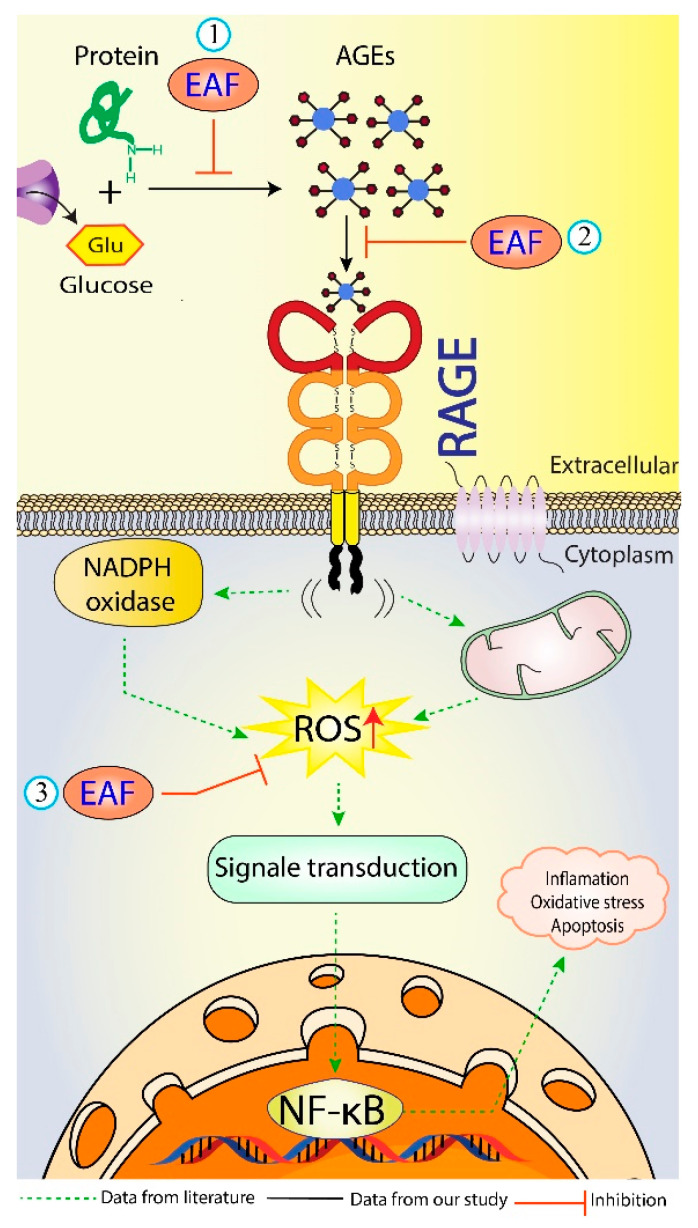
Figure 6.
Schematic representation showing the possible antiglycation mechanisms of EAF of E. fragilis. (1) Inhibition of harmful AGEs formation, (2) Blocking of AGEs-RAGE interaction, and (3) Inhibition of ROS formation during glycation. AGEs = advanced glycation end products; RAGE = receptor of AGEs; ROS = reactive oxygen species.