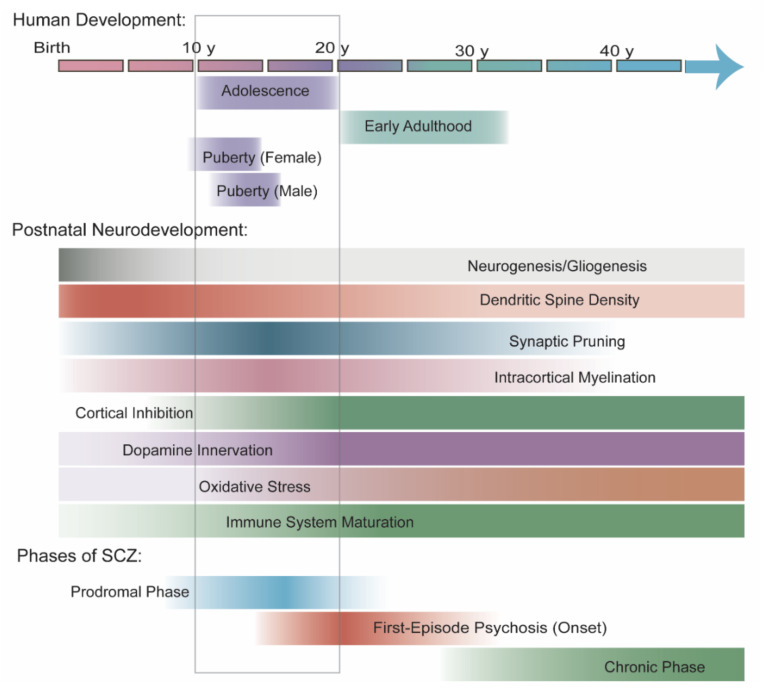
Figure 3.
Overview of human postnatal neurodevelopment and the stages of SCZ. The prodromal phase of SCZ typically overlaps with adolescent development, and first-episode psychosis (and diagnosis) typically occurs in late adolescence or early adulthood. The chronic disease phase persists throughout adulthood. The onset of early SCZ symptoms during adolescence overlaps with many facets of brain maturation, including intracortical myelination, synaptic pruning, maturation of GABAergic and dopaminergic signaling in the PFC, increases in oxidative stress markers, and maturation of both the innate and adaptive immune systems. Dysregulation of any (or all) of these processes might contribute to symptom onset.