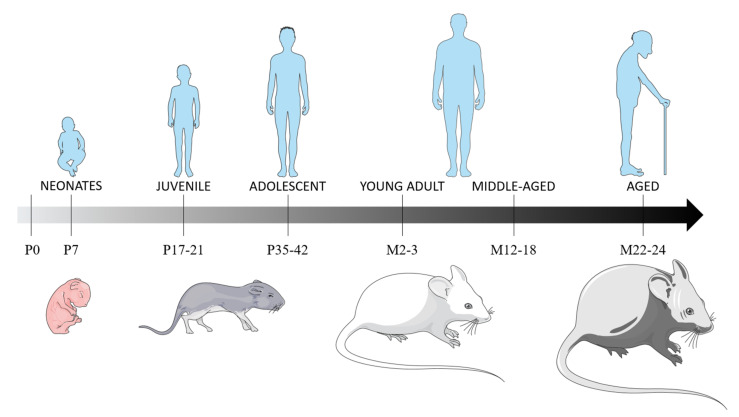
Figure 1.
Rats’ and mice’ age correspondence with humans, based on brain and metabolism development, and sexual maturation. The brain developmental period occurs during the first three post-natal weeks, with the main brain growth-spurt period in the first post-natal week, a period of maximal neuronal proliferation, glial proliferation and the establishment of synaptic connections [132,133]. At P11, the neurological development in rodents is equivalent of a child below the age of 4 years [134]. Rodents can be considered juvenile at P17-21, based on equivalent synapse formation and γ-aminobutyric acid synthesis than in humans [135]. P35 rodents can be considered equivalent to preadolescent humans [136], as they will have developed 90% of their adult metabolic process [137] and as their sexual maturity is achieved at P60 [138]. Abbreviations: P: postnatal day; M: postnatal months.