Abstract
Background
Depression is a common, easily ignored, accompanied disease of gastric cancer (GC) patients and is often observed with elevated plasma catecholamine levels. Depression frequently promotes GC progression and leads to poor clinical outcomes; however, the molecular mechanisms underlying depression‐induced GC progression remain poorly understood. We aimed to study the effects of depression on GC progression and explore possible mechanisms mediating the action of depression‐associated catecholamines on GC.
Methods
Depression states of GC patients were graded using the Patient Health Questionnaire‐9, and plasma catecholamine levels were examined by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Migrative and invasive GC cells were examined using transwell assays, and metastatic GC niches were imaged using bioluminescence technology in a depression mouse model established with chronic unpredictable mild stress. Mouse depression‐like behaviors were assessed through sucrose preference, forced swimming, and tail suspension tests. Characteristics of the neuroendocrine phenotype were observed via RT‐PCR, Western blotting, flow cytometry, and transmission electron microscopy.
Results
Fifty‐one GC patients (age: 53.61 ± 1.79 years; cancer duration: 3.71 ± 0.33 months; depression duration: 2.37 ± 0.38 months; male‐to‐female ratio: 1.55:1) were enrolled in the study. Depression grade was significantly higher in GC patients showing higher plasma levels of catecholamines (epinephrine: P = 0.018; noradrenaline: P = 0.009), higher oncogene metastasis‐associated in colon cancer‐1 (MACC1) level (P = 0.018), and metastasis (P < 0.001). Further, depression‐associated catecholamine specifically bound to the beta‐2 adrenergic receptor (β2‐AR) and upregulated MACC1 expression, and thus promoting neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation through direct binding between MACC1 and synaptophysin. Eventually, the neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation accelerated GC invasion in vitro and metastasis in vivo. However, β2‐AR antagonist ICI‐118,551 or MACC1 silencing effectively blocked the catecholamine‐induced neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation and eliminated depression‐enhanced GC migration and invasion. Moreover, β2‐AR blocking or MACC1 silencing prevented GC metastasis attributed to a neuroendocrine phenotype in a depression mouse model.
Conclusions
Catecholamine‐induced neuroendocrine phenotypes of GC cells led to depression‐accelerated GC invasion and metastasis via the β2‐AR/MACC1 axis, while β2‐AR antagonist or MACC1 silencing could reverse it, showing promising potential therapeutic strategies for improving the outcome of GC patients with comorbid depression.
Keywords: catecholamines, depression, gastric cancer, MACC1, neuroendocrine phenotype, psychological stress, tumor metastasis
Abbreviations
- AR
adrenergic receptor
- CHGA
chromogranin A
- CHGB
chromogranin B
- Co‐IP
co‐immunoprecipitation
- CUMS
chronic unpredictable mild stress
- DAPI
4',6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole
- DMSO
dimethyl sulfoxide
- ELISA
enzyme‐linked immunoassay
- ECM
extracellular matrix
- Epi
epinephrine
- FCM
flow cytometry
- FITC
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- GAPDH
glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase
- GC
gastric cancer
- GES‐1
gastric epithelial cell line
- GSEA
gene set enrichment analysis
- HPLC‐MS/MS
high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry
- IRS
immunoreactive score
- KRT8
keratin‐8
- MACC1
metastasis‐associated in colon cancer 1
- MMP9
matrix metallopeptidase 9
- NA
noradrenaline
- Phent
phentolamine
- PHQ‐9
Patient Health Questionnaire
- PPL
propranolol
- RFI
relative fluorescence intensity
- SYP
synaptophysin
- TEM
transmission electron microscopy
1. BACKGROUND
Gastric cancer (GC) is a public health problem and the third leading cause of cancer‐associated deaths worldwide [1, 2]. Depression, which is a common and easily overlooked concomitant disease, generally predicts the advanced clinical stage and poor prognosis for GC patients [3, 4, 5]. However, the precise mechanisms underlying depression‐associated poor outcomes in GC patients are not clearly understood.
Cancer patients with depression are under chronic psychological stress, potentially affecting cancer progression [6, 7]. During responses to chronic stress, several stress‐associated neurotransmitters are secreted, mainly involving catecholamines [8]. Catecholamines are comprised of epinephrine (Epi), noradrenaline (NA), and dopamine, with the former two being major secreted factors for responding to adverse stress [8, 9, 10]. While in the tumor microenvironment, catecholamines can facilitate the growth, migration, and metastasis of several tumors [11], including breast cancer [12], lung cancer [13], and colon cancer [14]. Current studies have proved that catecholamines promote epithelial‐mesenchymal transition (EMT) by activating the c‐Jun signaling pathway in GC [15, 16]. Meanwhile, it has been found that catecholamines, as the neurotransmitter, can affect tumor characteristics, such as phenotypic transformation [15], apoptosis [17], and drug resistance [18], particularly transformation from the epithelial phenotype to the neuroendocrine‐like phenotype, which has attracted much attention to date [19, 20]. The acquisition of a neuroendocrine phenotype in cancer cells is also strongly associated with neoplasm metastasis [21], drug resistance [22], and advanced cancer stage [23].
In addition, activation of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor (c‐Met) regulated neuroendocrine features by increasing the expression of neuroendocrine markers—SYP, CD44, and chromogranin A (CHGA), and then promoted metastasis in advanced prostate cancer [24]. Stein et al. [25] and our group [26] have noted that c‐Met transcriptional levels were controlled by metastasis‐associated with colon cancer 1 (MACC1), an oncogene regulated by c‐Jun through binding to its promoter region [27]. Moreover, we had demonstrated that upregulated MACC1 expression could promote EMT in GC [28]. Hence, based on the ability of MACC1 to regulate cellular phenotypic plasticity and the effects of its regulatory networks on the induction of neuroendocrine phenotype of tumor cells, we suspected that MACC1 might play an important role in promoting tumor metastasis through neuroendocrine phenotype reprogramming.
In this study, we aimed to determine the effects of depression on GC progression, explore the possible signaling pathway underlying the actions of depression‐associated catecholamines on cancer cells, and reveal the specific mechanism of how the catecholamine/beta‐2 adrenergic receptor (β2‐AR)/MACC1 axis induce neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation and then promote GC metastatic progression. Then, we further investigated a possible therapeutic strategy of targeting β2‐AR or MACC1 in GC, especially with depression.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Patients, blood specimens, and tissue samples
To evaluate depression status, 51 patients with gastric adenocarcinoma pathologically diagnosed at Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University (Guangzhou, Guangdong, China) between September, 2017 and February, 2019 were enrolled and assessed by using the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ‐9) Depression Scale [29]. The median depression score was used as the cutoff value for distinguishing high and low levels of depression in GC patients, as previously described [30]. Twenty healthy volunteers without any malignancies were recruited from Southern Medical University (Guangzhou, Guangdong, China) to serve as the control group. The blood samples of all participants were collected to measure catecholamine levels and MACC1 concentration in plasma.
To analyze the correlation between SYP and MACC1 expression, postoperative tumor biopsies and adjacent normal tissues from 53 GC patients were collected. The 53 GC patients did not have neoadjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy and had been pathologically diagnosed with gastric adenocarcinoma in Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University between February, 2016 and February, 2019. Those GC patients who have controversial pathological diagnoses and did not have sufficient information allowing for estimation were excluded.
All patients and volunteers consented to an institutional review board‐approved protocol that allowed for comprehensive analysis of tumor and blood samples (Nanfang Hospital Ethics Review Board, Southern Medical University). This study conformed to the Declaration of Helsinki and the International Ethical Guidelines for Biomedical Research Involving Human Subjects. Each participant was required to sign an informed consent form.
2.2. Animals
BALB/c nude mice (male, 2‐3 weeks old) were obtained from the Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center (SCXK 2013‐0002, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China) and were used to establish a model of depression caused by chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS), which has been widely applied as an animal depression model [31, 32]. Briefly, mice were treated with different kinds of stressors including restraint in cylinder for 4 h, cage tilting to 45 degrees for 24 h, tail nipping for 1 min, swimming in 4°C cold water or 45°C hot water for 5 min, wet bedding for 24 h, level shaking for 10 min, light/dark cycle inversion for 24 h, and food or water deprivation overnight. Each mouse received one of these stressors daily and randomly at different times of the day, and the same stressor would not be repeated within a week and two consecutive days in order to weaken the predictability of each stressor. Control mice did not receive any stressors and were fed by food and water freely. All mice were weighed once a week during the experimental phase.
All animal experimental procedures followed specific pathogen‐free (SPF) standards and conformed to the guidelines of the Laboratory Animal Center of Southern Medical University. Animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University.
2.3. Reagents and antibodies
A Trizol kit was purchased from Takara (Tokyo, Japan), and a SYBR Green I Master kit was obtained from Roche (Penzberg, Germany) for reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (RT‐PCR) analyses. Lipofectamine 2000 reagent and Opti‐MEM® were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA) and selected using an RNA interference assay. MACC1 ELISA kit was acquired from CUSABIO (Wuhan, Hubei, China). Reference standard of Epi and NA were from Solarbio (Beijing, China). Aspartic acid, ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid (EGTA), Mg2+‐ATP, 5‐nitro‐2‐(3‐phenlypropylamino) benzoic acid, and thapsigarin were acquired from Sigma‐Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and selected for high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC‐MS/MS). Ca(OH)2, CaCl2, N‐methyl‐D‐glucamine, and 3,4‐diaminopyridine were purchased from Macklin Biochemical Co. (Shanghai, China) for patch‐clamp recordings. N‐phenylanthtanilic acid and 4‐(2‐hydroxyethyl)‐1‐piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) were from BBI Life Sciences (Shanghai, China) and used for patch‐clamp recordings. Detailed information of other reagents and antibodies in this work are described in Supplementary Table S1‐2.
2.4. High performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC‐MS/MS)
We detected the presence of catecholamines, Epi, and NA in the plasma as previously described [33]. Blood specimens were collected in chilled vacutainer tubes with ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) and immediately centrifuged at 4°C for 10 min at the speed of 16,000 rpm. After plasma collection, supernatants were subjected to the 4000 Q TRAP LC/MS/MS system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) to determine the content of catecholamines. Samples were analyzed using the UltiMate 3000 HPLC system (Dionex, Thermo Scientific, Logan, UT, USA), and eluants were analyzed using the 4000 Q TRAP tandem mass spectrometer, which was operated in the electrospray positive mode (ES+) and monitored by multiple reactions. Concentrations of Epi and NA were obtained from standard curves made of Epi and NA standards, respectively.
2.5. Cell culture and treatment
Human GC cell lines BGC823 (China's Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China) and MKN45 (Japanese Collection of Research Bioresources Cell Bank, Ibaraki, Osaka, Japan), which usually present moderate MACC1 expression [28, 34], and a human immortalized gastric epithelial cell line GES‐1 (China's Academy of Sciences) were cultured in complete RPMI‐1640 medium (HyClone, Thermo Scientific, Logan, UT, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37°C. All cell lines were authenticated by Short Tandem Repeat profiling (January 27, 2015).
For treatment with AR agonists, GC cells were incubated with Epi (0.1‐10 μmol/L), NA (10 μmol/L), isoprenaline (10 μmol/L), salbutamol (50 μmol/L), or dobutamine (10 μmol/L) for the indicated time points. For AR antagonist studies, cells were pre‐incubated with propranolol (5 μmol/L), ICI‐118,551 (10 μmol/L), or phentolamine (10 μmol/L) for 6 h before Epi stimulation. All treatments followed cell starvation in a serum‐free medium for 6 h. JNK1/2/3 inhibitors SP600125 (5 μmol/L) and JNK‐IN‐8 (5 μmol/L) were used to inhibit the c‐Jun signaling pathway for 6 h before Epi stimulation. After transfection with MACC1 siRNA for 48 h, the cells were treated with Epi (10 μmol/L) to investigate neuroendocrine characteristics and invasion of GC cells.
2.6. RNA interference and gene overexpression
The small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting SYP or MACC1 and control siRNA (GEMA Co., Suzhou, Jiangsu, China) were transfected into GC cells as previously described [35]. Briefly, GC cells (2 × 104 cells/well) were seeded in 6‐well plates until reached 30%‐40% confluence. Then, 50 nmol/L siRNA was transfected into cells by using Lipofectamine 2000 Transfection Reagent and Opti‐MEM (Thermo Scientific). After 48 h transfection, cells were managed with other treatments. MACC1 cDNA (oeMACC1) or MACC1‐specific short hairpin RNA (shMACC1) and the control sequences were severally transfected into BGC823 and MKN45 cell lines for stably expression, as described in our previous studies [26, 36]. For SYP gene overexpression, BGC823 and MKN45 cell were cultured in 6‐well plates, and then the plasmids pBaBb‐SYP (oeSYP) or control vectors (Obio Technology, Shanghai, China) were transfected into GC cells for 48 h. All operational procedures were conducted according to the manufactures’ instructions, as previously described [26]. Specific sequences are showed in Supplementary Table S3.
2.7. RT‐PCR and Western blotting
RT‐PCR and Western blotting assays were conducted as previously described [34]. For RT‐PCR assay, total RNA was extracted from GC cells and then used to synthesize cDNA using a First Strand cDNA Synthesis kit (Takara, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Further, cDNA samples were subjected to real‐time quantitative RT‐PCR (LightCycler 480 system, Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) for quantitation of gene expression. All cDNA samples were run in triplicate. The primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Table S4.
For Western blotting assay, total proteins were prepared using RIPA lysis buffer, protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Beyotime, Shanghai, China). Proteins were estimated and equal quantity was resolved by SDS‐polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS‐PAGE). After being transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes, the blots were immunoblotted with primary antibodies at 4°C overnight. Then, blots were probed by using secondary fluorescence antibody (LI‐COR, Lincoln, NE, USA), then scanned and visualized using an Odyssey Infrared Imaging System (LI‐COR).
2.8. Immunofluorescence assay
The cell immunofluorescence assay was conducted as previously described [37]. Briefly, GC cells (1 × 104 cells/well) were seeded in confocal dishes and incubated overnight. Following different treatments, cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde at 4°C for 30 min. After permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X‐100 (Beyotime) and blocked with 10% BSA, cells were incubated with primary antibodies at 4°C overnight. Then, cells were incubated with red/green fluorescence‐conjugated goat anti‐rabbit antibody (AlexaFluor 488) and red fluorescence‐conjugated goat anti‐mouse antibody (Cy3) at room temperature for 1 h and then incubated with 4',6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI, Beyotime) in methanol for 10 min. Finally, cells were washed with PBS, observed and captured under a confocal microscope (Olympus FV1000, Tokyo, Japan).
2.9. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
An H‐7000FA scanning transmission electron microscope (HITACHI, Tokyo, Japan) was used to observe and count neuroendocrine‐like dense‐cored secretory vesicles in GC cells. After different treatments, GC cells were harvested, fixed overnight with 2.5% glutaraldehyde at 4°C, dehydrated, and embedded into a resin pellet. Cells were then scanned under TEM. Simultaneously, images of dense‐cored secretory vesicles were captured and measured to determine their quantity and size by using the AnalySIS Pro (Version 3.2, Ammanford, Carmarthenshire, UK) program. The rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex were captured routinely in all cells. During the analysis of dense‐core secretory vesicles, the observer was blinded to the identity of the cells.
2.10. Flow cytometry (FCM)
Ca2+‐sensitive fluorescent dye Fluo‐4‐AM was used to estimate intracellular Ca2+. In brief, GC cells (5 × 105 cells/well) were plated in 6‐well plates for 24 h and then subjected to predetermined treatments. After digestion, centrifugation and collection, cells were transferred to microcentrifuge tubes and co‐cultured with 5 μmol/L Fluo‐4‐AM (KeyGene, Shanghai, China) in dark at 37°C for 60 min, according to the manufacturer’ protocol. Then, the cells were incubated with indicator‐free solution (Opti‐MEM) for 30 min. After treatment with Tapsigargin (5 μmol/L), CaCl2 (2 mmol/L) in a PBS solution was added to cells. At last, intracellular Ca2+ was measured by flow cytometry with an emission wavelength of 516 nm and excitation wavelength of 494 nm. Each experiment was repeated three times.
2.11. Patch‐clamp recordings
Electrophysiological measurements were performed using the whole‐cell configuration of the patch‐clamp technique with the HEKA amplifier (EPC 10, HEKA Electronics, Reutlingen, Germany), as we had previously published [28]. GC cells were plated on cover slips and then gently moved to a small chamber under an inverted microscope (Nikon Microscope ECLIPSE FN1, Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). The glass pipette electrodes (Warner Instruments, Hammed, CT, USA), which were connected to the amplifier for amplifying membrane currents and potentials, were applied to orientate gastric cells by using a 3D‐micromanipullator (MP‐225, Sutter Instruments Company, CA, USA). After rupturing cell membrane and achieving whole‐cell configuration, the voltage pulses were employed, starting from ‐100 mV to +60 mV in 10‐mV increments with a duration of 100 ms. Signals were measured by the HEKA amplifier, and data were acquired by the Patchmaster software (HEKA Electronics, Reutlingen, Germany). All whole‐cell recordings were utilized at least 10 min after rupturing cell membrane.
2.12. Enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
MACC1 secretion in the supernatant of GC cells or in the plasma of patients was measured by a double‐antibody sandwich ELISA method as previously described [38]. After adding 100 μL standard stock solution, control solution and cell supernatant samples collected by centrifugation to a 96‐well plate, the plates were covered and incubated at 4°C for 90 min. Subsequently, MACC1 detection reagent, the streptavidin‐horseradish peroxidase (HRP) solution, was added to each well and incubated in turn. Then, colors were developed with 3,3’,5,5’‐tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) buffer, and the reaction was terminated by stop solution. Finally, the microplates were read by an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (SpectraMax M5, Molecular Devices, CA, USA) at 450 nm for measuring absorbance values. Results were calculated according to a calibration curve derived from the standards. All experiments were repeated three times.
2.13. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
IHC analysis was conducted according to the Dako Envision System (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) similar to our previous study [26]. Briefly, paraffin‐embedded tissues were cut into 4 μm sections. Then, each slice was dewaxed and gradually hydrated. After antigens were repaired and incubated within 3% H2O2 for eliminating endogenous nonspecific staining, the sections were incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C. After washing, the sections were subsequently incubated with secondary antibodies. Color developments were detected by incubation of 3,3’‐diaminobenzidine (DAB) solution. The tissue slices were then counterstained with hematoxylin, dehydrated, and mounted. The stained slices were captured by a light microscope (Olympus 1×71).
For MACC1, SYP, and Vimentin immuohistochemical staining, the staining intensity of each section was scored as 0 (negative), 1 (weak), 2 (moderate), or 3 (strong), and the staining extent depended on the positive percentage of the stained area was scored as 0 (0%), 1 (1%‐25%), 2 (26%‐50%), 3 (51%‐75%), or 4 (76%‐100%). The product of the above two values was the final staining score (0‐12) of each slice for MACC1, SYP and Vimentin expression. All scoring was blinded and evaluated by an experienced pathologist.
2.14. Co‐immunoprecipitation (Co‐IP)
Co‐immunoprecipitation was conducted using the Dynabeads Protein A kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer's recommended protocols [39]. In brief, Dynabeads were severally suspended with 10 μg anti‐MACC1 antibody or anti‐SYP antibody in a 200 μL Binding & Washing Buffer and then incubated with rotation for 30 min at 25°C. After washing for three times with 200 μL Binding & Washing Buffer in a tube on magnet, the Dynabead‐Ab complex were mixed with cell lysate samples (including antigen; Ag) and then co‐incubated with rotation for 30 min at 25°C. Next, the Dynabead‐Ab‐Ag complexes were washed thrice and gently resuspended with 20 μL Elution Buffer and 10 μL NuPAGE LDS Sample buffer at 70°C for 10 min. Finally, the supernatant/sample was obtained from tube on magnet and then analyzed by Western blotting.
2.15. Transwell migration and invasion assays
The GC cell migration and invasion experiments were performed using 24‐well Boyden's chambers (Costar, NY, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions, as previously described [39]. Briefly, the 8.0‐μm polycarbonate membranes of chambers were coated with 25 μg Corning® Matrigel® Basement Membrane Matrix (Bedford, MA, USA) or not. Further, cells (8 × 104 /well) were seeded in the upper chamber with 200 μL RPMI‐1640 medium (FBS‐free), while the lower chamber was supplemented with 600 μL complete medium containing 10% FBS. After 37°C incubation for 48 h, cells that migrated or invaded the underside of the polycarbonate membrane were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 1 h and then stained by crystal violet. Finally, cells captured by an inverted microscope (Olympus) and counted. Each experiment was repeated three times.
2.16. CUMS and mouse behavior assessments
A modified CUMS procedure was performed as described in Supplementary Table S5. After CUMS exposure, the depression behaviors of the mice were measured by the sucrose preference test (SPT), tail suspension test (TST), and forced swimming test (FST), as described previously [30]. Firstly, in the SPT, mice were housed singly and given access to pure water (100 mL) and 1% sucrose solution (100 mL) at the same time without food feeding. After 3 h, the preference for sucrose of mice, calculated as the sucrose consumption ratio (%), was gauged as a percentage of the intake sucrose solution relative to total consumption of these two liquids. Next, during the TST, mice were hung upside down with adhesive tape at a distance of 1 cm from their tail tip. Evaluating for a period of 6 min, the duration of immobility was measured for the last 5 min following habituation of 1 min. At last, in the FST, mice were individually placed in a lucid vertical cylinder (height: 13 cm and diameter: 3 cm) containing water at the height of 6 cm (about 25°C). In the 6‐min evaluation period, the duration of immobility was reckoned for the last 5 min following habituation of 1 min.
2.17. Mouse lung metastatic tumor model
At the 3rd week after CUMS treatment, two groups of mice under chronic stress and two control groups (10 mice/group) were severally injected with 3 × 106 MKN45 cells transfected with Lv‐GFP‐Luc (Obio corporation, Shanghai, China) via the caudal vein for constructing a GC lung metastasis model. Next, the four groups received PBS or ICI‐118,551 (5 mg/kg) by daily intraperitoneal injections for 4 weeks. Similarly, in another set of experiments, two groups of mice under CUMS and two control groups (10 mice/group) were serially injected with 3 × 106 shNC‐ or shMACC1‐transfected GC cells through the caudal vein. Sequentially, after 4‐week CUMS treatment, mice were anesthetized, and lung metastatic tumors were monitored by bioluminescence images acquired using a Bruker Multispectral FX PRO and In‐Vivo Xtreme systems (Billerica, MA, USA) at the Central Laboratory of Southern Medical University.
Finally, after depression behavior assessments and blood collection from the bulbus oculi, all mice were euthanized at the end of the entire 7‐week CUMS exposure. The lungs were excised and photographed, and metastatic tumor nodules with a diameter larger than 1 mm were counted. Then, the lungs were fixed in 4% buffered formalin and embedded in paraffin. The 4 μm tissue sections were cut and then used in Vimentin IHC analysis, Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining, and Masson's trichrome staining. In addition, metastatic tumors obtained from lungs were used for protein preparation and RNA extraction.
2.18. H&E and Masson's trichrome staining
Both staining analyses were conducted as previously described [40]. Tumor tissues were fixed in 10% formalin for 1 day, then embedded in paraffin and cut into 4‐μm thick sections, eventually stained with H&E and Masson's trichrome staining kits (Beyotime).
2.19. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)
To identify the remarkable differential signaling and gene expression between depressed and non‐depressed cancer patients, data from the GEO database (GSE9116, refer to: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE9116) were obtained and subjected to GSEA. The GSE9116 is based on primary ovarian carcinomas from 10 patients with high or low symptoms of psychological depression and experiment type is expression profiling by array. Specific to GSEA, 1000 gene set permutations were performed for every analysis. The gene and signaling between the groups was significantly enriched according to terms with |NES| > 1, normal P < 0.05, and FDR q < 0.25.
2.20. Statistical analyses
Data in this study were analyzed using SPSS 19.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Data are presented as mean ± standard error of means unless otherwise stated. The Student's t‐test or one‐way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare continuous variables. The Chi‐square test was used to compare categorical variables. Pearson's correlation and Spearman's correlation tests were used to analyze the correlation between two variables.
3. RESULTS
3.1. Depression state was associated with high levels of plasma catecholamines, MACC1, and metastasis biomarkers in GC patients
To explore the correlation between depression state and GC progression, 51 GC patients and 20 healthy volunteers were recruited in this study. Depression levels were rated according to the PHQ‐9 self‐rating scale [29]. Catecholamines (Epi and NA) from blood samples were measured by HPLC‐MS/MS (Supplementary Figure S1). Firstly, we analyzed the correlation between clinical characteristics and the PHQ‐9 score as a continuous variable. Results showed that the PHQ‐9 score was positively correlated with serum levels of Epi (r = 0.51, P < 0.001), NA (r = 0.54, P < 0.001), and MACC1 (r = 0.55, P < 0.001) by the Pearson's correlation test (Supplementary Figure S2A‐C). Moreover, the PHQ‐9 score was positively correlated with the TNM stage (r = 0.65, P < 0.001) and metastasis (r = 0.64, P < 0.001) by the Spearman's correlation test (Supplementary Figure S2D‐E). These results suggest that depression is clinically important in GC progression. Next, we found that PHQ‐9 scores, plasma Epi and NA, and MACC1 levels were elevated in GC patients, compared with healthy controls (Figure 1A). Then GC patients were divided into high and low depression states using the median PHQ‐9 score. We found that high depression state indicated advanced TNM stages (P < 0.001), more metastasis (P < 0.001), as well as higher plasma Epi (P = 0.018) and NA levels (P = 0.009), as shown in Table 1. MACC1, which we previously reported in GC progression [26], was detected by ELISA. Results showed high depression state also indicated higher levels of MACC1 expression (P = 0.018; Table 1). Furthermore, there existed positive relationships between MACC1 and Epi or NA levels (r = 0.66, P < 0.001; r = 0.56, P < 0.001, respectively; Figure 1B). These data suggest that depression is closely related to biomarkers of metastasis in GC and that several molecular mediators, namely catecholamines and/or MACC1, might be involved.
FIGURE 1.
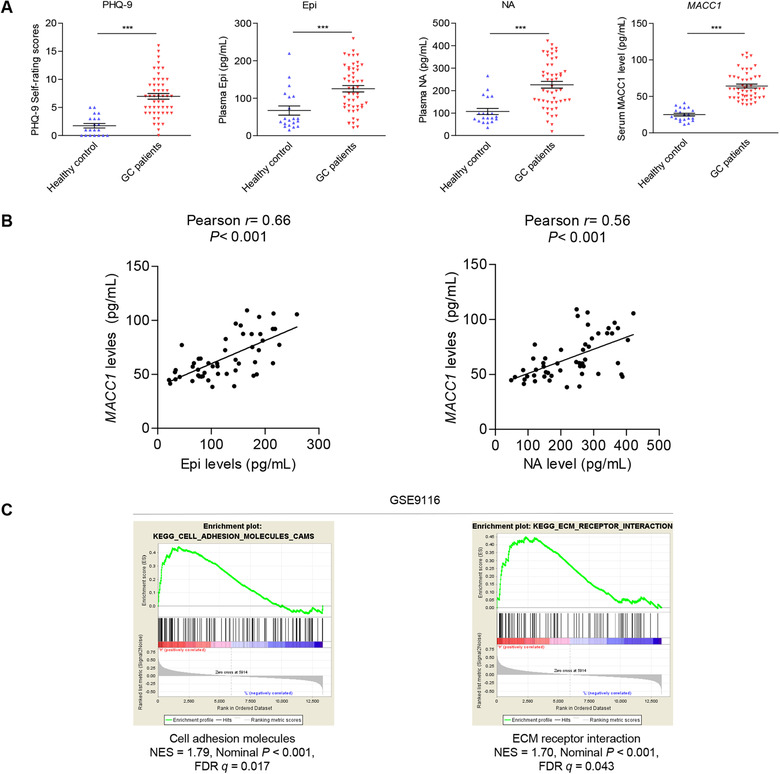
Depression is positively associated with plasma catecholamines, serum MACC1 levels, and biomarkers of metastasis in GC patients. (A) PHQ‐9 self‐rating scores, plasma catecholamines, and serum MACC1 levels were detected in 20 healthy volunteers and 51 GC patients. (B) Correlations between MACC1 levels and Epi or NA in plasma from 51 GC patients were analyzed. (C) GSEA diagram of cell adhesion molecules, and ECM receptor interaction gene sets in the GSE9116 database of depressed and non‐depressed cancer patients (refer to https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE9116 for more information). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. P values were calculated using two‐tailed unpaired Student's t‐tests (A) and Pearson's correlation analysis (B). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Abbreviations: ECM: extracellular matrix; ELISA: enzyme‐linked immunoassay; Epi: epinephrine; GC: gastric cancer; GSEA: gene set enrichment analysis; HPLC‐MS/MS: high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry; MACC1: metastasis‐associated in colon cancer 1; NA: noradrenaline; PHQ‐9: Patient Health Questionnaire‐9.
TABLE 1.
Associations between depression and clinicopathological features in 51 GC patients
| Depressive level [cases (%)] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature | Total [cases (%)] | Low | High | P value |
| All patients | 51 (100.0) | 24 (47.1) | 27 (52.9) | |
| Age (years) | 0.178 | |||
| ≥55 | 21 (41.2) | 12 (57.1) | 9 (42.9) | |
| <55 | 30 (58.8) | 12 (40.0) | 18 (60.0) | |
| Gender | 0.301 | |||
| Male | 31 (60.8) | 16 (51.6) | 15 (8.4) | |
| Female | 20 (39.2) | 8 (40.0) | 12 (60.0) | |
| TNM stage | < 0.001 | |||
| II‐III | 13 (25.5) | 12 (92.3) | 1 (7.7) | |
| IV | 38 (74.5) | 12 (31.6) | 26 (68.4) | |
| Distant metastasis | < 0.001 | |||
| Yes | 38 (74.5) | 12 (31.6) | 26 (68.4) | |
| No | 13 (25.5) | 12 (92.3) | 1 (7.7) | |
| Serum MACC1 level (pg/mL) | 0.018 | |||
| <60.03 | 25 (49.0) | 16 (64.0) | 9 (36.0) | |
| ≥60.03 | 26 (51.0) | 8 (30.8) | 18 (69.2) | |
| Plasma Epi level (pg/mL) | 0.018 | |||
| <125.6 | 25 (49.0) | 16 (64.0) | 9 (36.0) | |
| ≥125.6 | 26 (51.0) | 8 (30.8) | 18(69.2) | |
| Plasma NA level (pg/mL) | 0.009 | |||
| <218.5 | 22 (43.1) | 15 (68.2) | 7 (31.8) | |
| ≥218.5 | 29 (56.9) | 9 (31.0) | 20 (69.0) | |
Abbreviation: T, tumor; N, lymph node; M, metastasis; MACC1, metastasis‐associated in colon cancer‐1; Epi, epinephrine; NA, noradrenaline.
To investigate possible mechanisms behind the impact of depression on GC metastasis, GSEA demonstrated that the highly enriched genes in GC patients with low and high depression status from GEO databases (GSE9116) were relevant to cell adhesion molecules and extracellular matrix (ECM) receptor interaction (Figure 1C). The results reveal that depression might affect the invasion and metastasis of GC through cell‐cell adhesive modification and/or ECM remodeling.
3.2. Depression‐associated catecholamines promoted MACC1 expression mediated by the β2‐AR signaling pathway in GC cells
The activation of the c‐Jun signaling pathway by catecholamines in GC has been reported previously [16], and c‐Jun could bind to the MACC1 promoter region and regulate its transcriptional expression [27]. Thereby, we hypothesized that depression‐associated catecholamines could upregulate MACC1 in GC. Firstly, we observed that Epi and NA significantly upregulated the expression and secretion levels of MACC1 in BGC823 and MKN45 GC cells (Figure 2A‐B and Supplementary Figure S3A‐B). In addition, a significant dose‐dependent increase in MACC1 expression was observed in both GC cell lines after treatment for 12 h with different concentration of Epi (Figure 2C and Supplementary Figure S3C). Moreover, at a concentration of 10 μmol/L, Epi also promoted MACC1 expression in a time‐dependent manner (Figure 2C and Supplementary Figure S3D). However, the effect of catecholamines in GES‐1 cells was minimal (Supplementary Figure S3A‐B, E). Then, we found that SP600125 and JNK‐IN‐8, both inhibitors of c‐Jun, blocked Epi‐induced MACC1 upregulation (Figure 2D).
FIGURE 2.
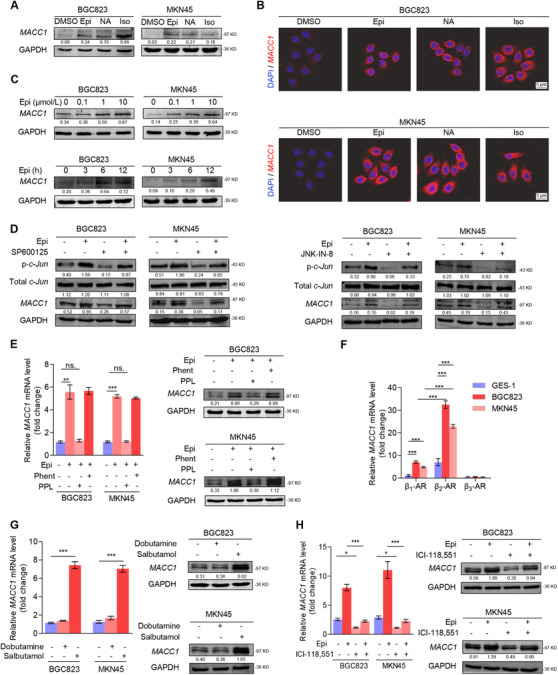
Catecholamines upregulate MACC1 expression through activation of the β2‐AR/c‐Jun signal pathway in GC cells. (A) MACC1 protein expression in BGC823 and MKN45 cells after treatment with DMSO, 10 μmol/L Epi, 10 μmol/L NA, and 10 μmol/L Iso for 12 h was quantified by Western blotting analysis. (B) Representative immunofluorescence images of BGC823 and MKN45 cells show the presence of red‐fluorescent MACC1 expression after treatment with DMSO, 10 μmol/L Epi, 10 μmol/L NA, and 10 μmol/L Iso for 12 h. GC cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (C) MACC1 protein expression in BGC823 and MKN45 cells after treatment with several Epi concentrations (0, 0.1, 1, and 10 μmol/L) for 12 h or with 10 μmol/L Epi for multiple time intervals (0, 3, 6 and 12 h) was quantified by Western blotting analysis. (D) MACC1, total c‐Jun, and phosphorylated c‐Jun protein expression in BGC823 and MKN45 cells after treatment with either 5 μmol/L SP600125 (6 h) or 5 μmol/L JNK‐IN‐8 (6 h) followed by 10 μmol/L Epi stimulation for 12 h were quantified by Western blotting. (E) MACC1 mRNA expression and protein expression in BGC823 and MKN45 cells were measured by quantitative PCR and Western blotting, respectively, after treatment with either 10 μmol/L Phent or 5 μmol/L PPL (6 h) followed by 10 μmol/L Epi stimulation for 12 h. (F) Quantitative PCR assay was used to quantify the mRNA levels of β1‐AR, β2‐AR, and β3‐AR in human immortalized GES‐1 and GC BGC823, and MKN45 cell lines. (G) MACC1 mRNA expression and protein expression in BGC823 and MKN45 cells after treatment with 50 μmol/L salbutamol (12 h) or 10 μmol/L dobutamine (12 h). (H) MACC1 mRNA expression and protein expression in BGC823 and MKN45 cells after treatment with 10 μmol/L ICI‐118,551 (6 h) followed by 10 μmol/L Epi stimulation for 12 h. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. P values were calculated using the one‐way ANOVA . *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns., not significant. α‐Actin and GAPDH served as loading controls in q‐PCR and Western blotting assays, respectively. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Abbreviations: AR: adrenergic receptor; DAPI: 4',6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide; Epi: epinephrine; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; GC: gastric cancer; GES‐1: gastric epithelial cell line; Iso: isoprenaline; MACC1: metastasis‐associated in colon cancer 1; NA: noradrenaline; Phent: phentolamine; PPL: propranolol.
To further confirm the binding site of catecholamines on GC cells, we incubated BGC823 and MKN45 cells with phentolamine, an α‐AR inhibitor, or propranolol (PPL), a β‐AR inhibitor, for 6 h before Epi stimulation, and found that PPL but not phentolamine blocked Epi‐induced MACC1 elevation (Figure 2E). Elevated MACC1 expression was also seen in BGC823 and MKN45 cells after treatment with isoprenaline, a β‐AR agonist (Figure 2A‐B and Supplementary Figure S3A‐B). These results indicated that β‐AR, not α‐AR, played a key role on catecholamine‐induced MACC1 expression. In addition, we found that the mRNA levels of β1‐ and β2‐ARs were significantly higher in GC cells than in GES‐1 cells, with β2‐AR being more highly expressed than β1‐AR in GC cells, while β3‐AR was not different between GC and GES‐1 cells (Figure 2F). Then, we noticed that treatment with salbutamol, a β2‐AR agonist, but not dobutamine, a β1‐AR agonist, induced MACC1 expression in GC cells, which was analogous to the effect of Epi treatment (Figure 2G). Thus, we pre‐treated GC cells with ICI‐118,551, a specific β2‐AR antagonist, for 6 h and observed that Epi‐induced MACC1 production was hindered (Figure 2H). All these results confirmed that activation of the β2‐AR/c‐Jun signaling pathway significantly contributed to the catecholamine‐induced MACC1 production in GC.
3.3. Catecholamines induced the neuroendocrine phenotype of GC cells by upregulating MACC1
As depression‐related chronic stress triggers the release of neurotransmitter catecholamines [27], we investigated whether depression‐induced catecholamines have such neuroendocrine‐like effects on tumors. We firstly treated GC cells with 10 μmol/L Epi for 12 h and found that GC cells showed the following neuroendocrine phenotypic transformations: (i) Epi treatment upregulated neuroendocrine markers SYP, CD44, and chromogranin A (CHGA) expression and downregulated epithelial marker keratin 8 (KRT8) expression (Figure 3A‐C); (ii) the number of neuroendocrine‐like secretory vesicles under Epi stimulation (n = 27, from 8 fields in 7 cells; mean diameter: 207.6 ± 22.1 nm) increased sharply compared with the control group (n = 10, from 11 fields in 10 cells; mean diameter: 218.6 ± 14.5 nm) (Figure 3D); and (iii) Epi activated Ca2+‐dependent secretory pathways (Figure 3E‐G) and increased intracellular Ca2+ currents (Figure 3H‐I). These results suggested that GC cells underwent the process of neuroendocrine phenotype transformation by Epi. However, we observed that MACC1 silencing completely abrogated expression of neuroendocrine phenotype biomarkers even after Epi stimulation in GC cells (Figure 4A‐B and Supplementary Figure S4A‐B). In addition, results indicated that the increased numbers of neuroendocrine‐like secretory vesicles under Epi stimulation were suppressed by MACC1 silencing (Supplementary Figure S4C). Similarly, Epi‐activated Ca2+‐dependent secretory pathways and Epi‐increased intracellular Ca2+ currents were both blocked by MACC1 silencing (Supplementary Figure S4D‐G). Meanwhile, we observed that the neuroendocrine phenotype characteristics of GC cells could be impaired by MACC1 independently (Figure 4A‐B and Supplementary Figure S4), which revealed the importance of MACC1 in the neuroendocrine phenotype of GC cells. Altogether, these results suggested that catecholamines induced the neuroendocrine phenotype in GC cells and that this process could be blocked by MACC1 inhibition, thus reinforcing the pivotal role of MACC1 in promoting catecholamine‐mediated neuroendocrine phenotype transformation in GC cells.
FIGURE 3.
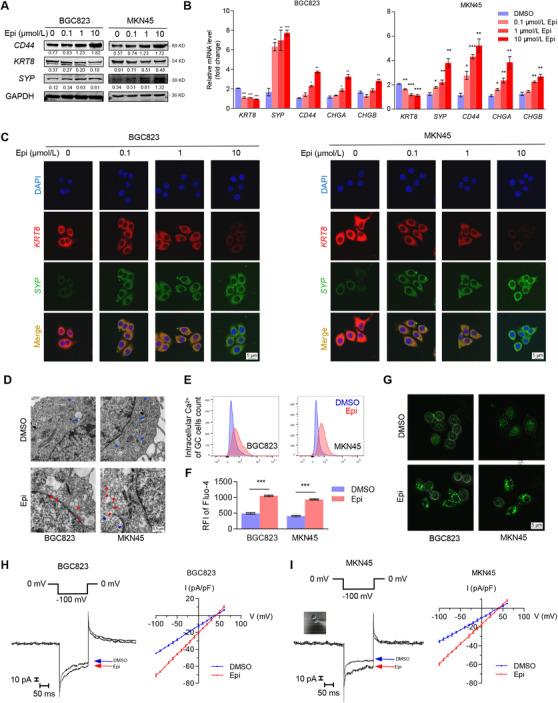
Catecholamines induce a neuroendocrine phenotype in GC cells. (A) Protein expression of selected cellular markers (epithelial marker, KRT8; neuroendocrine markers, SYP and CD44) were quantified in BGC823 and MKN45 cells by Western blotting after 12 h Epi treatment (0, 0.1, 1, and 10 μmol/L). (B) mRNA expression of selected cellular markers (epithelial marker, KRT8; neuroendocrine markers, SYP, CD44, CHGA, and CHGB) were measured in BGC823 and MKN45 cells by quantitative PCR after 12 h Epi treatment (0, 0.1, 1, and 10 μmol/L). (C) Representative immunofluorescence images of BGC823 and MKN45 cells show the presence of red‐fluorescent KRT8 and green‐fluorescent SYP expression after 12 h Epi treatment (0, 0.1, 1, and 10 μmol/L). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (D) Dense‐core secretory vesicles (red arrows) around the Golgi‐complex (blue arrows) were identified by TEM in BGC823 and MKN45 cells after treatment with DMSO or 10 μmol/L Epi for 12 h. Quantity and size of secretory vesicles were measured by the AnalySIS program. (E‐F) Intracellular Ca2+ BGC823 and MKN45 cells, marked with green‐fluorescent Fluo‐4‐AM (emission wavelength: 516 nm; excitation wavelength: 494 nm), were detected by FCM after treatment with DMSO or 10 μmol/L Epi for 12 h. (F) Corresponding alterations to RFI. (G) Representative immunofluorescence images of intracellular Ca2+ (Fluo‐4‐AM, green) in BGC823 and MKN45 cells after treatment with DMSO or 10 μmol/L Epi for 12 h. (H‐I) Individual tracings of Epi‐stimulated Ca2+ currents at ‐100 mV (left panel) and I/V plot of the Ca2+ currents recorded at each testing potential (right panel) of (H) BGC823 and (I) MKN45 cells. Data are shown as means ± SEM. P values were calculated using the one‐way ANOVA (B) and two‐tailed unpaired Student's t‐tests (F). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. α‐Actin and GAPDH served as loading controls in q‐PCR and Western blotting assays, respectively. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Abbreviations: CHGA: chromogranin A; CHGB: chromogranin B; DAPI: 4',6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide; Epi: epinephrine; FCM: flow cytometry; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; GC: gastric cancer; KRT8: keratin‐8; RFI: relative fluorescence intensity; SYP: synaptophysin; TEM: transmission electron microscopy.
FIGURE 4.
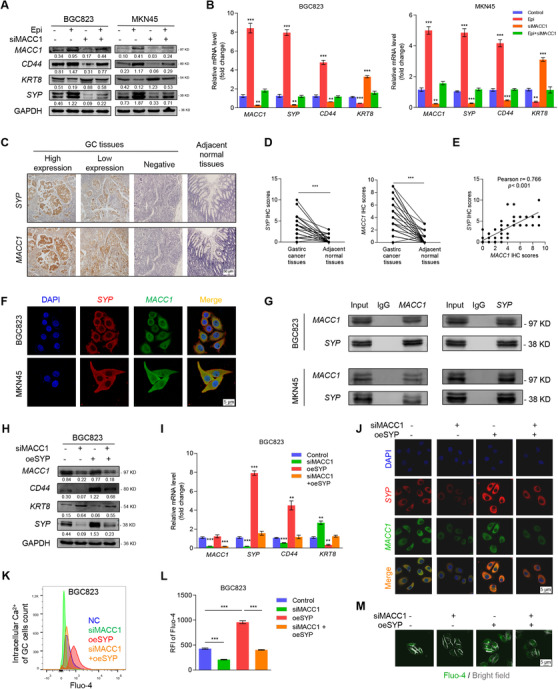
MACC1 induces the neuroendocrine phenotype of GC by directly binding to SYP. (A) Protein and (B) mRNA levels of MACC1, KRT8, SYP, and CD44 in siNC‐ or siMACC1‐expressing BGC823 and MKN45 GC cells after a 12 h incubation with 10 μmol/L Epi. (C) Representative immunohistochemistry images of SYP and MACC1 staining in GC and adjacent normal tissues. (D) IHC scores of SYP and MACC1 in 53 cases of gastric adenocarcinoma and adjacent normal tissues. (E) The correlation between SYP and MACC1 expression in 53 gastric adenocarcinoma tissues and adjacent normal tissues using Pearson's correlation analysis. (F) Representative images of BGC823 and MKN45 cells show the intracellular co‐localization of SYP (red) and MACC1 (green) by confocal microscopy. (G) Western blotting of BGC823 and MKN45 cells shows the interaction between SYP and MACC1 that were first identified by co‐IP. Mouse IgG served as a negative control. (H) Protein and (I) mRNA expression of MACC1, KRT8, SYP, and CD44 in untreated and siMACC1‐, oeSYP‐, or siMACC1+oeSYP‐treated BGC823 cells were quantified by Western blotting and q‐PCR, respectively. (J) Immunofluorescence images of BGC823 cells, described in (H), show the presence of red‐fluorescent and green‐fluorescent MACC1. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (K‐M) Intracellular Ca2+ of BGC823 cells with the same treatments as in (H) was marked with green‐fluorescent Fluo‐4‐AM and detected by FCM. The corresponding alterations to intracellular Ca2+ fluorescence intensity and representative fluorescence images are shown in (L) and (M). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. P values were calculated using the paired‐samples t‐test (D), Pearson's correlation analysis (E), and the one‐way ANOVA (B, I, L). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. α‐Actin and GAPDH served as loading controls in q‐PCR and Western blotting assays, respectively. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Abbreviations: Co‐IP: co‐immunoprecipitation; DAPI: 4',6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; Epi: epinephrine; FCM: flow cytometry; FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate; FST: forced swimming test; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; GC: gastric cancer; KRT8: keratin‐8; MACC1: metastasis‐associated in colon cancer 1; RFI: relative fluorescence intensity; SYP: synaptophysin.
3.4. Catecholamines induced neuroendocrine phenotype of GC by the direct binding between MACC1 and SYP
Upon investigating the underlying molecular mechanisms, we found that the co‐expression of MACC1 and SYP in GC tissues was detected by IHC analysis (Figure 4C) and the IHC scores of SYP and MACC1 were higher in the tumor samples than in the adjacent normal tissues (Figure 4D). Meanwhile, the IHC scores of SYP and MACC1 were positively correlated (r = 0.77, P < 0.001) in 53 GC tissues (Figure 4E). Co‐expression of MACC1 and SYP was also observed upon immunofluorescence assay (Figure 4F), and their direct interaction was confirmed by co‐immunoprecipitation (Figure 4G). We also found that Epi‐promoted SYP expression was inhibited by siMACC1 (Supplementary Figure S4A‐B). Further, siMACC1 treatment weakened the neuroendocrine phenotype, while oeSYP strengthened the neuroendocrine phenotype when used alone as well as rescued the siMACC1‐reduced neuroendocrine phenotype of both BGC823 (Figure 4H‐M) and MKN45 cells (Supplementary Figure S5). In addition, after the silencing efficiency of SYP (siRNA#1/siRNA#2) were determined (Supplementary Figure S6A‐C), we found that after SYP was knocked down, the expression of CD44 was decreased and KRT8 was upregulated in GC cells, while MACC1 expression was not affected (Supplementary Figure S6D‐E). In addition, intracellular Ca2+ decreased significantly after SYP silencing as well (Supplementary Figure S6F‐H). To sum up, these results suggested that SYP was a typical and representative marker of neuroendocrine phenotypic characteristics in GC and that MACC1 might induce a neuroendocrine phenotype in GC cells by directly binding to SYP, thus suggesting the MACC1/SYP signaling pathway could be a positive influencing factor on catecholamine‐induced neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation.
3.5. Neuroendocrine phenotype promoted invasion and migration of GC cells by the catecholamines/β2‐AR/MACC1 axis
When assessing the invasive and migrative potential of neuroendocrine phenotypic GC cells, we discovered that 24 h 10 μmol/L Epi treatment tremendously increased the number of invasive GC cells when compared with untreated cells, whereas siMACC1 completely abolished the effects of Epi on the invasion of neuroendocrine phenotypic GC cells (Figure 5A‐B), suggesting that MACC1 was also a key molecule for catecholamine‐induced GC invasion. At the same time, we found that oeSYP enhanced Epi‐induced invasion of GC cells even with MACC1 silencing (Figure 5A‐B). The GC cell migration assay showed similar results (Supplementary Figure S7A‐B). Moreover, we observed that oeSYP promoted Epi‐induced neuroendocrine phenotype of GC cells despite siMACC1 treatment (Figure 5C). To summarize, these data proved again that the MACC1/SYP signaling pathway played an important role in the catecholamine‐induced neuroendocrine phenotype, migration, and invasion of GC cells.
FIGURE 5.
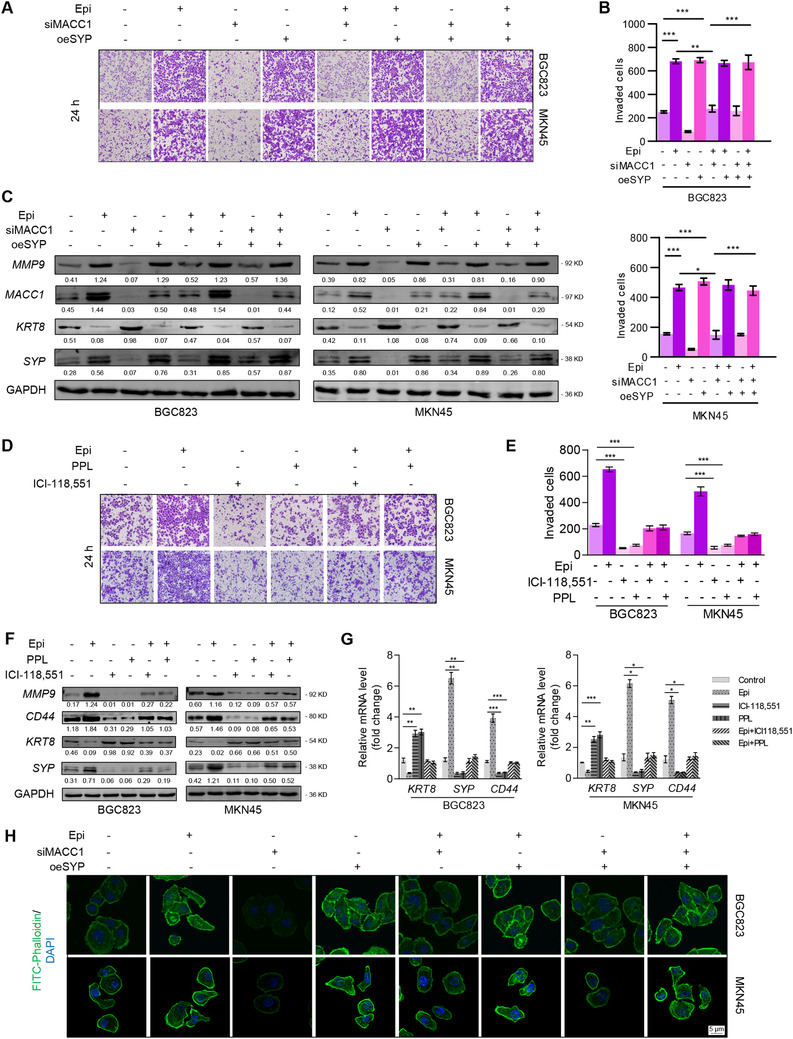
Neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation induced by the catecholamines/β2‐AR/MACC1 axis promotes the invasion of GC cells. (A) BGC823 and MKN45 cells cultured in Matrigel® transwells were treated with siNC, Epi, siMACC1, oeSYP, Epi+siMACC1, Epi+oeSYP, siMACC1+oeSYP, or Epi+siMACC1+oeSYP. Magnification: 100×. (B) Quantitative data of invasive BGC823 and MKN45 cells. Epi, 10 μmol/L for 24 h; cells were transfected with siNC, siMACC1, or oeSYP for 24 h. (C) Protein expression of MACC1, MMP9, KRT8, SYP, and CD44 in BGC823 and MKN45 cells treated as described in (A) were detected by Western blotting. (D) Representative images of invasive BGC823 and MKN45 cells treated with 10 μmol/L Epi for 12 h and 5 μmol/L PPL, 10 μmol/L ICI‐118,551 for 6 h or 5 μmol/L PPL, and 10 μmol/L ICI‐118,551 for 6 h before Epi treatment, respectively. Quantitative data are shown in (E). Magnification: 100×. Protein expression (F) and mRNA expression (G) of MMP9, KRT8, SYP, and CD44 in BGC823 and MKN45 cells treated as described in (D). (H) fluorescence images of cytoskeleton dyed with FITC‐phalloidin (green) in BGC823 and MKN45 cells treated as described in (A). Data are shown as means ± SEM. P values were calculated using the one‐way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. α‐Actin and GAPDH served as a loading control in q‐PCR and Western blotting assays, respectively. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Abbreviations: AR: adrenergic receptor; DAPI: 4',6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; ECM: extracellular matrix; Epi: epinephrine; FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; GC: gastric cancer; KRT8: keratin‐8; MACC1: metastasis‐associated in colon cancer 1; MMP9: matrix metallopeptidase 9; PPL: propranolol; RFI: relative fluorescence intensity; SYP: synaptophysin.
Next, to further survey the aberrant activation of the MACC1/SYP signaling pathway, we treated GC cells with PPL or ICI‐115,881 prior to Epi exposure. Inactivation of β‐AR by PPL or ICI‐118,551 completely blocked Epi‐promoted invasion (Figure 5D‐E), migration (Supplementary Figure S7C‐D), and the downregulation of SYP and CD44 (Figure 5F‐G and Supplementary Figure S8A). One possible mechanism behind this phenomenon was that oeSYP rekindled Epi‐induced MMP9 production (Figure 5C) and FITC‐phalloidin fluorescence intensity in GC cells (Figure 5H), suggesting that ECM remodeling and cellular adhesion were involved in the process. Moreover, we noticed that PPL or ICI‐115,881 completely blocked Epi‐induced MMP9 protein expression (Figure 5F) and Epi‐induced FITC‐phalloidin fluorescence intensity in GC cells (Supplementary Figure S8B). In conclusion, the catecholamines/β2‐AR/MACC1 axis was important for GC cells to possess enhanced aggressive ability, and this could be attributed to neuroendocrine phenotype‐associated ECM remodeling, which promoted GC invasion and migration.
3.6. Targeting β2‐AR blocked depression‐promoted neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation and lung metastasis of GC
Based on the results above, we hypothesized that β2‐AR is vital to GC invasion and metastasis under depression. We firstly constructed a lung metastasis mouse model via tail vein injection and used the CUMS depression mouse model to explore the role of β2‐AR in depression‐induced GC invasion and metastasis. Figure 6A shows the schematic of the experimental design for the CUMS mouse model construction, depression behavior assessments, and tumor analysis. In detail, compared with the non‐stressed groups, body weight increased slowly in the stressed groups (Figure 6B). Moreover, mice in the two stressed groups exhibited depression‐like behaviors seen as decreased sucrose consumption ratios and increased immobility time in both the forced swimming test and tail suspension test (Figure 6C), suggesting that depression mouse model was successfully induced by CUMS exposure. Further, we found that Epi and NA were higher in the depressed groups than in the non‐stressed groups through collecting blood samples from the orbit by HPLC‐MS/MS (Figure 6D). Using bioluminescent imaging, we found that daily intraperitoneal injections of 5 mg/kg ICI‐118,551 for 4 weeks completely eliminated depression‐induced GC lung metastasis after tumor transplantation (Figure 6E‐F). Moreover, we found that ICI‐118,551 effectively prevented depression‐induced micrometastasis in the lung (Figure 6G‐H) by detecting the micrometastasis biomarker Vimentin[41, 42]. In addition, ICI‐118,551 treatment blocked MACC1 elevation and neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation of metastatic tumors in mice with depression‐like behaviors, as shown in Figure 6I. These results reveal that depression promoted MACC1, neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation, and metastasis in tumor‐bearing mice and that β2‐AR blockade could reverse these.
FIGURE 6.
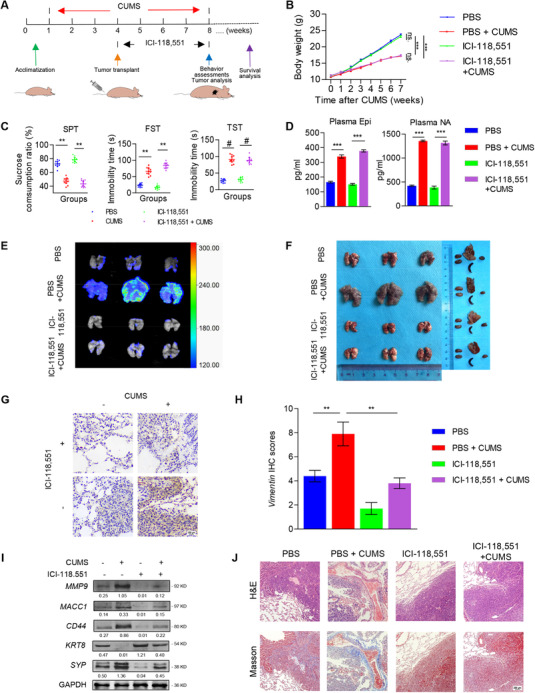
β2‐AR blockade inhibits depression‐induced lung metastasis of GC in a CUMS mouse model. (A) Schematic of the experimental design for the CUMS mouse model construction, behavior assessments, blood collection, and tumor analysis. (B) Body weight curves of mice treated with PBS, PBS+CUMS, ICI‐118,551, or ICI‐118,551+CUMS (10 mice per group). (C) Behavioral tests (SPT, FST, and TST) were performed after 7 weeks of CUMS. (D) Detection of plasma Epi and NA concentrations in blood. (E) Representative bioluminescence images of lung metastatic tumors in each group. (F) Images of gross lung metastatic tumors and other organs (the heart, liver, spleen, and kidney) in mice from each group. (G‐H) Representative images of Vimentin IHC staining (G) and IHC scores (H) in lung metastatic tumors from each group. (I) MACC1, KRT8, SYP, CD44, and MMP9 expression in lung metastatic tumors were detected by Western blotting. (J) Representative images of Masson's trichrome staining and H&E staining of lung metastatic tumors from each group. Data are shown as means ± SEM. P values were calculated using the one‐way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. α‐Actin and GAPDH served as a loading control in q‐PCR and Western blotting assays, respectively. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Abbreviations: AR: adrenergic receptor; CUMS: chronic unpredictable mild stress; DAPI: 4',6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; ECM: extracellular matrix; Epi: epinephrine; FST: forced swimming test; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; GC: gastric cancer; HPLC‐MS/MS: high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry; IRS: immunoreactive score; KRT8: keratin‐8; MACC1: metastasis‐associated in colon cancer 1; MMP9: matrix metallopeptidase 9; SPT: sucrose preference test; SYP: synaptophysin; TST: tail suspension test.
Then, we observed increased MMP9 expression in lung metastatic tumors of mice with depression‐like behaviors and that these effects were blocked in mice treated with ICI‐118,551 (Figure 6G). Moreover, H&E staining and the Masson's trichrome staining demonstrated that, in mice with depression‐like behaviors, lung metastatic tumors penetrated through the capsule and invaded into the stroma, resulting in ECM remodeling with increased collagen. However, these effects were reversed in depressed mice treated with ICI‐118,551 (Figure 6J), purporting that neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation had an impact on ECM remodeling in GC‐bearing mice with depression‐like behaviors. Overall, β2‐AR activation was critical for depression‐induced neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation, invasion, and metastasis of GC.
Finally, we inquired whether β2‐AR‐activated MACC1/SYP induced neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation, invasion, and metastasis of GC in a mouse model of depression. We used MKN45 cells with stable knockdown of MACC1 to construct a lung metastasis mouse model with depression (Supplementary Figure S9A‐C), and found that shMACC1 relieved depression‐evoked GC lung metastasis in mouse model of depression (Supplementary Figure S9D). Similarly, shMACC1 treatment prevented depression‐induced lung micrometastasis by detecting Vimentin (Supplementary Figure S9E‐F). Moreover, we found that increased MACC1 and SYP as well as reduced KRT8 expression of lung metastatic tumors in mice with depression‐like behaviors were reversed due to shMACC1 (Supplementary Figure S9G‐H). Likewise, Masson's trichrome staining also showed decreased collagen in depressed mice (Supplementary Figure S9I). Collectively, these results suggested that the activation of the catecholamines/β2‐AR/MACC1 axis was essential for promoting neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation, GC invasion, and metastasis during depression.
4. DISCUSSION
In this study, we revealed the presence of a depression‐activated catecholamine/β2‐AR/MACC1 signaling axis which promoted GC invasion and metastasis. Depression has been regarded as an independent risk factor for poor prognosis in the late stages of GC due to frequent metastatic events [3, 43]. We primarily discussed the molecular mechanism therein involved and found depression‐induced catecholamines, through β2‐AR/c‐Jun signaling, upregulated MACC1 which directly bonded to SYP, thus motivating neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation and eventually promoting GC invasion and metastasis. Finally, we proved that β2‐AR blocking or MACC1 intervention abrogated the depression‐induced GC invasion in vitro and metastasis in vivo (Figure 7).
FIGURE 7.
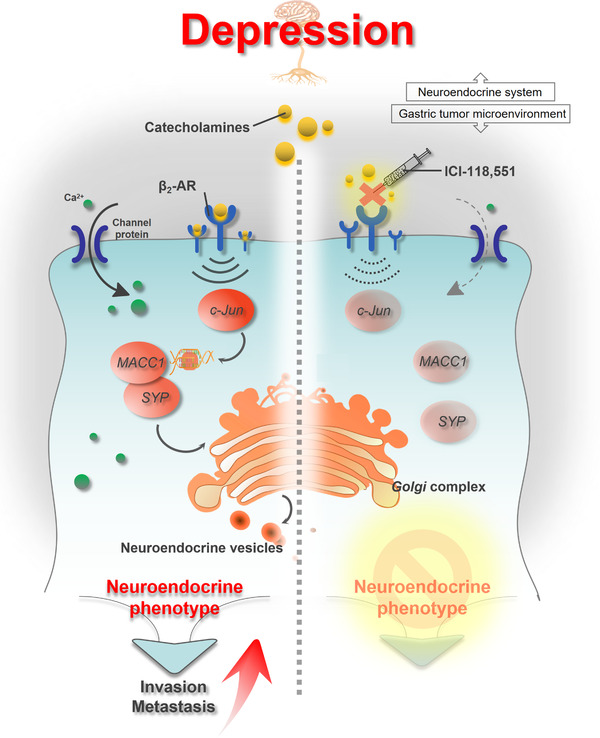
Schematic diagram. Depression promotes GC invasion and metastasis through neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation, while β2‐AR antagonist or targeting MACC1 effectively blocks the neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation and eliminates depression‐promoted migration, invasion, and distant metastasis of GC, which may be promising therapeutic strategies for GC patients. Abbreviations: AR: adrenergic receptor; Epi: epinephrine; GC: gastric cancer; keratin‐8; MACC1: metastasis‐associated in colon cancer 1; SYP: synaptophysin.
Recently, depression‐related chronic stress has been a common research focus. It is reported that continuous stress activates the hypothalamic‐pituitary‐adrenocortical (HPA) axis and/or the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), resulting in secretion of several stress‐associated neurotransmitters including catecholamines and cortisol [8, 44]. Among the secreted mediators, on the one hand, cortisol plays an important role in the progression of depressive disorders [45, 46], on the other hand, Epi and NA have been proven to be two major secreted catecholamines during the chronic stress‐induced neuroendocrine response, which could partly protect the body from adverse stimuli [9]. However, accumulating evidence revealed that catecholamines promoted tumor growth and progression in cancer patients [11, 16]. In our study, elevated catecholamines indicated more advanced TNM stage, suggesting that depression‐induced catecholamines accompany GC progression. Previous studies found that catecholamines by binding to ARs facilitated tumor development [47]. Activation of either α‐AR [48] or β‐AR [49] triggers the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)/protein kinase A (PKA)/c‐Jun signaling pathway and mediates the behaviors of malignancies [50, 51].
It is well known that c‐Jun serves as an upstream transcriptional factor of MACC1 in the tumor niche [27]. Our data showed that catecholamines upregulated MACC1 expression in GC cells in a c‐Jun‐dependent manner, suggesting that catecholamines probably increased MACC1 expression through the cAMP/PKA/c‐Jun signaling pathway. In addition, we found a positive relationship between catecholamines and the plasma MACC1 level in GC patients. To determine the exact target of catecholamines, we focused on ARs on cell membranes. The expression of MACC1 could be increased by a β‐AR agonist, isoproterenol, while it could be decreased by the β‐AR antagonist, propranolol. Further, the β2‐AR agonist salbutamol, but not the β1‐AR agonist dobutamine, stimulated MACC1 expression in GC cells. The following use of ICI‐118,551, a specific β2‐AR antagonist, also confirmed the main role of β2‐AR in MACC1‐mediated GC progression with the stimulus of catecholamine. Our study verified that, through binding to β2‐AR, depression‐related catecholamines activated the c‐Jun signaling pathway to upregulate the expression of MACC1.
Our previous study has explained that MACC1 reprograms cellular phenotype by accelerating EMT process in GC [26], evidenced by increased expression of mesenchymal phenotypic markers (CD44 and Vimentin) and decreased epithelial markers (E‐cadherin and β‐catenin). Interestingly, in this study, we found the neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation mediated by MACC1 for the following reasons: (i) Neuroendocrine cells share features with cancer stem cells and EMT cells [52, 53]; (ii) Mesenchymal and neuroendocrine cells share a common phenotypic marker, CD44 [54]; (iii) Tumor cells that shift from the epithelial to neuroendocrine phenotype are more aggressive [20, 21]. Our results showed that after treatment with Epi in vitro, both BGC823 and MKN45 GC cells transformed to a neuroendocrine phenotype in a MACC1‐dependent manner. Together, these results suggested that depression‐related catecholamines induced neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation, which could be affected by MACC1, in GC cells.
MACC1 is a transcription factor essential for activating c‐Met [25]. The activation of c‐Met can increase the expression of neuroendocrine markers, such as SYP, CD44, and CHGA [24]. In our study, MACC1 not only positively correlated with SYP but also directly bound to SYP to promote neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation. oeSYP enhanced the neuroendocrine features of GC cells, while silencing SYP diminished this effect in vitro. Moreover, we noticed that SYP did not affect MACC1 expression in GC, implying that MACC1 was upstream of SYP. The results above suggested that the MACC1/SYP signaling pathway could significantly modify neuroendocrine features in GC. In summary, MACC1 is an important regulatory gene of neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation, and it shows great potential as a new clinical marker for neoplastic neuroendocrine cells.
To explore the mechanisms of high invasive and metastatic performance of neuroendocrine phenotypic GC, we searched the GEO databases (GSE9116). After analyzing tumor samples from cancer patients with low or high depression state, we found that depression appeared to be strongly associated with cell adhesion molecules and ECM receptors. In our study, the inhibition of MACC1 in vitro prevented development of the catecholamine‐induced neuroendocrine phenotype, cytoskeleton alterations, and ECM remolding, suggesting that neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation, intercellular junction, and ECM reshaping in GC are correlated. Recent studies indicate that tumors with a neuroendocrine phenotype express low levels of E‐cadherin and high levels of Vimentin [53, 55], showing that neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation and EMT are closely correlated. Interestingly, we found GC neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation promoted the expression of Vimentin, which serves as a biomarker of micrometastases in vivo [41, 42]. Hence, we added new evidence that GC cells with neuroendocrine characteristics are beneficial to EMT, possibly through the regulation of cell‐cell adhesion and ECM remolding. However, when and how neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation synergizes with EMT to affect tumor invasion and metastasis need further investigations.
Based on the foregoing discussion, increased catecholamines during depression could bind to β2‐AR on GC and activate the expression of MACC1, which directly interacts with SYP to sustain the neuroendocrine phonotype and lead to aggressive GC invasion and metastasis. Here, we showed that the β2‐AR antagonist ICI‐118,551 could inhibit invasion and metastasis of GC both in vitro and vivo. This result emphasized that blocking β2‐AR signaling possesses great potential to reverse the depression‐evoked adverse effects on GC patients. Nonetheless, further clinical studies are warranted to provide evidence for its use as clinical treatment.
As for the limitations of our study, although the direct combination between MACC1 and SYP in protein level was found, the interaction between them remains complex. Further studies are needed in the future. Secondly, the use of β2‐AR antagonists was not investigated in clinical GC trials, which still need to be tested meticulously to prove its potential for clinical application.
5. CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we found that depression increased GC invasion and metastasis by neuroendocrine phenotypic transformation via the catecholamine/β2‐AR/MACC1 signaling axis. Hopefully, MACC1 may be a new marker of neuroendocrine‐like tumors, and MACC1 targeting and/or β2‐AR antagonism may be used as new targeted interventions for GC treatment, particularly in the growing population of GC patients with depression.
DECLARATIONS
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
Animal experimental procedures in this work were authorized by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University and followed the guidelines of the Laboratory Animal Centre of Southern Medical University. Clinical studies in this paper were approved by the Nanfang Hospital Ethics Review Board and conformed to International Ethical Guidelines for Biomedical Research Involving Human Subjects and all participants signed an Informed Consent Form.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA
The data that supports the findings of this study could be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
FUNDINGS
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81772580 and No. 81811530024 to Wangjun Liao, No. 82002530 to Changqie Pan), Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan (No. 201803010070 to Wangjun Liao).
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
CP and JW designed the study and performed the experiments. SZ preformed experimental statistical analysis. HS and YF performed the clinical data analysis from GC patients and carried out animal model experiments. ZH, MS and LL performed the data collection. JB, YL, CP and ZH did the data analysis and interpretation. All these works were planned and supervised by JC and WL. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Supporting information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank Yan Xia, Siqi Yu, Zhenzhen Wu and Yue Wu (Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China) for their technical assistances and valuable guidance during this study.
Pan C, Wu J, Zheng S, Sun H, Fang Y, Huang Z, et al. Depression accelerates gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by inducing a neuroendocrine phenotype via the catecholamine/β2‐AR/MACC1 axis. Cancer Commun. 2021;41:1049–1070. 10.1002/cac2.12198
Contributor Information
Jinzhang Chen, Email: chenjinzhang@smu.edu.cn.
Wangjun Liao, Email: liaowj@smu.edu.cn.
REFERENCES
- 1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca‐Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394‐424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Muro K, Van Cutsem E, Narita Y, Pentheroudakis G, Baba E, Li J, et al. Pan‐Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic gastric cancer: a JSMO–ESMO initiative endorsed by CSCO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:19‐33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Kang JI, Chung HC, Jeung H, Kim SJ, An SK, Namkoong K. FKBP5 polymorphisms as vulnerability to anxiety and depression in patients with advanced gastric cancer: A controlled and prospective study. Psychoneuroendocrino. 2012;37:1569‐76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Zabora J, BrintzenhofeSzoc K, Curbow B, Hooker C, Piantadosi S. The prevalence of psychological distress by cancer site. Psychooncology. 2001;10:19‐28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Delgado Guay M, Ferrer J, Rieber AG, Rhondali W, Tayjasanant S, Ochoa J, et al. Financial Distress and Its Associations With Physical and Emotional Symptoms and Quality of Life Among Advanced Cancer Patients. The Oncologist. 2015;20:1092‐8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Dai T, Wang B, Xiao Z, You Y, Tian S. Apelin‐13 Upregulates BDNF Against Chronic Stress‐induced Depression‐like Phenotypes by Ameliorating HPA Axis and Hippocampal Glucocorticoid Receptor Dysfunctions. Neuroscience. 2018;390:151‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Zhang J, Liu T, He Y, Pan H, Zhang W, Yin X, et al. Chronic Stress Remodels Synapses in an Amygdala Circuit–Specific Manner. Biol Psychiat. 2019;85:189‐201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Armaiz‐Pena GN, Lutgendorf SK, Cole SW, Sood AK. Neuroendocrine modulation of cancer progression. Brain, Behav, Immun. 2009;23:10‐5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Antoni MH, Lutgendorf SK, Cole SW, Dhabhar FS, Sephton SE, McDonald PG, et al. The influence of bio‐behavioural factors on tumour biology: pathways and mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:240‐8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Jin Shin K, Jin Lee Y, Ryoul Yang Y, Park S, Suh P, Yung Follo M, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying psychological stress and cancer. Curr Pharm Design. 2016;22:2389‐402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Allen JK, Armaiz‐Pena GN, Nagaraja AS, Sadaoui NC, Ortiz T, Dood R, et al. Sustained Adrenergic Signaling Promotes Intratumoral Innervation through BDNF Induction. Cancer Res. 2018;78:3233‐42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Haldar R, Shaashua L, Lavon H, Lyons YA, Zmora O, Sharon E, et al. Perioperative inhibition of β‐adrenergic and COX2 signaling in a clinical trial in breast cancer patients improves tumor Ki‐67 expression, serum cytokine levels, and PBMCs transcriptome. Brain, Behav, Immun. 2018;73:294‐309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Jang H, Boo H, Lee HJ, Min H, Lee H. Chronic Stress Facilitates Lung Tumorigenesis by Promoting Exocytosis of IGF2 in Lung Epithelial Cells. Cancer Res. 2016;76:6607‐19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Sorski L, Melamed R, Matzner P, Lavon H, Shaashua L, Rosenne E, et al. Reducing liver metastases of colon cancer in the context of extensive and minor surgeries through β‐adrenoceptors blockade and COX2 inhibition. Brain, Behav, Immun. 2016;58:91‐8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Shan T, Cui X, Li W, Lin W, Li Y, Chen X, et al. Novel regulatory program for norepinephrine‐induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in gastric adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Sci. 2014;105:847‐56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Shi M, Liu D, Duan H, Han C, Wei B, Qian L, et al. Catecholamine up‐regulates MMP‐7 expression by activating AP‐1 and STAT3 in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kang Y, Nagaraja AS, Armaiz‐Pena GN, Dorniak PL, Hu W, Rupaimoole R, et al. Adrenergic Stimulation of DUSP1 Impairs Chemotherapy Response in Ovarian Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:1713‐24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Reeder A, Attar M, Nazario L, Bathula C, Zhang A, Hochbaum D, et al. Stress hormones reduce the efficacy of paclitaxel in triple negative breast cancer through induction of DNA damage. Brit J Cancer. 2015;112:1461‐70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Balabanova S, Holmberg C, Steele I, Ebrahimi B, Rainbow L, Burdyga T, et al. The neuroendocrine phenotype of gastric myofibroblasts and its loss with cancer progression. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:1798‐806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Mu P, Zhang Z, Benelli M, Karthaus WR, Hoover E, Chen C, et al. SOX2 promotes lineage plasticity and antiandrogen resistance in TP53‐ and RB1‐deficient prostate cancer. Science. 2017;355:84‐8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Ku SY, Rosario S, Wang Y, Mu P, Seshadri M, Goodrich ZW, et al. Rb1 and Trp53 cooperate to suppress prostate cancer lineage plasticity, metastasis, and antiandrogen resistance. Science. 2017;355:78‐83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias‐Santagata D, Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, et al. Genotypic and Histological Evolution of Lung Cancers Acquiring Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:26r‐75r. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Niederst MJ, Sequist LV, Poirier JT, Mermel CH, Lockerman EL, Garcia AR, et al. RB loss in resistant EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinomas that transform to small‐cell lung cancer. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Gururajan M, Cavassani KA, Sievert M, Duan P, Lichterman J, Huang J, et al. SRC family kinase FYN promotes the neuroendocrine phenotype and visceral metastasis in advanced prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:44072‐83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Stein U, Walther W, Arlt F, Schwabe H, Smith J, Fichtner I, et al. MACC1, a newly identified key regulator of HGF‐MET signaling, predicts colon cancer metastasis. Nat Med. 2009;15:59‐67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Wang L, Wu Y, Lin L, Liu P, Huang H, Liao W, et al. Metastasis‐associated in colon cancer‐1 upregulation predicts a poor prognosis of gastric cancer, and promotes tumor cell proliferation and invasion. Int J Cancer. 2013;133:1419‐30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Juneja M, Ilm K, Schlag PM, Stein U. Promoter identification and transcriptional regulation of the metastasis gene MACC1 in colorectal cancer. Mol Oncol. 2013;7:929‐43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Xia J, Wang H, Huang H, Sun L, Dong S, Huang N, et al. Elevated Orai1 and STIM1 expressions upregulate MACC1 expression to promote tumor cell proliferation, metabolism, migration, and invasion in human gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2016;381:31‐40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Furukawa TA. Assessment of mood: Guides for clinicians. J Psychosom Res. 2010;68:581‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Cheng Y, Gao X, Li X, Cao Q, Zhao D, Zhou J, et al. Depression promotes prostate cancer invasion and metastasis via a sympathetic‐cAMP‐FAK signaling pathway. Oncogene. 2018;37:2953‐66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Thaker PH, Han LY, Kamat AA, Arevalo JM, Takahashi R, Lu C, et al. Chronic stress promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in a mouse model of ovarian carcinoma. Nat Med. 2006;12:939‐44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Le CP, Nowell CJ, Kim‐Fuchs C, Botteri E, Hiller JG, Ismail H, et al. Chronic stress in mice remodels lymph vasculature to promote tumour cell dissemination. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Wong JT, Malec PA, Mabrouk OS, Ro J, Dus M, Kennedy RT. Benzoyl chloride derivatization with liquid chromatography‐mass spectrometry for targeted metabolomics of neurochemicals in biological samples. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1446:78‐90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Lin L, Liu Y, Pan C, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Shao R, et al. Gastric cancer cells escape metabolic stress via the DLC3/MACC1 axis. Theranostics. 2019;9:2100‐14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Penrose HM, Cable C, Heller S, Ungerleider N, Nakhoul H, Baddoo M, et al. Loss of Forkhead Box O3 Facilitates Inflammatory Colon Cancer: Transcriptome Profiling of the Immune Landscape and Novel Targets. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2019;7:391‐408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Wang C, Wen Z, Xie J, Zhao Y, Zhao L, Zhang S, et al. MACC1 mediates chemotherapy sensitivity of 5‐FU and cisplatin via regulating MCT1 expression in gastric cancer. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2017;485:665‐71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Zhao Y, Liu Y, Lin L, Huang Q, He W, Zhang S, et al. The lncRNA MACC1‐AS1 promotes gastric cancer cell metabolic plasticity via AMPK/Lin28 mediated mRNA stability of MACC1. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Yu AL, Gilman AL, Ozkaynak MF, Naranjo A, Diccianni MB, Gan J, et al. Long‐Term Follow‐up of a Phase III Study of ch14.18 (Dinutuximab) + Cytokine Immunotherapy in Children with High‐Risk Neuroblastoma: COG Study ANBL0032. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27:2179‐89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Ogawa K, Lin Q, Li L, Bai X, Chen X, Chen H, et al. Aspartate β‐hydroxylase promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma metastasis through activation of SRC signaling pathway. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Wan X, Liu C, Chen YB, Gu M, Cai ZK, Chen Q, et al. Sulforaphane Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence Via the Nrf2‐ARE Pathway in a Rat Model. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44:1912‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Ye T, Yang M, Huang D, Wang X, Xue B, Tian N, et al. MicroRNA‐7 as a potential therapeutic target for aberrant NF‐κB‐driven distant metastasis of gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Canc Res. 2019;38:55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Wang X, Ye T, Xue B, Yang M, Li R, Xu X, et al. Mitochondrial GRIM‐19 deficiency facilitates gastric cancer metastasis through oncogenic ROS‐NRF2‐HO‐1 axis via a NRF2‐HO‐1 loop. Gastric Cancer. 2021;24:117‐32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Prieto JM, Atala J, Blanch J, Carreras E, Rovira M, Cirera E, et al. Role of Depression As a Predictor of Mortality Among Cancer Patients After Stem‐Cell Transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6063‐71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Vere CC, Streba CT, Streba LM, Ionescu AG, Sima F. Psychosocial stress and liver disease status. World J Gastroentero. 2009;15:2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Holsboer F, Ising M. Stress Hormone Regulation: Biological Role and Translation into Therapy. Annu Rev Psychol. 2010;61:81‐109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Miller GE, Chen E, Zhou ES. If it goes up, must it come down? Chronic stress and the hypothalamic‐pituitary‐adrenocortical axis in humans. Psychol Bull. 2007;133:25‐45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Renz BW, Takahashi R, Tanaka T, Macchini M, Hayakawa Y, Dantes Z, et al. β2 Adrenergic‐Neurotrophin Feedforward Loop Promotes Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Cell. 2018;33:75‐90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Wu D, Katz A, Lee CH, Simon MI. Activation of phospholipase C by alpha 1‐adrenergic receptors is mediated by the alpha subunits of Gq family. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1992;267:25798‐802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Carrasco GA, Van de Kar LD. Neuroendocrine pharmacology of stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;463:235‐72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Hui H, Fernando MA, Heaney AP. The α1‐adrenergic receptor antagonist doxazosin inhibits EGFR and NF‐κB signalling to induce breast cancer cell apoptosis. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44:160‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Valles SL, Benlloch M, Rodriguez ML, Mena S, Pellicer JA, Asensi M, et al. Stress hormones promote growth of B16‐F10 melanoma metastases: an interleukin 6‐ and glutathione‐dependent mechanism. J Transl Med. 2013;11:72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Jung Y, Cackowski FC, Yumoto K, Decker AM, Wang J, Kim JK, et al. CXCL12γ Promotes Metastatic Castration‐Resistant Prostate Cancer by Inducing Cancer Stem Cell and Neuroendocrine Phenotypes. Cancer Res. 2018;78:2026‐39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. McKeithen D, Graham T, Chung LWK, Odero‐Marah V. Snail transcription factor regulates neuroendocrine differentiation in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. The Prostate. 2010;70:982‐92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Palapattu GS, Wu C, Silvers CR, Martin HB, Williams K, Salamone L, et al. Selective expression of CD44, a putative prostate cancer stem cell marker, in neuroendocrine tumor cells of human prostate cancer. The Prostate. 2009;69:787‐98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Conteduca V, Aieta M, Amadori D, De Giorgi U. Neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer: Current and emerging therapy strategies. Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol. 2014;92:11‐24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Data Availability Statement
The data that supports the findings of this study could be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.


