Correction to: Mol Med (2021) 27:109 https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-021-00374-4
Following publication of the original article (Zhang et al. 2021), the authors informed us that they misused the wrong file of Fig. 7A. The correct Fig. 7 is given below.
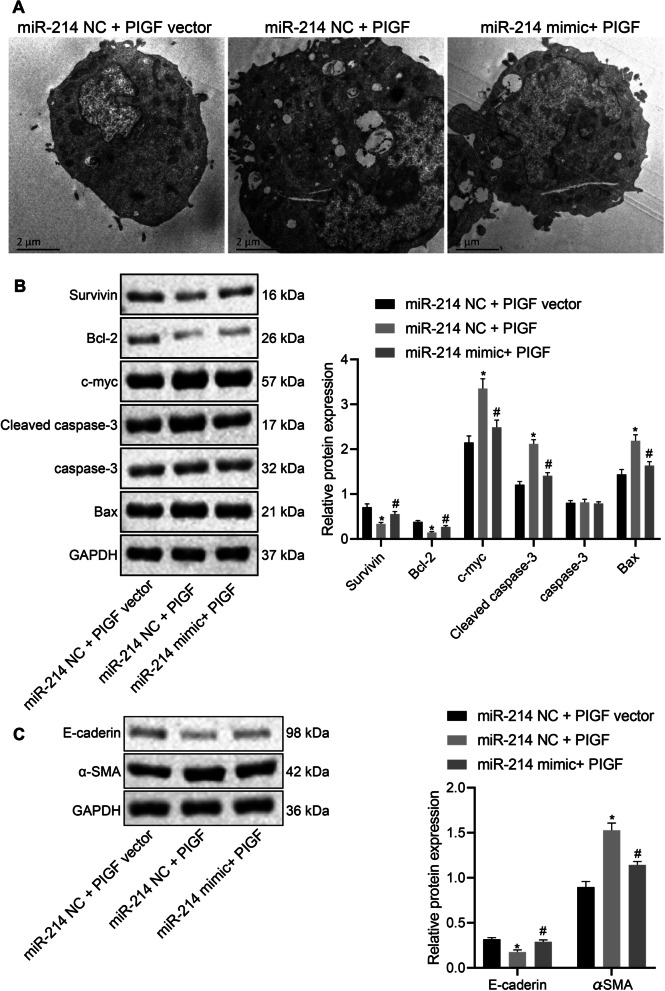
Fig. 7.
miR-214 overexpression blocks the effect of the activated STAT3 pathway on bronchial embryonic pulmonary epithelial cells by inhibiting PlGF. A The ultrastructure of alveolar epithelial cells under TEM (×10,000). B Western blot analysis to quantify the expression of antiapoptotic proteins (Survivin and Bcl-2) and proapoptotic proteins (Bax, c-myc, and cleaved caspase-3) proteins in embryonic pulmonary epithelial cells. C Western blot analysis to quantify the expression of the epithelial cell marker E-cadherin and the fibrosis marker α-SMA in embryonic pulmonary epithelial cells. Data are summarized as mean ± standard deviation. *p < 0.05 vs. pulmonary epithelial cells transfected with miR-214 NC and PlGF NC. #p < 0.05 vs. pulmonary epithelial cells transfected with miR-214 NC and PlGF. Multiple comparisons were performed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Each experiment was repeated three times
The original article has been corrected.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Reference
- Zhang Z-Q, Hong H, Li J, Li X-X, Huang X-M. MicroRNA-214 promotes alveolarization in neonatal rat models of bronchopulmonary dysplasia via the PlGF-dependent STAT3 pathway. Mol Med. 2021;27:109. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00374-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]