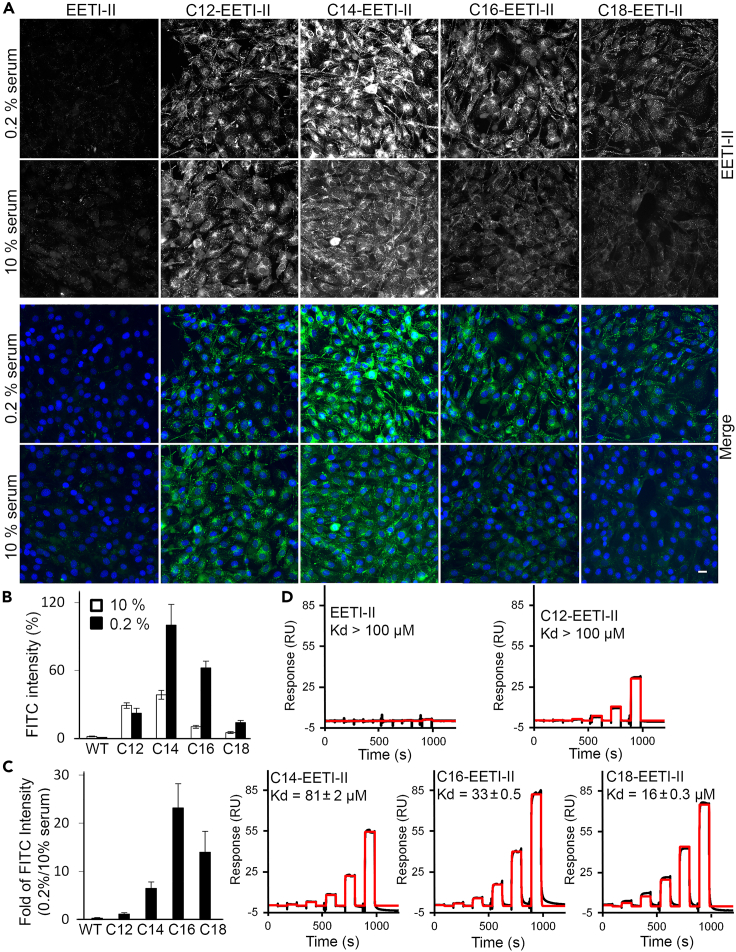
Figure 4.
Fatty acylated EETI-II peptides bind to serum albumin
(A–C) Cellular uptake of C14, C16, and C18-EETI-II is enhanced with reduced serum. NIH3T3 cells were preincubated with 10% or 0.2% FBS supplemented medium then incubated with WT or fatty acylated EETI-II-A488 (5 μM) for 2 h at 37°C in 10% or 0.2% FBS supplemented medium. Cells were washed, fixed with 4% PFA and processed as described in the STAR Methods section. Fluorescence images were captured on a high throughput ImageXpress Micro XL imaging system (Molecular Devices). Representative images from four independent experiments are shown. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(D) Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) shows fatty acylated EETI-II peptides bind to human serum albumin. SPR sensor chip SA was coated with biotinylated human serum albumin and subjected to the peptides at varying concentrations (30, 10, 3.33, 1.11, 0.37, 0.123 μM) in PBST (0.05% Tween 20). Shown are measured binding responses (black) and curve fits (red) to a two-state model, assuming two preferred fatty acid binding sites on albumin. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. Binding constant values represent mean ± S.E.M.