H2AX (γ-H2AX), and promotes spreading of the γ-H2AX signal to Mbp chromatin domains flanking DSBs (Savic et al., 2009). ATR plays a central role in replication stress responses (Yazinski and Zou, 2016), and is activated by ssDNA formed when blocked DNA polymerase decouples from the helicase and DNA unwinding continues ahead of the fork (Cortez, 2005). ATR is activated by a multi-step process that involves ATR-ATRIP recruitment to RPA-bound ssDNA, RAD17-RFC, Claspin, TopBP1, and 9-1-1 (Yazinski and Zou, 2016). ATR is also activated by an NBS1-dependent mechanism (Shiotani et al., 2013). Recently, ATR activation was shown to be mediated by the RPA-binding factor ETAA1 in an TopBP1-independent manner; dual inactivation of ETAA1 and TopBP1 abrogates ATR signaling and is synthetically lethal (Haahr et al., 2016). Activated ATR phosphorylates Chk1 which slows cell cycle progression in S/G2 phases and delays late origin firing (Yazinski and Zou, 2016).
All three PIKKs respond to DSBs and phosphorylate residues in RPA (Anantha et al., 2007; Oakley and Patrick, 2010; Ashley et al., 2014), yet they also have kinase-independent DDR roles. For example, distinct phenotypes result from DNA-PKcs null mutations vs kinase genetic inactivation or drug inhibition (Allen et al., 2003; Shrivastav et al., 2009; Menolfi and Zha, 2020), and cells lacking DNA-PKcs compensate by downregulating ATM expression (Peng et al., 2005; Shrivastav et al., 2009). Despite this crosstalk, current evidence indicates that DNA-PKcs promotes frank DSB repair by cNHEJ, ATM promotes frank DSB repair by HR, and ATR promotes repair of replication-associated DSBs by HR (Blackford and Jackson, 2017; Pilie et al., 2019).
Restarting Stalled and Collapsed Replication Forks
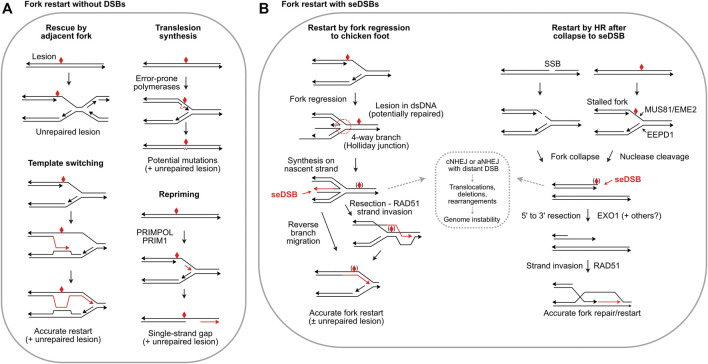
Given the central importance of DNA replication, it is not surprising multiple replication stress response mechanisms evolved. The initial response to replication stress is to stabilize replisomes at stalled forks to prevent fork collapse (Tye et al., 2021). Stalled forks often reverse to a so-called ‘chicken foot’ structure wherein nascent strands anneal, producing a four-way junction resembling a Holliday junction, but with a seDSB (Figure 2B). Fork protection involves the end resection inhibitor RIF1 (Mukherjee et al., 2019); MRNIP (Bennett et al., 2020); the de-ubiquitinating enzyme USP1 which suppresses translesion synthesis (TLS) by regulating PCNA (Lim et al., 2018); HR proteins RAD51, BRCA1, BRCA2 and FANCD2 (Schlacher et al., 2012; Rickman and Smogorzewska, 2019; Rickman et al., 2020); and the RAD51 regulator RADX (Bhat et al., 2018). Fork protection defects generally increase cytotoxicity of replication stress agents and are thus targets to augment cancer therapy. Fork protection can provide sufficient time to repair blocking lesions, but if not resolved in timely manner, adjacent forks may rescue stressed forks (Figure 2A), passively or through checkpoint activation of an adjacent dormant origin (Yekezare et al., 2013; Brambati et al., 2018).
FIGURE 2.
Fork restart mechanisms. (A) Fork restart mechanisms that do not create seDSBs. Illustrated are rescue by an adjacent fork, TLS, template switching, and repriming. Blocking lesions are shown by red symbols and repair or bypass synthesis is shown by red arrows. (B) Fork restart by fork regression, fork encounters with a single-strand break (SSB), or fork cleavage, which create seDSBs. Regressed forks allow synthesis past the blocking lesion using the nascent strand as template. Reverse branch migration restarts the fork, or RAD51 may load onto a resected end allowing strand invasion downstream of the blocking lesion. Blocking lesions may be bypassed or repaired, indicated by symbols in parentheses. Collapsed forks due to encounter with single-strand breaks or fork cleavage can restart by RAD51-mediated strand invasion, i.e., break-induced replication. The strand invasion restart pathways are mediated by HR; fork regression/reversal is not an HR pathway, but RAD51 is still required to protect the nascent strands in the chicken foot. HR defects and HR inhibitors may shunt seDSB intermediates to cNHEJ or aNHEJ (dashed box) causing genome instability.
Several fork restart mechanisms do not repair the blocking lesion, and thus are damage tolerance pathways. TLS involves transient replacement of replicative DNA polymerases with error-prone, TLS polymerases including Pol β, κ, η, τ, and ζ, and Rev1 (Goodman and Woodgate, 2013; Ma et al., 2020) (Figure 2A). Repriming by PRIMPOL and PRIM1 restarts replication downstream of blocking lesions, bypassing lesions and leaving single-strand gaps in nascent DNA (Quinet et al., 2021) (Figure 2A). Template switching uses sister chromatids to bypass blocking lesions and is generally error-free (Figure 2A), but poses risks of genome rearrangement from replisome switching to non-sister templates (Lehmann et al., 2020). Two additional restart pathways are fork reversal to a Holliday junction-like structure followed by fork restoration, and fork cleavage by structure-specific nucleases including the 3′ nuclease MUS81 (with EME2) (Pepe and West, 2014) and the 5’ nuclease EEPD1 (Wu et al., 2015; Sharma et al., 2020) (Figure 2B). Metnase is a structure-specific nuclease that promotes fork restart, but Metnase does not cleave stalled forks and instead may process flaps that arise later (Sharma et al., 2020). SLX1-SLX4 is another structure-specific nuclease that resolves branched replication intermediates, and although it cleaves many types of branched structures including replication fork structures in vitro, direct evidence that it cleaves stalled forks in vivo is lacking (Falquet and Rass, 2019; Xu et al., 2021). seDSBs at cleaved forks can be repaired and the fork re-established/restarted accurately if the end is resected and invades the sister chromatid (Figure 2B), often termed break-induced replication (BIR). Repair of collapsed forks by BIR may function primarily during S or G2 phases to ensure complete DNA replication prior to mitosis, but recent studies show that BIR also operates during mitotic DNA synthesis (MiDAS), an important mechanism for completing replication in common fragile sites, telomeres, and other under-replicated DNA during mitosis (Epum and Haber, 2021).
Minimizing Risks Associated With Replication Stress
Each fork rescue pathway poses risks: TLS is error-prone, producing point mutations, repriming yields vulnerable single-strand gaps, template switching poses risks of genome rearrangements (Figure 2A), and fork reversal/cleavage creates seDSBs which pose risks of aberrant cNHEJ causing genome rearrangements (Figure 2B). Interestingly, cNHEJ factors are present at seDSBs; similar to their presence at telomeres, cNHEJ factors at seDSBs may protect ends but further cNHEJ steps are suppressed (Sui et al., 2020; Audoynaud et al., 2021). Rescue by an adjacent fork might seem the least risky pathway: simply waiting for rescue by an adjacent fork (or repair of blocking lesion) would eliminate risks posed by other pathways. However, cells tightly regulate replication timing (and cell cycle progression), especially during embryonic development. The importance of timely fork restart is illustrated by increased genome instability, developmental defects, and cell death when fork restart is delayed by as little as 10 min (Kim et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2015; Chun et al., 2016). Timely fork restart probably limits the formation of toxic (cell lethal) recombination intermediates, thought to be unresolvable branched structures. In yeast, HR proteins and helicases drive formation of toxic recombination intermediates, and they are prevented or resolved by several factors including Srs2, Sgs1-Top3, Smc5/6, Mus81-Mms4, and Dna2 (Menolfi et al., 2015; Keyamura et al., 2016; Falquet et al., 2020). For example, toxic recombination intermediates cause synthetic lethality in sgs1Δ mus81Δ double mutants, but viability is restored by defects in HR genes including RAD51, RAD52, RAD54, RAD55 and RAD57 (Gangloff et al., 2000; Fabre et al., 2002; Bastin-Shanower et al., 2003).
Although it remains unclear how cells choose among various lesion bypass and fork restart pathways, it is likely that the types of blocking lesions, and the extent (local vs genome-wide) and duration of replication stress are determining factors. For example, certain blocking lesions may be promptly bypassed by TLS with sufficient accuracy, such as UV-induced T-T dimers (Washington et al., 2000), whereas specific types of lesions, high lesion loads, or persistent replication stress may require potentially riskier choices.
Despite the risks associated with seDSBs generated during fork regression and fork cleavage, these mechanisms are very common, particularly in human cells (Pepe and West, 2014; Zellweger et al., 2015; Meng and Zhao, 2017). The accuracy of HR-mediated fork restart may outweigh risks of error-prone bypass mechanisms like TLS. Given this, how might cells mitigate risks of cNHEJ acting on resulting seDSBs? A recently described mechanism operates at forks stalled by collision with opposing transcription R-loops in which MUS81 cleaves the fork, and the resulting ends are rejoined by LIG4-XRCC4 with assistance by RAD52-mediated strand annealing and PolD3, a non-catalytic subunit of Pol d (Chappidi et al., 2020). This pathway does not involve the core cNHEJ factor Ku, and thus prevents joining of the seDSB to other DSBs and genome instability. As noted above, resected DNA ends are poor cNHEJ substrates. As shown in Figure 2B, regressed forks initially have overhanging ends, unless or until nascent strand synthesis creates blunt ends. Thus, the overhanging ends in early fork regression intermediates are intrinsically protected from cNHEJ, and end-protection by RAD51 and other factors appears to reinforce cNHEJ suppression. In addition, ATM promotes dissociation of DNA-PK from seDSBs, suppressing cNHEJ (Britton et al., 2020). In the case of fork cleavage by either MUS81-EME2 or EEPD1 (or fork collapse at nicks), the initial state is a blunt, or nearly blunt seDSB, i.e., an excellent cNHEJ substate. Recent studies have shown that 5’ fork cleavage by EEPD1 is strongly biased toward end-resection because EEPD1 recruits the key resection nuclease EXO1 to cleaved forks (Wu et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2017). EEPD1 first appeared in late chordates/early vertebrates ∼450–670 Mya (Zerbino et al., 2018), and it may have been selected to augment MUS81-mediated fork restart to manage increased replication stress associated with expanding genomes. Metnase evolved even more recently, ∼50 Mya, (Cordaux et al., 2006), and Metnase also recruits EXO1 to cleaved forks (Kim et al., 2016). Thus, EEPD1 and Metnase both promote HR-mediated fork restart by recruiting EXO1 to promote resection, minimizing cNHEJ of seDSBs at cleaved forks. It is unknown whether resection is also promoted during MUS81-mediated fork restart. MUS81 is not known to interact with EXO1, although EXO1 and MRE11 degrade (unprotected) reversed forks that force fork rescue by MUS81 (Lemacon et al., 2017). The expansion of genomes in higher eukaryotes may have created selection pressure for EEPD1/Metnase fork processing nucleases coupled to EXO1, driving a shift toward accurate, HR-mediated fork restart.
Concluding Remarks
Replication stress is intimately tied to cancer etiology and treatment. Replication stress causes genome instability that drives cancer progression, and it is caused by oncogenic stress and damage induced by genotoxic chemo- and radiotherapeutics. The DDR plays critical roles in managing replication stress, and inhibitors of DDR factors are promising targets to effect tumor-specific cell killing in mono-therapy or as adjuncts to genotoxic therapy (O'Connor, 2015; Pearl et al., 2015; Kirsch, 2018; Pilie et al., 2019; Trenner and Sartori, 2019; Nickoloff et al., 2020b). Several specific and broader questions remain. For example, are forks cleaved by MUS81-EME2 also preferentially resected (by EXO1? by DNA2-BLM?) as with EEPD1-cleaved forks? How do different types of lesions, lesion loads, or the DDR determine choices among stressed fork restart mechanisms? And can we manipulate DDR signaling or structure-specific nucleases to more effectively and selectively kill tumor cells, in monotherapy or by augmenting conventional chemo- or radiotherapy? Clarifying these questions will promote the development more effective targeted cancer therapeutics.
Author Contributions
JN, NS, LT, SA, and RH wrote the manuscript and JN prepared the figures.
Funding
The Nickoloff lab was supported by NIH R01 GM084020 and American Lung Association grant LCD-686552. Research in the Hromas lab was supported by NIH R01 CA139429.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- Allen C., Halbrook J., Nickoloff J. A. (2003). Interactive Competition between Homologous Recombination and Non-homologous End Joining. Mol. Cancer Res. 1, 913–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anand R., Ranjha L., Cannavo E., Cejka P. (2016). Phosphorylated CtIP Functions as a Co-factor of the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 Endonuclease in DNA End Resection. Mol. Cel. 64, 940–950. 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.10.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anantha R. W., Vassin V. M., Borowiec J. A. (2007). Sequential and Synergistic Modification of Human RPA Stimulates Chromosomal DNA Repair. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 35910–35923. 10.1074/jbc.m704645200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anisenko A., Kan M., Shadrina O., Brattseva A., Gottikh M. (2020). Phosphorylation Targets of DNA-PK and Their Role in HIV-1 Replication. Cells 9, 1907. 10.3390/cells9081907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya R., Bassing C. H. (2017). V(D)J Recombination Exploits DNA Damage Responses to Promote Immunity. Trends Genet. 33, 479–489. 10.1016/j.tig.2017.04.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley A. K., Shrivastav M., Nie J., Amerin C., Troksa K., Glanzer J. G., et al. (2014). DNA-PK Phosphorylation of RPA32 Ser4/Ser8 Regulates Replication Stress Checkpoint Activation, fork Restart, Homologous Recombination and Mitotic Catastrophe. DNA Repair 21, 131–139. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.04.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audoynaud C., Vagner S., Lambert S. (2021). Non-homologous End-Joining at Challenged Replication forks: an RNA Connection? Trends Genet. 10.1016/j.tig.2021.06.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baillie K. E., Stirling P. C. (2021). Beyond Kinases: Targeting Replication Stress Proteins in Cancer Therapy. Trends Cancer 7, 430–446. 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.10.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow J. H., Faryabi R. B., Callén E., Wong N., Malhowski A., Chen H. T., et al. (2013). Identification of Early Replicating Fragile Sites that Contribute to Genome Instability. Cell 152, 620–632. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastin-Shanower S. A., Fricke W. M., Mullen J. R., Brill S. J. (2003). The Mechanism of Mus81-Mms4 Cleavage Site Selection Distinguishes it from the Homologous Endonuclease Rad1-Rad10. Mol. Cel. Biol. 23, 3487–3496. 10.1128/MCB.23.10.3487-3496.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett L. G., Wilkie A. M., Antonopoulou E., Ceppi I., Sanchez A., Vernon E. G., et al. (2020). MRNIP Is a Replication fork protection Factor. Sci. Adv. 6, eaba5974. 10.1126/sciadv.aba5974 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermejo R., Lai M. S., Foiani M. (2012). Preventing Replication Stress to Maintain Genome Stability: Resolving Conflicts between Replication and Transcription. Mol. Cel. 45, 710–718. 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.03.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava R., Onyango D. O., Stark J. M. (2016). Regulation of Single-Strand Annealing and its Role in Genome Maintenance. Trends Genet. 32, 566–575. 10.1016/j.tig.2016.06.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat K. P., Krishnamoorthy A., Dungrawala H., Garcin E. B., Modesti M., Cortez D. (2018). RADX Modulates RAD51 Activity to Control Replication fork protection. Cel Rep. 24, 538–545. 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.06.061 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billard P., Poncet D. A. (2019). Replication Stress at Telomeric and Mitochondrial DNA: Common Origins and Consequences on Ageing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 4959. 10.3390/ijms20194959 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackford A. N., Jackson S. P. (2017). ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK: the trinity at the Heart of the DNA Damage Response. Mol. Cel. 66, 801–817. 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochman M. L., Paeschke K., Zakian V. A. (2012). DNA Secondary Structures: Stability and Function of G-Quadruplex Structures. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 770–780. 10.1038/nrg3296 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambati A., Zardoni L., Achar Y. J., Piccini D., Galanti L., Colosio A., et al. (2018). Dormant Origins and fork protection Mechanisms rescue Sister forks Arrested by Transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, 1227–1239. 10.1093/nar/gkx945 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton S., Chanut P., Delteil C., Barboule N., Frit P., Calsou P. (2020). ATM Antagonizes NHEJ Proteins Assembly and DNA-Ends Synapsis at Single-Ended DNA Double Strand Breaks. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, 9710–9723. 10.1093/nar/gkaa723 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. H. Y., Pannunzio N. R., Adachi N., Lieber M. R. (2017). Non-homologous DNA End Joining and Alternative Pathways to Double-Strand Break Repair. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cel Biol. 18, 495–506. 10.1038/nrm.2017.48 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappidi N., Nascakova Z., Boleslavska B., Zellweger R., Isik E., Andrs M., et al. (2020). Fork Cleavage-Religation Cycle and Active Transcription Mediate Replication Restart after fork Stalling at Co-transcriptional R-Loops. Mol. Cel. 77, 528–541. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.10.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun C., Wu Y., Lee S.-H., Williamson E. A., Reinert B. L., Jaiswal A. S., et al. (2016). The Homologous Recombination Component EEPD1 Is Required for Genome Stability in Response to Developmental Stress of Vertebrate Embryogenesis. Cell Cycle 15, 957–962. 10.1080/15384101.2016.1151585 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccia A., Elledge S. J. (2010). The DNA Damage Response: Making it Safe to Play with Knives. Mol. Cel. 40, 179–204. 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordaux R., Udit S., Batzer M. A., Feschotte C. (2006). Birth of a Chimeric Primate Gene by Capture of the Transposase Gene from a mobile Element. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 103, 8101–8106. 10.1073/pnas.0601161103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortez D. (2015). Preventing Replication fork Collapse to Maintain Genome Integrity. DNA Repair 32, 149–157. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.04.026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortez D. (2005). Unwind and Slow Down: Checkpoint Activation by Helicase and Polymerase Uncoupling. Genes Dev. 19, 1007–1012. 10.1101/gad.1316905 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densham R. M., Morris J. R. (2019). Moving Mountains-The BRCA1 Promotion of DNA Resection. Front. Mol. Biosci. 6, 79. 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00079 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai A., Yan Y., Gerson S. L. (2018). Advances in Therapeutic Targeting of the DNA Damage Response in Cancer. DNA Repair 66-67, 24–29. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.04.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deweese J. E., Osheroff N. (2009). The DNA Cleavage Reaction of Topoisomerase II: Wolf in Sheep's Clothing. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 738–748. 10.1093/nar/gkn937 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C., Elledge S. J., Lehmann A. R., Lindahl T., Muzi-Falconi M. (Editors) (2014). “DNA Repair, Mutagenesis, and Other Responses to DNA Damage,” Cold Sprng Harbor (NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; ). [Google Scholar]
- Epum E. A., Haber J. E. (2021). DNA Replication: the Recombination Connection. Trends Cel Biol. S0962. 10.1016/j.tcb.2021.07.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre F., Chan A., Heyer W.-D., Gangloff S. (2002). Alternate Pathways Involving Sgs1/Top3, Mus81/Mms4, and Srs2 Prevent Formation of Toxic Recombination Intermediates from Single-Stranded Gaps Created by DNA Replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99, 16887–16892. 10.1073/pnas.252652399 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falquet B., Ölmezer G., Enkner F., Klein D., Challa K., Appanah R., et al. (2020). Disease-associated DNA2 Nuclease-Helicase Protects Cells from Lethal Chromosome Under-replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, 7265–7278. 10.1093/nar/gkaa524 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falquet B., Rass U. (2019). Structure-specific Endonucleases and the Resolution of Chromosome Underreplication. Genes 10, 232–254. 10.3390/genes10030232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feijoo P., Dominguez D., Tusell L., Genesca A. (2014). Telomere-dependent Genomic Integrity: Evolution of the Fusion-Bridge-Breakage Cycle Concept. Cpd 20, 6375–6385. 10.2174/1381612820666140630085416 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenech M., Kirsch-Volders M., Natarajan A. T., Surralles J., Crott J. W., Parry J., et al. (2011). Molecular Mechanisms of Micronucleus, Nucleoplasmic Bridge and Nuclear Bud Formation in Mammalian and Human Cells. Mutagenesis 26, 125–132. 10.1093/mutage/geq052 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadaleta M., Noguchi E. (2017). Regulation of DNA Replication through Natural Impediments in the Eukaryotic Genome. Genes 8, 98. 10.3390/genes8030098 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gangloff S., Soustelle C., Fabre F. (2000). Homologous Recombination Is Responsible for Cell Death in the Absence of the Sgs1 and Srs2 Helicases. Nat. Genet. 25, 192–194. 10.1038/76055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gates K. S. (2009). An Overview of Chemical Processes that Damage Cellular DNA: Spontaneous Hydrolysis, Alkylation, and Reactions with Radicals. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 22, 1747–1760. 10.1021/tx900242k [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-González B., Aguilera A. (2019). Transcription-mediated Replication Hindrance: a Major Driver of Genome Instability. Genes Dev. 33, 1008–1026. 10.1101/gad.324517.119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. F., Woodgate R. (2013). Translesion DNA Polymerases. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 5, a010363. 10.1101/cshperspect.a010363 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haahr P., Hoffmann S., Tollenaere M. A. X., Ho T., Toledo L. I., Mann M., et al. (2016). Activation of the ATR Kinase by the RPA-Binding Protein ETAA1. Nat. Cel Biol. 18, 1196–1207. 10.1038/ncb3422 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills S. A., Diffley J. F. X. (2014). DNA Replication and Oncogene-Induced Replicative Stress. Curr. Biol. 24, R435–R444. 10.1016/j.cub.2014.04.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iliakis G., Murmann T., Soni A. (2015). Alternative End-Joining Repair Pathways Are the Ultimate Backup for Abrogated Classical Non-homologous End-Joining and Homologous Recombination Repair: Implications for the Formation of Chromosome Translocations. Mutat. Research/Genetic Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenesis 793, 166–175. 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2015.07.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivessa A. S., Lenzmeier B. A., Bessler J. B., Goudsouzian L. K., Schnakenberg S. L., Zakian V. A. (2003). The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Helicase Rrm3p Facilitates Replication Past Nonhistone Protein-DNA Complexes. Mol. Cel. 12, 1525–1536. 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00456-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juan C. A., Pérez de la Lastra J. M., Plou F. J., Pérez-Lebeña E. (2021). The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4642. 10.3390/ijms22094642 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal S., Freudenreich C. H. (2019). The Role of fork Stalling and DNA Structures in Causing Chromosome Fragility. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 58, 270–283. 10.1002/gcc.22721 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyamura K., Arai K., Hishida T. (2016). Srs2 and Mus81-Mms4 Prevent Accumulation of Toxic Inter-homolog Recombination Intermediates. Plos Genet. 12, e1006136. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006136 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H.-S., Chen Q., Kim S.-K., Nickoloff J. A., Hromas R., Georgiadis M. M., et al. (2014). The DDN Catalytic Motif Is Required for Metnase Functions in Non-homologous End Joining (NHEJ) Repair and Replication Restart. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 10930–10938. 10.1074/jbc.m113.533216 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H.-S., Kim S.-K., Hromas R., Lee S.-H. (2015). The SET Domain Is Essential for Metnase Functions in Replication Restart and the 5’ End of SS-Overhang Cleavage. PLoS One 10, e0139418. 10.1371/journal.pone.0139418 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H.-S., Nickoloff J. A., Wu Y., Williamson E. A., Sidhu G. S., Reinert B. L., et al. (2017). Endonuclease EEPD1 Is a Gatekeeper for Repair of Stressed Replication forks. J. Biol. Chem. 292, 2795–2804. 10.1074/jbc.M116.758235 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H.-S., Williamson E. A., Nickoloff J. A., Hromas R. A., Lee S.-H. (2017). Metnase Mediates Loading of Exonuclease 1 onto Single Strand Overhang DNA for End Resection at Stalled Replication Forks. J. Biol. Chem. 292, 1414–1425. 10.1074/jbc.M116.745646 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch D. G. (2018). Current Opportunities and Future Vision of Precision Medicine in Radiation Oncology. Int. J. Radiat. Oncology. Biology. Physics 101, 267–270. 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.04.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotsantis P., Silva L. M., Irmscher S., Jones R. M., Folkes L., Gromak N., et al. (2016). Increased Global Transcription Activity as a Mechanism of Replication Stress in Cancer. Nat. Commun. 7, 13087. 10.1038/ncomms13087 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann C. P., Jiménez-Martín A., Branzei D., Tercero J. A. (2020). Prevention of Unwanted Recombination at Damaged Replication forks. Curr. Genet. 66, 1045–1051. 10.1007/s00294-020-01095-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaçon D., Jackson J., Quinet A., Brickner J. R., Li S., Yazinski S., et al. (2017). MRE11 and EXO1 Nucleases Degrade Reversed forks and Elicit MUS81-dependent fork rescue in BRCA2-Deficient Cells. Nat. Commun. 8, 860. 10.1038/s41467-017-01180-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligasová A., Raška I., Koberna K. (2009). Organization of Human Replicon: Singles or Zipping Couples? J. Struct. Biol. 165, 204–213. 10.1016/j.jsb.2008.11.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim K. S., Li H., Roberts E. A., Gaudiano E. F., Clairmont C., Sambel L. A., et al. (2018). USP1 Is Required for Replication fork protection in BRCA1-Deficient Tumors. Mol. Cel. 72, 925–941. 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.10.045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S., Opiyo S. O., Manthey K., Glanzer J. G., Ashley A. K., Amerin C., et al. (2012). Distinct Roles for DNA-PK, ATM and ATR in RPA Phosphorylation and Checkpoint Activation in Response to Replication Stress. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 10780–10794. 10.1093/nar/gks849 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma X., Tang T. S., Guo C. (2020). Regulation of Translesion DNA Synthesis in Mammalian Cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 61, 680–692. 10.1002/em.22359 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maranon D. G., Sharma N., Huang Y., Selemenakis P., Wang M., Altina N., et al. (2020). NUCKS1 Promotes RAD54 Activity in Homologous Recombination DNA Repair. J. Cel Biol. 219. 10.1083/jcb.201911049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marechal A., Zou L. (2013). DNA Damage Sensing by the ATM and ATR Kinases. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 5, a012716. 10.1101/cshperspect.a012716 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElhinny S. A. N., Kumar D., Clark A. B., Watt D. L., Watts B. E., Lundström E.-B., et al. (2010). Genome Instability Due to Ribonucleotide Incorporation into DNA. Nat. Chem. Biol. 6, 774–781. 10.1038/nchembio.424 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng X., Zhao X. (2017). Replication fork Regression and its Regulation. FEMS Yeast Res. 17, fow110. 10.1093/femsyr/fow110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menolfi D., Delamarre A., Lengronne A., Pasero P., Branzei D. (2015). Essential Roles of the Smc5/6 Complex in Replication through Natural Pausing Sites and Endogenous DNA Damage Tolerance. Mol. Cel. 60, 835–846. 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.10.023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menolfi D., Zha S. (2020). ATM, ATR and DNA-PKcs Kinases-The Lessons from the Mouse Models: Inhibition ≠ Deletion. Cell Biosci. 10, 8. 10.1186/s13578-020-0376-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirman Z., Lottersberger F., Takai H., Kibe T., Gong Y., Takai K., et al. (2018). 53BP1-RIF1-shieldin Counteracts DSB Resection through CST- and Polα-dependent Fill-In. Nature 560, 112–116. 10.1038/s41586-018-0324-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mladenov E., Magin S., Soni A., Iliakis G. (2016). DNA Double-Strand-Break Repair in Higher Eukaryotes and its Role in Genomic Instability and Cancer: Cell Cycle and Proliferation-dependent Regulation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 37-38, 51–64. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2016.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee C., Tripathi V., Manolika E. M., Heijink A. M., Ricci G., Merzouk S., et al. (2019). RIF1 Promotes Replication fork protection and Efficient Restart to Maintain Genome Stability. Nat. Commun. 10, 3287. 10.1038/s41467-019-11246-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murnane J. P. (2012). Telomere Dysfunction and Chromosome Instability. Mutat. Research/Fundamental Mol. Mech. Mutagenesis 730, 28–36. 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.04.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff J. A., Jones D., Lee S. H., Williamson E. A., Hromas R. (2017). Drugging the Cancers Addicted to DNA Repair. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 109, djx059. 10.1093/jnci/djx059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff J. A., De Haro L. P., Wray J., Hromas R. (2008). Mechanisms of Leukemia Translocations. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 15, 338–345. 10.1097/moh.0b013e328302f711 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff J. A., Sharma N., Taylor L. (2020a). Clustered DNA Double-Strand Breaks: Biological Effects and Relevance to Cancer Radiotherapy. Genes 11, 99–116. 10.3390/genes11010099 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff J. A., Taylor L., Sharma N., Kato T. A. (2020b). Exploiting DNA Repair Pathways for Tumor Sensitization, Mitigation of Resistance, and normal Tissue protection in Radiotherapy. Curr. Drug. Resist. 4, 244–263. 10.20517/cdr.2020.89 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niraj J., Färkkilä A., D'andrea A. D. (2019). The Fanconi Anemia Pathway in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 3, 457–478. 10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030617-050422 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley G. G., Patrick S. M. (2010). Replication Protein A: Directing Traffic at the Intersection of Replication and Repair. Front. Biosci. 15, 883–900. 10.2741/3652 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor M. J. (2015). Targeting the DNA Damage Response in Cancer. Mol. Cel. 60, 547–560. 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.10.040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl L. H., Schierz A. C., Ward S. E., Al-Lazikani B., Pearl F. M. G. (2015). Therapeutic Opportunities within the DNA Damage Response. Nat. Rev. Cancer 15, 166–180. 10.1038/nrc3891 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Y., Woods R. G., Beamish H., Ye R., Lees-Miller S. P., Lavin M. F., et al. (2005). Deficiency in the Catalytic Subunit of DNA-dependent Protein Kinase Causes Down-Regulation of ATM. Cancer Res. 65, 1670–1677. 10.1158/0008-5472.can-04-3451 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe A., West S. C. (2014). MUS81-EME2 Promotes Replication fork Restart. Cel Rep. 7, 1048–1055. 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petljak M., Maciejowski J. (2020). Molecular Origins of APOBEC-Associated Mutations in Cancer. DNA Repair 94, 102905. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102905 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piazza A., Heyer W.-D. (2019). Homologous Recombination and the Formation of Complex Genomic Rearrangements. Trends Cel Biol. 29, 135–149. 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.10.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilié P. G., Tang C., Mills G. B., Yap T. A. (2019). State-of-the-art Strategies for Targeting the DNA Damage Response in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 16, 81–104. 10.1038/s41571-018-0114-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pires E., Sung P., Wiese C. (2017). Role of RAD51AP1 in Homologous Recombination DNA Repair and Carcinogenesis. DNA Repair 59, 76–81. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.09.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggi L., Richard G.-F. (2021). Alternative DNA Structures In Vivo : Molecular Evidence and Remaining Questions. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 85. 10.1128/MMBR.00110-20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier Y., Barcelo J. M., Rao V. A., Sordet O., Jobson A. G., Thibaut L., et al. (2006). Repair of Topoisomerase I‐Mediated DNA Damage. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 81, 179–229. 10.1016/S0079-6603(06)81005-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinet A., Tirman S., Cybulla E., Meroni A., Vindigni A. (2021). To Skip or Not to Skip: Choosing Repriming to Tolerate DNA Damage. Mol. Cel. 81, 649–658. 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.01.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccio A. A., Schellenberg M. J., Williams R. S. (2020). Molecular Mechanisms of Topoisomerase 2 DNA-Protein Crosslink Resolution. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 77, 81–91. 10.1007/s00018-019-03367-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickman K. A., Noonan R. J., Lach F. P., Sridhar S., Wang A. T., Abhyankar A., et al. (2020). Distinct Roles of BRCA2 in Replication fork protection in Response to Hydroxyurea and DNA Interstrand Cross-Links. Genes Dev. 34, 832–846. 10.1101/gad.336446.120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickman K., Smogorzewska A. (2019). Advances in Understanding DNA Processing and protection at Stalled Replication forks. J. Cel Biol. 218, 1096–1107. 10.1083/jcb.201809012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos W. P., Kaina B. (2013). DNA Damage-Induced Cell Death: from Specific DNA Lesions to the DNA Damage Response and Apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 332, 237–248. 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.01.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallmyr A., Tomkinson A. E. (2018). Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks by Mammalian Alternative End-Joining Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 10536–10546. 10.1074/jbc.TM117.000375 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savic V., Yin B., Maas N. L., Bredemeyer A. L., Carpenter A. C., Helmink B. A., et al. (2009). Formation of Dynamic γ-H2AX Domains along Broken DNA Strands Is Distinctly Regulated by ATM and MDC1 and Dependent upon H2AX Densities in Chromatin. Mol. Cel. 34, 298–310. 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.04.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlacher K., Wu H., Jasin M. (2012). A Distinct Replication fork protection Pathway Connects Fanconi Anemia Tumor Suppressors to RAD51-Brca1/2. Cancer Cell 22, 106–116. 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.05.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma N., Speed M. C., Allen C. P., Maranon D. G., Williamson E., Singh S., et al. (2020). Distinct Roles of Structure-specific Endonucleases EEPD1 and Metnase in Replication Stress Responses. NAR Cancer 2, zcaa008. 10.1093/narcan/zcaa008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiotani B., Nguyen H. D., Håkansson P., Maréchal A., Tse A., Tahara H., et al. (2013). Two Distinct Modes of ATR Activation Orchestrated by Rad17 and Nbs1. Cel Rep. 3, 1651–1662. 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.04.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastav M., Miller C. A., De Haro L. P., Durant S. T., Chen B. P. C., Chen D. J., et al. (2009). DNA-PKcs and ATM Co-regulate DNA Double-Strand Break Repair. DNA Repair 8, 920–929. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.05.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simsek D., Brunet E., Wong S. Y.-W., Katyal S., Gao Y., Mckinnon P. J., et al. (2011). DNA Ligase III Promotes Alternative Nonhomologous End-Joining during Chromosomal Translocation Formation. Plos Genet. 7, e1002080. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002080 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel J., Adhikari S., Balasubramanian S. (2020). The Structure and Function of DNA G-Quadruplexes. Trends Chem. 2, 123–136. 10.1016/j.trechm.2019.07.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sui J., Zhang S., Chen B. P. C. (2020). DNA-dependent Protein Kinase in Telomere Maintenance and protection. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 25, 2. 10.1186/s11658-020-0199-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A., Pommier Y. (2019). Targeting Topoisomerase I in the Era of Precision Medicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 25, 6581–6589. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1089 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian H., Gao Z., Li H., Zhang B., Wang G., Zhang Q., et al. (2015). DNA Damage Response - A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer Prevention and Cancer Therapy. Cancer Lett. 358, 8–16. 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.12.038 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trenner A., Sartori A. A. (2019). Harnessing DNA Double-Strand Break Repair for Cancer Treatment. Front. Oncol. 9, 1388. 10.3389/fonc.2019.01388 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubbs A., Nussenzweig A. (2017). Endogenous DNA Damage as a Source of Genomic Instability in Cancer. Cell 168, 644–656. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutt A., Bertwistle D., Valentine J., Gabriel A., Swift S., Ross G., et al. (2001). Mutation in Brca2 Stimulates Error-Prone Homology-Directed Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks Occurring between Repeated Sequences. EMBO J. 20, 4704–4716. 10.1093/emboj/20.17.4704 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tye S., Ronson G. E., Morris J. R. (2021). A fork in the Road: Where Homologous Recombination and Stalled Replication fork protection Part Ways. Semin. Cel Dev. Biol. 113, 14–26. 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.07.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesela E., Chroma K., Turi Z., Mistrik M. (2017). Common Chemical Inductors of Replication Stress: Focus on Cell‐Based Studies. Biomolecules 7, 19. 10.3390/biom7010019 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Washington M. T., Johnson R. E., Prakash S., Prakash L. (2000). Accuracy of Thymine-Thymine Dimer Bypass by Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA Polymerase Eta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 97, 3094–3099. 10.1073/pnas.050491997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock D. M., Richardson C. A., Elliott B., Jasin M. (2006). Modeling Oncogenic Translocations: Distinct Roles for Double-Strand Break Repair Pathways in Translocation Formation in Mammalian Cells. DNA Repair 5, 1065–1074. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.05.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. S., Smith D. J., Marjavaara L., Lujan S. A., Chabes A., Kunkel T. A. (2013). Topoisomerase 1-mediated Removal of Ribonucleotides from Nascent Leading-Strand DNA. Mol. Cel. 49, 1010–1015. 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.12.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. D., Shah S. S., Heyer W.-D. (2018). Homologous Recombination and the Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 10524–10535. 10.1074/jbc.TM118.000372 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y., Lee S.-H., Williamson E. A., Reinert B. L., Cho J. H., Xia F., et al. (2015). EEPD1 Rescues Stressed Replication forks and Maintains Genome Stability by Promoting End Resection and Homologous Recombination Repair. Plos Genet. 11, e1005675. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005675 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu B., Boohaker R. (2014). The Versatile Functions of ATM Kinase. Biomed. J. 37, 3–9. 10.4103/2319-4170.125655 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X., Wang M., Sun J., Yu Z., Li G., Yang N., et al. (2021). Structure Specific DNA Recognition by the SLX1-SLX4 Endonuclease Complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, 7740–7752. 10.1093/nar/gkab542 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazinski S. A., Zou L. (2016). Functions, Regulation, and Therapeutic Implications of the ATR Checkpoint Pathway. Annu. Rev. Genet. 50, 155–173. 10.1146/annurev-genet-121415-121658 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yekezare M., Gómez-González B., Diffley J. F. X. (2013). Controlling DNA Replication Origins in Response to DNA Damage - Inhibit Globally, Activate Locally. J. Cel Sci. 126, 1297–1306. 10.1242/jcs.096701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannini L., Delia D., Buscemi G. (2014). CHK2 Kinase in the DNA Damage Response and beyond. J. Mol. Cel Biol. 6, 442–457. 10.1093/jmcb/mju045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zellweger R., Dalcher D., Mutreja K., Berti M., Schmid J. A., Herrador R., et al. (2015). Rad51-mediated Replication fork Reversal Is a Global Response to Genotoxic Treatments in Human Cells. J. Cel Biol. 208, 563–579. 10.1083/jcb.201406099 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeman M. K., Cimprich K. A. (2014). Causes and Consequences of Replication Stress. Nat. Cel Biol. 16, 2–9. 10.1038/ncb2897 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerbino D. R., Achuthan P., Akanni W., Amode M. R., Barrell D., Bhai J., et al. (2018). Ensembl 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, D754–D761. 10.1093/nar/gkx1098 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao F., Kim W., Kloeber J. A., Lou Z. (2020). DNA End Resection and its Role in DNA Replication and DSB Repair Choice in Mammalian Cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 52, 1705–1714. 10.1038/s12276-020-00519-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]