1. Case description
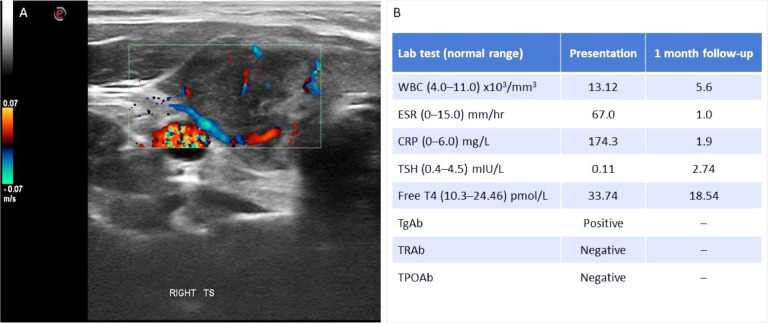
A 40-year-old woman developed malaise and severe anterior neck pain 12 hours after the second dose of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine (Pfizer/BioNTech). The pain peaked and plateaued at the fourth post-vaccination day. Her GP prescribed ibuprofen and azithromycin for presumed bacterial pharyngitis, with no avail. She visited our endocrine clinic 26 days post-vaccination with ongoing symptoms including bony aches, exhaustion, emotional lability, palpitations and hyperhidrosis. Upon general examination she was haemodynamically stable but with significant neck tenderness (visual acuity score = 8/10). There was no previous COVID-19 nor any other medical nor medication history. Neck sonography revealed a heterogeneous thyroid parenchyma, modest enlargement of the gland and diffusely hypoechoic appearances, reduced vascularity and associated reactive lymphadenopathy (Figure 1 A). Laboratory tests revealed thyrotoxicosis, leucocytosis and elevated inflammatory markers ( Figure 1 B).
Fig. 1.
Ultrasound scan (panel A) showed typical features of thyroiditis (heterogeneous parenchyma with diffuse hypoechoic areas, reduced vascularity and reactive lymph nodes) which resolved a month later. Laboratory tests (panel B) showed thyrotoxicosis and raised inflammatory markers at presentation which also resolved a month later. WBC, white blood cells. ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate. CRP, C-reactive protein. TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone. Free T4, free thyroxine. TgAb, thyroglobulin antibodies. TRAb, TSH-receptor antibodies. TPOAb, thyroid peroxidase antibodies.
2. Diagnosis
Subacute thyroiditis
3. Discussion
She was treated with prednisolone (40mg daily reducing regime) and propranolol. Full symptom resolution occurred within 24–48 hours. On re-assessment one month later, her sonographic appearance had improved, with minor inflammation, and laboratory tests showed normal inflammatory markers and thyroid function.
Classical subacute thyroiditis (SAT), also known as granulomatous or de Quervain's thyroiditis, follows a triphasic pattern of initial thyrotoxicosis, followed by transient hypothyroidism (5–15% develop permanent hypothyroidism), and spontaneous resolution [1]. It has been described following viral illnesses (including SARS-CoV-2) as well as vaccinations. A limited number of cases described SAT associated to different SARS-CoV-2 vaccines (mRNA, adenovector, inactivated vaccines) (Supplementary Table 1). Possible pathophysiological mechanisms include molecular mimicry whereby antibodies directed against SARS-CoV-2 proteins cross-react with thyroid antigens [2], immune reaction involving thyroid antibodies, or binding of spike protein to endothelial cells that can lead to mitochondrial damage and cause thyroid dysfunction [3].
The national pharmacovigilance authority of Cyprus confirmed that this is the first case of SAT temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2 vaccination reported nationally (personal communication), with over 1 million administered doses at the time of writing. A survey of Cypriot Endocrine Society members identified no further cases to date. SARS-CoV-2-vaccination-associated SAT appears to follow a clinical course and response to conventional treatments identical to classical SAT. Vaccination should not be withheld considering the low incidence and straightforward management of SAT. Physicians should be aware of this possible complication to ensure prompt recognition and appropriate management.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patient for giving consent to publication. We also thank the Cypriot Endocrine Society and the national pharmacovigilance authority (Pharmaceutical Services, Ministry of Health) of Cyprus.
Footnotes
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2021.10.008.
Appendix. Supplementary materials
References
- 1.Mundy-Baird G, Kyriacou A, Syed AA. De Quervain subacute thyroiditis. CMAJ. 2021;193(26):E1007. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.202787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vojdani A, Vojdani E, Kharrazian D. Reaction of human monoclonal antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 proteins with tissue antigens: implications for autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2021;11 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.617089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lei Y, Zhang J, Schiavon CR, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein impairs endothelial function via downregulation of ACE 2. Circ Res. 2021;128(9):1323–1326. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.