Abstract
In this study we describe the identification and structure-function analysis of a novel death-associated protein (DAP) kinase-related protein, DRP-1. DRP-1 is a 42-kDa Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM)-regulated serine threonine kinase which shows high degree of homology to DAP kinase. The region of homology spans the catalytic domain and the CaM-regulatory region, whereas the remaining C-terminal part of the protein differs completely from DAP kinase and displays no homology to any known protein. The catalytic domain is also homologous to the recently identified ZIP kinase and to a lesser extent to the catalytic domains of DRAK1 and -2. Thus, DAP kinase DRP-1, ZIP kinase, and DRAK1/2 together form a novel subfamily of serine/threonine kinases. DRP-1 is localized to the cytoplasm, as shown by immunostaining and cellular fractionation assays. It binds to CaM, undergoes autophosphorylation, and phosphorylates an exogenous substrate, the myosin light chain, in a Ca2+/CaM-dependent manner. The truncated protein, deleted of the CaM-regulatory domain, was converted into a constitutively active kinase. Ectopically expressed DRP-1 induced apoptosis in various types of cells. Cell killing by DRP-1 was dependent on two features: the status of the catalytic activity, and the presence of the C-terminal 40 amino acids shown to be required for self-dimerization of the kinase. Interestingly, further deletion of the CaM-regulatory region could override the indispensable role of the C-terminal tail in apoptosis and generated a “superkiller” mutant. A dominant negative fragment of DAP kinase encompassing the death domain was found to block apoptosis induced by DRP-1. Conversely, a catalytically inactive mutant of DRP-1, which functioned in a dominant negative manner, was significantly less effective in blocking cell death induced by DAP kinase. Possible functional connections between DAP kinase and DRP-1 are discussed.
Apoptosis is a genetically controlled cell death process which is important at various developmental stages as well as for cell maintenance and tissue homeostasis (16). During the last few years, many of the key players in this process, including receptors, adapter proteins, proteases, and other positive and negative regulators, have been identified (13, 33). One of the positive mediators of apoptosis, which was cloned in our laboratory, is death-associated protein (DAP) kinase (9). This protein was discovered by a functional approach to gene cloning, based on transfections of mammalian cells with antisense cDNA libraries and subsequent isolation of death-protective cDNA fragments (9, 10, 19, 20, 23). The antisense cDNA of DAP kinase protected HeLa cells from gamma interferon-induced cell death, and this property served as the basis for its selection. DAP kinase is a calcium/calmodulin (CaM)-regulated serine/threonine protein kinase (160 kDa), associated with actin microfilaments (6, 9). Its structure contains at least two additional domains that might mediate interactions with other proteins: ankyrin repeats, and a typical death domain located at the C-terminal part of the protein (9, 12). Overexpression of DAP kinase in various cell lines results in cell death, and this death-promoting effect of DAP kinase depends on at least three features: catalytic activity, presence of the death domain, and correct intracellular localization (6, 7). Several independent lines of evidence proved that DAP kinase is involved in apoptosis triggered by different external signals including gamma interferon, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), activated Fas receptors, and detachment of cells from the extracellular matrix (6, 7, 9, 15). A tumor-suppressive function was recently attributed to DAP kinase, coupling the control of apoptosis to metastasis (15).
Recent studies have implicated several serine/threonine kinases in the regulation of programmed cell death, either as death-promoting or as death-protecting proteins (1, 3). One such candidate is the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/stress-activated protein kinase (2, 32). In one example it was shown to mediate apoptosis induced by detachment from extracellular matrix (named anoikis) (4). In that system, the JNK pathway is activated by MEKK-1, whose kinase activity is stimulated by caspase cleavage (4). JNK may antagonize the antiapoptotic activity of Bcl-2 by phosphorylation (24, 27). Another serine/threonine kinase is RIP, which, like DAP kinase, possesses the death domain. RIP was shown to positively mediate apoptosis in cell cultures (30). However, in vivo studies performed in RIP-deficient mice documented another aspect of its function, i.e., its ability to exert antiapoptotic effects by mediating the TNF-α-induced activation of NF-κB (18). Other RIP members, RIP2 and RIP3, were also recently identified and shown to possess proapoptotic effects (25, 31, 34). Among the negative regulators of apoptosis is the protein kinase Akt (protein kinase B). This protein was shown to phosphorylate BAD, thereby preventing it from dimerizing with and blocking the antiapoptotic activity of BCL-XL (8, 11). Akt was also recently shown to phosphorylate procaspase-9, thus blocking its normal processing and activation (5).
Recently, the isolation and characterization of three novel kinases, homologous in their catalytic domains to DAP kinase, have been reported (17, 22, 29). One protein, named ZIP (Dlk) kinase, was found to be 80% identical to DAP kinase within the kinase domain, yet it lacks the CaM-regulatory domain and the other domains and motifs characteristic of DAP kinase. ZIP kinase contains a leucine zipper domain at the C terminus and is localized to the nucleus (17, 22). The activation of ZIP kinase occurs by a different mechanism involving homodimerization, mediated by its leucine zipper domain. Another two novel, closely related proteins, DRAK1 and DRAK2, which share ∼50% identity with the kinase domain of DAP kinase, were also recently characterized (29). Like ZIP kinase, the DRAK1 and DRAK2 proteins also lack the CaM-regulatory domain. Ectopic expression of the three wild-type kinases, but not of their catalytically inactive mutants, induced morphological changes characteristic of apoptosis (17, 29). In the case of ZIP kinase, the data on its death-inducing properties in some cells are still controversial (22).
Here we report on the cloning and biochemical and functional characterization of a novel member of the DAP kinase subfamily of serine/threonine kinases, a 42-kDa protein named DAP kinase-related protein kinase 1 (DRP-1). Unlike ZIP kinase and the DRAK proteins, DRP-1 contains a typical CaM domain resembling that of DAP kinase and by that mean appears to be the closest homologue to DAP kinase. The carboxy-terminal tail encompassing the last 40 amino acids has no homology to other known proteins and was found to be required for self-dimerization. In vitro kinase assays confirmed the ability of DRP-1 to undergo autophosphorylation and to phosphorylate an exogenous substrate, myosin light chain (MLC), in a Ca2+/CaM-dependent manner. The enzyme became constitutively active upon deletion of the CaM-regulatory domain. The ectopically expressed DRP-1 was shown to be localized to the cytoplasm as a detergent-soluble form, with minor association to matrix-insoluble elements. Its function was implicated in apoptosis based on the finding that it induced apoptotic cell death when overexpressed and that a catalytically inactive DRP-1 mutant reduced cell death triggered by the ectopic expression of p55 TNF receptors (TNFR). The death-promoting effects of DRP-1 depended on the functionality of the catalytic domain and on the presence of the C-terminal tail, yet further deletion of the CaM-regulatory domain abrogated the requirement for the C-terminal tail. Cell death induced by DRP-1 was blocked specifically by the death domain of DAP kinase, suggesting a possible cross talk between these two kinases.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
cDNA cloning and Northern blotting.
A PCR fragment of 364 bp was obtained from a λgt11 human spleen cDNA library (Clontech), using primers from the deduced DRP-1 sequence (1047-GGCCGGATGAGGACCTGAGG-1066 and 1411-TCCACACTCCCACCCCAGACTC-1390). To obtain the full-length cDNA of DRP-1, we screened the same cDNA library with the radiolabeled PCR product. A 1,742-bp cDNA clone was subcloned into a BlueScript vector for restriction enzyme mapping and DNA sequencing and into pcDNA3 (from positions 8 to 1144) for expression in cells. A 580-bp 3′ fragment from the full-length cDNA of DRP-1 subcloned into pT7T3D vector was generated by HindIII-XhoI digestion (nucleotides 977 to 1557) and used to probe poly(A)+ RNA prepared by a standard procedure from various cell lines.
Preparation of anti-DRP-1 antibodies and immunoblot analysis.
Polyclonal antibodies were generated by injecting DRP-1–FLAG fusion protein, excised from polyacrylamide gels, into New Zealand White rabbits. The antibodies were titrated against the recombinant DRP-1 expressed in 293 cells. Transfections of 293 cells, cell lysate preparation, and immunoblotting conditions were as previously described in detail (6).
In vitro transcription and translation assay.
A fragment starting at a methionine in position 62 and extending to the end of the cDNA clone was subcloned into the pRSET-C vector and used as a template for in vitro transcription from the T7 promoter. This RNA was translated in reticulocyte lysate (TnT T7 Quick Coupled Transcription/Translation system; Promega) by conventional procedures, with [35S]methionine (Amersham) as a labeled precursor. The reaction product was then run on a sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)–12% polyacrylamide gel, followed by sodium salicylate incubation for signal amplification. The gel was dried and exposed to X-ray film.
In vitro kinase assay.
293 cells were transfected with various FLAG or hemagglutinin (HA) epitope-tagged DRP-1 constructs. Immunoprecipitation of the various ectopically expressed DRP-1 proteins from 150 μg of total extract was performed with 20 μl of anti-FLAG M2 gel (IBI, Kodak) in 500 μl of PLB (10 mM NaH2PO4 [pH 7.5], 100 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 0.1% SDS, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 5 mM EDTA) supplemented with protease and phosphatase inhibitors for 2 h at 4°C. Following three washes with PLB, the immunoprecipitates were washed once with reaction buffer (50 mM HEPES [pH 7.5], 20 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mg of bovine serum albumin per ml). The proteins bound to the beads were incubated at 30°C for 15 or 9 min, as indicated, in 50 μl of reaction buffer containing 15 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP (3 pmol), 50 μM ATP, and 5 μg of MLC (Sigma). In addition, either 1 μM bovine CaM (Sigma) plus 0.5 mM CaCl2 or 3 mM EGTA was added as indicated. Protein sample buffer was added to terminate the reaction, and after boiling, the proteins were analyzed on an SDS–11% polyacrylamide gel. The gel was blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane, and 32P-labeled proteins were visualized by autoradiography.
Immunostaining of cells.
FLAG-DRP-1-transfected or mock-transfected COS-7 cells were plated on glass coverslips (13-mm diameter). After 48 h, the cells were fixed and permeabilized by subsequent incubations in 3% formaldehyde, methanol, and acetone for 5, 5, and 2 min, respectively. The cells were blocked in 10% normal goat serum for 30 min and incubated with anti-FLAG antibodies (dilution of 1:100; IBI, Kodak) in 10% NGS for 60 min. Rhodamine-conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies (dilution of 1:200; Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories) and the nucleic acid dye Oligreen (dilution of 1:5,000; Molecular Probes) used for nuclear staining were then applied. The coverslips were mounted in Mowiol and examined under a fluorescence microscope.
Detergent extraction assay.
Subconfluent cultures of transfected COS-7 cells, grown on a 9-cm-diameter plate, were washed once with phosphate-buffered saline and then with morpholineethanesulfonic acid (MES) buffer (50 mM MES [pH 6.8], 2.5 mM EGTA, 2.5 mM MgCl2). The cells were extracted for 3 min with 0.5 ml of 0.5% Triton X-100 in MES buffer supplemented with protease inhibitors. The supernatant (the soluble fraction) was collected and centrifuged for 2 min at 16,000 × g at 4°C, and the cleared supernatant was then transferred to new tubes. Two volumes of cold ethanol was added, and following an overnight incubation at −20°C, pellets (10 min at 16,000 × g at 4°C) were resuspended in 200 μl of 2× protein sample buffer without dye. The detergent-insoluble matrix, remaining on the plate, was extracted in 200 μl of 2× protein sample buffer and scraped from the plate with a rubber policeman; 100 μg of protein extracts from soluble fractions and equivalent volumes of insoluble fractions were loaded into SDS–10% polyacrylamide gels and resolved by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). Western blot analysis was then performed with monoclonal anti-FLAG antibodies (dilution of 1:200; IBI, Kodak).
Cell lines, transfections, and apoptotic assays.
All cell lines were grown in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (Biological Industries) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (Bio-Lab). For transient transfection, 105 cells were seeded per well in a six-well plate a day before transfection. Transfections were done by the calcium phosphate method or by using SuperFect transfection reagent (Qiagen). For cell death assays by overexpression, a mixture containing 1.5 μg of cell death-inducing plasmid (pCDNA3 expressing the different DRP-1 constructs or mutant DAPk ΔCaM [see below]) and 0.5 μg of plasmid pEGFP-NI (Clontech) was used. Nuclear staining of 293 cells transfected by the DRP-1 Δ73 mutant was done 60 h after transfection, using Hoechst dye (2 μg/ml; Molecular Probes). For the cell death protection assays in Fig. 8B, the mixture consisted of 1.2 μg of DRP-1, 0.5 μg of a plasmid to be tested for cell death protection (expressing the DAP kinase death domain [DAPk-DD], DN [dominant negative] FADD, or luciferase as a negative control), and 0.5 μg of plasmid pEGFP-NI. For cell death protection assays in Fig. 8C, the mixture consisted of 1.3 μg of cell death-inducing plasmid (either DRP-1 or wild-type DAP kinase), 0.75 μg of a plasmid to be tested for cell death protection (expressing DRP-1 K42A or luciferase as a negative control), and 0.5 μg of plasmid pEGFP-NI. For cell death protection from p55 TNFR shown in Fig. 8C, the mixture consisted of 0.1 μg of p55 TNFR, 1.6 μg of a plasmid to be tested for cell death protection (expressing DRP-1 K42A, FADD DD, or luciferase), and 0.5 μg of plasmid pEGFP-NI. Cells were counted and photographed 24 h after transfection. For each transfection, at least three fields, each consisting of at least 100 green fluorescent protein (GFP)-positive cells, were scored for apoptotic cells according to their morphology. When indicated, cell lysates were prepared from the transient transfection at 24 h for protein analysis. Transfections of rat embryonic fibroblasts (REFs) and fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis of transfected fibroblasts for DNA content distribution were performed as previously described in detail (21).
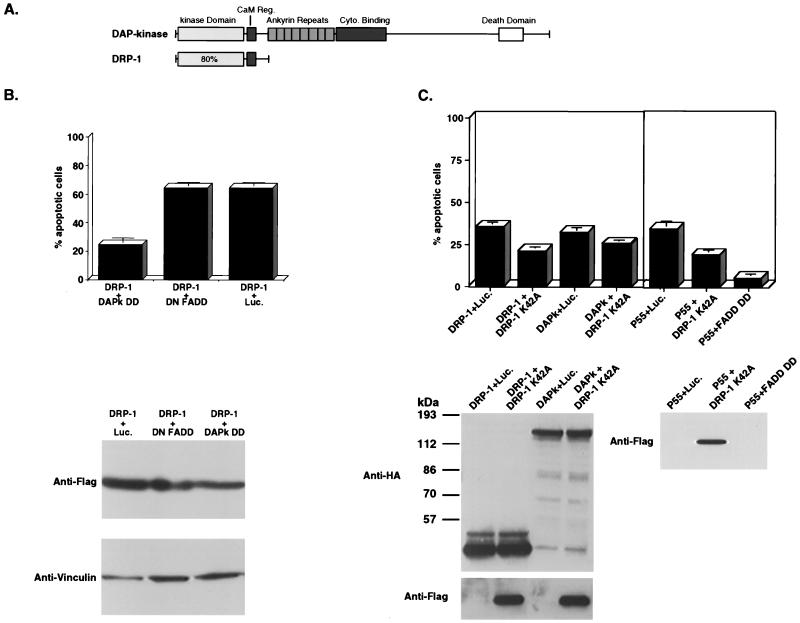
FIG. 8.
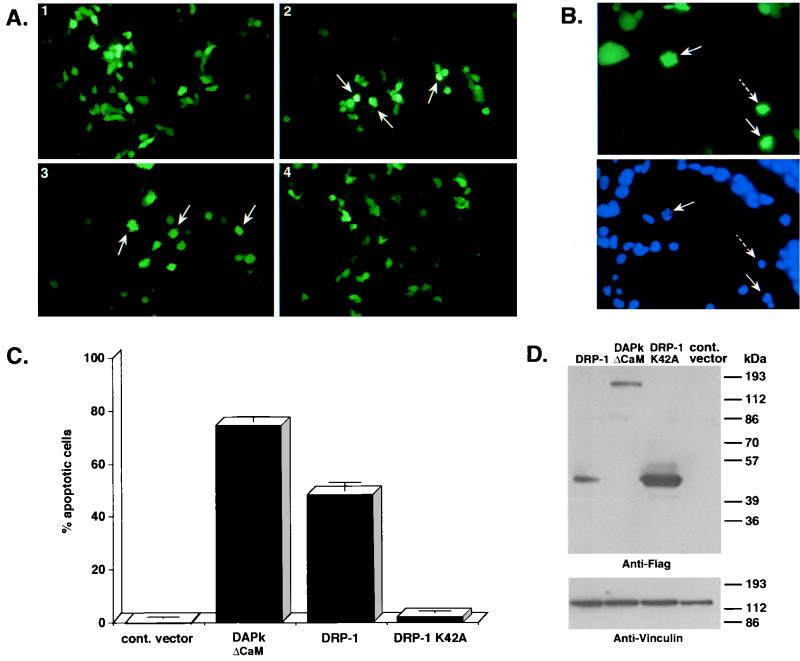
Death protection assays. (A) Schematic representation of DRP-1 and DAP kinase. (B) DAP kinase death domain protects from DRP-1-induced cell death. Top, 293 cells (105 cells/well) were cotransfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type DRP-1 and GFP (0.5 μg/well) as described for Fig. 5. To each transfection the indicated plasmid (DAPk DD, DN FADD, or luciferase [Luc.] in pCDNA3) was also added (0.5 μg/well). Scores are percentages of apoptotic cells given as the mean ± standard deviation and calculated from triplicates of 100 cells each. This experiment was repeated three times with reproducible results. Bottom, DRP-1 protein expression in transfected 293 cells. Proteins extracted from the transfected cells were separated by SDS-PAGE on a 10% gel and blotted to a nitrocellulose membrane. The blot was reacted with anti-FLAG antibodies for DRP-1 detection and antivinculin antibodies to quantitate the loaded protein amounts. The proteins were prepared from the same experiment shown in the top part of panel B. (C) DRP-1 K42A mutant protects from DRP-1 and p55 TNFR-induced cell deaths. Top, 293 cells (105 cells/well) were cotransfected with HA-tagged wild-type DRP-1 or HA-tagged wild-type DAP kinase (1.3 μg/well; left) or p55 TNFR (0.1 μg/well; right) and GFP (0.5 μg/well) as described for Fig. 5. To each transfection was added: the indicated plasmid DRP-1-FLAG K42A or luciferase in pCDNA3 (0.75 μg/well; left) or DRP-1-FLAG K42A, FADD DD, or luciferase in pCDNA3 (1.6 μg/well; right). Scores are the percentage of apoptotic cells given as the mean ± standard deviation and calculated from triplicates of 100 cells each. This experiment was repeated three times with reproducible results. Bottom, DRP-1-HA, HA-DAP kinase, and DRP-1-FLAG K42A protein expression in 293 transfected cells. The proteins were prepared from the same experiment as shown in the upper part of panel C.
Coimmunoprecipitation assays.
293 cells grown in 90-mm-diameter plates (106 cells/plate) were cotransfected with 5 μg of FLAG-tagged or HA-tagged DRP-1 and 20 μg of HA-tagged or FLAG-tagged RFX1-ΔSmaI (28) (deleted at amino acids 603 to 913), respectively, or with DRP-1-HA and DRP-1-FLAG (5 μg of each). Immunoprecipitation of DRP-1 or RFX1-ΔSmaI from 1 mg of total extract was done with anti-FLAG M2 gel or Protein-G PLUS-agarose (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) conjugated to anti-HA antibodies. Detection of bound proteins was performed by Western blot analysis using anti-HA antibodies (dilution of 1:1,000; BAbCo) or anti-FLAG antibodies. For the deletion mutant study, 5 μg of FLAG-tagged full-length DRP-1 was cotransfected with 5 μg of HA-tagged DRP-1 deletion mutants. Immunoprecipitation of DRP-1 from 1 mg of total extract was performed with anti-FLAG M2 gel as described above. Detection of coimmunoprecipitated proteins (mutant or full-length DRP-1) was done with anti-HA antibodies.
CaM overlay assay.
Transfections with the indicated HA-tagged proteins into 293 cells, preparation of cell lysates, immunoprecipitation, and immunoblotting were performed as previously described in detail (6). The overlay assay was performed as previously detailed (6). The membranes were preincubated for 1 h in CaM binding buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM CaCl2) containing 5% nonfat dry milk powder. Recombinant 35S-labeled CaM was added, and the membrane was subjected to gentle shaking at room temperature for 16 h, washed three times (5 min each) in CaM binding buffer, dried, and exposed to a phosphorimager. The various proteins were detected with anti-HA antibodies in a standard Western blot procedure.
Multiple sequence alignments and phylogenetic tree.
The amino acid sequences were aligned manually according to Hanks and Quinn's alignment (14), with refinements, using the ClustalX program. The phylogenic tree is based on the neighbor-joining method (paupsearch program; Genetics Computer Group package version 9).
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers.
The nucleotide sequence reported in this paper has been submitted to the GenBank/EBI data bank (accession no. AF052941). The murine DRP-1 is also deposited at the GenBank/EBI Data Bank (accession no. AF052942).
RESULTS
Cloning of DRP-1.
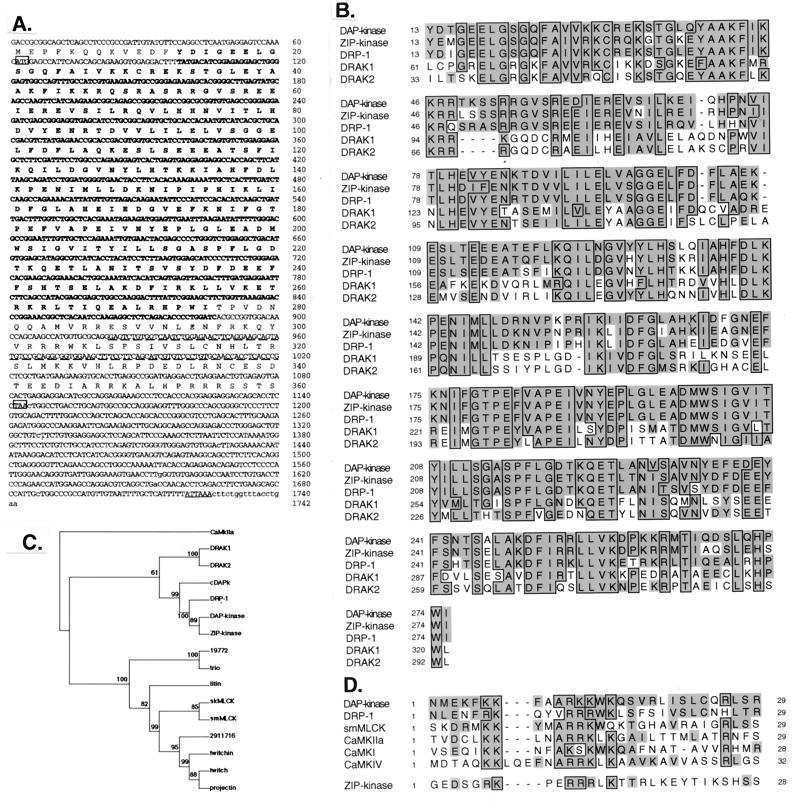
To identify proteins that share homologous sequences with DAP kinase, we searched expressed sequence tag (EST) databases with the BLASTN program. Two ESTs from human and murine origin showed remarkable amino acid homology to the catalytic domains of DAP kinase and the recently identified protein ZIP kinase (79.5 and 80.2% identity, respectively). We performed a second EST search using the 5′ and the 3′ ends of the human EST and identified a few more overlapping ESTs. A putative novel cDNA sequence was generated and used to design primers for cloning the full-length cDNA. PCR performed on human spleen cDNA library amplified a 364-bp fragment that was further used to screen the same library. The full-length cDNA was then isolated, subcloned into BlueScript vector, and sequenced. The isolated cDNA is 1,742 bp long, coding for a protein which comprises 360 amino acids. The deduced amino acid sequence predicted a serine/threonine kinase domain with all of the 12 characterized subdomains present (14) (Fig. 1A). Sequence alignment indicates that the catalytic domain of DRP-1 is 80% identical to that of DAP kinase and ZIP kinase yet less identical (50%) to the newly identified DRAK proteins (Fig. 1B). We performed a multiple sequence alignment of 18 proteins that show high scores of homology to the DAP kinase catalytic domain (not shown). This alignment classifies a novel protein subfamily composed of DAP kinase, ZIP kinase, DRP-1, and the Caenorhabditis elegans DAP kinase (cDAPk). The DRAK proteins form another closely related group. Local high-homology segments unique to this subfamily are the SRRGV loop located between αB and αC and two amino acids (PR or PH) appearing in β8. Phylogenetic analyses, based on the multiple sequence alignment of the catalytic domains and performed according to the neighbor-joining (Fig. 1C), maximum-likelihood, and maximum-parsimony methods (not shown), show that DAP kinase, ZIP kinase, DRP-1, and cDAPk are indeed grouped into a distinct clade with high bootstrap probabilities. DRAK1 and DRAK2 form another clade sharing a putative common ancestor to the other DAP kinase-related proteins. Similar to DAP kinase and unlike ZIP kinase, DRP-1 carries a typical CaM-regulatory region adjacent to its catalytic domain (extending between amino acids 288 and 320) (Fig. 1A and D). Compared with other kinases such as CaM kinase IIa (CaKIIa) and MLC kinase (MLCK), DRP-1 has the highest homology to DAP kinase in the CaM-regulatory region (Fig. 1D). The remaining short stretch of 40 amino acids at the C-terminal part of DRP-1 (amino acids 320 to 360) displays no homology to any known protein. Thus, beyond the catalytic domain, DRP-1 differs considerably from DAP kinase. The latter is longer (1,431 amino acids long) and displays a different multidomain structure (see also the scheme in Fig. 8A).
FIG. 1.
Sequence of the DRP-1 cDNA clone and alignments to related kinases. (A) Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of human DRP-1. Initiation (ATG) and stop (TAA) codons are boxed. A polyadenylation signal (ATTAAA) is underlined. The kinase domain and the CaM-regulatory regions are in bold and underlined by dashes, respectively. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of the serine/threonine kinase domains of the related proteins DAP kinase, ZIP kinase, DRP-1, and DRAK1 and -2. Alignment was done as described by Hanks and Quinn (14). Identical amino acids are boxed; homologous amino acids according to PAM250 matrix are shown in grey. (C) Phylogenic rooted neighbor-joining tree of the 16 catalytic domains belonging to proteins closely related to DAP kinase. Numbers shown are bootstrap values. Confidence values lower than 50% are considered unreliable. CaMKIIa was used as a representative of other CaM kinases and was outgrouped to root the tree. smMLCK and skMLCK, smooth muscle and skeletal MLCK, respectively. (D) Multiple sequence alignment of the CaM-regulatory regions of DAP kinase, DRP-1, smMLCK, CaMKIIa, CaMKI, and CaMKIV. Alignment was done manually, keeping the conserved (boxed) regions aligned to each other. The corresponding region of ZIP kinase which does not contain homology to DAP kinase and DRP-1 CaM-regulatory regions is given at the bottom.
Expression of recombinant and endogenous DRP-1.
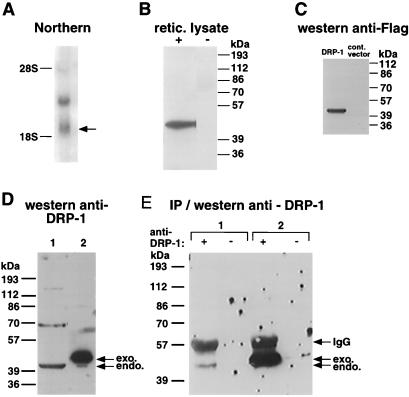
To check the mRNA expression of DRP-1, we prepared poly(A)+ RNA from human cells (MCF-7 breast carcinoma cell line) and hybridized it to a probe corresponding to the less conserved region of DRP-1 (nucleotides 977 to 1557). Two major mRNA transcripts approximately 1.9 and 3.8 kb in size were detected (Fig. 2A). The short mRNA transcript matches in its size to the cloned cDNA [i.e., 1,742 bp plus the poly(A) tail], whereas the longer mRNA may correspond to an alternatively spliced transcript or to some other, unidentified mRNA. PCR analysis of various cDNA libraries and the data gathered from EST searches indicate that human DRP-1 is widely expressed and can be detected at least in the spleen, colon, breast, and leukocytes (not shown).
FIG. 2.
mRNA and protein expression of DRP-1. (A) Northern blot analysis of DRP-1 mRNA. A 580-bp 3′ fragment from the full-length cDNA of DRP-1 was used to probe poly(A)+ RNA prepared from MCF-7 cells. (B) In vitro translation of DRP-1. In vitro-transcribed DRP-1 mRNA was programmed in reticulocyte lysate. The translated protein, 42 kDa in size, is shown. (C) Protein expression of recombinant DRP-1 in HeLa cells. FLAG-tagged DRP-1 cloned in the pCDNA3 vector was transfected into HeLa cells; 24 h following transfection, cells were harvested and lysed. Extracted proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and then immunoblotted with anti-FLAG antibodies. A protein band at ∼42 kDa is shown. (D and E) Expression of endogenous (endo.) DRP-1 protein. (D) Western analysis in which 100 μg of protein lysates of MCF-7 cells (1) and 30 μg of protein lysates of 293 cells transfected by DRP-1-FLAG (2) were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with 9% anti-DRP-1 serum. exo., exogenous. (E) IP/Western analysis in which 3 mg of protein lysates of MCF-7 cells (1) or 300 μg of protein lysates of 293 cells transfected by DRP-1-FLAG (2) was immunoprecipitated overnight with (+) or without (−) 50 μl of anti DRP-1 serum. The proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with 9% anti-DRP-1 serum. Arrows indicate positions of the endogenous and exogenous DRP-1 and the position of immunoglobulin G (IgG) heavy-chain protein.
In vitro transcription and translation assays, done with reticulocyte lysates and the cloned DRP-1 cDNA as a template (starting from the ATG at positions 62 to 65), generated a single protein band about 42 kDa in size, as predicted by its sequence (Fig. 2B). We then cloned a FLAG-tagged DRP-1 into pCDNA3 vector and expressed it in HeLa cells. A single band of about 42 kDa was evident upon immunoblot analysis of the cell lysates with anti-FLAG antibodies (Fig. 2C).
Polyclonal antibodies were raised against the recombinant DRP-1 protein. When reacted with immunoblots containing human cell lysates, they recognized a band at the predicted size (it migrated faster than the recombinant FLAG-tagged protein; Fig. 2D, compare lanes 1 to 2). The other, higher bands, which reacted with the anti-DRP-1 antibodies, turned out to be nonspecific, since only the 42-kDa protein could be immunoprecipitated by the antibodies (Fig. 2E, lane 1).
Cellular localization of ectopically expressed DRP-1.
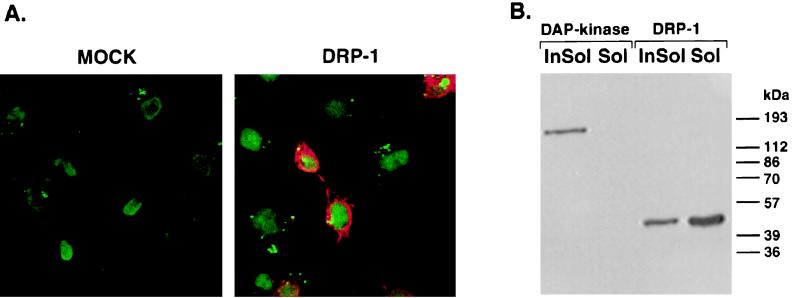
To determine the cellular localization of the exogenous DRP-1, we expressed the FLAG-tagged DRP-1 in COS-7 cells. Immunoblot analysis showed that DRP-1 is expressed in these cells (not shown). For the immunostaining procedure, nontransfected and DRP-1-transfected COS-7 cells were fixed and reacted both with Oligreen for nuclear staining and with anti-FLAG antibodies for DRP-1 staining. Specific DRP-1 staining was detected in the cytoplasm of these cells (Fig. 3A). We then performed a gentle cell extraction with nonionic detergent (0.5% Triton X-100) that removes lipids and soluble proteins, leaving intact the detergent-insoluble matrix composed of the nucleus, the cytoskeleton framework, and cytoskeleton-associated proteins. In contrast to the ectopically expressed DAP kinase, which is exclusively localized to the cytoskeleton and hence found only in detergent-insoluble fractions (6) (Fig. 3B), DRP-1 was preferentially eluted from the detergent-soluble fraction, with only a small amount remaining in the insoluble fraction (Fig. 3B). Thus, we conclude that ectopically expressed DRP-1 is a soluble, cytoplasmic protein with minor association with insoluble matrix components.
FIG. 3.
Intracellular localization of DRP-1 in COS-7 cells. (A) COS-7 cells were transfected by a FLAG-tagged DRP-1 cloned in pCDNA3 vector, fixed and permeabilized in 1% formaldehyde, and treated with methanol-acetone. Fixed cells were then reacted with Oligreen for nuclear staining (green) and with anti-FLAG antibodies for DRP-1 detection (red). Cells were visualized under a fluorescence microscope. (B) Detergent extraction of COS-7 cells. COS-7 cells were transfected with a pCDNA3 vector expressing either FLAG-tagged DRP-1 or DAP kinase. The cells were then extracted with 0.5% Triton X-100 to form soluble fractions (Sol) and insoluble fractions (InSol) as described in Materials and Methods. The protein extracts were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE (10% gel) and blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was reacted with anti-FLAG antibodies.
Intrinsic kinase activity of DRP-1.
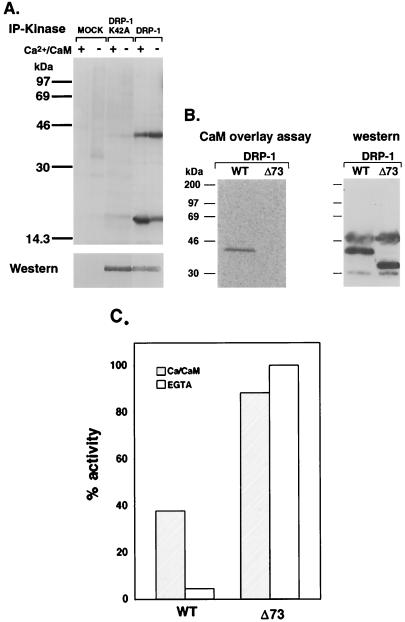
To test whether DRP-1 functions as a kinase, as predicted from the amino acid sequence, we performed an in vitro kinase assay using MLC as an exogenous substrate. This substrate was chosen since it is phosphorylated by DAP kinase (6). DRP-1 was transfected into human kidney 293 cells, immunoprecipitated, and incubated with MLC in the presence and absence of Ca2+ and CaM. Both MLC phosphorylation and DRP-1 autophosphorylation were evident (Fig. 4A). The addition of Ca2+/CaM to the reaction mixture increased the amount of phosphorylated MLC, suggesting that the enzyme is regulated by binding to CaM (Fig. 4A and C). Indeed, the full-length DRP-1 could bind directly CaM, as assessed by incubating membranes containing the immunoprecipitated protein with labeled CaM (Fig. 4B). Truncation of the last 73 amino acids, a stretch which includes the 33 amino acids of the CaM-regulatory domain (Δ73 mutant), abolished CaM binding (Fig. 4B) and converted the enzyme to a constitutively active form, fully functional in the absence of externally added Ca2+/CaM and in the presence of EGTA (Fig. 4C). This gain of function in the catalytic activity is in accordance with the assumption that, like DAP kinase, DRP-1 is negatively regulated by the autoinhibitory CaM-binding domain and that this inhibition is removed by the binding of Ca2+/CaM. A catalytically inactive mutant of DRP-1 (DRP-1 K42A), did not phosphorylate MLC and failed to undergo autophosphorylation even though higher amounts of DRP-1 protein were present (Fig. 4A). Thus, DRP-1 functions in vitro as a kinase that is capable of phosphorylating itself and an external substrate; the latter property is stimulated by the addition of Ca2+ and CaM.
FIG. 4.
In vitro kinase activity and CaM binding of DRP-1. (A) DRP-1-FLAG and DRP-1-FLAG mutant (K42A) proteins were assayed in vitro for kinase activity in the presence or absence of Ca2+/CaM as described in Materials and Methods. The proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE on an 11% gel and blotted to a nitrocellulose membrane. Top, autophosphorylation of DRP-1 (42 kDa) and MLC phosphorylation (17 kDa), respectively, after exposure to X-ray film; bottom, DRP-1 proteins after incubation of the same blot with anti-FLAG antibodies and ECL detection. (B) Cell lysates were prepared from 293 cells transfected with wild-type (WT) DRP-1-HA or DRP-1-HA Δ73 mutant and separated by PAGE-SDS on a 12% gel. Blotted proteins were reacted with recombinant 35S-labeled CaM (left); exogenous proteins were detected with anti-HA antibodies in a standard Western blot procedure (right). (C) Graph showing the relative amount of MLC phosphorylation by wild-type DRP-1 or DRP-1 Δ73 mutant in the presence or absence of Ca2+/CaM. Phosphorylation levels were determined by phosphorimaging of 32P-labeled MLC bands. Values were normalized according to the DRP-1 recombinant protein levels used in each phosphorylation assay. Phosphorylation of MLC by DRP-1 Δ73 in the absence of Ca2+/CaM was taken as the maximal phosphorylation activity.
DRP-1 induces apoptosis in a variety of cell lines.
The high homology to DAP kinase in the kinase and CaM-binding regions prompted us to check whether DRP-1 is involved in apoptosis. The wild-type DRP-1 and the catalytic inactive mutant of DRP-1 (DRP-1 K42A), each cloned in pCDNA3 vector, were transfected into 293 cells. To quantitate the number of apoptotic cells, we cotransfected these constructs with a vector expressing GFP. The latter was used as a marker to visualize the transfected cells and to assess the apoptotic frequency among the transfectants according to morphological alterations. Apoptotic cells were scored after 24 h. Overexpression of DRP-1 resulted in apoptotic cell death (50 to 60%), compared to the basal level of apoptotic cells caused by transfection of a nonrelevant (luciferase) gene (Fig. 5A and C). The first and very prominent morphological changes occurred at the membrane level, since a major fraction of the GFP-positive green cells showed cytoplasmic blebbing (26) (Fig. 5A-3). In addition, some of the transfected cells detached from the plate. DNA staining by Hoechst was used to monitor the status of the nucleus in the DRP-1-transfected cells, at 60 h posttransfection. Most of the GFP-positive cells displayed condensed nuclei; some of the nuclei appeared fragmented (Fig. 5B). In these experiments, the activated DAP kinase mutant lacking the autoinhibitory CaM-regulatory region (DAPk ΔCaM) yielded apoptotic values of 70 to 80% (Fig. 5C). In contrast, when these cells were transfected with the kinase-inactive mutant of DRP-1 (DRP-1 K42A; Fig. 5A-4 and C), no apoptosis was observed. Western blot analysis of transfected cells with anti-FLAG antibodies confirmed the expression of both the exogenous wild-type and K42A mutant versions of DRP-1 (Fig. 5D). Similar results were observed in human SV-80 fibroblasts (not shown).
FIG. 5.
Ectopic expression of DRP-1 induces cell death. (A) 293 cells (105 cells/well) were cotransfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type DRP-1 or K42A mutant DRP-1 (1.5 μg/well) and GFP (0.5 μg/well). GFP-positive cells were visualized under a fluorescence microscope and scored for appearance of apoptotic morphology 24 h after transfection. Apoptotic cells are indicated by arrows. Images 1 to 4 correspond to 293 cells transfected by pCDNA3-luciferase (negative control), pCDNA3-ΔCaM DAP kinase (positive control), pCDNA3-DRP-1, and pCDNA3-DRP-1 K42A. (B) Nuclear staining of DRP-1-transfected cells. Top, GFP staining of 293 cells transfected by DRP-1 Δ73 mutant (1.5 μg/well); bottom, Hoechst nuclear staining of the same cells. Pictures were taken 60 h posttransfection. Solid arrows, cells with condensed and fragmented chromatin; dashed arrows, cells with condensed chromatin. (C) Scores of apoptotic cells. Graphs show the percentage of apoptotic cells resulting from the above-mentioned transfections (mean ± standard deviation calculated from triplicates of 100 cells each). The scores were taken from the same experiment as shown in panel A. This experiment was repeated six times with reproducible results. (D) DRP-1 protein expression in transfected 293 cells. Proteins extracted from the transfected cells were separated by SDS-PAGE on a 10% gel and blotted to a nitrocellulose membrane. The blot was reacted with anti-FLAG antibodies for DRP-1 detection and antivinculin antibodies (dilution of 1:300; Sigma) to quantitate the loaded protein amounts. The proteins were prepared from the same experiment as shown in panel A.
The effect of ectopically expressed DRP-1 on the DNA content of primary REFs was also assessed, as previously described in detail (21). REFs were cotransfected with DRP-1 and a membrane-bound form of GFP and after 48 h subjected to FACS analysis of their DNA content. A fraction of cells displaying a sub-G1 DNA content (27%), indicative of cells containing fragmented DNA, appeared exclusively in the DRP-1-transfected cells, not in cells transfected with a control vector (7%) or with the DRP-1 K42A mutant (9%). No effect on cell cycle distribution of the viable cells was found (not shown).
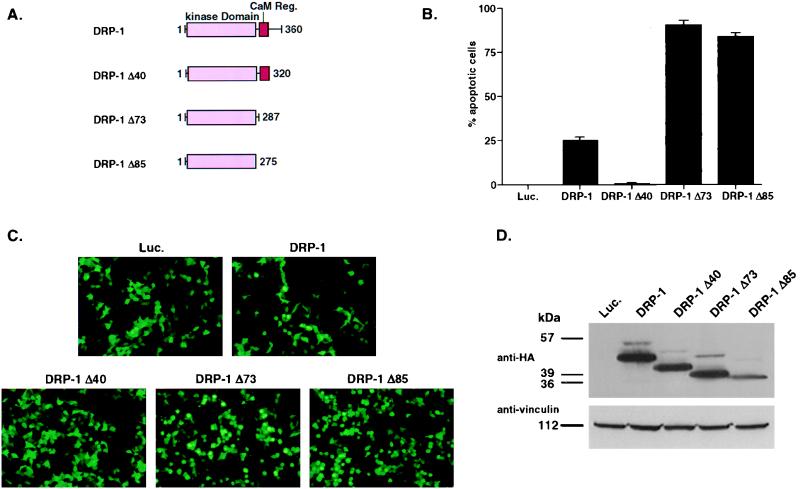
Deletion of the C-terminal tail of DRP-1 abolishes its apoptotic activity, while further truncation of the CaM-regulatory region strongly enhances the apoptotic effect.
To further understand the mode of DRP-1 action in apoptosis, we generated constructs containing C-terminal truncations of DRP-1 tagged by HA (Fig. 6A). DRP-1 Δ40 lacks the most C-terminal part of DRP-1, which displays no homology to any known protein. DRP-1 Δ73 lacks, in addition to that, the CaM-regulatory region of DRP-1, and DRP-1 Δ85 contains only the catalytic domain. The wild-type DRP-1 and the various truncation mutants of DRP-1 were transfected into 293 cells at comparable amounts (see the legend to Fig. 6). Induction of apoptotic cell death was assessed by scoring GFP-positive cells. Overexpression of the wild-type DRP-1 in these experiments resulted in apoptosis (25%), while DRP-1 Δ40 had no effect in these assays. On the other hand, further truncations of the CaM-regulatory region yielded mutants (Δ73 and Δ85) which acted as “superkillers” (∼90% apoptosis) (Fig. 6B and C). Western blot analysis of transfected cells with anti-HA antibodies confirmed the expression of all DRP-1 forms (Fig. 6D). These experiments support the finding that the apoptotic effect of DRP-1 is dependent on its kinase activity, since as shown in Fig. 4, removal of the autoinhibitory CaM-regulatory region generates a constitutively active kinase. In addition, these experiments revealed the existence of a positive module in the C-terminal region of DRP-1, which is necessary for its proapoptotic effect, provided that the CaM-regulatory region is still present. In the absence of the CaM-regulatory region, the C-terminal tail becomes dispensable.
FIG. 6.
Ectopic expression of DRP-1 deletion mutants. (A) Schematic representation of DRP-1 deletion mutants. (B) Scores of apoptotic cells. Graphs show the percentage of apoptotic cells resulting from cotransfections of 293 cells with 1.2 μg of HA-tagged wild-type DRP-1 or various deletion mutants of DRP-1 (mean ± standard deviation calculated from triplicates of 100 cells each). This experiment was repeated three times with reproducible results. (C) Pictures were taken from the experiment described above, corresponding to 293 cells transfected with pCDNA3-luciferase (Luc.; negative control), pCDNA3-DRP-1, pCDNA3-DRP-1 Δ40, pCDNA3-DRP-1 Δ73, and pCDNA3-DRP-1 Δ85. (D) DRP-1 protein expression in transfected 293 cells. Proteins extracted from the transfected cells were separated by SDS-PAGE on a 10% gel and blotted to nitrocellulose membrane. The blot was reacted with anti-HA antibodies for DRP-1 detection and antivinculin antibodies to quantitate the loaded protein amounts. The proteins were prepared from the same experiment as shown in panel B.
The C-terminal part of DRP-1 functions as a homodimerization domain.
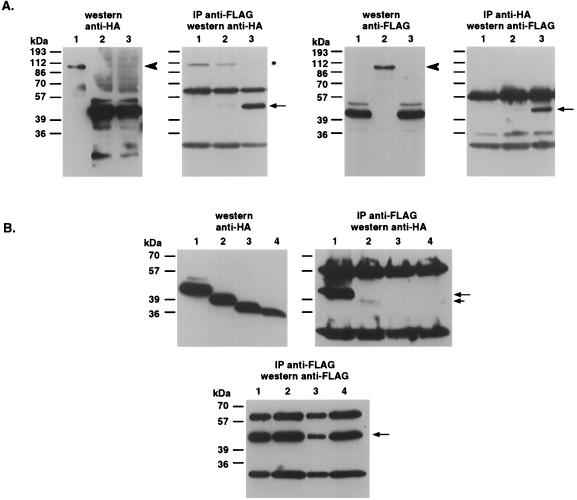
Western analysis performed on proteins extracted from 293 cells transfected with FLAG-tagged DRP-1 revealed, in some cases, an additional band of approximately 85 kDa (not shown). This observation led us to test whether DRP-1 can undergo homodimerization. To this end, we cotransfected two constructs expressing DRP-1 fused to either a FLAG or an HA tag into 293 cells and performed classical pull-down experiments with each of the two epitopes. FLAG-tagged DRP-1 was shown to bind specifically HA-tagged DRP-1 in both immunoprecipitation directions (Fig. 7A, lanes 3 in both IP panels). No binding of DRP-1-HA to FLAG beads or to the irrelevant cytoplasmic protein RFX-ΔSmaI (28) could be observed (Fig. 7A, IP anti-FLAG panel, lane 2 or lanes 1 and 2, respectively). Also, we could not detect nonspecific binding of DRP-1-FLAG to HA beads or to RFX-ΔSmaI protein (Fig. 7A, IP anti-HA panel, lane 1 or lanes 1 and 2, respectively). Western analysis confirmed the expression of all proteins in these cell extracts (Fig. 7A, Western panels).
FIG. 7.
DRP-1 undergoes homodimerization via its C-terminal tail. (A) Wild-type DRP-1 undergoes specific homodimerization. 293 cells growing in 90-mm-diameter plates were cotransfected with the following constructs: lane 1, DRP-1-FLAG (5 μg) plus RFX1-ΔSmaI-HA (20 μg; used as an intrinsic control to rule out nonspecific binding of DRP-1-FLAG to HA beads or to an irrelevant gene); lane 2, RFX-ΔSmaI-FLAG plus DRP-1-HA (control to rule out nonspecific attachment of DRP-1-HA to FLAG beads or to an irrelevant gene); lane 3, DRP-1-FLAG plus DRP-1-HA. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with either anti-FLAG antibodies (left) or anti-HA antibodies (right). The total levels of transfected proteins are shown on immunoblots. (B) Truncation of C-terminal 40 amino acids of DRP-1 abolishes its homodimerization. Lanes 1 to 4 correspond to cotransfections (5 μg of each construct per 90-mm-diameter plate) with DRP-1-FLAG plus DRP-1-HA, DRP-1-FLAG plus DRP-1-Δ40-HA, DRP-1-FLAG plus DRP-1-Δ73-HA, and DRP-1-FLAG plus DRP-1-Δ85-HA, respectively. The lower panel quantitates the immunoprecipitation efficiency of DRP-1-FLAG with the anti-FLAG antibodies. Solid arrows, immunoprecipitated DRP-1; short arrow, immunoprecipitated DRP-1 Δ40; arrowhead, RFX-ΔSmaI; asterisk, nonspecific band.
Next we tried to map the domain which may be required for the homodimerization of DRP-1. To this end, DRP-1-FLAG was expressed in tandem with the various deletion mutants of DRP-1 tagged by HA. We could detect strong binding of DRP-1-FLAG to the wild-type DRP-1-HA, whereas binding to DRP-1 Δ40, Δ73, and Δ85 was minimal or undetectable (Fig. 7B, upper IP panel, compare lane 1 to lanes 2 to 4). Western analysis confirmed the expression of wild-type DRP-1-HA and all other DRP-1-HA deletion mutants in these transfections (Fig. 7B, Western panel). The lower IP panel depicts the presence of wild-type DRP-1-FLAG in all these immunoprecipitates. Thus, we concluded that a region spanning the C-terminal 40 amino acids of DRP-1 is required for its homodimerization. This homodimerization is probably required for the apoptotic effect of DRP-1, since DRP-1-Δ40 lost the ability to induce apoptosis in 293 cells (Fig. 6B and C).
DAP kinase death domain protects from DRP-1-induced apoptosis.
The sequence homology between DRP-1 and DAP kinase within the catalytic domain, the common regulation by Ca2+/calmodulin, and the finding that both proteins induced apoptosis upon overexpression raised the possibility that they function along a common apoptotic pathway. To assess a possible functional cross talk between the two kinases, dominant negative mutants derived from each of the two kinases were used. We first tested whether a fragment of DAP kinase encompassing the death domain (DAPk DD) affected DRP-1-induced cell death. This fragment of DAP kinase was previously shown to act as a specific dominant negative mutant, negating the effects of the full-length protein when ectopically expressed (7). Interestingly, we found by cotransfection experiments that DAPk DD protected 293 cells from cell death induced by DRP-1 (Fig. 8B). A control transfection including DRP-1 and a nonrelevant luciferase DNA excluded the possibility that inhibition is simply due to larger amount of DNA used in the transfection. Moreover, the effect of DAPk DD was specific, since the death domain of FADD (also named DN FADD) failed to manifest a similar effect (Fig. 8B). Western blot analysis of transfected cells using anti-FLAG antibodies confirmed the expression of the exogenous DRP-1 in all transfections (Fig. 8B).
In the reciprocal experiment, the catalytically inactive DRP-1 K42A mutant (FLAG tagged) was assayed in cotransfection experiments, assuming that it will function in a dominant negative manner. To test this possibility, the mutant was first cotransfected with the wild-type DRP-1 (HA tagged) and was found to confer protection against the apoptotic effects of the wild-type protein without affecting its expression levels (Fig. 8C). The latter observation attributed to this mutant a moderate yet significant neutralizing function against wild-type DRP-1. Nevertheless, when cells were killed by DAP kinase, the extent of protection which was conveyed by DRP-1 K42A was significantly less despite the fact that the direct target, i.e., the endogenous DRP-1, is expressed at lower levels than the recombinant DRP-1 in the previous experiments. In contrast, the same mutant was effective in protecting 293 cells from cell death induced by another stimulus—the ectopically expressed p55 TNFR (Fig. 8C; the death domain of FADD, which is a potent blocker of TNF signaling at the receptor level, served as a positive control). Together, the cotransfection experiments suggest that in certain genetic constellations, the death-promoting effects of DRP-1 may depend on active DAP kinase whereas a major yet not exclusive molecular arm emanating from DAP kinase is refractory to DRP-1 inactivation.
DISCUSSION
In this study we describe the cloning and characterization of a novel serine/threonine kinase with remarkable homology to the catalytic and CaM-regulatory domains of DAP kinase. This kinase, named DRP-1, is a 42-kDa cytoplasmic protein which when ectopically expressed exhibits minor associations with insoluble matrix elements. Another protein, ZIP kinase, which by virtue of its sequence homology to the kinase domain of DAP kinase is also a member of the DAP kinase-related protein subfamily, was recently identified (17, 22). Unlike DAP kinase and DRP-1, ZIP kinase is a nuclear protein which, instead of being regulated by a CaM-binding domain, is activated only by homodimerization via its leucine zipper motifs (17). ZIP kinase-induced cell death is controlled by its ability to undergo homodimerization. To this group of kinases, another two less homologous nuclear proteins, DRAK1 and DRAK2, were recently added (29). Together they form a novel subfamily of serine/threonine kinases, as is evident from multiple sequence and phylogenetic analyses.
To check the cellular functions of DRP-1, we overexpressed wild-type DRP-1 in various cell lines and found that it induced apoptosis as measured by various parameters. Unlike the wild-type DRP-1, a kinase-inactive mutant of DRP-1 (DRP-1 K42A) did not induce apoptosis, although it was expressed at a similar level in the transfected cells. In vitro kinase assays confirmed that DRP-1 K42A is indeed unable to phosphorylate the MLC substrate. Such dependence on the catalytic activity for apoptotic function is apparent also in the other members of DAP kinase-related proteins (17, 29). In addition, a truncated form of DRP-1 which lacks the CaM-regulatory region displayed a constitutively active kinase and induced very high levels of apoptosis, thus further confirming the dependence of apoptosis on the overall catalytic activity.
The deletion mutant study presented here confirms the existence of yet another module responsible for apoptotic induction, which is located at the C-terminal part of DRP-1. This part of DRP-1 is also essential for its dimerization. Thus, we can conclude that homodimerization is a requirement for the functionality of this kinase in apoptosis, although this property can be completely overridden by a further deletion of the CaM-regulatory region. It is presently not clear how the dimerization influences the death-promoting effects of DRP-1 and whether self-dimerization has an impact on the catalytic activity. Another challenging question is why the C-terminal tail is functionally required only when the CaM-regulatory domain is present. So far, the conventional conditions of in vitro phosphorylation assays have not resolved the issue (not shown), and it is clear that some fine-tuning of the biochemical assessments is required.
The high homology in the kinase domains of DAP kinase and DRP-1 and the finding that they are both localized to the cytoplasm (in either soluble or insoluble form) imply that they may use the same or closely related substrates. The phosphorylation sites for these kinases on the substrate may be either different or identical. Thus, these kinases may cooperate to induce apoptosis in the same cell type or, alternatively, may function independently in different cell types, tissues, or organs in response to different stimuli or in different time frames. Another possibility is that these kinases act sequentially along the same signaling pathway to induce apoptosis. Here we provide the first observations that support the assumption that these kinases may be functionally linked to each other in some constellations. This is illustrated by the ability of a dominant negative form of DAP kinase (DAPk DD) to block apoptosis induced by DRP-1. Also the finding that both, DAP kinase (7) and DRP-1 (Fig. 8C) mediate killing by TNF is consistent with this scenario. These results indicate the need for a long-term study to establish whether direct or indirect interactions exist between DAP kinase and DRP-1. It should be mentioned that in the reciprocal approach, the effect of the dominant negative DRP-1 on DAP kinase was much less pronounced. A simple interpretation of these data would be to place DRP-1 upstream to DAP kinase; however, a definitive conclusion still awaits detailed biochemical data on the nature of the cross talk between these two kinases. Finally, it will be of interest to study whether DRP-1, like DAP kinase, acts as a tumor suppressor gene, subjected to loss of function in human tumors.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The first two authors contributed equally to this work.
We thank D. Wallach for providing the expression vector carrying the DN-MORT, M. Rubinstein for the Clontech spleen cDNA library, and Y. Shaul for the RFX-ΔSmaI construct. We thank T. Raveh for conducting the REF death assays.
This work was supported by the Israel Foundation, which is administered by the Israel Academy of Science and Humanities, and by QBI Ltd. A.K. is the incumbent of the Helena Rubinstein Chair of Cancer Research.
ADDENDUM IN PROOF
After the submission of the manuscript, a work describing some initial characteristics of human and mouse DRP-1 homologues was published (T. Kawai, F. Nomura, K. Hoshino, N. G. Copeland, D. J. Gilbert, N. A. Jenkins, and S. Akira, Oncogene 18:3471–3480, 1999).
REFERENCES
- 1.Anderson P. Kinase cascades regulating entry into apoptosis. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1997;61:33–46. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.61.1.33-46.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Basu S, Kolesnick R. Stress signals for apoptosis: ceramide and c-Jun kinase. Oncogene. 1998;17:3277–3285. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bokoch G M. Caspase-mediated activation of PAK2 during apoptosis: proteolytic kinase activation as a general mechanism of apoptotic signal transduction? Cell Death Differ. 1998;5:637–645. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cardone M H, Salvesen G S, Widmann C, Johnson G, Frisch S M. The regulation of anoikis: MEKK-1 activation requires cleavage by caspases. Cell. 1997;90:315–323. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80339-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cardone M H, Roy N, Stennicke H R, Salvesen G S, Franke T F, Stanbridge E, Frisch S, Reed J C. Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science. 1998;282:1318–1321. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5392.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cohen O, Feinstein E, Kimchi A. DAP-kinase is a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent, cytoskeletal-associated protein kinase, with cell death-inducing functions that depend on its catalytic activity. EMBO J. 1997;16:998–1008. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.5.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cohen O, Inbal B, Kissil J L, Spivak-Kroizman T, Raveh T, Berissi H, Feinstein E, Spivak T, Kimchi A. DAP-kinase participates in TNF-α and Fas-induced apoptosis and its function requires the death domain. J Cell Biol. 1999;146:141–148. doi: 10.1083/jcb.146.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Datta S R, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg M E. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell. 1997;91:231–241. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80405-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Deiss L P, Feinstein E, Berissi H, Cohen O, Kimchi A. Identification of a novel serine/threonine kinase and a novel 15-kD protein as potential mediators of the gamma interferon-induced cell death. Genes Dev. 1995;9:15–30. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Deiss L P, Kimchi A. A genetic tool used to identify thioredoxin as a mediator of a growth inhibitory signal. Science. 1991;252:117–120. doi: 10.1126/science.1901424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.del Peso L, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Page C, Herrera R, Nunez G. Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD through the protein kinase Akt. Science. 1997;278:687–689. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5338.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Feinstein E, Kimchi A, Wallach D, Boldin M, Varfolomeev E. The death domain: a module shared by proteins with diverse cellular functions. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20:342–344. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Green D, Kroemer G. The central executioners of apoptosis: caspases or mitochondria? Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8:267–271. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(98)01273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hanks S K, Quinn A M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Inbal B, Cohen O, Polak-Charcon S, Kopolovic J, Vadai E, Eisenbach L, Kimchi A. DAP kinase links the control of apoptosis to metastasis. Nature. 1997;390:180–184. doi: 10.1038/36599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jacobson M D, Weil M, Raff M C. Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell. 1997;88:347–354. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81873-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kawai T, Matsumoto M, Takeda K, Sanjo H, Akira S. ZIP kinase, a novel serine/threonine kinase which mediates apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:1642–1651. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.3.1642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kelliher M A, Grimm S, Ishida Y, Kuo F, Stanger B Z, Leder P. The death domain kinase RIP mediates the TNF-induced NF-kappaB signal. Immunity. 1998;8:297–303. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80535-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kimchi A. DAP genes: novel apoptotic genes isolated by a functional approach to gene cloning. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1377:F13–F33. doi: 10.1016/s0304-419x(98)00002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kissil J L, Kimchi A. Death-associated proteins: from gene identification to the analysis of their apoptotic and tumour suppressive functions. Mol Med Today. 1998;4:268–74. doi: 10.1016/s1357-4310(98)01263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kissil J L, Cohen O, Raveh T, Kimchi A. DAP-kinase loss of expression in various carcinoma and B-cell lymphoma cell lines: possible implications for role as tumor suppressor gene. EMBO J. 1999;18:353–362. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kogel D, Plottner O, Landsberg G, Christian S, Scheidtmann K H. Cloning and characterization of Dlk, a novel serine/threonine kinase that is tightly associated with chromatin and phosphorylates core histones. Oncogene. 1998;17:2645–2654. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Levy-Strumpf N, Kimchi A. Death associated proteins (DAPs): from gene identification to the analysis of their apoptotic and tumor suppressive functions. Oncogene. 1998;17:3331–3340. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Maundrell K, Antonsson B, Magnenat E, Camps M, Muda M, Chabert C, Gillieron C, Boschert U, Vial-Knecht E, Martinou J C, Arkinstall S. Bcl-2 undergoes phosphorylation by c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinases in the presence of the constitutively active GTP-binding protein Rac1. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:25238–25342. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.40.25238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.McCarthy J V, Ni J, Dixit V M. RIP2 is a novel NF-kappaB-activating and cell death-inducing kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:16968–16975. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.27.16968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.McCarthy N J, Whyte M K B, Gilbert C S, Evan G I. Inhibition of Ced-3/ICE-related proteases does not prevent cell death induced by oncogenes, DNA damage, or the Bcl-2 homologue Bak. J Cell Biol. 1997;136:215–227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.136.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Park J, Kim I, Oh Y J, Lee K, Han P L, Choi E J. Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase antagonizes an anti-apoptotic action of Bcl-2. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:16725–16728. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.27.16725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Reith W, Barras E, Satola S, Kobr M, Reinhart D, Herrero-Sanchez C, Mach B. Cloning of the major histocompatibility complex class II promoter binding protein affected in a hereditary defect in class II gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:4200–4204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sanjo H, Kawai T, Akira S. DRAKs, novel serine/threonine kinases related to death-associated protein kinase that trigger apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:29066–29071. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.44.29066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stanger B Z, Leder P, Lee T H, Kim E, Seed B. RIP: a novel protein containing a death domain that interacts with Fas/APO-1 (CD95) in yeast and causes cell death. Cell. 1995;81:513–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sun X, Lee J, Navas T, Baldwin D T, Stewart T A, Dixit V M. RIP3, a novel apoptosis-inducing kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:16871–16875. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.24.16871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Verheij M, Ruiter G A, Zerp S F, van Blitterswijk W J, Fuks Z, Haimovitz-Friedman A, Bartelink H. The role of the stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK/JNK) signaling pathway in radiation-induced apoptosis. Radiother Oncol. 1998;47:225–232. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(98)00007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.White E. Life, death, and the pursuit of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1–15. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yu P W, Huang B C, Shen M, Quast J, Chan E, Xu X, Nolan G P, Payan D G, Luo Y. Identification of RIP3, a RIP-like kinase that activates apoptosis and NFkappaB. Curr Biol. 1999;9:539–542. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]