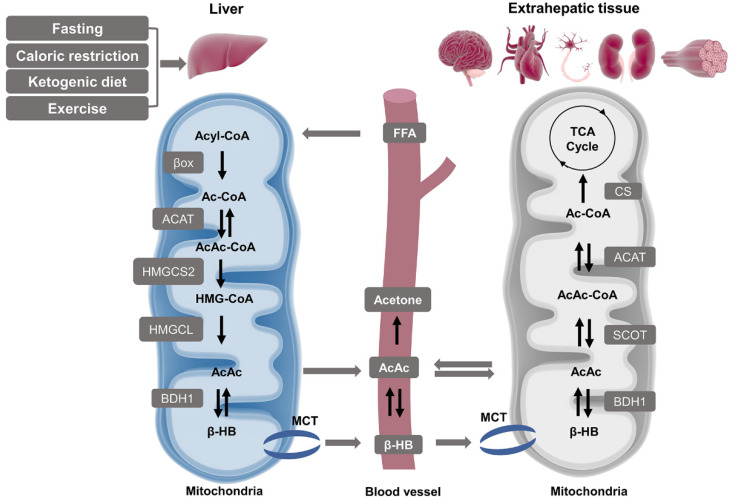
Figure 2.
Pathways of ketogenesis in liver and ketolysis in extrahepatic tissues. Hepatic mitochondria act as the primary site for the synthesis of blood ketone bodies by using fatty acids-derived Ac-CoA which is generated by β oxidation. The following process requires four enzymes: ACAT, HMGCS2, HMGCL, and BDH1, and the intermediate product covers AcAc-CoA, HMG-CoA, and AcAc. β-HB is finally produced and released to the bloodstream and uptaken by extrahepatic tissues such as the brain, heart, neurons, kidneys, and muscles through MCT. Both β-HB and AcAc can be oxidized and converted to Ac-CoA and produce ATP via the TCA cycle as an alternative energy source. Abbreviations: AcAc, acetoacetate; AcAc-CoA, acetoacetyl CoA; ACAT, acetyl-CoA A acetyltransferase; Ac-CoA, acetyl CoA; BDH1, β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase 1; β-HB, β-hydroxybutyrate; βox, β oxidation; CS, citrate synthase; FFA, free fatty acid; HMGCL, HMG-CoA lyase; HMGCS2, 3-hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA; MCT, monocarboxylate transporter; SCOT, succinyl-CoA:3-oxoacid CoA transferase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid.