Error in Figure/Table
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 4 : M. leprae 3b-HSD is a source of reductive power as published. Instead of original Figure 4 image, the Supplementary Figure 4 was duplicated and published as Figure 4 , and the correct one is not on the published version of the article. The corrected Figure 4 : M. leprae 3b-HSD is a source of reductive power appears below. The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
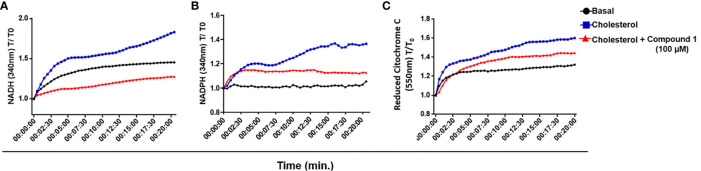
Figure 4.
M. leprae 3β-HSD is a source of reductive power. (A, B) NAD+ and NADP + reduction to NADH and NADPH, respectively, by 3β-HSD activity was measured in a temporal kinetic curve every 30 s for 20 min at 340 nm. (C) Cytochrome C reduction was determined measuring the reduced form of Cytochrome C at 550 nm every 30 s for 20 min. In all conditions M. leprae WCL was incubated with 200 µM cholesterol, alone (blue) or in the presence of 100 µM compound 1 (red). A condition without cholesterol addition was also included as a control of basal levels (black). Representative of 3 independent experiments.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.