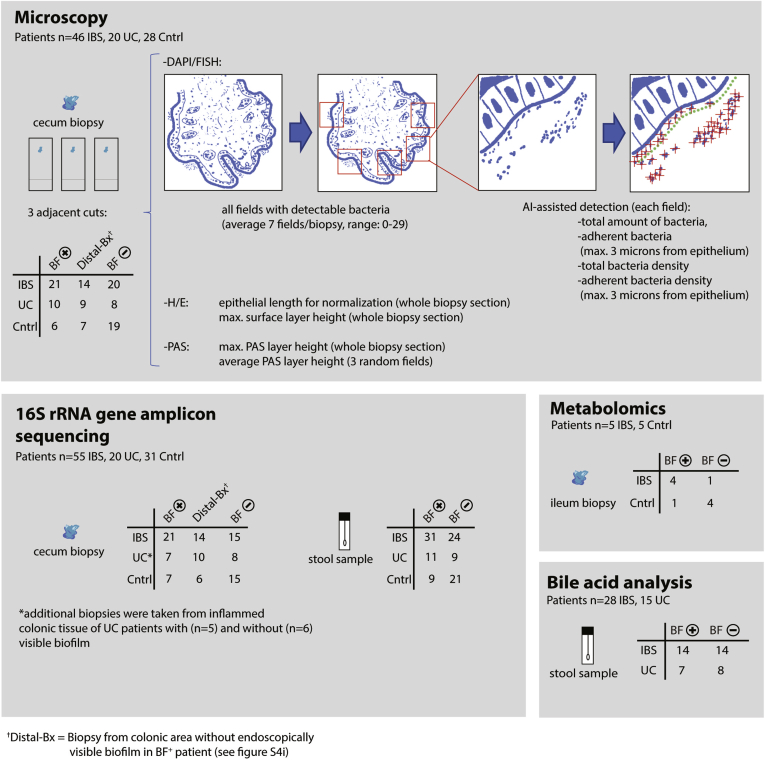
Supplementary Figure 3.
Description of in-depth molecular and microscopic analysis in a subset of the primary cohort. Depiction of in-depth microscopic and molecular analysis, including sample material, patient cohorts, and sample number. Microscopic analysis (top panel): analysis was performed on methacarn-fixed cecal biopsies (endoscopically BF+, BF–, and areas without biofilm from BF+ patients [Distal-Bx]), 3 adjacent sections from each biopsy were processed for DAPI/FISH, H&E, and PAS analysis. Confocal microscopy images were obtained from all areas of the whole section with visible bacteria in the DAPI channel. Each image was subjected to artificial intelligence–assisted quantification of bacteria to calculate total number of bacteria normalized to length of epithelium per section (amount of bacteria); maximum density of bacteria in one 144.7 × 144.7 μm confocal microscopy image per section (bacterial density); number of bacteria 3 μm from the epithelium, normalized to length of epithelium per section (adherent bacteria); and maximum density of bacteria up to 3 μm distal from the epithelium in one 144 × 144 μm confocal microscopy image per section (adherent bacteria density). H&E-stained sections were analyzed for the whole length of the epithelium (for normalization) and maximum width of H&E surface layer on top of epithelium per section (surface layer). PAS-stained sections were analyzed for average and maximum width of PAS-stained surface layer on top of epithelium per section (average PAS layer height, maximum PAS layer height). 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing (bottom left panel) was performed from snap-frozen cecal biopsies (BF+ and BF– and areas without biofilm from BF+ patients [Distal-Bx]) and stool samples (BF+ and BF–). Metabolomics (bottom right panel) was performed on snap-frozen ileal biopsies (BF+ and BF–). BA analysis (bottom right panel) was performed on stool samples (BF+ and BF–).