Abstract
Background:
Cannabis effects are predominantly mediated by pharmacological actions on cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptors. Prior positron emission tomography (PET) studies in individuals who use cannabis included almost exclusively males. PET studies in females are needed because there are sex differences in cannabis effects, progression to Cannabis Use Disorder (CUD), and withdrawal symptom severity.
Methods:
Females with CUD (N=10) completed two double-blind cannabis smoking sessions (Session 1: placebo; Session 2: active) and acute cannabis effects were assessed. After Session 2, participants underwent three days of monitored cannabis abstinence; mood, craving, and withdrawal symptoms were assessed and a PET scan (radiotracer: [11C]OMAR) followed. [11C]OMAR Distribution volume (VT) from these participants was compared with VT of age/BMI-similar female non-users of cannabis (“healthy controls”; N=10). VT was also compared between female and male healthy controls (N=7).
Results:
Females with CUD displayed significantly lower VT than female healthy controls in specific brain regions (hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate, insula). Amygdala VT was negatively correlated with mood changes (Anger/Hostility) during abstinence, but VT was not correlated with other withdrawal symptoms or cannabis effects. Among healthy controls, females had significantly higher VT than males in all brain regions examined.
Conclusions:
Chronic cannabis use appears to foster downregulation of CB1 receptors in women, as observed previously in men, and there are inherent sex differences in CB1 availability. Future studies should elucidate the timecourse of CB1 downregulation among females who use cannabis and examine the relation between CB1 availability and cannabis effects among other populations (e.g., infrequent users; medicinal users).
Introduction
Cannabis use has increased in recent years as legalization of the drug has expanded. In the U.S., where cannabis is now legal for medicinal purposes in 35 states and non-medicinal (“recreational”) purposes in 15 states, the percentage of adults reporting past-year cannabis use increased from 10.4% in 2002 to 17.5% in 20191,2. One negative consequence of chronic cannabis use is the potential for development of Cannabis Use Disorder (CUD)3–5. Individuals with CUD may experience various problems related to their cannabis use such as an inability to stop using despite medical or psychosocial problems, development of tolerance, and emergence of withdrawal symptoms upon abstinence3. Given that in the U.S. alone, approximately 6.4 million people have CUD2, further understanding of the neurological consequences associated with regular cannabis use is needed.
The endocannabinoid system is comprised of two main G protein-coupled receptors: cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) and type 2 (CB2). The two main endogenous ligands which bind to, and activate, these receptor subtypes are N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG)6,7. The primary psychoactive constituent of cannabis (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol; THC) is a partial agonist at CB1 and CB2 receptors8 and is believed to be the main driver of the hallmark effects (e.g., subjective “high”, paranoia, cognitive impairment) synonymous with using THC-dominant cannabis9–12. Cannabis/THC produces such a wide range of acute effects because CB1 receptors are located in high density in many brain regions, including those involved in drug reward, mood, motor functioning, learning, and higher-order cognition13–17.
In prior positron emission tomography (PET) studies15,16,18, individuals who used cannabis chronically displayed significantly lower CB1 receptor availability than healthy controls (i.e., non-users of cannabis), suggesting repeated cannabis use produces CB1 downregulation. These studies are limited, however, because they included nearly all male participants; of the three prior applicable studies, two15,18 included exclusively males and the other16 only included two females. Importantly, key sex differences have been observed following both acute and long-term cannabis exposure. First, females are more sensitive to acute cannabis effects than males. After smoking cannabis, females report higher ratings on subjective items of abuse liability (e.g., “good drug effect”) than males matched for cannabis-use characteristics19. Among individuals who use cannabis infrequently, women report stronger negative/adverse cannabis effects (e.g., “anxious/nervous”) than men20. In another study21, females and males smoked a cannabis joint ad libitum; females experienced similar magnitude of pharmacodynamic effects as males, despite the fact that they smoked significantly less and were exposed to less THC than males. Second, upon abstinence from regular cannabis use, females exhibit more severe withdrawal symptoms than males22,23; moreover, CUD reduces self-reported quality of life to a greater extent in females vs. males24. Finally, relative to men, women show an accelerated trajectory from their first use of cannabis to the development of CUD (i.e., a “telescoping effect”)25,26. Taken together, these findings underscore the need for neuroimaging studies with female participants to elucidate potential neuroadaptations of CB1 receptors related to chronic cannabis use, and to examine whether individual-level characteristics (e.g., acute drug effects, magnitude of withdrawal) are related to CB1 receptor availability.
This study extends prior PET studies that included predominantly male participants by comparing CB1 receptor availability in females with CUD to that of female healthy controls (i.e., non-users). Females with CUD completed two cannabis self-administration sessions and a monitored three-day period of cannabis abstinence, and we explored the relation between acute cannabis effects and mood/craving/withdrawal and CB1 receptor availability. The length of the inpatient stay was set at three days based on prior studies which have shown that cannabis withdrawal symptoms typically emerge and peak within the first three days after cessation.27,28 We hypothesized that females with CUD would show lower CB1 availability compared to female controls. We also hypothesized that CB1 availability in regions associated with mood regulation (i.e., amygdala, hippocampus) would be correlated with negative mood, craving, and withdrawal symptoms during cannabis abstinence, while CB1 availability in regions associated with reward, cognition, and/or motor functioning (i.e., cingulate, frontal cortex, putamen, ventral striatum) would be correlated with acute pharmacodynamic effects of cannabis.
As a secondary aim, we compared CB1 availability in male and female healthy controls to explore potential CB1 sex differences, unrelated to cannabis use. Preliminary studies of non-cannabis users have detected differences in CB1 availability between men and women, but have opposing results; one study showed higher CB1 availability in men29 and two others14,30 showed higher CB1 availability in women. We extend these studies by imaging female participants in the same menstrual cycle phase (follicular) to minimize the influence of hormonal changes on radiotracer binding to CB1 receptors.
Methods
The present study was conducted at the Johns Hopkins University (JHU) Behavioral Pharmacology Research Unit, the JHU Clinical Research Unit (CRU), and the JHU Hospital PET Imaging Center. The JHU School of Medicine Institutional Review Board approved all study procedures which were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was registered on ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03204305).
Participants
This report describes data for three sets of participants: 1) women with CUD; 2) contemporary female healthy controls; 3) female and male historical healthy controls. All participants provided written informed consent prior to being enrolled in the study.
Females with CUD and Contemporary Female Controls.
Healthy female volunteers (18–50 years old) who used cannabis or did not use cannabis were recruited from the Baltimore metropolitan area using online and print media advertisements. Potential study candidates first completed a brief telephone screen and those who appeared eligible were invited for an in-person screening visit where they were interviewed using a battery of diagnostic and psychological instruments to determine study eligibility. Recent drug/alcohol use was assessed via the 90-day Timeline Follow-Back31 and participants also completed the Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI)32 for DSM-V (MINI, v.7) to determine whether they met criteria for any psychiatric conditions or substance use disorders. Candidates also completed a medical assessment that included a medical history review, an electrocardiogram (EKG), routine blood testing (chemistry, hematology, serology), urine drug toxicology and pregnancy tests, breath alcohol and exhaled CO tests, and a physical examination. Participants were also trained on cognitive performance tasks (see below) at the screening session until they reached a stable baseline to avoid practice effects during the drug administration sessions.
Primary inclusion criteria for women who used cannabis were: use of cannabis, on average, ≥25 days per month in the past three months; positive urine specimen for cannabis; meet DSM-V criteria for moderate or severe CUD; and report ≥2 cannabis withdrawal symptoms during a past cannabis abstinence period. For healthy contemporary controls, primary inclusion criteria were: no cannabis use for >12 months; ≤5 lifetime cannabis uses; and negative urine test for cannabis.
Primary exclusion criteria for all contemporary participants included: psychiatric or substance use disorder (aside from CUD for cannabis users); serious medical condition; medication use that may impact participant safety or interfere with study outcomes (e.g., hormonal contraceptives); seeking treatment for cannabis-related problems; unstable hypertension; positive test for pregnancy or illicit drugs (aside from cannabis for women with CUD); past-year radiation exposure that would result in cumulative exposure of ≥5 rem after study completion; and clinically-significant EKG or incidental MRI finding.
Historical Male and Female Healthy Controls.
Historical healthy controls who did not use cannabis were selected from datasets for prior [11C]OMAR studies of males13 and females (Klarman Family Foundation, unpublished). Historical controls were selected to match age and BMI ranges for women with CUD from the current study.
Historical controls met similar inclusion/exclusion criteria: good health (e.g., medical history, lab results, physical examination); no psychiatric or substance-use disorders; no self-reported drug use or heavy alcohol use in the last 90 days; negative urine test for common drugs of abuse (e.g., amphetamine, cocaine, opiates, cannabis, etc.).
Procedures
Cannabis Administration Sessions.
Cannabis users completed two acute drug administration sessions in which they smoked cannabis, via a hand-held pipe, containing either ~0mg THC or 25mg THC; participants and research staff were blinded to THC dose. Active and placebo cannabis was obtained from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Drug supply program. Cannabis was stored in a freezer and rehydrated (for at least 24 hours) before being administered to participants. Sessions were completed in a fixed order (session 1: placebo; session 2: active) so that the time since last cannabis use would be consistent for all participants during subsequent procedures. Active cannabis had a high concentration of THC (13.4%) and a low concentration (<1%) of cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabinol (CBN). Placebo cannabis contained <0.01% THC and did not contain detectable levels of CBD or CBN. The quantity of plant material in the pipe was the same for placebo and active sessions (186.6 mg). After each drug administration, research staff returned the pipe to BPRU pharmacy staff who confirmed, via visual inspection, that all plant material had turned to ash (this indicated that the full dose was administered).
Prior to drug administration in each session, participants were fed a standard low-fat breakfast (~300 calories), had IV catheter placed in their forearm vein, had a baseline blood sample collected, and completed baseline pharmacodynamic measures (i.e., cognitive performance, subjective effects, vital signs). Blood samples were collected and pharmacodynamic measures were completed periodically (i.e., 15–30 min intervals) for three hours following cannabis administration. During each session, participants were instructed to smoke the entire contents of the pipe (which was pre-loaded with either placebo or active cannabis by BPRU pharmacy staff) ad libitum within a 10-minute period; the pipe was fitted with a metal top to obstruct the view of the plant material and preserve the study blind, as active and placebo cannabis may differ in color.
Inpatient Period.
Immediately following session 2, females with CUD were admitted to an inpatient facility (the CRU) for three days. During this time, participants were medically monitored and could not use cannabis or any other drugs and were not permitted to have visitors. Mood, craving, and withdrawal symptoms were assessed twice daily (see below).
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
Prior to their PET scan, all participants completed a volumetric MRI scan, on a 3-T Prisma scanner, using a spoiled GRASS (gradient recalled acquisition in steady state) SPGR sequence. The purpose of the MRI scan was to enable sampling of PET data in specific brain regions of interest (or volumes of interest; VOI) for each individual participant (see below).
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan.
PET scans were completed on a Siemens ECAT HRRT brain-dedicated high resolution scanner33 using the radiotracer [11C]OMAR. Women with CUD completed their scan after three days of monitored cannabis abstinence, while healthy controls completed their scan during an outpatient visit. A facemask was custom-made for each participant to minimize head movement during the scan. An intravenous catheter was inserted into a forearm vein to allow for injection of the radioligand. An arterial catheter was also inserted into the radial artery at the wrist, on the hand opposite the intravenous catheter, to allow for repeated blood sampling. Following a 6-minute attenuation scan, a slow bolus dose (over 1 minute) of [11C]OMAR (18–20 millicurie, mCi) was administered intravenously and acquisition of dynamic PET data in 3-D list mode commenced, which lasted 90 minutes. Specific activity and mass of [11C]OMAR was comparable across participants (see supplementary Table 1).
For approximately the first 5 minutes of the scan, arterial blood samples (~2 mL) were collected rapidly (every 5 seconds). Larger blood samples (~5 mL) were collected at 5, 10, 30, 60, and 90 minutes. PET scans were performed on a Siemens ECAT HRRT brain-only PET scanner (Siemens Healthcare, Knoxville, TN) which has expected resolutions of less than 2.5mm in three directions33.
PET scans were reconstructed using the iterative ordered-subset expectation-maximization (OSEM) algorithm which corrected for normalization, attenuation, scatter, random, and dead-time34. The frame schedule used was as follows: four 15-seconds, four 30-seconds, three 1-minute, two 2-minute, five 4-minute, and twelve 5-minute frames. This resulted in a total of 30 frames for the 90-minute scan. Each PET frame consisted of 256 (left-to-right) by 256 (nasion-to-inion) by 207 (neck-to-cranium) of cubic voxels (1.27mm).
Radioactivity concentrations of [11C]OMAR in plasma were measured with a cross-calibrated gamma counter and corrected for physical decay relative to the tracer injection time. Fractions of radioactive metabolites in plasma were quantified using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)13. Time-radioactivity curves (TACs) of metabolite-corrected fractions were obtained by interpolating parent fractions from HPLC at blood sampling times using the shape-preserving piecewise cubic interpolation function of Matlab (MathWorks, Natick, Massachusetts).
Additional Procedures for Female Participants.
At screening, all women (including historical controls) provided details on their recent menstrual history. Upon enrollment, women were instructed to track their menstrual cycles and to report their first day of menstruation to staff. PET scan dates were scheduled within the first 12 days of their menstrual phase to target the follicular phase. Blood samples were collected on the day of the PET scan for analysis of plasma progesterone to verify they were in the follicular phase; all females (i.e., contemporary and historical participants) were confirmed to be in their follicular phase at the time of their scan based on blood progesterone concentrations being <1.0 ng/ml.
Outcome Measures
Cannabis Administration Sessions.
Pharmacodynamic outcomes measured during the two cannabis administration sessions included: 1) subjective drug effects, assessed with a 21-item Drug Effect Questionnaire (DEQ) that consisted of items reflective of positive/reinforcing drug effects (e.g., “like drug effect”), negative/aversive effects (e.g., “unpleasant drug effect”), and mood states related specifically to cannabis intoxication (e.g, “paranoid”; “hungry/have munchies”)11,12. Items were presented individually on a 100mm visual analog scale; 2) cognitive and psychomotor performance, assessed with three computerized tasks previously shown to be sensitive to cannabis intoxication: the Digit Symbol Substitution Task (DSST)35, the Divided Attention Task (DAT)36, and the Paced Auditory Serial Addition Task (PASAT)37; for detailed descriptions of these tasks see11,12, and 3) vital signs (i.e., heart rate and systolic/diastolic blood pressure). Blood samples were collected in each session and analyzed (via LC-MS/MS11,38,39) for concentrations of THC and its two primary metabolites (11-OH-THC and THCCOOH).
Inpatient Period.
Each day during the inpatient stay, women with CUD completed a series of psychological self-report instruments including: the Marijuana Withdrawal Checklist (MWC)27, the Marijuana Craving Questionnaire Short Form (MCQ-SF)40, and the Profile of Mood States (POMS)-2 Adult Short Form41,42; these were also all given prior to sessions 1 and 2 (when participants were using cannabis as usual).
On the MWC, participants rated the severity of 32 symptoms on a scale of 0 (not at all) to 3 (severe); several items were non-specific in nature to minimize response bias. Items assessed a combination of mood (e.g., “depressed mood”; “nervousness/anxiety”) and physiological symptoms (e.g., “sweating”; “stomach pains”; “dizziness”) and collectively yielded a composite withdrawal discomfort score. On the MCQ-SF, cannabis-related craving was assessed with 14 items which were reflective of four distinct dimensions of craving (i.e., compulsivity, emotionality, expectancy, and purposefulness). The POMS-2-Short evaluates six distinct dimensions of mood (i.e., Tension/Anxiety, Anger/Hostility, Vigor/Activity, Fatigue/Inertia, Depression/Dejection, and Confusion/Bewilderment) using 35 separate subjective items (5 of the items are “dummy items” that are not incorporated into overall domain scores). In addition to the individual subscales, the POMS-2-Short also yields a total mood disturbance score.
Volumes of Interest (VOIs).
MRIs were submitted to Freesurfer software version 6.043 (http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu) for automated parcellation of brain regions. We focused on eight VOIs (ventral striatum, amygdala, putamen, cingulate, globus pallidus, insula, frontal cortex, and hippocampus); these brain regions were chosen a priori because they are associated with drug reward, mood, cognition, motor function, and/or habit learning. The frontal cortex VOI included original Freeserver VOIs belonging to the frontal cortex44. The VOIs were transferred to PET space by utilizing MRI-to-PET co-registration parameters, using the co-registration module of SPM12 (https://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm), and applied on PET frames to obtain TACs for each VOI.
[11C]OMAR Distribution Volume (VT).
VT values of individual regions were obtained by plasma-reference graphical analysis, PRGA13,45. A composite VT was calculated as weighted means of original Freesurfer VOIs of the above eight regions (minus the ventral striatum) and the cerebellum, anterior and posterior cingulate cortices, occipital, parietal and temporal cortices, and thalamus, to closely approximate the composite regions defined by D’Souza et al., 201615.
Data Analysis
Peak change-from-baseline pharmacodynamic data from the cannabis administration sessions were analyzed using linear mixed models. These analyses included the 14 participants who completed the active and placebo sessions. Separate analyses were conducted for each outcome, cannabis dose (active vs placebo) was the lone factor in the models, and the covariance structure used was compound symmetry (CS). Bonferroni corrections were made to reduce family-wise error rate.
For the MWC, MCQ-SF, and POMS-2-Short, paired samples t-tests compared baseline scores (i.e., when participants were using cannabis as usual before the second cannabis smoking session) to peak scores observed during cannabis abstinence. Bonferroni corrections were made to reduce family-wise error rate.
VT (in each VOI) was compared between: 1) females with CUD who completed the PET scan (N=10) and female healthy controls (N=10, two contemporary and eight historical controls) and 2) female and male healthy controls (N=7), using the following approach: a robust linear regression model with group status (e.g., CUD vs. control) encoded as a dummy variable, age as a covariate, and VT for the eight VOIs as the dependent variables, followed by post-hoc comparisons (Tukey’s HSD) between groups. Composite VT was compared between the same groups using independent samples t-tests.
Correlations (Spearman’s ρ) explored relations between: 1) VT in the amygdala, hippocampus, and composite VT and severity of cannabis withdrawal symptoms, mood disturbance, and craving during the inpatient stay (peak-change-from-baseline), 2) VT in the ventral striatum, cingulate, frontal cortex, putamen, and composite VT and positive subjective effects and cognitive performance (peak-change-from-baseline) following active cannabis administration. These specific correlations were hypothesis-driven and decided on a priori (see introduction). Significance was set at p<.05 for all analyses. Bonferroni corrections were made to reduce family-wise error rate.
Statistical parametric mapping (SPM) tested for VT differences between groups of interest (i.e., females with CUD vs. female healthy controls and male vs. female healthy controls), without restriction of VOIs. VT maps were generated by applying PRGA to PET voxels. MRIs were spatially normalized to Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space using SPM-supplied probabilistic templates. VT maps were spatially normalized by applying parameters of PET-to-MRI co-registration and MRI spatial normalization parameters and smoothed by a Gaussian kernel of 8 mm (full-width at half-maximum, FWHM). Clusters are reported when the extent threshold exceeded p<0.05, false-discovery-rate (FDR)-corrected, while setting height threshold at p<0.005, uncorrected.
Results
Participants
Table 1 depicts participant demographic characteristics. BMI and age were compared across groups of interest using independent samples t-tests (i.e., females with CUD vs. female healthy controls; male vs. female healthy controls). Neither BMI or age differed significantly across these groups. Figure 1 (CONSORT diagram), shows the participation flow of females with CUD and contemporary controls.
Table 1.
Demographic Characteristics
| Mean (SD) or Number | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Females with CUD (N=10) | Female HC (N=10) | Male HC (N=7) |
| Age (years) | 23.2 (2.7) | 25.5 (5.0) | 29.6 (6.9) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.7 (6.0) | 23.6 (4.3) | 24.4 (2.1) |
| Race: Caucasian (#) | 4 | 9 | 1 |
| Race: Black/AA (#) | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| Race: Other or unknown (#) | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Cigarette Smokers (#) | 1* | 1# | 0 |
| Grams Cannabis Used/Day | 4.8 (3.0) | N/A | N/A |
| Days of Cannabis Use in Past 90 | 83.6 (10.4) | N/A | N/A |
| Age of First Cannabis Use | 15.3 (3.0) | N/A | N/A |
| Years of Cannabis Use | 7.9 (4.3) | N/A | N/A |
| Moderate Cannabis Dependence (#) | 7 | N/A | N/A |
| Severe Cannabis Dependence (#) | 3 | N/A | N/A |
Note: CUD = cannabis use disorder; HC = healthy controls; AA = African American; BMI = body mass index; N/A = not applicable for those participants. Two of 10 female HC were contemporary participants while remaining 8 were historical controls.
= smoked 2 cigarettes/day;
= smoked 3 cigarettes/week.
BMI data missing for 2 male healthy controls.
Figure 1:
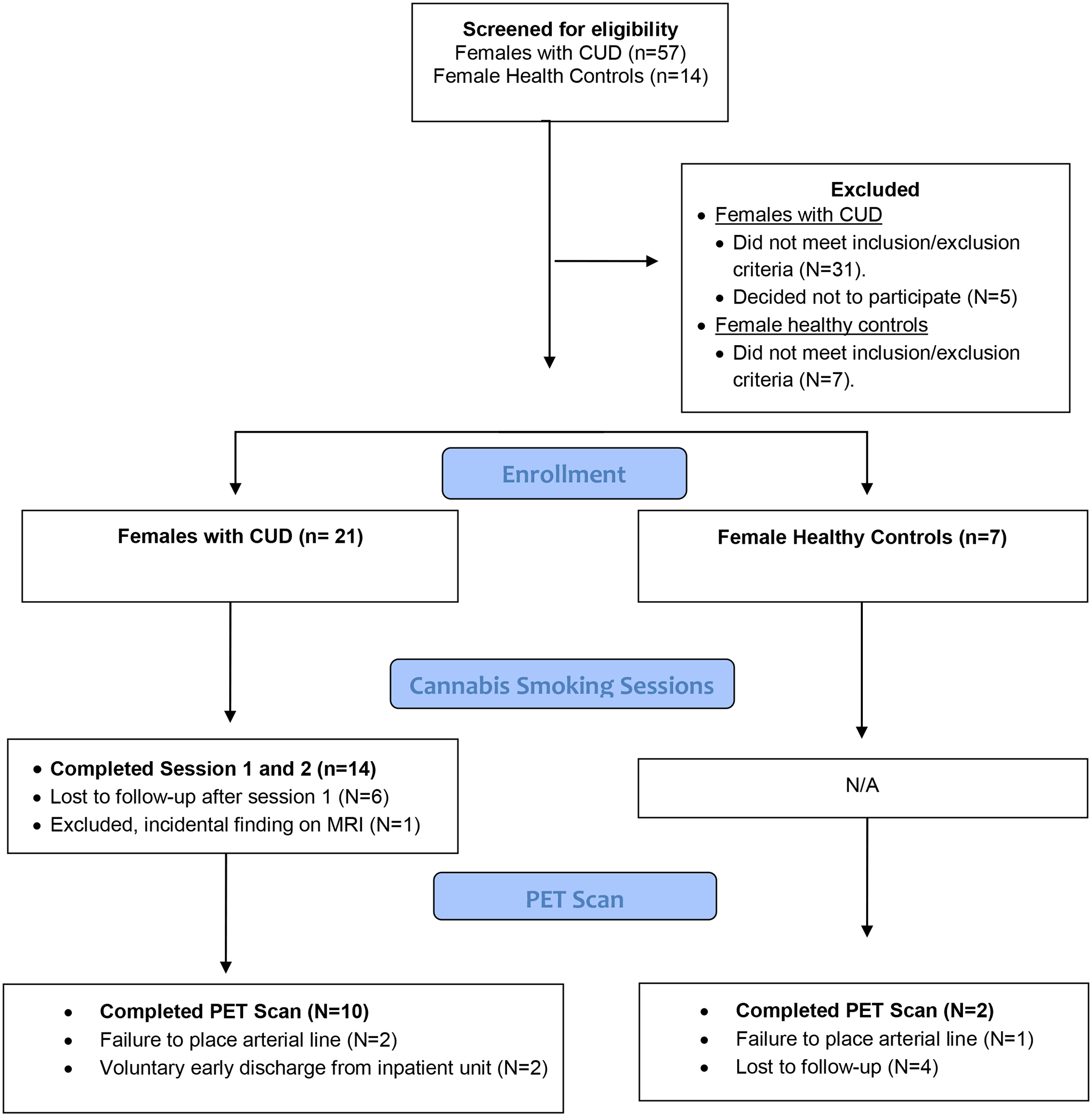
CONSORT diagram. N/A= not applicable for that participant group.
Cannabis Administration Session Data
Figure 2 depicts data from cannabis administration sessions. Participants (N=14) reported higher ratings for “Drug Effect” (F=31.32, p<.001), “Pleasant” (F=21.10, p<.001), “Like” (F=19.16, p<.001), and “Throat Irritated” (F=5.15, p=.04) in the active session relative to placebo; “Drug Effect” (F=31.32, p=.001), “Pleasant” (F=21.10, p=.01), and “Like” (F=19.16, p=.02) each remained significant after the Bonferroni correction was applied, but “Throat Irritated” did not survive the alpha correction. DSST performance was worse in the active, compared to placebo condition (F=9.0, p=.01), though this result did not remain significant after applying the alpha correction. DAT and PASAT performance did not differ between sessions. Heart rate increased significantly (F=26.79, p<.001) after active cannabis administration relative to placebo and this finding remained significant with the Bonferroni correction (F=26.79, p=.001) (see Supplementary Table 2 for full results for pharmacodynamic data).
Figure 2:
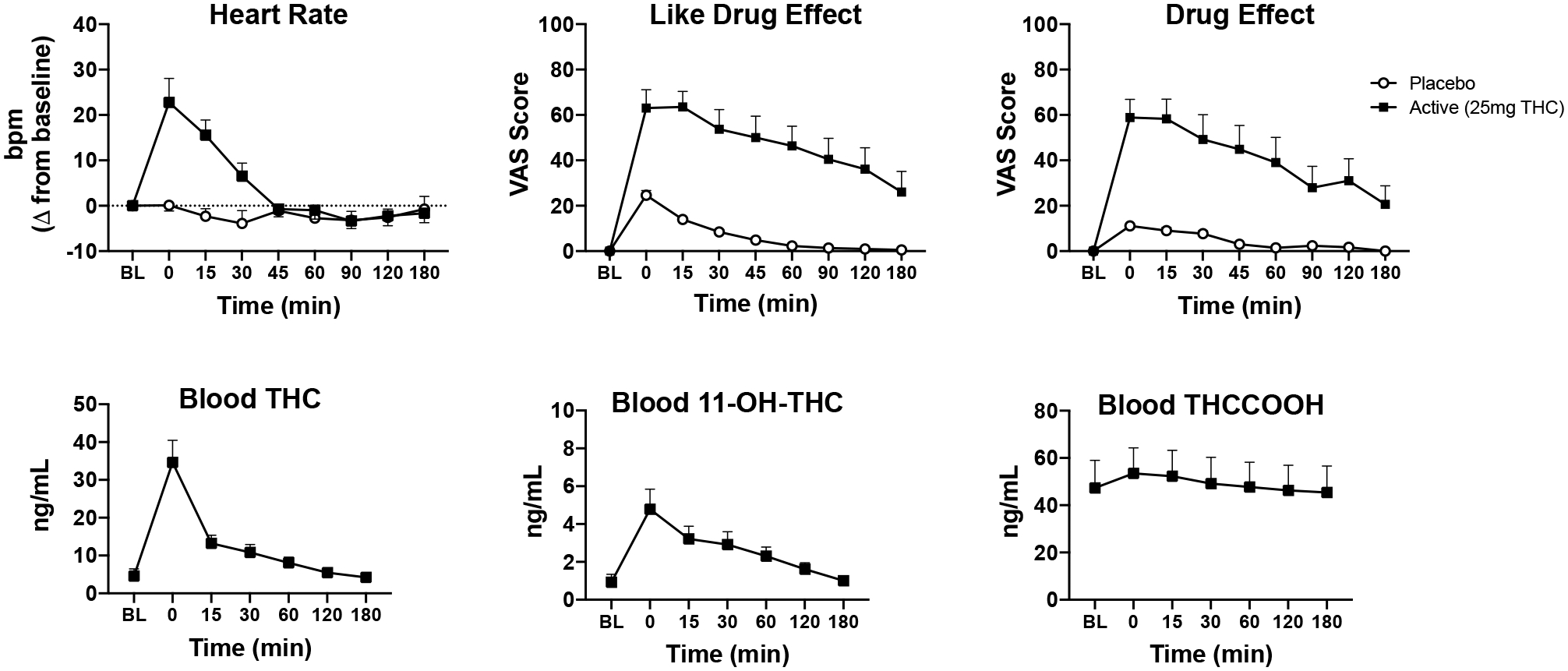
Mean (+SEM) data for heart rate (beats per min, bpm), subjective drug effect ratings (“Drug Effect” and “Like”), and blood concentrations of THC and THC metabolites (11-OH-THC, THCCOOH), over time for female cannabis users (N=14) during the two acute cannabis administration sessions: placebo (i.e., 0 mg THC) and active (i.e., 25 mg THC). Note that blood THC data are only displayed from active sessions.
Inpatient Abstinence Data
POMS-2-Short scores for Depression/Dejection” (t=−2.86, p=.02), Tension/Anxiety (t=−3.28, p=.01), and Vigor/Activity (t=−10.58, p<.001) were elevated during cannabis abstinence relative to baseline (i.e., cannabis use as usual); however, once the Bonferroni alpha corrections were applied, only Vigor/Activity remained significant (t=−10.58, p<.001). MWC composite withdrawal discomfort score (t=−2.52, p=.03) and MCQ-SF compulsivity (t=−2.51, p=.03) and expectancy scores (t=−2.41, p=.04) increased during cannabis abstinence relative to baseline, but the significant findings on the MCQ-SF did not survive the alpha correction (see Supplementary Table 3 for full results for inpatient cannabis abstinence data).
[11C]OMAR Distribution Volume (VT) Comparisons
As shown in Figure 3, females with CUD displayed lower VT than female healthy controls in the amygdala (estimated difference, ED=−0.28+/−0.11, t=−2.51, p=0.02), cingulate (ED=−0.25+/−0.11, t=−2.36, p=0.03), hippocampus (ED=−0.27+/−0.11, t=−2.35, p=0.03) and insula (ED=−0.25+/−0.11, t=−2.23, p=0.04); VT in the other four VOIs (ventral striatum, putamen, globus pallidus, frontal cortex) and composite VT did not differ significantly between these two groups.
Figure 3:
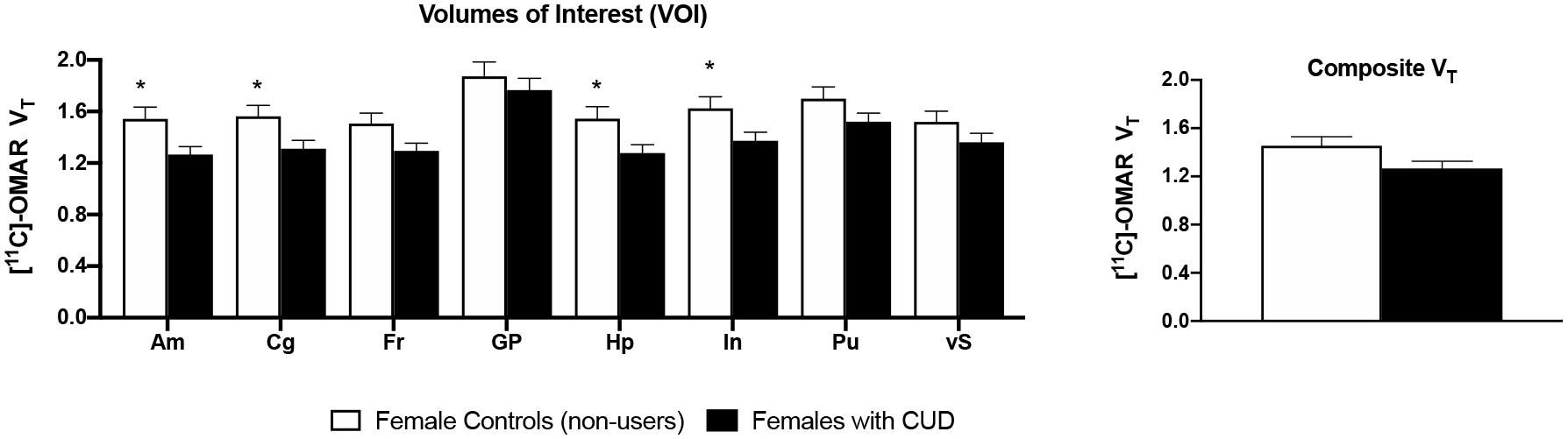
Mean (+SEM) VT values for 8 volumes of interest (VOIs) and composite VT. Asterisks (*) signify significant differences between females with CUD and female healthy controls who did not use cannabis (p<.05). On average, females with CUD showed a 16–18% decrease in VT in the amygdala, cingulate, hippocampus, and insula compared with controls.
As shown in Figure 4, female healthy controls displayed higher VT than male healthy controls in the amygdala (ED=0.40+/−0.12, t=3.22, p<0.01), cingulate (ED=0.37+/−0.12, t=3.20, p<0.01), frontal cortex (ED=0.33+/−0.11, t=2.97, p<0.01), globus pallidus (ED=0.49+/−0.15, t=3.18, p<0.01), hippocampus (ED=0.35+/−0.13, t=2.76, p=0.01), insula (ED=0.38+/−0.12, t=3.10, p<0.01), putamen (ED=0.39+/−0.13, t=3.10, p<0.01), and ventral striatum (ED=0.31+/−0.12, t=2.68, p=0.02). Composite VT was higher in female vs. male controls (t=2.95, p=0.01).
Figure 4:
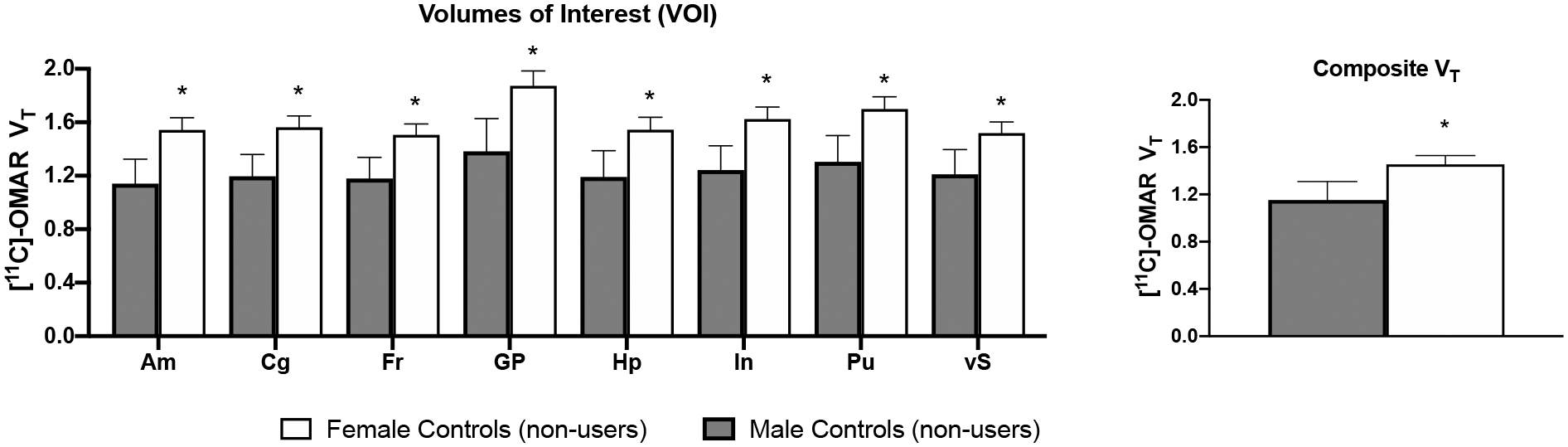
Mean (+SEM) VT values for 8 volumes of interest (VOIs) and composite VT. Asterisks (*) signify significant differences between male and female healthy controls who did not use cannabis (p<.05). On average, female controls showed a 20–26% increase in VT in the 8 VOIs and a 21% increase in composite VT compared with male controls.
Correlations Between VT and Behavioral Outcomes Among Females with CUD
VT in the amygdala and hippocampus were negatively correlated with peak-change-from-baseline scores for Anger/Hostility on the POMS-2-Short (amygdala: ρ=−.79, p=.007; hippocampus: ρ=−.69, p=0.03). Peak-change-from-baseline scores for MCQ-SF Factor 4 (purposefulness) were positively correlated with hippocampus VT (ρ=.73, p=0.02). Once the Bonferroni alpha corrections were applied, the correlation between VT in the amygdala and Anger/Hostility on POMS-2-Short remained significant (ρ=−.79, p=.047), but the other two significant correlations noted above did not survive the alpha correction (see supplementary Table 4). There were no other significant correlations between amygdala and hippocampus VT (nor composite VT) and inpatient data.
There were no significant correlations between VT in the ventral striatum, cingulate, frontal cortex, and putamen (nor composite VT) and pharmacodynamic effects including positive subjective effects and cognitive performance (see supplementary Table 4 for full correlation results).
SPM Voxel-Wise VT Comparisons
Female healthy controls showed extended areas of greater VT compared with male healthy controls (p<0.001, FDR-corrected at cluster level; kE=96478 (777.2mL). The peak T (7.09) was observed (at −36, −32, 42) in the left postcentral gyrus (see Supplementary Figure 1). No above-threshold clusters were observed between females with CUD and female controls.
Discussion
Females with CUD displayed 16–18% lower VT, on average, in the amygdala, cingulate, hippocampus, and insula after three days of monitored cannabis abstinence when compared with female healthy controls. In three prior CB1 PET studies with predominantly male participants15,16,18, comparable (or lower) reductions in VT were observed in individuals who used cannabis regularly relative to healthy controls. Taken together with findings from these other studies, our results suggest that repeated cannabis exposure can foster downregulation of CB1 receptors, though, importantly, the present study is the first to show this effect in females with CUD. A clear causal link between chronic THC exposure and CB1 receptor downregulation has been well established in preclinical research46–49 which further supports our conclusion that chronic cannabis use led to CB1 downregulation among females with CUD in this study. However, more research is needed to understand how chronic cannabis use and different aspects of cannabis use disorder (e.g., withdrawal) impact CB1 receptor availability.
An alternative possible explanation for females with CUD having lower VT is that residual THC interfered with radiotracer binding. However, several lines of evidence cast doubt on this possibility. The radiotracer used ([11C]OMAR) was developed as an antagonist/inverse agonist, in part, because this would reduce the extent to which CB1 agonists (e.g., THC) interfere with its binding. Similar to the present study, D’Souza et al., 201615 found that males with CUD had lower VT than healthy controls; the authors noted that they performed experiments showing intravenously-administered THC did not interfere with [11C]OMAR binding in non-human primates. Similarly, our group verified that acute THC administration (10–40 mg/kg; IP injection) did not displace [11C]OMAR in rodents (Wong, unpublished findings). Moreover, in other preclinical research, mice chronically given THC did not have residual THC in their brains one day after THC cessation and the affinity of a CB1 antagonist (i.e., [3H]SR141716) did not differ between the mice given THC vs. those that were given vehicle following THC cessation50. Thus, overall, we are confident based on the available data that our results are suggestive of CB1 downregulation in females with CUD, as opposed to differential radiotracer binding from residual THC in these individuals vs. healthy controls.
Notably, in prior studies of males with CUD15,18, CB1 downregulation reversed with continued cannabis abstinence. For example, in one study18, male cannabis users had lower regional VT than controls at baseline (i.e., <24 hours into a monitored cannabis abstinence period). When scanned again after 13–32 days of abstinence, VT had increased significantly relative to baseline. In another study15, male cannabis users had lower composite and regional VT than controls at baseline, when participants were not intoxicated nor experiencing any symptoms of cannabis withdrawal, and CB1 receptor downregulation was no longer evident after just 48 hours of cannabis abstinence; interestingly, in the present study, VT differences were observed in some brain regions between females with CUD and healthy controls 72 hours after cannabis abstinence, suggesting the extent of CB1 downregulation may have been greater or more persistent in the females in this study relative to the males in the D’Souza et al., 2016 study15. Overall, these collective findings suggest that CB1 downregulation reflects a state, rather than a trait, condition and may be an explanatory mechanism for the development of aspects of CUD including tolerance, dependence, and craving/withdrawal symptoms during abstinence.
Unlike two prior CB1-focused PET studies16,18, the vast majority of participants in this study did not use tobacco products. Thus, the lower VT observed in females with CUD was not due to tobacco use, which has been associated with lower CB1 receptor availability in men51. Because cannabis and tobacco are often used concurrently52–54 and users of both substances report more severe withdrawal during abstinence than those who use tobacco or cannabis alone55, future PET studies should systematically evaluate the independent and combined effects of nicotine/tobacco and cannabis use on CB1 availability.
Significant negative correlations were detected between VT in the amygdala and hippocampus and Anger/Hostility, a common symptom of cannabis withdrawal28, indicating that participants with greater increases in Anger/Hostility during cannabis abstinence had lower VT in these regions. Though participants exhibited increases in other withdrawal symptoms and craving during monitored cannabis abstinence, these outcomes were of low magnitude (which is not uncommon in residential research settings) and not correlated with VT of specific brain regions, nor composite VT. Of the two other studies that examined relations between VT and cannabis withdrawal/craving symptoms among males, one found a significant correlation between composite VT and withdrawal severity15 while the other found no associations between VT (of various brain regions) and cannabis withdrawal/craving18. Additional studies are needed to clarify whether VT is related to cannabis withdrawal severity or craving during abstinence observed in an outpatient setting, and whether these relations differ between men and women.
Among healthy controls, females displayed greater VT compared with males. These findings are consistent with two prior PET studies14,30, but this is the first study to show this effect in males and females matched by age and BMI and with all females completing PET imaging in their follicular menstrual phase. Contrary to the present study, one PET study29 showed higher regional VT in male vs. female non-cannabis users, though importantly, this study did not control for menstrual phase; thus, differences in circulating hormone levels may have may have contributed to these discrepant findings. There are similar discrepancies across preclinical studies with respect to the directionality of CB1 receptor availability differences between males and females. There is some preclinical evidence that CB1-related sex differences are influenced by hormones and may be brain region-specific. For example, in one study,56 female rats had higher densities of CB1 receptors in the amygdala compared with males, but lower CB1 density in the hypothalamus than males; moreover, this effect was sex steroid-dependent, as an ovariectomy resulted in upregulation of CB1 receptors in some regions among females.56
Also of relevance, the Laurikainen et al study29 used a different CB1 radiotracer ([18F]FMPEP-d2) than the present study and other studies with consistent findings to ours. There are noteworthy differences between [11C]OMAR and [18F]FMPEP-d2 that may also explain the conflicting results between the present study and the Laurikainen et al study29. First, [11C]OMAR is an antagonist/inverse agonist whereas [18F]FMPEP-d2 is an inverse agonist. CB1 receptors exist in either active or inactive states (agonists have a strong preference for binding to active sites whereas antagonists bind to both inactive and active sites similarly)57. Moreover, it has been posited that CB1 agonists may temporarily alter the proportion of active vs. inactive sites, such that more active sites are available in the presence of agonists57. Thus, it is possible binding of inverse agonist radiotracers such as [18F]FMPEP-d2 may be impacted by endogenous endocannabinoid agonists. Second, the brain kinetics of [11C]OMAR and [18F]FMPEP-d2 are distinct and require different types of mathematical modeling. In general, the kinetics of [11C]OMAR are faster than [18F]FMPEP-d2, allowing for quantification of VT in a relatively shorter time (i.e., 90-minutes). Conversely, [18F]FMPEP-d2 kinetics are far slower, with a longer terminal clearance and half-life due to higher CB1 affinity; thus, [18F]FMPEP-d2 requires longer scan times and mathematical modeling to account for the delayed washout time58. Ultimately, studies directly comparing VT derived from [11C]OMAR vs. [18F]FMPEP-d2 in the same individuals (controlling for hormone levels) are likely needed to fully understand the source of the differences across studies.
Nevertheless, results from the present study suggest that women possess innate differences in CB1 receptor availability relative to men. These innate differences may be an explanatory mechanism for cannabis-related sex differences observed in prior studies. For example, relative to men, women report stronger ratings for abuse-related subjective effects (e.g., “take again”) after cannabis self-administration19 and develop CUD at a faster rate following cannabis initiation25,26; both of these findings could be influenced by women’s innately higher VT in regions involved with drug reward (e.g., ventral striatum). Additionally, women exhibit more severe withdrawal symptoms upon abstinence from regular cannabis use than men22,23 and women are more susceptible to experiencing adverse acute effects of cannabis (e.g., acute paranoia, anxiety)20; such findings could at least be partially explained by women’s innately higher VT in regions such as the amygdala.
The strengths of the present study included rigorous control for age and BMI with group matching, limiting tobacco use, and controlling for time since last cannabis use and menstrual cycle phase for PET scans. However, this study had several limitations. First, only females with moderate to severe CUD were included. Thus, although cannabis use and CUD severity was similar among participants, it is unclear whether our findings apply to females who use cannabis less frequently; future studies may also consider including both males and females with CUD to explore whether any study findings differ as a function of sex (e.g., magnitude of CB1 downregulation). Second, only one PET scan was conducted. Future studies of females with CUD should include PET scans during typical cannabis use and several times during cannabis abstinence to better understand temporal alterations in VT. Third, during the cannabis administration sessions, only one active dose of cannabis was administered (25mg THC). Given that these participants used cannabis daily, they were likely tolerant to the effects of cannabis, particularly at this modest dose. It may be beneficial in future studies of this nature to administer higher doses of THC and/or to include individuals who use cannabis intermittently. Fourth, the relatively small sample size may have limited our statistical power for some analyses, particularly for the correlations between VT values and behavioral outcomes. Lastly, as mentioned above, cannabis withdrawal symptoms were measured in an inpatient research setting, which may have influenced responding.
In sum, females with CUD had lower CB1 receptor availability in various brain regions relative to female healthy controls who did not use cannabis. This suggests that, as has been observed previously in males15,18, chronic cannabis use fosters downregulation of CB1 receptors in females. This study also found that, among non-users of cannabis, females generally displayed higher CB1 availability than males. Lastly, CB1 availability (in the amygdala and hippocampus) was negatively correlated with subjective Anger/Hostility ratings during monitored cannabis abstinence, but was not correlated with other withdrawal symptoms or acute cannabis effects. With cannabis legalization continually expanding, it is important to examine the relationship between CB1 availability and behavioral outcomes among a variety of cannabis-using populations (e.g., infrequent vs. daily users; medicinal vs. “recreational” users; young vs. middle-age vs. older adults with CUD).
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Figure 1: Statistical parametric mapping (SPM) analysis revealed a large cluster (p < 0.01, FDR-corrected, consisting of 96478 voxels) showing greater VT values in female healthy controls compared with male healthy controls. The peak T (7.09) was observed (at −36, −32, 42) in the left postcentral gyrus.
Acknowledgments:
We thank the support staff of the Johns Hopkins University (JHU) Behavioral Pharmacology Research Unit, the JHU Clinical Research Unit (Bayview campus), and the Johns Hopkins Hospital (JHH) PET Imaging Center for outstanding contributions to the implementation of this study. We also thank the many individuals involved with the NIDA Drug Supply Program for providing cannabis used in this study and Immunalysis Corporation (Pomona, CA) for conducting blood testing for cannabinoids. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Funding:
This research was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA): R21DA043963 and T32DA07209. Inpatient visits in this study was supported in part by the Johns Hopkins ICTR which is funded by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) through the Clinical & Translational Science Awards Program. Historical female controls were drawn from a prior study supported by the Klarman Family Foundation. Male historical controls were drawn prior studies supported by NIH DA000412; MH079017.
Conflicts of Interest:
Dr. Spindle has served as a paid consultant for Canopy Health Innovations Inc., Dr. Vandrey has served as a paid consultant for Canopy Health Innovations Inc., and has received honoraria for serving on the scientific advisory boards of FSD Pharma and Present Life Corporation. Dr. Wong has been the PI on studies funded by Roche Neuroscience, LB pharmaceuticals, and Lundbeck. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- 1.SAMHSA. Results from the 2019 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Compton WM, Han B, Jones CM, Blanco C. Cannabis use disorders among adults in the United States during a time of increasing use of cannabis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;204:107468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Montoya ID, Weiss SR. Cannabis Use Disorders. Springer; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Volkow ND, Swanson JM, Evins AE, et al. Effects of cannabis use on human behavior, including cognition, motivation, and psychosis: a review. Jama Psychiat. 2016;73(3):292–297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lee DC, Schlienz NJ, Peters EN, et al. Systematic review of outcome domains and measures used in psychosocial and pharmacological treatment trials for cannabis use disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;194:500–517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Howlett A, Barth F, Bonner T, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacological reviews. 2002;54(2):161–202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pertwee RG. Pharmacology of cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Pharmacology & therapeutics. 1997;74(2):129–180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pertwee RG. Ligands that target cannabinoid receptors in the brain: from THC to anandamide and beyond. Addiction biology. 2008;13(2):147–159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schwope DM, Bosker WM, Ramaekers JG, Gorelick DA, Huestis MA. Psychomotor performance, subjective and physiological effects and whole blood Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol concentrations in heavy, chronic cannabis smokers following acute smoked cannabis. J Anal Toxicol. 2012;36(6):405–412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Newmeyer MN, Swortwood MJ, Abulseoud OA, Huestis MA. Subjective and physiological effects, and expired carbon monoxide concentrations in frequent and occasional cannabis smokers following smoked, vaporized, and oral cannabis administration. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;175:67–76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vandrey R, Herrmann ES, Mitchell JM, et al. Pharmacokinetic Profile of Oral Cannabis in Humans: Blood and Oral Fluid Disposition and Relation to Pharmacodynamic Outcomes. J Anal Toxicol. 2017;41(2):83–99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Spindle TR, Cone EJ, Schlienz NJ, et al. Acute Effects of Smoked and Vaporized Cannabis in Healthy Adults Who Infrequently Use Cannabis: A Crossover Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2018;1(7):e184841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wong DF, Kuwabara H, Horti AG, et al. Quantification of cerebral cannabinoid receptors subtype 1 (CB1) in healthy subjects and schizophrenia by the novel PET radioligand [11C]OMAR. Neuroimage. 2010;52(4):1505–1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Normandin MD, Zheng MQ, Lin KS, et al. Imaging the cannabinoid CB1 receptor in humans with [11C]OMAR: assessment of kinetic analysis methods, test-retest reproducibility, and gender differences. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015;35(8):1313–1322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.D’Souza DC, Cortes-Briones JA, Ranganathan M, et al. Rapid Changes in CB1 Receptor Availability in Cannabis Dependent Males after Abstinence from Cannabis. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2016;1(1):60–67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ceccarini J, Kuepper R, Kemels D, van Os J, Henquet C, Van Laere K. [18F]MK-9470 PET measurement of cannabinoid CB1 receptor availability in chronic cannabis users. Addict Biol. 2015;20(2):357–367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Terry GE, Liow JS, Zoghbi SS, et al. Quantitation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in healthy human brain using positron emission tomography and an inverse agonist radioligand. Neuroimage. 2009;48(2):362–370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hirvonen J, Goodwin RS, Li CT, et al. Reversible and regionally selective downregulation of brain cannabinoid CB1 receptors in chronic daily cannabis smokers. Mol Psychiatry. 2012;17(6):642–649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cooper ZD, Haney M. Investigation of sex-dependent effects of cannabis in daily cannabis smokers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014;136:85–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sholler DJ, Strickland JC, Spindle TR, Weerts EM, Vandrey R. Sex differences in the acute effects of oral and vaporized cannabis among healthy adults. Addict Biol. 2020:e12968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Matheson J, Sproule B, Di Ciano P, et al. Sex differences in the acute effects of smoked cannabis: evidence from a human laboratory study of young adults. Psychopharmacology. 2020;237(2):305–316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Herrmann ES, Weerts EM, Vandrey R. Sex differences in cannabis withdrawal symptoms among treatment-seeking cannabis users. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;23(6):415–421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Schlienz NJ, Budney AJ, Lee DC, Vandrey R. Cannabis Withdrawal: A Review of Neurobiological Mechanisms and Sex Differences. Curr Addict Rep. 2017;4(2):75–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lev-Ran S, Imtiaz S, Taylor BJ, Shield KD, Rehm J, Le Foll B. Gender differences in health-related quality of life among cannabis users: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Drug Alcohol Depen. 2012;123(1–3):190–200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ehlers CL, Gizer IR, Vieten C, et al. Cannabis dependence in the San Francisco Family Study: age of onset of use, DSM-IV symptoms, withdrawal, and heritability. Addict Behav. 2010;35(2):102–110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schepis TS, Desai RA, Cavallo DA, et al. Gender differences in adolescent marijuana use and associated psychosocial characteristics. J Addict Med. 2011;5(1):65–73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Budney AJ, Moore BA, Vandrey RG, Hughes JR. The time course and significance of cannabis withdrawal. Journal of abnormal psychology. 2003;112(3):393–402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Budney AJ, Hughes JR, Moore BA, Vandrey R. Review of the validity and significance of cannabis withdrawal syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161(11):1967–1977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Laurikainen H, Tuominen L, Tikka M, et al. Sex difference in brain CB1 receptor availability in man. Neuroimage. 2019;184:834–842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Neumeister A, Normandin MD, Pietrzak RH, et al. Elevated brain cannabinoid CB1 receptor availability in post-traumatic stress disorder: a positron emission tomography study. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18(9):1034–1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sobell LC, Sobell MB. Timeline follow-back: a technique for asses- sing self-reported alcohol consumption. In: Allen JP, Litten RZ, ed. Measuring Alcohol Consumption: Psychosocial and Biochemical Methods. Totowa, NJ: Human Press; 1992:41–72. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan KH, et al. The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59 Suppl 20:22–33;quiz 34–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sossi V, De Jong HW, Barker WC, et al. The second generation HRRT-a multi-centre scanner performance investigation. Paper presented at: IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, 20052005. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rahmim A, Cheng JC, Blinder S, Camborde ML, Sossi V. Statistical dynamic image reconstruction in state-of-the-art high-resolution PET. Phys Med Biol. 2005;50(20):4887–4912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jaeger J Digit Symbol Substitution Test: The Case for Sensitivity Over Specificity in Neuropsychological Testing. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2018;38(5):513–519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kleykamp BA, Griffiths RR, Mintzer MZ. Dose effects of triazolam and alcohol on cognitive performance in healthy volunteers. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2010;18(1):1–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gronwall DM. Paced auditory serial-addition task: a measure of recovery from concussion. Percept Mot Skills. 1977;44(2):367–373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Spindle TR, Cone EJ, Schlienz NJ, et al. Acute Pharmacokinetic Profile of Smoked and Vaporized Cannabis in Human Blood and Oral Fluid. J Anal Toxicol. 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Coulter C, Miller E, Crompton K, Moore C. Tetrahydrocannabinol and two of its metabolites in whole blood using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol. 2008;32(8):653–658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Heishman SJ, Evans RJ, Singleton EG, Levin KH, Copersino ML, Gorelick DA. Reliability and validity of a short form of the Marijuana Craving Questionnaire. Drug and alcohol dependence. 2009;102(1–3):35–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.McNair DM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF. EDITS manual profile of mood states. San Diego: Educational and Industrial Testing Service.; 1992 [Google Scholar]
- 42.Curran SL, Andrykowski MA, Studts JL. Short Form of the Profile of Mood States (POMS-SF): Psychometric information. Psychological Assessment. 1995;7(1):80–83. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fischl B, Van Der Kouwe A, Destrieux C, et al. Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cerebral cortex. 2004;14(1):11–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Desikan RS, Segonne F, Fischl B, et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage. 2006;31(3):968–980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND, et al. Graphical analysis of reversible radioligand binding from time-activity measurements applied to [N-11C-methyl]-(−)-cocaine PET studies in human subjects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1990;10(5):740–747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Breivogel CS, Childers SR, Deadwyler SA, Hampson RE, Vogt LJ, Sim-Selley LJ. Chronic delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol treatment produces a time-dependent loss of cannabinoid receptors and cannabinoid receptor-activated G proteins in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1999;73(6):2447–2459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sim-Selley LJ. Regulation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the central nervous system by chronic cannabinoids. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2003;15(2):91–119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sim-Selley LJ, Schechter NS, Rorrer WK, et al. Prolonged recovery rate of CB1 receptor adaptation after cessation of long-term cannabinoid administration. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;70(3):986–996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.McKinney DL, Cassidy MP, Collier LM, et al. Dose-related differences in the regional pattern of cannabinoid receptor adaptation and in vivo tolerance development to delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;324(2):664–673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sim-Selley LJ, Schechter NS, Rorrer WK, et al. Prolonged recovery rate of CB1 receptor adaptation after cessation of long-term cannabinoid administration. Molecular pharmacology. 2006;70(3):986–996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hirvonen J, Zanotti-Fregonara P, Gorelick DA, et al. Decreased cannabinoid CB1 receptors in male tobacco smokers examined with positron emission tomography. Biological psychiatry. 2018;84(10):715–721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schauer GL, Berg CJ, Kegler MC, Donovan DM, Windle M. Assessing the overlap between tobacco and marijuana: Trends in patterns of co-use of tobacco and marijuana in adults from 2003–2012. Addict Behav. 2015;49:26–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Schauer GL, Rosenberry ZR, Peters EN. Marijuana and tobacco co-administration in blunts, spliffs, and mulled cigarettes: A systematic literature review. Addict Behav. 2016;64:200–211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ksinan AJ, Spindle TR, Thomas NS, Eissenberg T, Spit for Science Working g, Dick DM. E-cigarette use is prospectively associated with initiation of cannabis among college students. Addict Behav. 2020;106:106312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Vandrey RG, Budney AJ, Hughes JR, Liguori A. A within-subject comparison of withdrawal symptoms during abstinence from cannabis, tobacco, and both substances. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008;92(1–3):48–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Riebe CJ, Hill MN, Lee TT, Hillard CJ, Gorzalka BB. Estrogenic regulation of limbic cannabinoid receptor binding. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2010;35(8):1265–1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gullapalli S, Amrutkar D, Gupta S, et al. Characterization of active and inactive states of CB1 receptor and the differential binding state modulation by cannabinoid agonists, antagonists and inverse agonists. Neuropharmacology. 2010;58(8):1215–1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hirvonen J, Terry GE, Halldin C, Pike VW, Innis RB. Approaches to quantify radioligands that wash out slowly from target organs. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37(5):917–919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Figure 1: Statistical parametric mapping (SPM) analysis revealed a large cluster (p < 0.01, FDR-corrected, consisting of 96478 voxels) showing greater VT values in female healthy controls compared with male healthy controls. The peak T (7.09) was observed (at −36, −32, 42) in the left postcentral gyrus.


