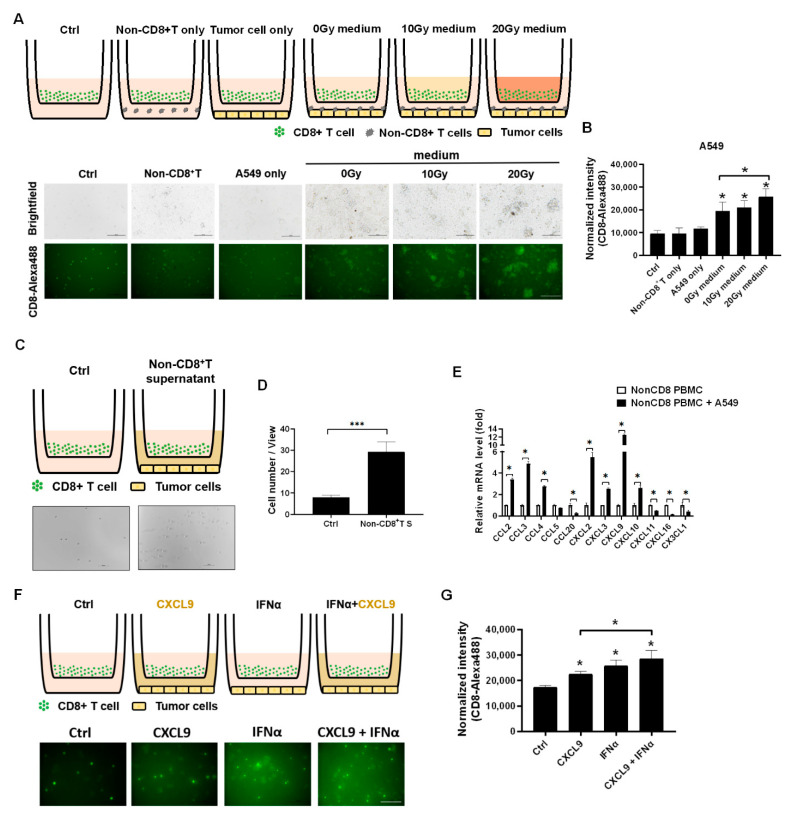
Figure 2.
Irradiation-treated A549 medium and nonCD8+ PBMCs supernatant increased CD8+ T cell migration in vitro. (A) The isolated CD8+ T cells treated with the irradiation-treated A549 medium loaded on top of a 0.3 μm plate and lung cancer A549 or PC9 cells with nonCD8+ PBMCs loaded on down well for 24-h incubation. The CD8+ T cells were pre-labeled with Alexa488-labeled anti-CD8 antibody. (B) Quantitation of Alexa488 fluorescence representing CD8+ T cell migration activity was measured and compared based on 3-times repeat. (C) Since the A549 with nonCD8+ PBMCs enhanced CD8+ T cell migration, the supernatant of A549 with nonCD8+ PBMCs post 24 h was collected and investigated whether which increased CD8+ T cell migration. (D) CD8+ T cells migrating through 0.3 μm transwell were calculated and compared based on 3-times repeat. (E) The chemokines associated with CD8+ T cell trafficking were detected in nonCD8+ PBMCs after incubation with A549 for 24 h, including CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CCL20, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, CXCL16, and CX3CL1. (F) The healthy CD8+ T cells were treated with individual 20 ng/mL of CXCL9 or IFNα for 24 h and (G) the Alexa488 fluorescence was captured and measured based on 3-times repeat. The quantification was calculated based on 3-times repeat in qPCR assay. Scale bar, 100 μm. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001.