Abstract
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been identified as critical contributors in tumor progression for many types of cancer. However, their functions in gallbladder cancer (GBC) have not been systematically clarified. In this study, the clinical significance, biological function, and underlying mechanism of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 in GBC were investigated. The quantitative real-time PCR result indicated that lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 was found to be recurrently downregulated in GBC tumor samples. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that decreased lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 expression level was associated with poor survival of GBC patients (p = 0.025). Then, both in vitro and in vivo experiments elucidated that the overexpression of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 suppressed the migration and invasion abilities of GBC cells and promoted the sensitivity to gemcitabine of GBC cells. Furthermore, we found that lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 physically interacted with c-Jun protein and decreased the phosphorylation on serine-73 (c-Jun-Ser73), which might cause the enhancement of the migration, invasion, and sensitivity to gemcitabine of GBC tumor cells. In conclusion, our study identified lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 as a promising prognostic indicator for patients with GBC, providing insights into the molecular pathogenesis of GBC. lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 is a potential therapeutic combination for gemcitabine in GBC treatment.
Keywords: long non-coding RNAs, gallbladder cancer, chemo-resistance, c-Jun, phosphorylation
Graphical abstract
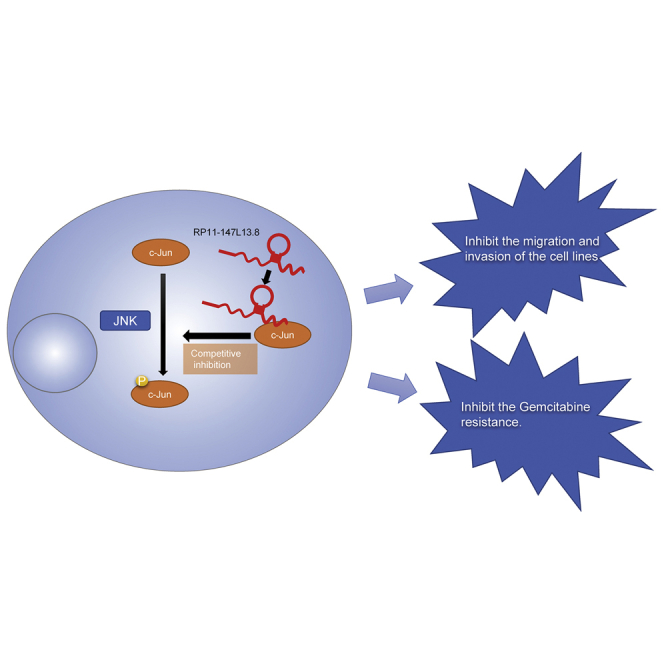
In this study, it was found that lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 could physically interact with c-Jun protein and decreased the phosphorylation on serine-73 (c-Jun-Ser73), which might cause the enhancement of the migration, invasion, and sensitivity to gemcitabine of GBC tumor cells.
Introduction
Gallbladder cancer (GBC), the most common biliary tract malignancy, is also the fifth most common digestive tract malignancy worldwide, with approximately 2.5 in 100,000 persons affected.1,2 The prognosis of advanced GBC is poor, with a survival time of less than 1 year, regardless of adjuvant therapy of standard chemotherapy.3 Currently, surgical resection remains the only curative treatment for GBC patients, with a 5-year survival rate of 90% for T1-stage patients.4 However, due to the lack of specific symptoms and signs, the majority of GBC patients were diagnosed at an advanced stage and not appropriate for resection. Herein, the prognosis of gallbladder cancer is dismal. The emergence of adjuvant therapy based on chemotherapy provided a chance to prolong the survival of patients with gallbladder cancer.5 Unfortunately, it has been reported that GBC is not sensitive to chemotherapeutic drugs.6 Hence, it is urgent to reveal the underlying molecular mechanisms associated with GBC chemo-resistance and figure out the way to solve it.
With the wide application of next-generation sequencing, more and more long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been identified. lncRNAs are defined as transcripts composed of more than 200 bp in length with no or weak protein-coding abilities, which was previously recognized as transcriptional “noise” initially.7 In recent years, many functions of lncRNAs have been reported in regulating various biological processes, such as cell differentiation, apoptosis, and immune escape.8 Besides, lncRNAs could exert their biological function by preventing RNA and protein from binding to intended targets, acting as host genes for microRNAs, and serving as molecular scaffolds to guide proteins to their direct chromosomal targets.9, 10, 11 Recently, accumulating evidence indicated that lncRNAs contribute a lot to the initiation and progression of the tumor, including hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, and cholangiocarcinoma.12, 13, 14 As for GBC, increasing attention has been attracted by the biological role of lncRNA in cancer progression. For instance, a lncRNA PVT1 has been reported in the tumor progression of GBC through regulating the miR-143/hexokinase 2 (HK2) axis in GBC.15 Another lncRNA H19 was also reported that could influence the progression of GBC through regulating FOXM1 expression by competitively binding endogenous miR-342-3p.16 Moreover, lncRNA GBCDRlnc1 could regulate the autophagy process to promote the chemo-resistance of the gallbladder.17
Oncogene c-Jun is located in the 1p32.1 region of the human chromosome, and its encoded protein was identified as FOS binding protein P39, which was composed of 334 amino acids.18 c-Jun protein has two major separate protein domains that could be phosphorylated. One is located at the C-terminal, which is very close in proximity to the DNA binding domain. These sites are Thr214, Ser226, and Ser 232, which are often phosphorylated by glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) and casein kinase (CK2II) phosphorylases. When these sites are dephosphorylated, c-Jun protein will be released from the inhibitory effect of cell resting-state factor to promote the cell growth. Another phosphorylation domain has a high affinity in the ser63, ser73, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases (JNKs), and delta domains in the transactivated domain. The phosphorylation of ser63 and ser73 would rapidly induce the transcriptional activation function.19 The function of the c-Jun DNA binding and dimerization domain is to bind DNA and form a basic leucine zipper domain with the FOS family or other jun family proteins. This homologous or dimerization binding constitutes an important transcription factor activating protein 1 (AP-1), which plays a role in transcriptional activation. Specifically, several studies have shown that phosphorylation of ser63 and ser73 sites of c-jun can affect cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and other biological functions through the JNK signaling pathway and promote the occurrence and development of human malignant tumors.20,21 Recent studies have found the aberrant expression of c-Jun exists in gallbladder carcinoma, which may be closely related to the occurrence and development of gallbladder carcinoma. Additionally, many studies have found that c-Jun, a key gene of the JNK signaling pathway, plays a key role in regulating chemotherapy resistance in human malignant tumors. For instance, Roszak et al.22 found that c-Jun was upregulated in leukemia cells HL-60 and promoted arsenic trioxide drug resistance by regulating the JNK signaling pathway. However, it remains unclear how the c-jun influences chemo-resistance in GBC, which deserves further exploration.
In our study, we characterized the transcriptional landscape of lncRNAs in paired GBC tissues and drug-resistant GBC cell lines and identified hundreds of lncRNAs that showed dysregulation in GBC tumor samples. We found and further validated that the long intergenic non-coding RNA, lncRNA RP11-147L13.8, was recurrently downregulated in GBC tumor tissue and drug-resistant cell lines. Moreover, its low expression predicted poor outcomes for GBC patients. Functional assays in GBC cell lines revealed that lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 could substantially suppress the migration and invasion of GBC tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo. Besides, our study suggested that the overexpression of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 could enhance gemcitabine sensitivity on GBC cells. In terms of the underlying mechanism, our further analysis revealed that lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 physically interacted with c-Jun protein by binding delta bZIP domain to inhibit the phosphorylation of c-jun-Ser73 in GBC cell lines. Our study shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying the progression of GBC and provided insights into the therapeutic strategy for GBC patients.
Results
Transcriptional landscape and dysregulation of lncRNAs in GBC
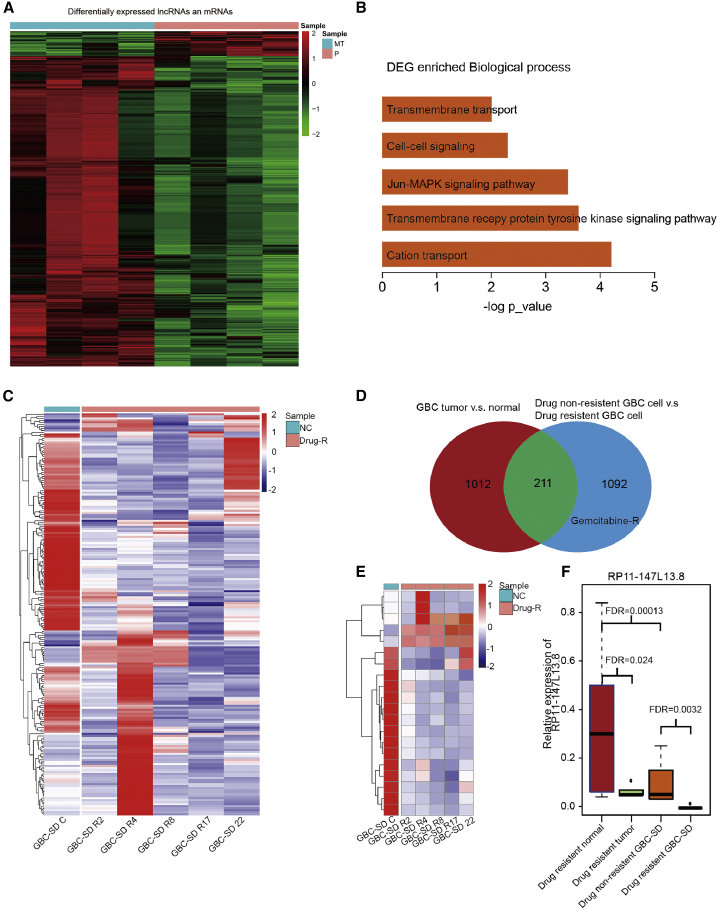
The expression profiles of four paired GBC samples were extracted to investigate the comprehensive dysregulation and potential biological roles of lncRNAs in the carcinogenesis processes of GBC. Our analysis detected 1,012 lncRNAs and 1,254 mRNAs that showed different expression levels in the microarray data (Figure 1A). Then, the further Gene Ontology (GO) analysis indicated that these different expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs might be involved in five biological processes, including transmembrane transport, cell-cell signaling, Jun-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway, and cation transport (Figure 1B). Furthermore, to investigate the potential biological role of lncRNA in the drug resistance in GBC, the expression profiles of normal GBC-SD and drug-resistant GBC-SD cell lines were obtained and analyzed, which turned out that 1,092 lncRNAs showed different expression level (Figure 1C). We found out that 211 lncRNAs were both differentially expressed in GBC tumor tissue and drug-resistant GBC cell lines (Figures 1D and 1E). Besides, the top ten upregulated and downregulated differently expressed lncRNAs (Figures S1A and S1B) were validated in 24 pairs of GBC and adjacent normal tissues, which turned out that only RP11-147L13.8 WAS significantly downregulated in tumor tissues (Figure S1C). Finally, the expression level of this lncRNA was lower in drug-resistant tumors and drug-resistant GBC-SD cell lines (Figure 1F). Therefore, we hypothesized that lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 might be related to the tumor formation and chemo-resistance in GBC, and further investigation was conducted.
Figure 1.
The expression level of long non-coding RNA RP11-147L13.8 was downregulated in tumor tissue and chemo-resistant cell lines in gallbladder cancer
(A) The heatmap presented the expression level of the expression profiles of lncRNAs and mRNAs between 4 pairs of GBC tissue and normal tissue. (B) The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) enriched biological process includes transmembrane transport, cell-cell signaling, Jun-MAPK signaling pathway, transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway, and cation transport. (C) The DEGs between GBC-SD and drug-resistant GBC-SD cells are shown. (D) 1,223 genes were differently expressed between GBC tumor tissues and normal tissues, although 1,303 genes were differentially expressed between normal GBC cell lines and drug-resistant GBC cell lines. Besides, 211 overlap genes were found between two gene sets. (E) The top 20 different expressed lncRNAs between GBC-SD and drug-resistant GBC-SD cell lines are shown. (F) The expression level of RP11-147L13.8 was significantly downregulated in drug-resistant tumor tissues and drug-resistant GBC-SD cell lines.
RP11-147L13.8 is recurrently downregulated and associated with poor overall survival outcomes in GBC patients
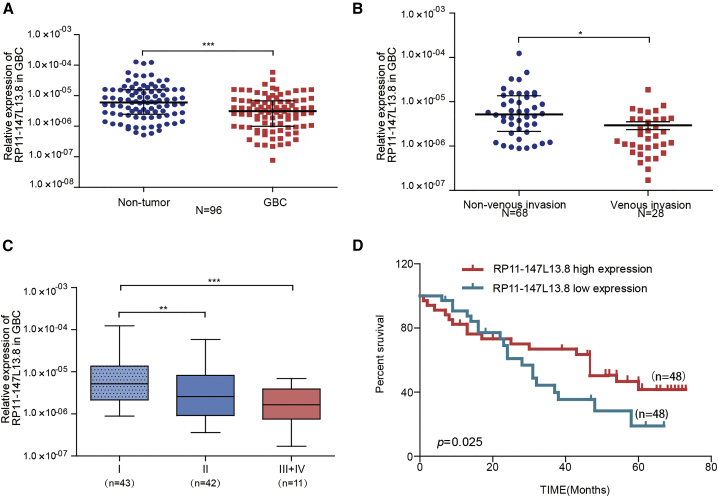
To investigate the clinical significance of RP11-147L13.8, qPCR was used to evaluate the expression of this lncRNA in 96 paired GBC patients, which turned out that this lncRNA was significantly downregulated in GBC tumor tissues, as compared with the adjacent no-tumor tissues (p < 0.0001; Figure 2A). Detail clinicopathological parameters have been listed in Table 1. Further analyses indicated that the expression level of RP11-147L13.8 was significantly lower in patients with venous invasion as compared with patients without venous invasion (p = 0.0115; Figure 2B). In the meantime, the expression level of this lncRNA was significantly lower in patients with advanced tumor, lymph node, metastasis (TNM) stage (Figure 2C). Then, the median expression level was selected as the cutoff value for this lncRNA. Accordingly, patients were divided into high and low groups. Survival analysis indicated that patients in the low group were associated with poor 5-year overall survival (p = 0.025; Figure 2D). Besides, high expression level of this lncRNA positively correlated with small tumor size, lower venous invasion rate, and early TNM stage in GBC patients (Table 2). Therefore, these results indicated that RP11-147L13.8 was a potential prognostic biomarker for GBC patients and might be involved in the formation and metastasis of GBC.
Figure 2.
The clinical and prognostic significances of RP11-147L13.8 in GBC patients
(A) RP11-147L13.8 is downregulated in tumor tissue compared with the adjacent non-tumor tissue (n = 96). Data represent median ± 95% confidence interval (CI). Wilcoxon signed rank test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (B) RP11-147L13.8 is downregulated in tumor tissue with venous invasion compared with the adjacent non-tumor tissue. Data represent median ± 95% confidence interval (CI). Wilcoxon signed-rank test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (C) The expression level of RP11-147L13.8 is lower in GBC patients with advanced TNM stage. Data represent median ± 95% confidence interval (CI). Wilcoxon signed-rank test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (D) Patients with low expression of RP11-147L13.8 were associated with poorer overall survival (log rank test; p = 0.025).
Table 1.
The baseline information of the 96 GBC patients enrolled in this study
| Characteristics | Patient number |
|---|---|
| Age, years | |
| ≤60 years | 50 |
| >60 years | 46 |
| Gender | |
| Male | 56 |
| Female | 40 |
| Diabetes mellitus | |
| No | 53 |
| Yes | 43 |
| CA19-9a(U/mL) | |
| ≤37 | 47 |
| >37 | 43 |
| Tumor size (cm) | |
| ≤2.5 | 56 |
| >2.5 | 40 |
| Lymph node metastasis | |
| No | 54 |
| Yes | 42 |
| Grade | |
| Well-differentiated | 21 |
| Moderately differentiated | 46 |
| Poorly differentiated | 29 |
| TNM stage | |
| I | 43 |
| II | 42 |
| III+IV | 11 |
CA19-9 data are from 90 patients (data missing for 6 patients).
Table 2.
Correlations between the RP11-147l13.8 expression level and clinicopathological characteristics in GBC patients
| Characteristics |
RP11-147l13.8 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n = 48) | High (n = 48) | p value | |
| Age, years | |||
| ≤60 | 27 | 23 | 0.414 |
| >60 | 21 | 25 | |
| Gender | |||
| Female | 29 | 27 | 0.679 |
| Male | 19 | 21 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | |||
| No | 25 | 28 | 0.538 |
| Yes | 23 | 20 | |
| CA 19-9 (U/mL) | |||
| ≤37 | 26 | 21 | 0.841 |
| >37 | 19 | 24 | |
| Tumor size (cm) | |||
| ≤2.5 | 21 | 35 | 0.004 |
| >2.5 | 27 | 13 | |
| Venous invasion | |||
| No | 28 | 40 | p < 0.001 |
| Yes | 20 | 8 | |
| Grade | |||
| Well-differentiated | 7 | 14 | 0.224 |
| Moderately differentiated | 25 | 21 | |
| Poorly differentiated | 16 | 13 | |
| TNM stage | |||
| I+II | 39 | 46 | 0.025 |
| III+IV | 9 | 2 | |
Pearson chi-square test and Fisher’s exact test. CA 19-9, carbohydrate antigen 19-9; TNM, tumor, lymph node, metastasis.
The detailed information of this lncRNA was presented in Figures S2 and S3. The lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 was predicted to possess no protein-coding potential by the LNCipedia database (Figure S2).23 Meanwhile, Coding-Potential Assessment Tool (CPAT) online software24 could not predict the protein-coding potentiality of this lncRNA (Figure S2). The expression profile of this lncRNA across pan-human cancer and pan-human tissues was presented in Figure S3A. The 5′ and 3′ rapid amplification of complementary DNA ends (RACE) assays revealed the full length of RP11-147L13.8 dominant isoform is about 2,919 bp (Figure S3B). The expression levels of RP11-147L13.8 were different across different GBC cell lines, wherein GBC-SD cells expressed the highest RP11-147L13.8 and NOZ expressed the lowest (Figure S3C). Besides, RP11-147L13.8 was expressed in both cytoplasm and nucleus (cytoplasm: 35%; nucleus: 65%; Figure S3D).
RP11-147L13.8 suppresses migration and invasion abilities of GBC cells in vitro and in vivo
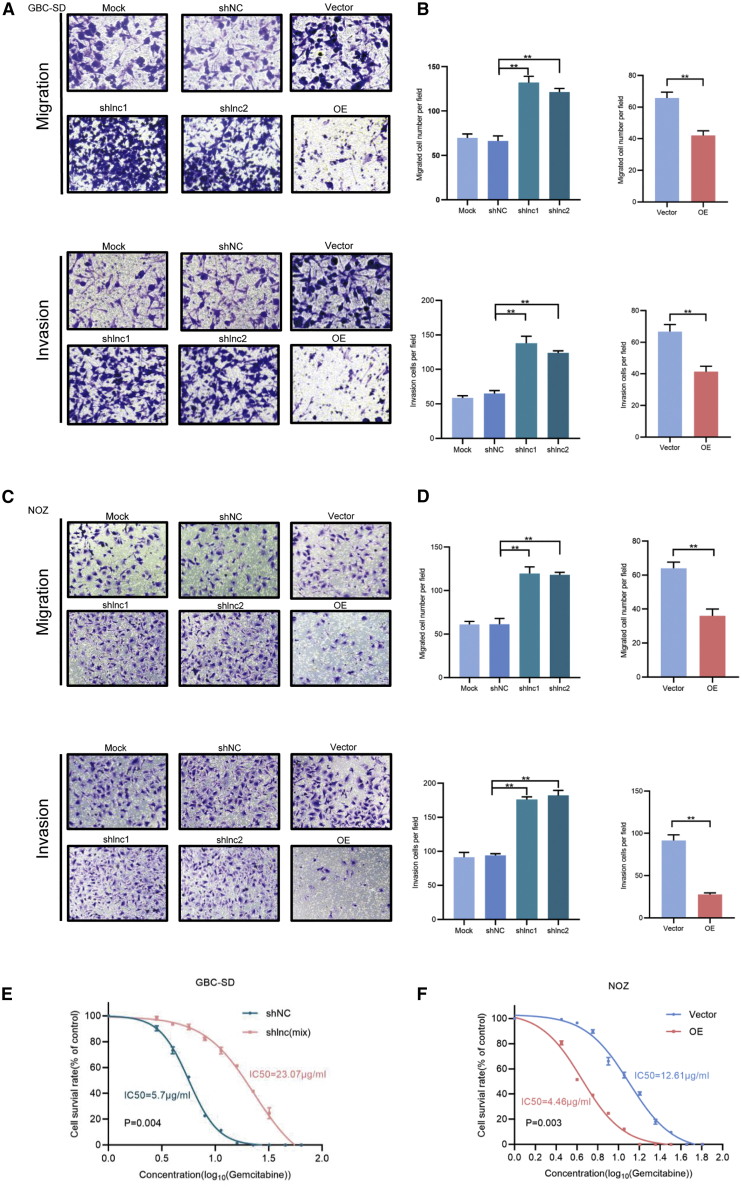
To investigate the biological function of RP11-147L13.8, a stable knockdown and overexpression cell line was constructed; the altered change in the expression level of this lncRNA was presented in Figure S3E. Next, functional assays were further performed to determine the biological effects of RP11-147L13.8 on GBC cell lines. The knockdown of RP11-147L13.8 significantly promoted the migration and invasion abilities of GBC-SD cell lines, although the overexpression of RP11-147L13.8 significantly suppressed the migratory and invasive abilities of GBC-SD cell lines (Figures 3A and 3B). Similar results were observed in NOZ cell lines (Figures 3C and 3D). These results suggested that RP11-147L13.8 could suppress the migratory and invasive abilities of GBC tumor cells in vitro.
Figure 3.
The overexpression of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 suppressed the migration and invasion ability and enhanced the drug sensitivity in GBC cell lines
(A) The overexpression of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 suppressed the migration ability in GBC-SD cell lines, although the overexpression of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 suppressed the invasion ability in GBC-SD cell lines. Magnification, 200×. Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). Paired Student’s t test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (B) The downregulation of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 promotes the migration ability in GBC-SD cell lines, although the downregulation of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 promotes the invasion ability in GBC-SD cell lines. Magnification, 200×. Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). Paired Student’s t test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (C) The overexpression of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 suppresses the migration ability in NOZ cell lines, although the downregulation of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 promotes the migration ability in NOZ cell lines. Magnification, 200×. Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). Paired Student’s t test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (D) The overexpression of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 suppresses the invasion ability in NOZ cell lines, although the downregulation of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 promotes the invasion ability in NOZ cell lines. Magnification, 200×. Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). Paired Student’s t test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (E) The downregulation of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 promotes the drug-resistant ability in GBC-SD cell lines. Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). Paired Student’s t test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (F) The overexpression of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 suppressed the drug-resistant ability in NOZ cell lines. Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). Paired Student’s t test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
In vivo experiment was further carried out to demonstrate the effects of RP11-147L13.8 on cell migration and metastasis. No significant differences were observed in the tumor volume and tumor weight. The metastatic nodules in both liver and lung were significantly increased in the RP11-147L13.8 knockdown group. Furthermore, the hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining results showed a dramatic increase of metastatic foci derived from cells of the RP11-147L13.8 knockdown group in liver and lung tissue sites (Figures S4E and S4F). Thus, these observations demonstrated that RP11-147L13.8 might suppress the tumor metastasis both in vitro and in vivo.
RP11-147L13.8 enhances drug sensitivity of gemcitabine in GBC tumor cell lines
To further explore the functional role of RP11-147L13.8 in the drug resistance of GBC, we investigated its effects on the treatment with gemcitabine, which is usually used in chemotherapy for GBC patients. The knockdown of RP11-147L13.8 dramatically increased the IC50 in gemcitabine-treated GBC-SD cells (short hairpin RNA for RP11-147L13.8 (shNC) versus shlnc(mix):5.7 μg/mL versus 23.07 μg/mL; Figure 3E). Moreover, the overexpression of RP11-147L13.8 significantly reduces the IC50 in gemcitabine-treated NOZ cell lines (shNC versus shlnc(mix):4.46 μg/mL versus 12.61 μg/mL; Figure 3F).
RP11-147L13.8 interacts with c-Jun and suppresses the c-Jun-ser73 phosphorylation via inhibiting the JNK in GBC cells
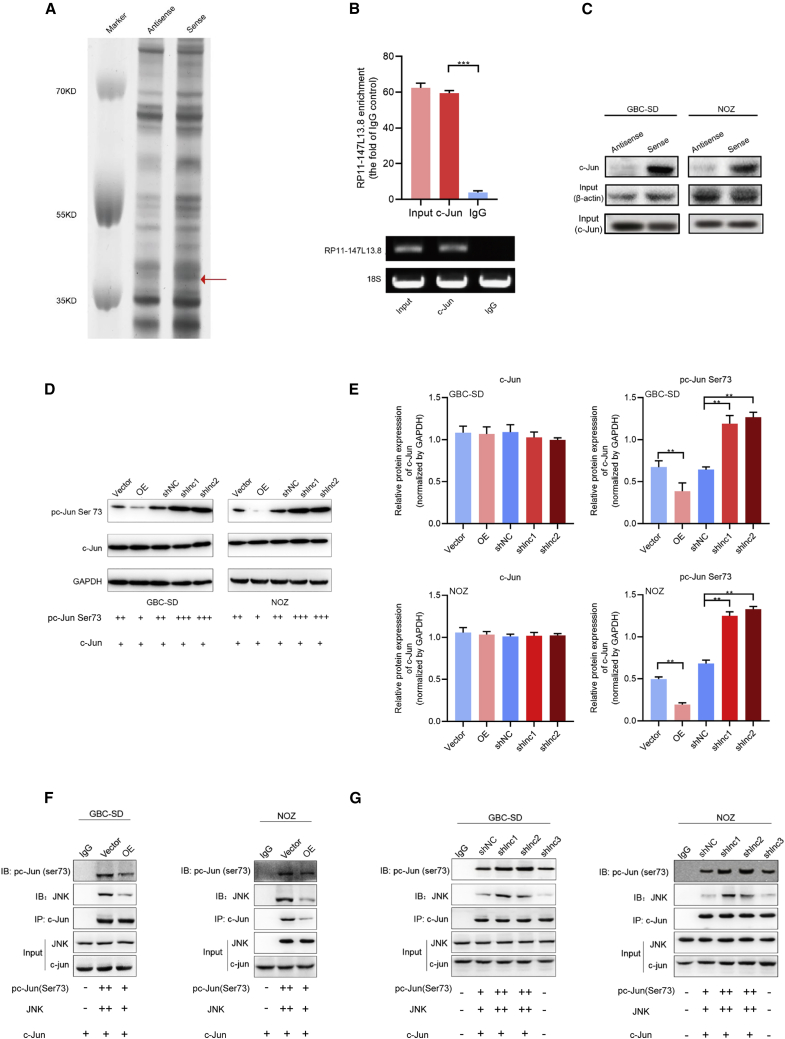
For a better understanding of how RP11-147L13.8 performs its activities in gallbladder carcinogenesis and tumor progression, RNA pull-down assays were conducted to identify RP11-147L13.8-related proteins in GBC cells. The mass spectrometry analyses following RP11-147L13.8 pull-down experiments revealed specific protein bands that bind with the RP11-147L13.8 (Figure 4A). Based on the filtrations of high-confidence scores (no less than 100 in mass spectrometric assays) and absence in corresponding anti-sense groups, nine proteins that might interact with RP11-147L13.8 were obtained (Table S3). The RP11-147L13.8-c-Jun interaction was further verified by RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays, wherein RP11-147L13.8 was significantly enriched in c-Jun antibody, but not immunoglobulin G (IgG) control (Figure 4B). Our western blot results confirmed that c-Jun protein was specifically associated with sense, but not anti-sense, RP11-147L13.8 (Figure 4C). Besides, the western blot result indicated that the overexpression of RP11-147l13.8 could suppress the ser73 phosphorylation of the c-Jun protein, although the knockdown of RP11-147l13.8 could promote the ser73 phosphorylation of the c-Jun protein in both GBC-SD and NOZ cell lines (Figures 4D and 4E).
Figure 4.
RP11-147L13.8interacts with c-Jun and suppresses the c-Jun-ser73 phosphorylation via inhibiting the JNK in GBC cells
(A) RP11-147L13.8 pull-down assay analyzed by SDS-PAGE. (B) The RP11-147L13.8-c-Jun interaction was verified by RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays, wherein RP11-147L13.8 was significantly enriched in c-Jun antibody, but not IgG control. (C) The western blot results, which confirmed that c-Jun protein was specifically associated with sense, but not anti-sense, RP11-147L13.8 in both GBC-SD and NOZ cell lines are shown. (D and E) The overexpression of RP11-147l13.8 could suppress the ser73 phosphorylation of the c-Jun protein, although the knockdown of RP11-147l13.8 could promote the ser73 phosphorylation of the c-Jun protein in both GBC-SD and NOZ cell lines. Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). (F) The co-immunoprecipitation experiment indicated that the overexpression of RP11-147L13.8 could competitively inhibit the interaction between the JNK and c-Jun protein, which results in the ser73 dephosphorylation of c-Jun protein in both GBC-SD and NOZ cell lines. (G) The co-immunoprecipitation experiment indicated that the knockdown of RP11-147L13.8 could enhance the interaction between the JNK and c-Jun protein, which results in the ser73 phosphorylation of c-Jun protein in both GBC-SD and NOZ cell lines.
To further investigate how the lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 influences the ser73 phosphorylation of the c-Jun protein, a co-immunoprecipitation (coIP) experiment was performed in the RP11-147L13.8 knockdown and RP11-147L13.8 overexpression GBC cell lines. The coIP results indicated that the overexpression of RP11-147L13.8 could competitively inhibit the interaction between the JNK and c-Jun protein in both GBC-SD and NOZ, which results in the ser73 dephosphorylation of c-Jun protein (Figure 4F). In contrast, the knockdown of the RP11-147L13.8 could promote the ser73 phosphorylation of c-Jun protein in two GBC cell lines (Figure 4G). Besides, the expression levels of c-Jun-ser73 in 24 GBC tissues were evaluated through immunohistochemistry (IHC) (Figure S5A). Then, Kaplan-Meier analysis indicated that patients with higher expression of c-Jun-ser73 phosphorylation were associated with poorer overall survival (Figure S5B). Meanwhile, our data indicated that the expression level of RP11-147L13.8 was negatively correlated with the expression level of c-Jun-ser73 (R = −0.63; p = 0.002; Figure S5C). Taken together, all these data indicated that RP11-147L13.8 could suppress the c-Jun-ser73 phosphorylation.
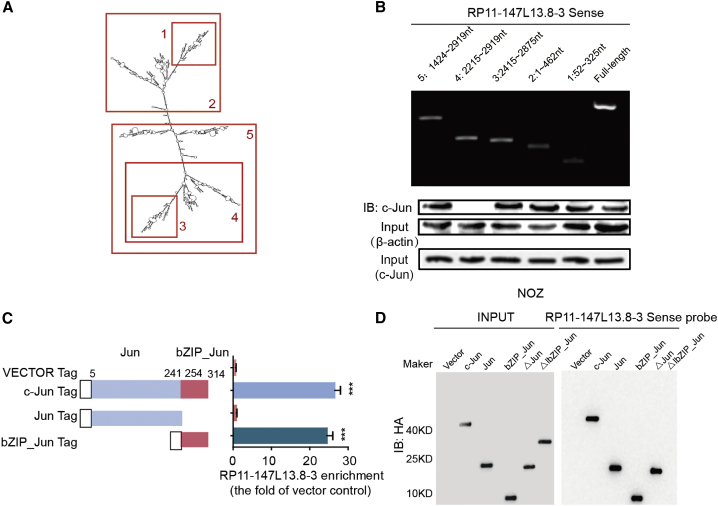
RP11-147L13.8 interacts with c-Jun via binding with the basic region leucine zipper (bZIP) Jun domain of the JUN protein
Further investigation was carried out to determine the biological roles of the specific RP11-147L13.8 fragment that binds the c-Jun protein; a series of deletions was constructed to map the truncated RP11-147L13.8 fragments with c-Jun protein. The results of deletion mapping analyses showed that the 2,215- to 2,919-nt fragment of RP11-147L13.8 was required for its interaction with the c-Jun protein (Figures 5A and 5B). Moreover, our RIP assays revealed that the bZIP domain of c-Jun was responsible for the binding with RP11-147L13.8 (Figure 5C). Specifically, the interaction between c-Jun and RP11-147L13.8 was significantly abolished under the deletion of the bZIP_Jun domain (Figure 5D). In summary, all these data further demonstrated that RP11-147L13.8 interacts with c-Jun via binding with the bZIP domain of the c-Jun protein, which might explain the biological function of this lncRNA.
Figure 5.
LncRNA RP11-147L13.8 was specifically interacted with the bZIP domain of c-Jun protein
(A) The structure of lncRNA RP11-147L13.8. (B) Immunoblotting detection of c-Jun protein in the pull-down samples is shown. The full-length sense biotinylated-RP11-147L13.8 and truncated biotinylated-RP11-147L13.8 sequence (no. 1 deletes 52–325 bp; no. 2 deletes 1–462 bp; no. 3 deletes 2,415–2,875 bp; no. 4 deletes 2,215–2,919 bp; no. 5 deletes ∼1,421–2,919 bp) were analyzed. β-actin and c-Jun serve as input control. (C) The RIP and qPCR results determined the enrichment of RP11-147L13.8 binding with each c-Jun domain. (D) The pull-down assay and western blot results for different domains of c-Jun protein in NOZ cell lines, which confirmed that lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 specifically interacted with the bZIP domain.
The rescue assay confirmed that lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 performs its biological function by suppressing the c-Jun-ser73 phosphorylation in GBC cell lines
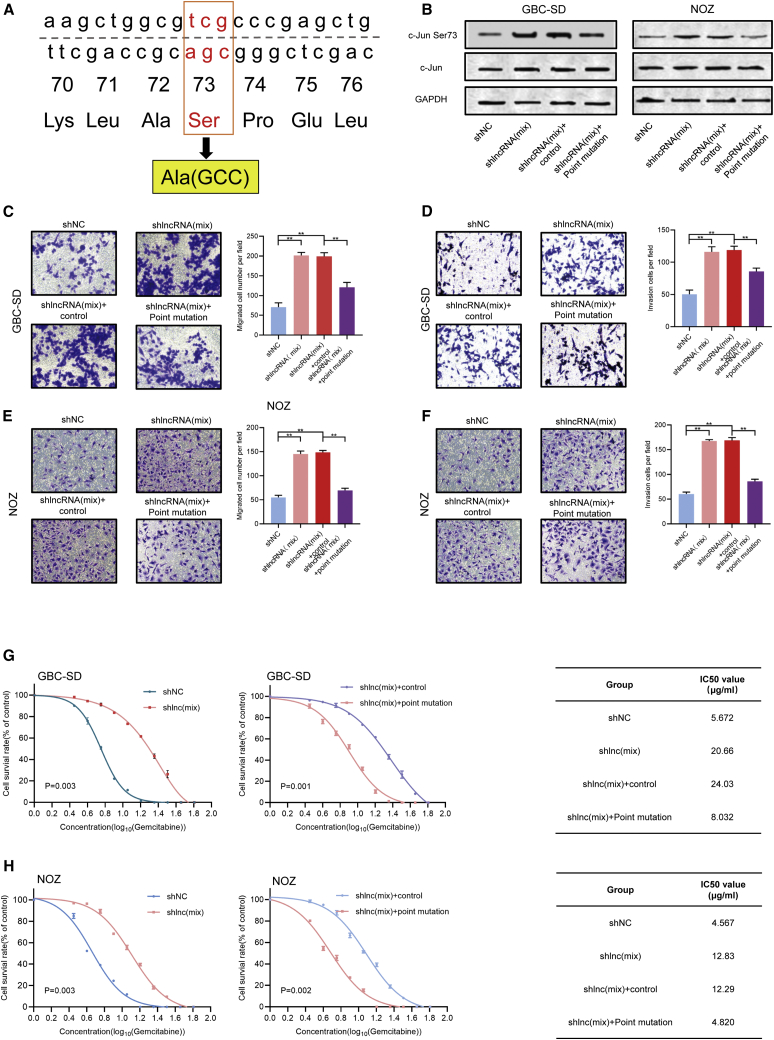
To further validate that RP11-147L13.8 performs its biological function through suppressing the c-Jun-ser73 phosphorylation, a rescue assay was performed. To reverse the c-Jun-ser73 phosphorylation, a point mutation experiment was carried out, which changed the Ser at 73 sites into Ala (Figure 6A). After transfection, the western blot result validated the efficiency of point mutation, which indicated that the point mutation could significantly inhibit the c-Jun-Ser 73 phosphorylation in both GBC-SD and NOZ cell lines (Figure 6B). Then, transwell assay indicated that the knockdown of this lncRNA could promote the migration (Figure 6C) and invasive (Figure 6D) ability of the GBC-SD cell line, although after the point mutation, the overexpression of this lncRNA could suppress the migration (Figure 6C) and invasive (Figure 6D) ability of GBC-SD. Meanwhile, similar results were observed in the NOZ cell line (Figures 6E and 6F). In terms of the influence on the drug-resistant ability of GBC cell lines, Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay indicated that the knockdown of this lncRNA could increase the IC50 value for gemcitabine in both GBC-SD (Figure 6G) and NOZ (Figure 6H) cell lines, indicating that knockdown of this lncRNA could promote the resistant ability to gemcitabine in both GBC-SD and NOZ cell lines. After the point mutation, the IC50 value for gemcitabine significantly decreased in both GBC-SD (Figure 6G) and NOZ (Figure 6H) cell lines, indicating that point mutation could reverse the biological effect of this lncRNA on the gemcitabine-resistant ability of GBC cell lines.
Figure 6.
The rescue assay confirmed that lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 performs its biological function through suppressing the c-Jun-ser73 phosphorylation in GBC cell lines
(A) The strategy of the point mutation. The Ser at 73 sites of JUN was changed into Ala. (B) After transfection, the phosphorylation of c-Jun has been suppressed in both GBC-SD and NOZ cell lines (three biological replicates). (C) After the knockdown of lncRNA, the migration ability of GBC-SD has been promoted, although after the point mutation, the migration ability of the knockdown GBC-SD has been suppressed. Magnification, 200×. Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (D) After the knockdown of lncRNA, the invasion ability of GBC-SD has been promoted, although after the point mutation, the invasion ability of the knockdown GBC-SD has been suppressed. Magnification, 200×. Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (E) After the knockdown of lncRNA, the migration ability of NOZ has been promoted, although after the point mutation, the migration ability of the knockdown GBC-SD has been suppressed. Magnification, 200×. Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (F) After the knockdown of lncRNA, the invasion ability of NOZ has been promoted, although after the point mutation, the invasion ability of the knockdown GBC-SD has been suppressed. Magnification, 200×. Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (G) After the knockdown of lncRNA, the IC50 value of GBC-SD for gemcitabine was significantly upregulated (shNC versus shlnc(mix): 5.672 μg/mL versus 20.66 μg/mL). After the point mutation, the IC50 value of GBC-SD for gemcitabine was significantly decreased (shlnc(mix)+control versus shlnc(mix)+point mutation: 24.03 μg/mL versus 8.032 μg/mL). Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). Student’s t test. (H) After the knockdown of lncRNA, the IC50 value of NOZ for gemcitabine was significantly upregulated (shNC versus shlnc(mix): 4.567 μg/mL versus 12.830 μg/mL). After the point mutation, the IC50 value of GBC-SD for gemcitabine was significantly decreased (shlnc(mix)+control versus shlnc(mix)+point mutation: 12.29 versus 4.820 μg/mL). Data represent mean ± SEM (three biological replicates). Student’s t test.
Taken together, all these results confirmed that lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 performs its biological function by suppressing the c-Jun-ser73 phosphorylation in GBC cell lines.
Discussion
Recently, many findings suggest that lncRNAs play an important role in the initiation and progression of GBC. Here, we investigated the clinical significance and biological role of a novel lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 in GBC. In terms of the clinical significance, the lower expression of this lncRNA was associated with a higher lymph node metastasis rate and predicted poorer overall survival rates in patients with GBC. As for the biological role, RP11-147L13.8 showed strong tumor suppressor activity through suppressing GBC tumor migration and invasion in vitro, suggesting that this lncRNA might inhibit the metastasis of GBC. In terms of mechanism, this lncRNA might suppress the c-Jun-ser73 phosphorylation via binding with the delta bZIP domain of c-Jun in GBC to induce its suppressing function.
Currently, numerous studies indicated that lncRNAs could serve as prognostic biomarkers for GBC patients.25,26 Consistent with previous studies, in our study, we observed that the higher expression level of this lncRNA was positively associated with earlier TNM stage and better overall survival, indicating that this lncRNA might be a potential prognostic biomarker in GBC.
Recently, emerging evidence indicated that lncRNAs play an important role in regulating the progression of GBC. For instance, lncRNA GBCDRlnc1 might induce chemo-resistance of GBC cells through activating autophagy. Additionally, lncRNA HGBC stabilized by Human antigen R (HuR) promotes GBC progression by regulating the miR-502-3p/SET/protein kinase B (AKT) axis.27 Consistent with these studies, we found that the overexpression of the novel lncRNA RP11-147L13.8 played an important role in suppressing the tumor invasion, metastasis, and chemo-resistance in GBC. Several sets of evidence supported our conclusion. At first, this lncRNA was significantly downregulated in GBC tissue, GBC patients with venous invasion, and drug-resistant GBC-SD cells, suggesting that RP11-147L13.8 might be involved in the biological process of GBC. Next, the in vitro and in vivo experiments indicated that the downregulation of RP11-147L13.8 was significantly promoted, although the overexpression of RP11-147L13.8 significantly inhibited migration and invasion abilities of GBC cell lines. In terms of the chemo-resistant ability, we found out that patients with a high expression level of this lncRNA were sensitive to chemotherapy. All these results demonstrated that the aberrant expression of this lncRNA could regulate the progression, metastasis, and chemo-resistance of chemotherapy.
The lncRNA could exert its biological function through binding with specific protein or transcription factors. For instance, the interaction of FAL1 with BMI1, an essential subunit of PRC1, regulates its protein stability. Another lncRNA, lnc-dendritic cells (lnc-DCs) binds to the transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT3) in the cytoplasm and prevents its dephosphorylation by SH2-containing protein tyrosine phos-phatase-1 (SHP1), thereby activating STAT3 and thus dendritic cell differentiation. In our study, to figure out the underlying mechanism of the biological function of RP11-147L13.8, pull-down assay, RIP, and coIP experiments were performed, which indicated that this lncRNA might exert its function via interacting with the bZip domain of the c-Jun protein, which resulted in the suppression of c-Jun-ser73 phosphorylation of c-Jun protein through competitively inhibiting the interaction between the JNK and c-Jun protein. The phosphorylation of c-Jun on Ser73 could also promote tumorigenesis in breast cancer.28 These results might explain the biological role of this lncRNA. However, further investigation was needed to explain how the c-Jun protein regulates the biological features of GBC.
Among the treatments, gemcitabine is recommended as adjuvant therapy for patients with advanced-stage GBC in clinical practice.29,30 However, resistance to gemcitabine is often observed and tightly associated with dismal prognosis in GBC.6 Moreover, lncRNA has been reported in the studies of gemcitabine resistance in GBC.17,31 In our study, our IC50 analysis revealed that RP11-147L13.8 could enhance the drug sensitivity of gemcitabine in GBC-SD and NOZ cells. Besides, our results indicated that RP11-147L13.8 exerted its impact on gemcitabine resistance through regulating the phosphorylation of the c-Jun protein. Previously, several studies reported that c-Jun protein played an important role in inducing the drug resistance of gemcitabine resistance, including breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, and bladder cancer.32, 33, 34, 35 All these studies further supported our findings. This suggested that the combinatorial use of gemcitabine and RP11-147L13.8 transcriptional promoters might produce better therapeutic effects for advanced-stage GBC patients, which shed new insights into the clinical treatment for GBC patients.
In conclusion, our study demonstrated that RP11-147L13.8 might serve as a tumor-suppressing gene and a prognostic biomarker in GBC, which could inhibit the migration, invasion, and chemo-resistance ability of GBC cells via modulating the phosphorylation of the c-Jun protein, thus providing a potential therapeutic target for GBC treatment.
Materials and methods
Cell lines and human clinical samples
The human GBC cell line GBC-SD was purchased from the Type Culture Collection of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China), although the human GBC cell line NOZ was provided by the Tumor Cytology Research Unit (Medical College, Tongji University, Shanghai, China). Four paired fresh GBC tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues were collected for the lncRNA microarray analysis, although 96 pairs of fresh GBC tissues and matched adjacent non-tumor tissues from different patients were collected for quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis. All these patients received surgical resection of their primary tumors in curative intent between 2011 and 2015 at Zhongshan Hospital. All enrolled patients met the following criteria as previously described:36 (1) they were all pathologically confirmed GBC patients; (2) there was no other anti-cancer treatment history before surgical treatment; (3) there were no concurrence and history of other malignant tumors; (4) all patients had received complete removal of macroscopic tumors and pathological examination had confirmed the negative resection margin; and (5) all patients had complete clinicopathological and follow-up data. The written informed consent was obtained from patients. Ethical approval was obtained from the Zhongshan Hospital Research Ethics Committee and was carried out following the Declaration of Helsinki.
RNA sequencing
The RNA sequencing was performed as previously described.14 Details were listed in the supplemental information.
Differential expression analysis
The gene read counts of samples in four paired tumor and adjacent normal were used for differential expression analysis. The DESeq2 was implicated to carry out the analysis. In the differential analysis, lncRNA genes with false discovery rate (FDR) ≤ 0.05 (Benjamini-Hochberg corrected p value) and |log2 fold-change| ≥ 1 were determined as significantly differentially expressed genes. The enriched biological themes were identified by using the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID).37,38
Quantitative real-time PCR assay
The TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was used to extract the total RNA of the clinical tissue and cell lines in this study. According to the instructions of the reverse transcriptase kit (Takara Bio, Dalian, China), the total RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA in the LifePro Thermal Cycler (Hangzhou Bioer Technology, Hangzhou, China). The qRT-PCR was utilized to determine relative RNA levels, which were measured through a 7900 Real-Time PCR System with the SDS 2.3 software sequence detection system (Applied Biosystem, USE) using the SYBR Green (Takara) method. β-actin was employed as an internal control to normalize the relative RNA levels in each sample and then the relative RNA levels were calculated by utilizing the 2-ΔΔCt relative quantification method.39 The primer used for this experiment was listed in Table S1.
Northern blot assays and western blot assays
The details of northern blot assays and western blot assays were listed in the supplemental information.
IHC and analysis
The IHC and analysis were carried out as previously described.40 Quantification criteria of IHC staining were the same as the previous study by two independent pathologists.41
RNA interference and lentivirus construction
The details of RNA interference and lentivirus construction were listed in the supplemental information.
In vitro cell migration and invasion assays and in vivo metastasis assays
The details of in vitro cell migration and invasion assays and in vivo metastasis assays were listed in the supplemental information.
In vitro cellular IC50 assays
The sh-RP11-147L13.8 GBC-SD cells, pCDH RP11-147L13.8 NOZ cells, and corresponding vector cells were seeded in the flat-bottomed plates (96 wells). Ten concentration gradients of gemcitabine were performed to determine the half-maximal inhibitory concentrations that inhibit cell viability (IC50 values) in 100 μL suspended cells (5,000 cells) in each plate well. After 48 h culture, the CCK-8 assays (Dojindo, Kyushu, Japan) were employed to evaluate the cell viability.
RNA pull-down assays, mass spectrometry analyses, and RIP assays
To explore the underlying mechanism of RP11-147L13.8, RNA pull-down assay, mass spectrometry analyses, and RIP assays were performed. The details of the experiments were presented in the supplemental information.
Immunoblotting analysis and coIP
Immunoprecipitation was carried out as described previously.42 Details of the immunoblotting analysis and coIP were listed in the supplemental information.
Survival analysis
Survival analysis was performed as described in a previous study.43
Statistical analysis
Data were displayed in the mean ± SEM (standard error of the mean) or median with interquartile range form. The Student’s t test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to evaluate the differences between the two groups. The correlation between RP11-147L13.8 RNA levels and overall survival of GBC patients was estimated via the log rank test. Besides, the chi-square test was carried out to assess the functional impact of RP11-147L13.8 on GBC cell lines metastasis in vivo. All statistical calculations in this study were performed in the R environment. Unless specially stated, a two-tailed p < 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81872352 and82072682), Shanghai Top Priority Clinical Medical Center and Key Discipline Construction Plan (2017ZZ02007), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (21ZR1459100), and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (20DZ2254500). We thank Prof. Jiwei Zhang for his assistance in this manuscript.
Author contributions
Houbao Liu, Han Liu, and S.S. designed and supervised the study. B.Z., J.W., W.S., K.F., and W.W. performed data analysis and functional experiments. Xiaojian Ni, Z.G., D.Z., Xiaoling Ni, and T.S. collected and managed patient samples. S.S., Houbao Liu, Han Liu, and B.Z. wrote and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2021.08.016.
Contributor Information
Han Liu, Email: liu.han@zs-hospital.sh.cn.
Houbao Liu, Email: liu.houbao@zs-hospital.sh.cn.
Sheng Shen, Email: shen.sheng@zs-hospital.sh.cn.
Supplemental information
References
- 1.Henley S.J., Weir H.K., Jim M.A., Watson M., Richardson L.C. Gallbladder cancer incidence and mortality, United States 1999-2011. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2015;24:1319–1326. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-15-0199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020;70:7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Misra S.P., Dwivedi M. Pancreaticobiliary ductal union. Gut. 1990;31:1144–1149. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.10.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shindoh J., de Aretxabala X., Aloia T.A., Roa J.C., Roa I., Zimmitti G., Javle M., Conrad C., Maru D.M., Aoki T. Tumor location is a strong predictor of tumor progression and survival in T2 gallbladder cancer: an international multicenter study. Ann. Surg. 2015;261:733–739. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Horgan A.M., Amir E., Walter T., Knox J.J. Adjuvant therapy in the treatment of biliary tract cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012;30:1934–1940. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.40.5381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Goetze T.O. Gallbladder carcinoma: prognostic factors and therapeutic options. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015;21:12211–12217. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gutschner T., Diederichs S. The hallmarks of cancer: a long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol. 2012;9:703–719. doi: 10.4161/rna.20481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gibb E.A., Brown C.J., Lam W.L. The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol. Cancer. 2011;10:38. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gupta R.A., Shah N., Wang K.C., Kim J., Horlings H.M., Wong D.J., Tsai M.C., Hung T., Argani P., Rinn J.L. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature. 2010;464:1071–1076. doi: 10.1038/nature08975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tsai M.C., Manor O., Wan Y., Mosammaparast N., Wang J.K., Lan F., Shi Y., Segal E., Chang H.Y. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science. 2010;329:689–693. doi: 10.1126/science.1192002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang L., Bu P., Ai Y., Srinivasan T., Chen H.J., Xiang K., Lipkin S.M., Shen X. A long non-coding RNA targets microRNA miR-34a to regulate colon cancer stem cell asymmetric division. eLife. 2016;5:e14620. doi: 10.7554/eLife.14620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ni W., Yao S., Zhou Y., Liu Y., Huang P., Zhou A., Liu J., Che L., Li J. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 inhibits progression of colorectal cancer by interacting with and triggering YAP phosphorylation and degradation and is negatively regulated by the m6A reader YTHDF3. Mol. Cancer. 2019;18:143. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1079-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Qin G., Tu X., Li H., Cao P., Chen X., Song J., Han H., Li Y., Guo B., Yang L. Long noncoding RNA p53-stabilizing and activating RNA promotes p53 signaling by inhibiting heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K deSUMOylation and suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2020;71:112–129. doi: 10.1002/hep.30793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shen S., Wang J., Zheng B., Tao Y., Li M., Wang Y., Ni X., Suo T., Liu H., Liu H., Zhang J. LINC01714 enhances gemcitabine sensitivity by modulating FOXO3 phosphorylation in cholangiocarcinoma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2020;19:446–457. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.11.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen J., Yu Y., Li H., Hu Q., Chen X., He Y., Xue C., Ren F., Ren Z., Li J. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 promotes tumor progression by regulating the miR-143/HK2 axis in gallbladder cancer. Mol. Cancer. 2019;18:33. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-0947-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang S.H., Ma F., Tang Z.H., Wu X.C., Cai Q., Zhang M.D., Weng M.Z., Zhou D., Wang J.D., Quan Z.W. Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates FOXM1 expression by competitively binding endogenous miR-342-3p in gallbladder cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;35:160. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0436-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cai Q., Wang S., Jin L., Weng M., Zhou D., Wang J., Tang Z., Quan Z. Long non-coding RNA GBCDRlnc1 induces chemoresistance of gallbladder cancer cells by activating autophagy. Mol. Cancer. 2019;18:82. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1016-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Vogt P.K. Fortuitous convergences: the beginnings of JUN. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:465–469. doi: 10.1038/nrc818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hoeffler W.K., Levinson A.D., Bauer E.A. Activation of c-Jun transcription factor by substitution of a charged residue in its N-terminal domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:1305–1312. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.7.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mishra R.K., Potteti H.R., Tamatam C.R., Elangovan I., Reddy S.P. c-Jun is required for nuclear factor-κB-dependent, LPS-stimulated Fos-related antigen-1 transcription in alveolar macrophages. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016;55:667–674. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0028OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yang L., Liu C.C., Zheng H., Kanekiyo T., Atagi Y., Jia L., Wang D., N’songo A., Can D., Xu H. LRP1 modulates the microglial immune response via regulation of JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Neuroinflammation. 2016;13:304. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0772-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Roszak J., Smok-Pieniążek A., Stępnik M. Transcriptomic analysis of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway reveals the dual role of the c-Jun oncogene in cytotoxicity and the development of resistance in HL-60 leukemia cells in response to arsenic trioxide. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017;26:1335–1342. doi: 10.17219/acem/65475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Volders P.J., Helsens K., Wang X., Menten B., Martens L., Gevaert K., Vandesompele J., Mestdagh P. LNCipedia: a database for annotated human lncRNA transcript sequences and structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D246–D251. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang L., Park H.J., Dasari S., Wang S., Kocher J.P., Li W. CPAT: Coding-Potential Assessment Tool using an alignment-free logistic regression model. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:e74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang S.H., Wu X.C., Zhang M.D., Weng M.Z., Zhou D., Quan Z.W. Upregulation of H19 indicates a poor prognosis in gallbladder carcinoma and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015;6:15–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wu X.S., Wang X.A., Wu W.G., Hu Y.P., Li M.L., Ding Q., Weng H., Shu Y.J., Liu T.Y., Jiang L. MALAT1 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of gallbladder cancer cells by activating the ERK/MAPK pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014;15:806–814. doi: 10.4161/cbt.28584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hu Y.P., Jin Y.P., Wu X.S., Yang Y., Li Y.S., Li H.F., Xiang S.S., Song X.L., Jiang L., Zhang Y.J. LncRNA-HGBC stabilized by HuR promotes gallbladder cancer progression by regulating miR-502-3p/SET/AKT axis. Mol. Cancer. 2019;18:167. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1097-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhang Y., Baysac K.C., Yee L.F., Saporita A.J., Weber J.D. Elevated DDX21 regulates c-Jun activity and rRNA processing in human breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 2014;16:449. doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0449-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lee D.G., Lee S.H., Kim J.S., Park J., Cho Y.L., Kim K.S., Jo D.Y., Song I.C., Kim N., Yun H.J. Loss of NDRG2 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gallbladder carcinoma cells through MMP-19-mediated Slug expression. J. Hepatol. 2015;63:1429–1439. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Xu S., Zhan M., Jiang C., He M., Yang L., Shen H., Huang S., Huang X., Lin R., Shi Y. Genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies ELP5 as a determinant of gemcitabine sensitivity in gallbladder cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:5492. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13420-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xue Z., Yang B., Xu Q., Zhu X., Qin G. Long non-coding RNA SSTR5-AS1 facilitates gemcitabine resistance via stabilizing NONO in gallbladder carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020;522:952–959. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Huang X.L., Zhang H., Yang X.Y., Dong X.Y., Xie X.Y., Yin H.B., Gou X., Lin Y., He W.Y. Activation of a c-Jun N-terminal kinase-mediated autophagy pathway attenuates the anticancer activity of gemcitabine in human bladder cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2017;28:596–602. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ren X., Zhao W., Du Y., Zhang T., You L., Zhao Y. Activator protein 1 promotes gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer by upregulating its downstream target Bim. Oncol. Lett. 2016;12:4732–4738. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tu M., Li H., Lv N., Xi C., Lu Z., Wei J., Chen J., Guo F., Jiang K., Song G. Vasohibin 2 reduces chemosensitivity to gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer cells via Jun proto-oncogene dependent transactivation of ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2. Mol. Cancer. 2017;16:66. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0619-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wu Z.H., Lin C., Liu M.M., Zhang J., Tao Z.H., Hu X.C. Src inhibition can synergize with gemcitabine and reverse resistance in triple negative breast cancer cells via the AKT/c-Jun pathway. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0169230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shen S., Wang J.W., Zheng B.H., Ni X.J., Gao Z.H., Zhang D.X., Lu P.X., Ni X.L., Suo T., Liu H.B., Liu H. The lnc-CITED2-2:1 inhibits metastasis via inhibiting CITED2 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gallbladder cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020;10:e116. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Huang W., Sherman B.T., Lempicki R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009;4:44–57. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Huang W., Sherman B.T., Lempicki R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:1–13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Li Z., Zhang J., Liu X., Li S., Wang Q., Di Chen, Hu Z., Yu T., Ding J., Li J. The LINC01138 drives malignancies via activating arginine methyltransferase 5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:1572. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04006-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Liu L.Z., Zhang Z., Zheng B.H., Shi Y., Duan M., Ma L.J., Wang Z.C., Dong L.Q., Dong P.P., Shi J.Y. CCL15 recruits suppressive monocytes to facilitate immune escape and disease progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2019;69:143–159. doi: 10.1002/hep.30134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Duan F., Wu H., Jia D., Wu W., Ren S., Wang L., Song S., Guo X., Liu F., Ruan Y., Gu J. O-GlcNAcylation of RACK1 promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2018;68:1191–1202. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fan K., Zhang D., Li M., Shen S., Wang J., Ni X., Gong Z., Zheng B., Gao Z., Ni X. Carboxyl-terminal polypeptide fragment of MUC16 combing stathmin1 promotes gallbladder cancer cell migration and invasion. Med. Oncol. 2020;37:114. doi: 10.1007/s12032-020-01438-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zheng B.H., Ma J.Q., Tian L.Y., Dong L.Q., Song G.H., Pan J.M., Liu Y.M., Yang S.X., Wang X.Y., Zhang X.M. The distribution of immune cells within combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma predicts clinical outcome. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020;10:45–56. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.