Important Compound Classes
Title
Substituted 2,3-Benzodiazepines Derivatives
Patent Publication Number
WO 2021/152113 A1
Publication Date
August 5, 2021
Priority Application
EP 20154860.9
Priority Date
January 31, 2020
Inventors
Siegel, S.; Cromm, P.; Haendler, B.; Luh, L. M.; Junemann, K.; Steigemann, P.; Gorjanacz, M.; Stockigt, D.
Assignee Company
Bayer Aktiengesellschaft, Germany
Disease Area
Benign hyperplasia, atherosclerotic disorders, sepsis, autoimmune disorders, vascular disorders, viral infections, fungal infections, neurodegenerative disorders, inflammatory disorders, and for the control of male fertility
Biological Target
BRD4
Summary
The human bromodomain and extra C-terminal domain (BET) protein family has four members, BRD2, BRD3, BRD4, and BRDT. They each contain two related bromodomains and one extra C-terminal domain. The bromodomains are protein regions that recognize acetylated lysine residues. Acetylated lysines are often found in the N-terminal region of histones and are characteristic features of an open chromatin structure which is permissive for active gene transcription.
Mechanistically, BET proteins play important roles in cell growth and in the cell cycle. They are associated with mitotic chromosomes, suggesting a role in epigenetic memory. BRD4 is important for the postmitotic reactivation of gene transcription. BET proteins play an important role in various types of tumors. BET inhibitors also show efficacy in solid tumors including prostate cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, lung cancer, pancreas cancer, colorectal cancer, gastric cancer and glioblastoma.
BET proteins are also involved in viral infections. BRD4 binds to the E2 protein of various papilloma viruses and is important for the survival of the viruses in latently infected cells. BRD4 plays an important role in HIV replication. BET proteins are also involved in fungal infections. BET proteins regulate the expression of the ApoA1 gene which plays an important role in atherosclerosis and in inflammatory processes. A role of BET proteins in obesity and neurological disorders has been described.
The present application describes a series of novel substituted 2,3-benzodiazepines derivatives as bromodomain BRD4 inhibitors for the treatment of benign hyperplasia, atherosclerotic disorders, sepsis, autoimmune disorders, vascular disorders, viral infections, fungal infections, neurodegenerative disorders, inflammatory disorders, and for the control of male fertility. Further, the application discloses compounds and their preparation, use, pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
R1 = cyclopropyl, −(C1–C2)-alkyl, methoxy or methylamino;
A =  ,
,  wherein ** represents connection
point to RL;
wherein ** represents connection
point to RL;
RL = (C1–C20) alkyl chain, in which one or more carbon atom can be optionally replaced by −O–, −N(RL1)– or −C(O)–, or by a 4, 5, or 6 membered carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring, excluding combinations such as −O–O–, −N(RL1)–N(RL1)–, −C(O)–C(O)–, −N(RL1)–O–, −C(O)–O–C(O)–, and in which RL1 = H or (C1–C6)–alkyl; and
E3 LB represents a group selected from:  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 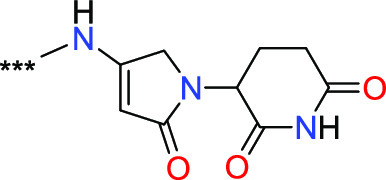 ,
,  , wherein *** indicates the point
of attachment of a group with RL.
, wherein *** indicates the point
of attachment of a group with RL.
Key Structures
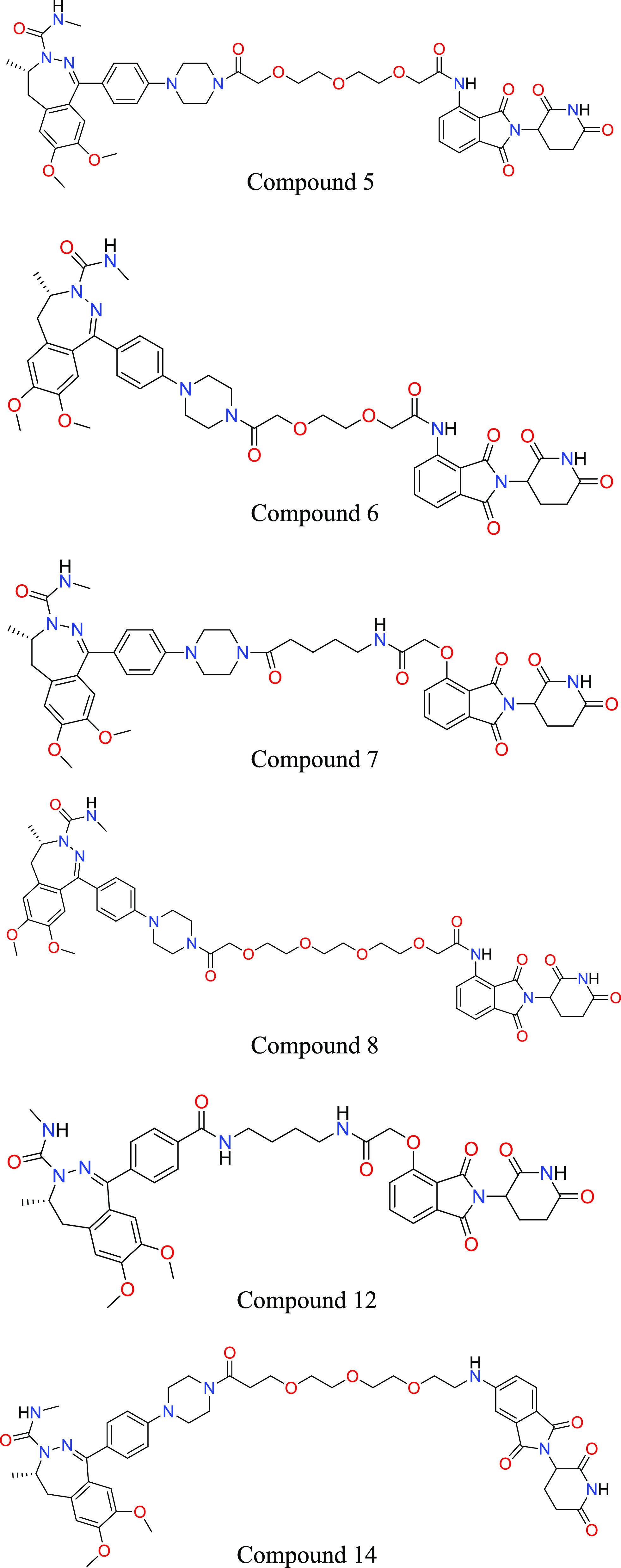
Biological Assay
BRD4 bromodomain 1 (BD1) and BRD4 bromodomain 2 (BD2) interaction assays were performed. The interaction between purified recombinant human BRD4 bromodomain 1 (BD1) or BRD4 bromodomain 2 (BD2) and a synthetic, biotin-labeled acetylated peptide derived from histone H4 was determined using the TR-FRET technology. The reactions were performed in a volume of 5 μL in 384-well black microtiter plates, and measurements were done with a PHERAstar reader using a HTRF module. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit BRD4. The BRD4 (BD1) IC50 (nM) and BRD4 (BD2) IC50 (nM) are shown in the following table.
Biological Data
The table below
shows representative
compounds were tested for BRD4 inhibition. The biological data obtained
from testing representative examples are listed in the following table.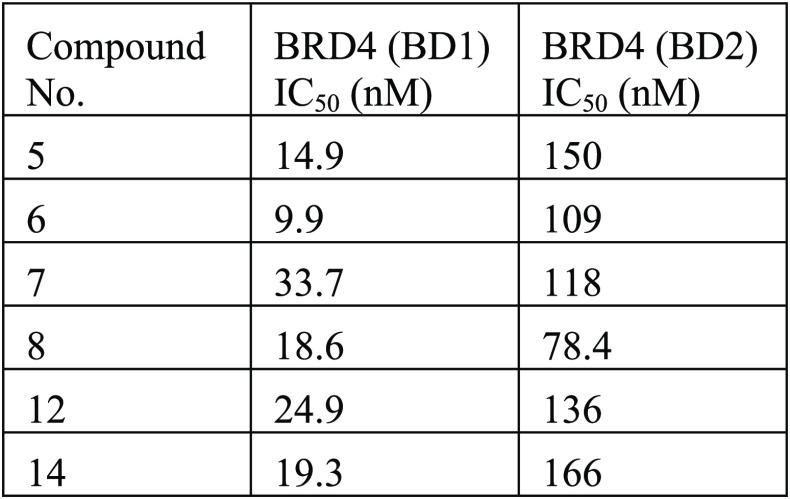
Claims
Total claims: 12
Compound claims: 8
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 1
Use of compound claims: 3
Recent Review Articles
-
1.
Tang P.; Zhang J.; Liu J.; Chiang C.; Ouyang L.. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 2419.
-
2.
Kulikowski E.; Rakai B. D.; Wong N. C. W.. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 223.
-
3.
Salahong T.; Schwartz C.; Sungthong R.. Viruses 2021, 13, 1026.
-
4.
Li L.; Xie W.; Gui Y.; Zheng X.. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 4829.
-
5.
Yang H.; Wei L.; Xun Y.; Yang A.; You H.. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 21, 1.
-
6.
Singh M. B.; Sartor G. C.. Neuropharmacology 2020, 181, 108306.
The author declares no competing financial interest.
Special Issue
Published as part of the ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters special issue “Epigenetics 2022”.



