Fig. 1.
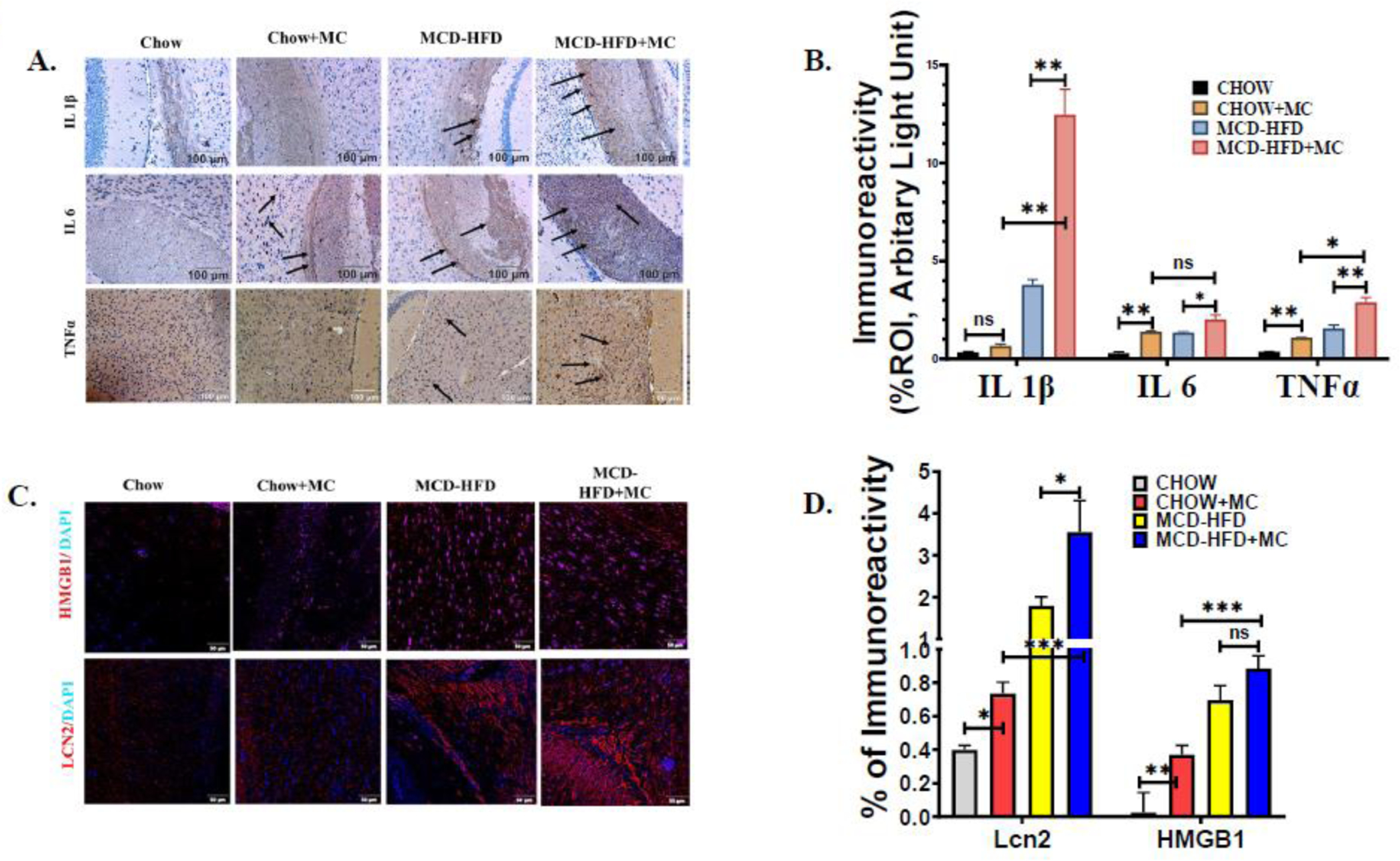
MC-LR exposure results in increased expression of Proinflammatory cytokines, HMGB1, and Lipocalin 2 in brain sections of NAFLD/NASH mice. The in vivo experimental groups include WT Chow diet-fed mice (Chow), WT chow diet-fed mice exposed to MC-LR (Chow+MC), WT mice fed with methionine choline-deficient and high-fat diet (MCD-HFD), and another WT methionine choline-deficient and a high-fat diet-fed group of mice exposed to MC-LR (MCD-HFD+MC). (A.) Immunoreactivity of IL 1β, IL 6, and TNFα expression as depicted by immunohistochemistry images in brain sections from Chow, Chow+MC, MCD-HFD, and MCD-HFD+MC mice groups. All images were taken at × 20 magnification (Scale: 100 μm) and immunoreactivity was indicated by black arrows. (B.) Morphometric analysis of IL 1β, IL 6, and TNFα immunoreactivity [mean data plotted on y-axis was measured as % positive immunoreactive area (% ROI) in arbitrary light units from three different microscopic fields] in Chow, Chow+MC, MCD-HFD, and MCD-HFD+MC mice groups (*p< 0.05, **p< 0.01, ns=non-significant). (C.) Immunoreactivity of HMGB1 (red) and Lcn2 (red) in brain sections counterstained with DAPI from Chow, Chow+MC, MCD-HFD, and MCD-HFD+MC mice groups as shown by immunofluorescence microscopy. All images were taken at × 40 magnification (Scale: 50 μm) (D.) Morphometric analysis of HMGB1, and Lcn2 immunoreactivity [mean data plotted on y-axis was measured as % positive immunoreactive area (% ROI) in arbitrary light units from three different microscopic fields] in Chow, Chow+MC, MCD-HFD, and MCD-HFD+MC mice groups (*p< 0.05, **p< 0.01, ***p< 0.001, ns=non-significant). All statistical significance was tested by performing unpaired t-test between the groups (*p< 0.05, **p< 0.01, ***p< 0.001, ns=non-significant), followed by Bonferroni Dunn Post hoc corrections.
