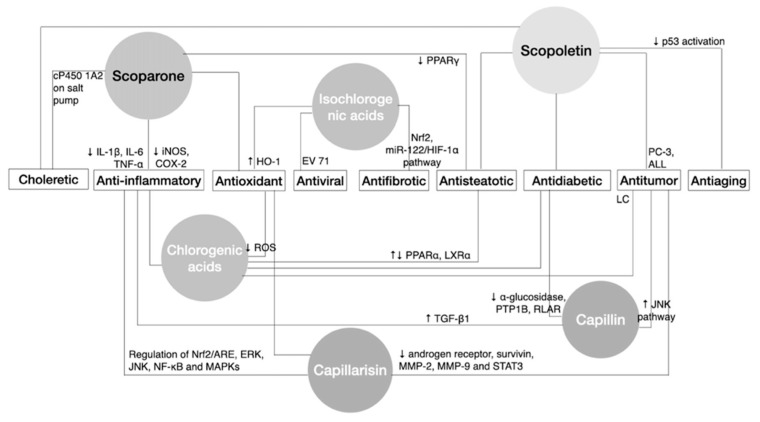
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the bioactive components of Artemisia capillaris contributing to its therapeutic effects. Bioactive compounds include scoparone, scopoletin, capillarisin, capillin, chlorogenic acid, and isochlorogenic acid, which induce pharmacological effects of A. capillaris in a synergistic manner. PC-3: prostate cancer cells; ALL: acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells; LC: lung cancer cells; ↓ decrease or inhibit effects; ↑ increase or enhance effects; ↓↑ modulate effects.