Abstract
Purpose:
To compare the outcomes of iStent vs. iStent inject implantation combined with phacoemulsification.
Methods:
This single center retrospective comparative case series included subjects with open angle glaucoma who underwent iStent or iStent inject implantation combined with phacoemulsification with ≥1 year follow-up. The main outcome measures were in-group and between-group changes in intraocular pressure (IOP) and medication number, proportion of eyes that achieved IOP ≤15 mmHg, and surgical success defined as 20% IOP reduction from baseline at 6/12 months. Univariate/multivariate regression analyses were done to identify predictors of surgical failure.
Results:
One hundred ninety-seven eyes of 148 patients were included (122 iStent, 75 iStent inject). Both groups achieved significant IOP and medication reduction at months 6/12 (P < 0.05). At month 6, IOP was significantly lower in iStent inject vs. iStent eyes (P = 0.003), but the difference was insignificant by month 12 (P = 0.172). Medication number was comparable in both groups at months 6/12 (P > 0.05). More iStent inject eyes achieved IOP ≤15 mmHg at month 6 (P = 0.003) and 12 (P = 0.047). Surgical success was comparable in both groups at months 6/12 (P > 0.05). Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed similar cumulative rate of surgical failure at year-1 in both groups (P = 0.644). The multivariate model identified older age (P = 0.017) and lower baseline IOP (P = 0.002) as the strongest predictors of surgical failure.
Conclusion:
Compared to iStent, iStent inject achieved lower IOP at month 6 and higher proportion of eyes achieved IOP ≤15 mmHg at month 6/12. However, surgical success was similar in both groups. Predictors of surgical failure were older age and lower baseline IOP rather than the stent type.
Keywords: iStent, iStent inject, minimally invasive glaucoma surgery, open angle glaucoma, phacoemulsification, trabecular microbypass stent
Glaucoma is a leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide.[1,2] Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is one of the major risk factors for development and progression of open angle glaucoma (OAG) and its reduction is considered the only intervention proved to slow progression of the disease.[3] IOP reduction is currently achieved by topical hypotensive medications, laser therapy, or incisional surgical procedures. However, poor compliance and tolerability have been an issue with medications,[4] and serious complications have been associated with incisional surgeries.[5] Recently, minimally invasive glaucoma surgeries have emerged to provide safer and effective IOP reduction.[6]
Trabecular microbypass stents work by improving conventional trabecular outflow through Schlemm’s canal, bypassing the trabecular meshwork, which is considered the major site of aqueous outflow resistance in OAG.[7] iStent® (Glaukos Corporation, Laguna Hills, CA, USA) was the first trabecular microbypass stent to be approved in the United States. Several studies have proved its efficacy and safety either as a solo procedure[8,9,10] or combined with phacoemulsification.[11,12,13] Further studies comparing the effect of single vs. multiple stent implantation have reported increasing therapeutic efficacy with each additional stent.[14,15,16]
The second generation iStent inject® (Glaukos Corporation, Laguna Hills, CA, USA) was developed with a modified injector allowing surgeons to implant both stents with a single entry into the eye. The head of the device has four side outlets in addition to the central one, theoretically allowing multidirectional aqueous outflow.[17] The device is also designed for a simplified surgical technique compared to the first generation. iStent inject efficacy and safety have been studied either standalone[18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26] or combined with phacoemulsification.[17,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34] However, the literature comparing both devices is relatively limited.[35,36,37,38]
Methods
Study design
This was a single-center, retrospective comparative case series. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Wills Eye Hospital in December 2020 and was in accordance with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act regulations. As this was a retrospective study with deidentified data, informed consent was not required. The medical records of consecutive patients who underwent phacoemulsification combined with iStent or iStent inject implantation for OAG at Wills Eye Hospital between 2016 and 2019 were reviewed. Patients were matched for age and baseline visual acuity (VA), IOP, and medication number.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Patients aged ≥18 years diagnosed with OAG including primary open angle glaucoma (POAG), pigmentary glaucoma (PG), pseudoexfoliation glaucoma, and normal tension glaucoma (NTG) were included. Preoperative glaucoma diagnosis and severity were based on the American Academy of Ophthalmology and Medicare International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems diagnosis criteria.[39] Eyes with prior intraocular surgery or less than 1-year follow-up were excluded. Due to its relatively recent approval, iStent inject eyes that completed 6-month follow-up were also included for month-6 analysis.
Patient visits
Visits at baseline, postoperative day 1, week 1, months 1, 3, 6, and 12 were reviewed from electronic medical records. Demographic data including age, sex, and race as well as glaucoma type and severity were collected. Preoperative clinical data included VA, IOP, topical glaucoma medications, cup to disc ratio, and gonioscopy findings. Postoperative data included VA, IOP, glaucoma medications, postoperative complications, and need for additional glaucoma surgery.
Surgical procedure
Seven surgeons at Wills Eye Hospital participated in this study. The choice of the stent was based on the availability of iStent only before 2018 and the surgeon preference following iStent inject release. Device implantation occurred after phacoemulsification. Through a temporal clear corneal incision and under direct-gonioscopic visualization, the self-trephinating tip of the iStent was used to penetrate the trabecular meshwork. Once the device was placed in the Schlemm’s canal, the inserter button was depressed to release the device. The inserter tip was used to fully drive the iStent into the canal [Fig. 1, Supplementary Video 1]. For iStent inject, the sleeve of the injector was retracted, revealing the trocar and microinsertion tube. The trocar was penetrated through the trabecular meshwork, and the delivery button was depressed to implant the first stent and the second stent placed 2–3 clock hours away [Fig. 2, Supplementary Video 2].
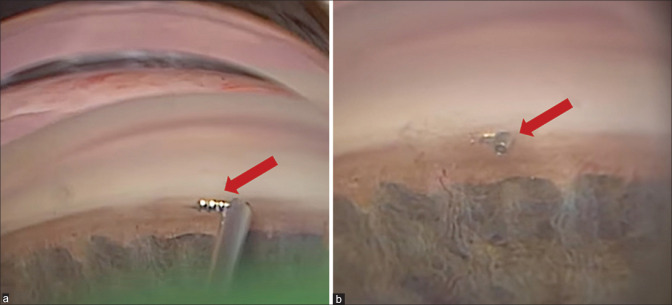
Figure 1.
Intraoperative gonioscopic view of Single iStent. (a) iStent in the injector before implantation (arrow). (b) iStent successfully implanted in the Schlemm’s canal (arrow). Courtesy of Dr Reza Razeghinejad, Glaucoma Service, Wills Eye Hospital
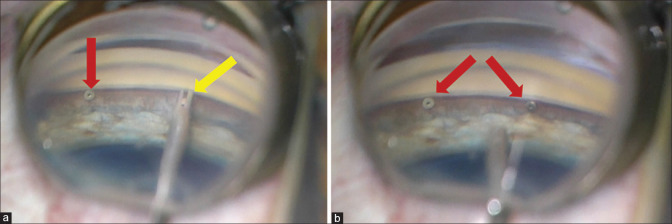
Figure 2.
Intraoperative gonioscopic view of double iStent inject. (a) The first iStent inject embedded in the Schlemm’s canal (red arrow) and the second one in the injector before implantation (yellow arrow). (b) Both iStent inject devices are successfully implanted in the Schlemm’s canal (arrows). Courtesy of Dr Reza Razeghinejad, Glaucoma Service, Wills Eye Hospital
Outcome measures
The primary outcome measures were in-group and between-group comparisons of IOP and medication number, proportions of eyes that achieved the effectiveness endpoint as IOP ≤15 mmHg, and surgical success defined as 20% or more IOP reduction from the baseline at 6 and 12 months. Predictors of failure were analyzed using univariate and multivariate regression analyses. Safety measures included intraoperative and postoperative adverse events, need for reoperation for complications or glaucoma, and changes in VA.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software version 27.0 (IBM Analytics, Chicago, IL, USA). Snellen VA measurements were converted to logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution (logMAR) VA equivalents for the purpose of data analysis. Continuous variables were presented as mean ± standard deviation. Proportions (%) were used to describe categorical variables. Two-sided Student’s t-tests and Chi-square tests (Fisher exact tests) were used to compare treatment groups for continuous and categorical variables, respectively. Paired sample t-tests and McNemar test were used to compare continuous and categorical variables within the same group, respectively. Analysis of covariance was performed for between-group comparisons after adjusting for the baseline characteristics. P values < 0.05 were considered significant. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis with log-rank tests were used to report cumulative rate of surgical failure. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify factors predictive of surgical failure. Variables in the univariate analysis with P values ≤ 0.2 were entered into the multivariate regression model using the forward stepwise Wald method. Hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals were generated for both univariate and multivariate regression models. Estimation of sample size (80% power and an alpha of 0.05) was performed by considering prior outcomes from a retrospective comparative case series, which detected a significantly greater IOP reduction for iStent inject eyes than for iStent eyes at month 12 with a sample size of 70 and 67 in each study group, respectively.[36] A mixed effect linear model was done to account for the use of two eyes from a single patient with the surgical eye variable was added as a random effect.
Results
Baseline characteristics
One hundred ninety-seven eyes of 148 patients were included (122 iStent, 75 iStent inject). Baseline characteristics are displayed in Table 1. Age, sex, and ocular characteristics were comparable between groups. White race was predominant in the iStent group and represented 73.5%, while Black individuals were more prevalent in the iStent inject group and represented 42.0% (P < 0.001). POAG was the most common diagnosis (82.7%) with no difference between groups (P = 0.956). Most of eyes (91.4%) had mild to moderate disease with no difference between groups (P = 0.929). All patients completed 6-month follow-up. By month 12, all iStent eyes (N = 122) and only 60/75 of the iStent inject eyes were available for the analysis.
Table 1.
Baseline Characteristics in the iStent and iStent inject Groups
| iStent n=98 | iStent inject n=50 | Total n=148 | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age: Years | 76.3±7.8 | 73.5±8.3 | 75.3±8.1 | 0.100 | |
| Sex, Females: n (%) | 52 (53.1) | 31 (62.0) | 83 (56.1) | 0.382 | |
| Race: n (%) | White | 72 (73.5) | 19 (38.0) | 91 (61.5) | < 0.001 |
| Black | 18 (18.4) | 21 (42.0) | 39 (26.4) | ||
| Asian | 5 (5.1) | 5 (10.0) | 10 (6.8) | ||
| Others | 3 (3.1) | 5 (10.0) | 8 (5.4) | ||
|
| |||||
| iStent n=122 | iStent inject n=75 | Total n=197 | P | ||
|
| |||||
| Study Eye, Right: n (%) | 58 (47.5) | 37 (49.3) | 95 (48.2) | 0.883 | |
| Glaucoma Type: n (%) | POAG | 100 (82.0) | 63 (84.0) | 163 (82.7) | 0.956 |
| PG | 3 (2.5) | 2 (2.7) | 5 (2.5) | ||
| PXG | 7 (5.7) | 3 (4.0) | 10 (5.1) | ||
| NTG | 12 (9.8) | 7 (9.3) | 19 (9.7) | ||
| Glaucoma Severity | Mild | 49 (40.2) | 32 (42.7) | 81 (41.1) | 0.929 |
| Moderate | 62 (50.8) | 37 (49.3) | 99 (50.3) | ||
| Severe | 11 (9.0) | 6 (8.0) | 17 (8.6) | ||
| Visual Acuity: LogMAR | 0.31±0.33 | 0.38±0.38 | 0.34±0.35 | 0.152 | |
| Intraocular Pressure: mmHg | 16.2±2.9 | 15.4±4.4 | 15.9±3.5 | 0.171 | |
| Medication Number | 2.0±1.0 | 1.7±1.1 | 1.9±1.0 | 0.100 | |
| Cup to Disc Ratio | 0.6±0.2 | 0.7±0.2 | 0.7±0.2 | 0.323 | |
| Visual Field Mean Deviation: dB | -9.1±5.3 | -8.9±4.9 | -9.0±5.1 | 0.978 | |
| Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness: Microns | 69.1±10.0 | 70.2±10.1 | 69.5±9.9 | 0.899 | |
| Central Corneal Thickness: Microns | 532.0±26.0 | 528.0±24.0 | 530.0±25.0 | 0.911 | |
POAG: primary open angle glaucoma, PG: pigmentary glaucoma, PXG: Pseudoexfoliation glaucoma, and NTG: normal tension glaucoma
Intraocular pressure
Both study groups experienced significant IOP reduction through months 6 and 12. Mean IOP in the iStent eyes was reduced from 16.2 ± 2.9 mmHg at baseline to 14.9 ± 3.6 mmHg at month 6 (1.3 ± 3.4 mmHg IOP reduction, P < 0.001) and to 15.1 ± 3.5 mmHg at month 12 (1.1 ± 3.3 mmHg IOP reduction, P < 0.001). In iStent inject group, mean IOP was reduced from 15.4 ± 4.4 at baseline to 13.2 ± 3.9 mmHg at month 6 (2.2 ± 4.1 mmHg IOP reduction, P < 0.001). By month 12, the available 60 iStent inject eyes maintained significantly lower IOP (14.0 ± 5.2) mmHg compared to their baseline (1.5 ± 5.0 IOP reduction, P = 0.023). Months 6 and 12 outcomes of both study groups are displayed in Table 2.
Table 2.
In-group Comparison of Month 6 and Month 12 Outcomes in the iStent and iStent inject Groups
| Baseline | Month 6 | Difference | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| iStent (n=122) | ||||
| Visual Acuity: LogMAR | 0.31±0.33 | 0.17±0.38 | 0.15±0.33 | < 0.001 |
| Intraocular Pressure: mmHg | 16.2±2.9 | 14.9±3.6 | 1.3±3.4 | < 0.001 |
| Medication Number | 2.0±1.0 | 1.3±1.0 | 0.7±0.9 | < 0.001 |
| iStent inject (n=75) | ||||
| Visual Acuity: LogMAR | 0.38±0.38 | 0.17±0.37 | 0.21±0.22 | < 0.001 |
| Intraocular Pressure: mmHg | 15.4±4.4 | 13.2±3.9 | 2.2±4.1 | < 0.001 |
| Medication Number | 1.7±1.1 | 1.4±1.1 | 0.3±1.1 | 0.014 |
|
| ||||
| Baseline | Month 12 | Difference | P | |
|
| ||||
| iStent (n=122) | ||||
| Visual Acuity: LogMAR | 0.31±0.33 | 0.17±0.37 | 0.14±0.32 | < 0.001 |
| Intraocular Pressure: mmHg | 16.2±2.9 | 15.1±3.5 | 1.1±3.3 | < 0.001 |
| Medication Number | 2.0±1.0 | 1.3±1.0 | 0.7±0.9 | < 0.001 |
| iStent inject (n=60) | ||||
| Visual Acuity: LogMAR | 0.41±0.40 | 0.17±0.37 | 0.24±0.24 | < 0.001 |
| Intraocular Pressure: mmHg | 15.6±4.7 | 14.0±5.2 | 1.5±5.0 | 0.023 |
| Medication Number | 1.9±1.1 | 1.5±1.2 | 0.4±1.1 | 0.011 |
| Visual Field Mean Deviation: dB | -8.9±4.9 | -7.5±5.0 | -1.4±3.8 | 0.013 |
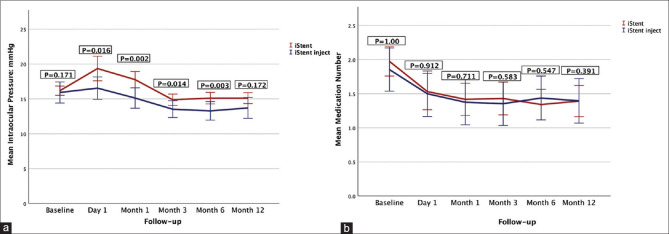
Regarding between-group comparison, the IOP was significantly lower in the iStent inject compared to the iStent eyes at month 6 (P = 0.003), and this difference remained significant even after adjusting for the baseline IOP using analysis of covariance testing. However, this significant difference was not maintained by month 12 (P = 0.172). Fig. 3a shows IOP changes in both groups over time. Proportion of eyes with IOP ≤15 mmHg was significantly higher in the iStent inject group (70.7%) compared to the iStent group (49.2%) (P = 0.003) at month 6. The same trend continued through month 12, with significantly higher proportions of iStent inject eyes (61.4%) maintained IOP ≤15 mmHg as compared to 46.7% of iStent eyes (P = 0.047).
Figure 3.
(a) Intraocular pressure changes over time in the iStent and iStent inject groups. iStent inject eyes had significantly lower intraocular pressure in the first 6 months. At month 12, the difference was insignificant. (b) Medication number changes over time in the iStent and iStent inject groups. Both groups had similar medication number at all postoperative visits
At month 6, 50.8% of the iStent eyes and 60.0% of the iStent inject eyes achieved surgical success defined as 20% or more IOP reduction, but this difference was insignificant (P = 0.240). By month 12, lower proportions in both groups maintained 20% IOP reduction (47.5 and 50.0%, respectively; P = 0.875). Kaplan–Meier survival analysis [Fig. 4] comparing cumulative rate of surgical failure between iStent (N = 122) and iStent inject (N = 75) eyes at 1 year revealed no difference between the groups (P = 0.644).
Figure 4.
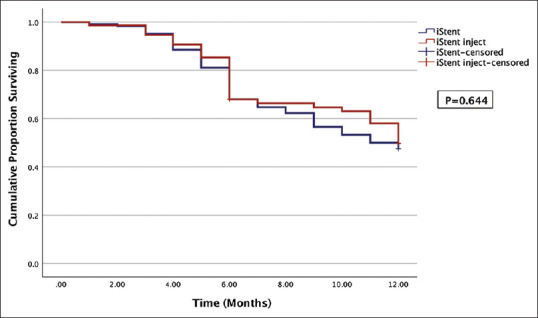
Kaplan–Meier survival curve of surgical failure in the iStent and iStent inject groups. Both groups demonstrated similar cumulative rate of failure over 1 year
Based on findings from the univariate regression analysis, a multivariate model including age, sex, baseline IOP, and baseline cup to disc ratio was created [Table 3]. This model (P < 0.001) demonstrated that older age (P = 0.017) and lower baseline IOP (P = 0.002) were the strongest predictors of surgical failure at month 12. Race, glaucoma type, and stent type were not significant predictors of surgical failure. Although female sex (P = 0.027) and eyes with smaller cup to disc ratio (P = 0.088) tended to have more failure in the univariate analysis, these covariates were insignificant in the multivariate model.
Table 3.
Predictors of Month 12 Surgical Failure Using Univariate and Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis
| Univariate Analysis | Success n=88 | Failure n=94 | Wald | P | Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||||||
| Age: Years | 74.5±8.8 | 76.5±7.9 | 2.718 | 0.099 | 1.031 | 0.994-1.068 | |
| Sex, Female: n (%) | 47 (53.4) | 64 (68.1) | 4.913 | 0.027 | 1.988 | 1.083-3.649 | |
| Race n (%) | White | 65 (73.9) | 74 (78.7) | ||||
| Black | 15 (17.0) | 18 (19.1) | 0.722 | 0.396 | 0.837 | 0.555-1.262 | |
| Asian | 5 (5.7) | 1 (1.1) | |||||
| Others | 3 (3.4) | 1 (1.1) | |||||
| Etiology | |||||||
| Glaucoma Type: n (%) | POAG | 75 (85.2) | 77 (81.9) | 1.628 | 0.202 | 0.898 | 0.760-1.060 |
| PG | 3 (3.4) | 1 (1.1) | |||||
| PXG | 5 (5.7) | 4 (4.3) | |||||
| NTG | 5 (5.7) | 12 (12.7) | |||||
| Baseline Intraocular Pressure: mmHg | 16.7±3.6 | 15.3±3.4 | 6.219 | 0.013 | 0.894 | 0.819-0.976 | |
| Baseline Cup to Disc Ratio | 0.7±0.2 | 0.6±0.2 | 2.907 | 0.088 | 0.138 | 0.014-1.344 | |
| Surgery | |||||||
| Surgery Type: n (%) | iStent | 58 (65.9) | 64 (68.1) | 0.000 | 0.983 | 1.007 | 0.536-1.890 |
| iStent inject | 30 (34.1) | 30 (31.9) | |||||
|
| |||||||
| Multivariate Analysis P<0.001 | Success n=85 | Failure n=94 | Wald | P | Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|
| |||||||
| Age: Years | 74.5±8.8 | 76.5±7.9 | 5.723 | 0.017 | 1.111 | 1.019-1.210 | |
| Sex, Female: n (%) | 47 (53.4) | 64 (68.1) | 0.392 | 0.531 | 1.615 | 0.360-7.244 | |
| Baseline Intraocular Pressure: mmHg | 16.7±3.6 | 15.3±3.4 | 9.144 | 0.002 | 0.708 | 0.566-0.885 | |
| Baseline Cup to Disc Ratio | 0.7±0.2 | 0.6±0.2 | 1.461 | 0.211 | 0.015 | 0.000-2.170 | |
POAG: primary open angle glaucoma, PG: pigmentary glaucoma, PXG: Pseudoexfoliation glaucoma, NTG: normal tension glaucoma, and IOP: intraocular pressure
A mixed effect linear model was done to account for the use of two eyes from a single patient. This model showed that the surgical eye (right vs. left) was not a significant covariate for month 12 surgical failure (P = 0.853) effectively nullifying which eye/eyes were picked for each patient since it is random.
Medical therapy
There was a significant reduction in the need for medical therapy in both treatment groups through months 6 and 12. Mean number of glaucoma medications in the iStent group decreased from 2.0 ± 1.0 at baseline to 1.3 ± 1.0 at month 6 and remained the same at month 12 (0.7 ± 0.9 medication reduction, P < 0.001). Mean number of glaucoma medications in the iStent inject group decreased from 1.7 ± 1.1 at baseline to 1.4 ± 1.1 at month 6 (0.3 ± 1.1 medication reduction, P = 0.014). At month 12, the available 60 iStent inject eyes maintained lower number of medications 1.5 ± 1.2 compared to their baseline 1.9 ± 1.1 (0.4 ± 1.1 medication reduction, P = 0.011).
Between-group comparison showed no significant difference in the medication number at monthS 6 (P = 0.547) and 12 (P = 0.391). Fig.3b shows medication number in both groups over time. Similar proportions of eyes in iStent vs. iStent inject groups were medication free at months 6 (30.3% vs. 26.7%, P = 0.630) and month 12 (28.7% vs. 25%, P = 0.724).
Visual acuity and visual field
VA significantly improved postoperatively [Table 2] with no difference between groups at month 6 (P = 0.432) and 12 (P = 0.967), which is consistent with expectations of combined cataract surgery. In the iStent group, mean LogMAR VA increased from 0.31 ± 0.33 at baseline to 0.17 ± 0.38 at month 6 (P < 0.001) and 0.17 ± 0.37 at month 12 (P < 0.001). In the iStent inject group, mean LogMAR VA increased from 0.38 ± 0.3 at baseline to 0.17 ± 0.37 at month 6 (P < 0.001), also eyes completed month 12 follow-up showed significant improvement in VA (0.17 ± 0.37) compared to their baseline (0.41 ± 0.40) (P < 0.001).
Visual field mean deviation showed significant improvement at month 12 in both the iStent (P = 0.011) and iStent inject (P = 0.013) groups compared to their baseline [Table 2]. This improvement may be related to improvement of generalized sensitivity following cataract surgery and rules out progression of glaucoma.
Safety
Both iStent and iStent groups demonstrated high safety profile. Intraoperative adverse events were minimal. Blood reflux was observed in five (4.1%) iStent eyes and two (2.7%) iStent inject eyes. Failure to implant the second stent occurred in seven (9.3%) iStent inject eyes. Posterior capsular rupture and anterior vitrectomy occurred in one iStent inject eye, and both stents were successfully implanted. Early postoperative complications including hyphema, corneal edema, and iritis were mild and transient in both groups. Postoperative day 1 pressure spikes defined as 10 mmHg IOP rise as compared to the baseline were significantly higher in the iStent vs. iStent inject group (11.5% vs. 2.7%, respectively; P = 0.032). Only one iStent inject eye developed postcataract cystoid macular edema that required repeated posterior subtenon triamcinolone injection. Otherwise, no eyes experienced decline in the VA at any time point postoperatively. By month 12, reoperation for glaucoma was not required for any iStent inject eyes, while two iStent eyes underwent invasive glaucoma surgery for uncontrolled IOP (trabeculectomy and tube shunt).
Discussion
This single-center retrospective comparative case series demonstrated that iStent and iStent inject devices combined with phacoemulsification effectively and safely reduced IOP and medication number over 1 year in OAG. The results showed favorable iStent inject outcomes vs. iStent in terms of lower IOP at month 6 and higher proportion of eyes with IOP ≤ 15 mmHg at months 6 and 12. However, surgical success was comparable in both groups at months 6 and 12. Multivariate regression model (P < 0.001) identified older age (P = 0.034) and lower baseline IOP (P = 0.003) as the strongest predictors of surgical failure at month 12.
Theoretically, iStent inject may have better efficacy given the modified design and the advantage of simultaneous implantation of two stents, which was shown to provide more IOP reduction in prior iStent studies that investigated the effect of multiple stent implantation.[14,15,16] However, direct comparisons between both devices were not conclusive.[35,36,37,38] Our study used several criteria to compare both devices (mean IOP and medication number, IOP ≤ 15 mmHg, and 20% IOP reduction) at two time points (months 6 and 12) and could not detect consistent superiority of iStent inject with all criteria at all time points.
The literature contains several studies on iStent and iStent inject with varying results. In a similar prospective comparative case series with 245 POAG eyes, mean IOP at month 12 was similar between groups, which was similar to our month-12 outcomes. Likewise, surgical success was similar with 56.0% of the iStent vs. 51.3% of the iStent inject eyes had achieved primary success (IOP ≤ 18 mmHg without medications) and 63.1% vs. 57.7% had achieved secondary success (IOP ≤ 18 mmHg with medication reduction).[35]
Manning et al.,[36] retrospectively included 137 eyes. At month-12, mean IOP was significantly reduced in both groups compared to baseline. The IOP reduction was significantly greater for iStent inject eyes than iStent eyes. Although our study demonstrated favorable IOP in the iStent inject group at month 6, the difference was insignificant by month 12 in contrast to this study. Both groups had high proportions of patients achieving IOP ≤18 mmHg, with greater proportions with iStent inject than iStent. Although we used IOP ≤15 mmHg as effectiveness endpoint giving the lower baseline IOP, we agreed with this study that more iStent inject eyes achieved the effectiveness endpoint as compared with iStent. Consistent with our results, both groups achieved significant medication reduction at month 12. However, a significantly higher proportion of iStent inject eyes were medication free, which was in contrast to our study that showed similar proportions of medication free eyes in both groups.
Another retrospective study showed conclusion in favor to iStent inject, with inclusion of 58 OAG eyes. At month 12, iStent inject eyes achieved significant IOP reduction, while iStent eyes did not. Mean IOP reduction was significantly greater in iStent inject eyes in contrast to our study that showed similar month-12 IOP in both groups. Similar to ours, both groups achieved significant medication reduction at month 12, but iStent inject eyes had a significantly lower medication number and more medication free eyes, which was in contrast to our results that showed similar medication number and medication free eyes in both groups.[37] The authors published the 6-month results in a separate cohort, as more patients were available for analysis (N = 73).[38] The results were comparable to our 6-month outcomes, with better IOP reduction in the iStent inject group and significantly more iStent inject eyes achieved IOP ≤18 mmHg.
Our study showed similar surgical success in both groups defined as 20% IOP reduction from the baseline at months 6 and 12. The multivariate model identified older age and lower baseline IOP as the strongest predictors of surgical failure at month 12 rather than the stent type. These findings demonstrated that the efficacy of trabecular stents may be augmented in eyes with higher IOP, in which the high-pressure gradient across the stent endings may lead to more aqueous outflow and subsequently more IOP reduction unlike eyes with low baseline IOP, in which the pressure gradient may not have been high enough to allow significant aqueous outflow through the stent. Likewise, eyes with NTG showed more failure at 1 year (12 failed vs. 5 successful eyes). Although this was statistically insignificant, it is in line with lower baseline IOP associated with higher failure. These findings were also similar to the outcomes of Salimi et al.,[32] study that added a linear regression model to identify predictors of postoperative IOP. The model showed that greater baseline preoperative IOP and thinner corneas were associated with higher IOP reduction.
Although our study was not powered to provide subgroup comparison, the regression analysis showed that glaucoma type was insignificant predictor of surgical failure. Compared to Klamann’s study,[24] they reported 100% failure in the PG, suggesting that iStent inject in phakic PG may have limitations. However, similarly, Klamann’s study was not powered to detect differences between glaucoma types, and further larger sample studies are required.
Similar to existing literature, both iStent and iStent inject demonstrated high safety profiles. Intraoperative complications were minimal and similar in both groups and included blood reflux, which is considered a sign of correct position and patency of the stent and was reported in prior studies.[24,25,27,40] Failure to implant the second stent occurred in 9.3% of iStent inject eyes, which was comparable to prior studies.[17,28,31,36] Postoperative adverse events were transient and required no additional interventions. Only two eyes required reoperation for glaucoma, which was similar to the reoperation rate in prior studies.[17,19,23,24,31,33,37,38,40]
Conclusion
Both iStent and iStent inject combined with phacoemulsification have effectively and safely reduced IOP and medication number over 1 year. Although iStent inject achieved lower IOP at month 6, both groups had similar IOP at month 12. Effectiveness endpoint as IOP ≤15 mmHg was achieved in more iStent inject eyes at months 6 and 12. However, surgical success defined as 20% IOP reduction was similar in both groups. Predictors of surgical failure were older age and lower baseline IOP, rather than the stent type.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Financial Disclosure:
WSS: None.
SSL: None.
AA: None.
JSM: Consultant: Aerie, Allergan, Glaukos, MicroOptx, Olleyes; Speaker: Aerie, Allergan, Haag Streit; Research: Aerie, Allergan, Glaukos, Diopsys, Haag Streit, Nicox, Olleyes, Santen
MRS: Consultant: Alcon, Allergan, Bausch and Lomb, Glaukos, Aerie, and Qura; Speaker: Alcon, Allergan, Aerie, and Bausch and Lomb.
NNK: Research: Allergan, Inc.
RR: None.
AGS: American Glaucoma Society Mentoring for Advancement of Physician Scientists Grant.
TRH: None
TME: None
SMS: None
DL: Consultant: Allergan, Inc. Research: Allergan, Inc. Speaker: Glaukos Corp.
Video Available on: www.ijo.in
Acknowledgements
Dr Reza Razeghinejad, MD, has provided his high-quality personal videos of iStent and iStent inject implantation to be added as Supplementary Materials 1 and 2.
References
- 1.Quigley HA, Broman AT. The number of people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006;90:262–7. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2005.081224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kingman S. Glaucoma is second leading cause of blindness globally. Bull World Health Organ. 2004;82:887–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sommer A. Intraocular pressure and glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989;107:186–8. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(89)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Newman-Casey PA, Robin AL, Blachley T, Farris K, Heisler M, Resnicow K, et al. The most common barriers to glaucoma medication adherence:A cross-sectional survey. Ophthalmology. 2015;122:1308–16. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2015.03.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gedde SJ, Herndon LW, Brandt JD, Budenz DL, Feuer WJ, Schiffman JC, et al. Postoperative complications in the Tube Versus Trabeculectomy (TVT) study during five years of follow-up. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012;153:804–14.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2011.10.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Saheb H, Ahmed IIK. Micro-invasive glaucoma surgery:Current perspectives and future directions. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2012;23:96–104. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0b013e32834ff1e7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Craven ER, Katz LJ, Wells JM, Giamporcaro JE Stent Study G. Cataract surgery with trabecular micro-bypass stent implantation in patients with mild-to-moderate open-angle glaucoma and cataract:Two-year follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012;38:1339–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2012.03.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Spiegel D, Wetzel W, Haffner DS, Hill RA. Initial clinical experience with the trabecular micro-bypass stent in patients with glaucoma. Adv Ther. 2007;24:161–70. doi: 10.1007/BF02850004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ahmed II, Katz LJ, Chang DF, Donnenfeld ED, Solomon KD, Voskanyan L, et al. Prospective evaluation of microinvasive glaucoma surgery with trabecular microbypass stents and prostaglandin in open-angle glaucoma. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014;40:1295–300. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2014.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Buchacra O, Duch S, Milla E, Stirbu O. One-year analysis of the iStent trabecular microbypass in secondary glaucoma. Clin Ophthalmol. 2011;5:321–6. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S15025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Samuelson TW, Katz LJ, Wells JM, Duh YJ, Giamporcaro JE Group USiS. Randomized evaluation of the trabecular micro-bypass stent with phacoemulsification in patients with glaucoma and cataract. Ophthalmology. 2011;118:459–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2010.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Patel I, de Klerk TA, Au L. Manchester iStent study:Early results from a prospective UK case series. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013;41:648–52. doi: 10.1111/ceo.12098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fea AM, Consolandi G, Zola M, Pignata G, Cannizzo P, Lavia C, et al. Micro-bypass implantation for primary open-angle glaucoma combined with phacoemulsification:4-year follow-up. J Ophthalmol. 2015;2015:795357. doi: 10.1155/2015/795357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Belovay GW, Naqi A, Chan BJ, Rateb M, Ahmed II. Using multiple trabecular micro-bypass stents in cataract patients to treat open-angle glaucoma. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012;38:1911–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2012.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.El Wardani M, Bergin C, Achache F, Sharkawi E. Evaluating the trabecular micro-bypass stent combined with phacoemulsification compared to phacoemulsification alone. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2015;232:442–5. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1545798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Katz LJ, Erb C, Carceller GA, Fea AM, Voskanyan L, Wells JM, et al. Prospective, randomized study of one, two, or three trabecular bypass stents in open-angle glaucoma subjects on topical hypotensive medication. Clin Ophthalmol. 2015;9:2313–20. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S96695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Samuelson TW, Sarkisian SR, Jr, Lubeck DM, Stiles MC, Duh YJ, Romo EA, et al. Prospective, randomized, controlled pivotal trial of an Ab interno implanted trabecular micro-bypass in primary open-angle glaucoma and cataract:Two-year results. Ophthalmology. 2019;126:811–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fea AM, Belda JI, Rekas M, Junemann A, Chang L, Pablo L, et al. Prospective unmasked randomized evaluation of the iStent inject ((R)) versus two ocular hypotensive agents in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014;8:875–82. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S59932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Voskanyan L, Garcia-Feijoo J, Belda JI, Fea A, Junemann A, Baudouin C, et al. Prospective, unmasked evaluation of the iStent (R) inject system for open-angle glaucoma:Synergy trial. Adv Ther. 2014;31:189–201. doi: 10.1007/s12325-014-0095-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Berdahl J, Voskanyan L, Myers JS, Hornbeak DM, Giamporcaro JE, Katz LJ, et al. Implantation of two second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents and topical travoprost in open-angle glaucoma not controlled on two preoperative medications:18-month follow-up. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017;45:797–802. doi: 10.1111/ceo.12958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lindstrom R, Lewis R, Hornbeak DM, Voskanyan L, Giamporcaro JE, Hovanesian J, et al. Outcomes following implantation of two second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents in patients with open-angle glaucoma on one medication:18-month follow-up. Adv Ther. 2016;33:2082–90. doi: 10.1007/s12325-016-0420-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lindstrom R, Sarkisian SR, Lewis R, Hovanesian J, Voskanyan L. Four-year outcomes of two second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents in patients with open-angle glaucoma on one medication. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020;14:71–80. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S235293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hengerer FH, Auffarth GU, Riffel C, Conrad-Hengerer I. Second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents as standalone treatment for glaucoma:A 36-month prospective study. Adv Ther. 2019;36:1606–17. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-00984-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Klamann MK, Gonnermann J, Pahlitzsch M, Maier AK, Joussen AM, Torun N, et al. iStent inject in phakic open angle glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015;253:941–7. doi: 10.1007/s00417-015-3014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Davids AM, Pahlitzsch M, Boeker A, Torun N, Bertelmann E, Maier-Wenzel AK, et al. iStent inject as a reasonable alternative procedure following failed trabeculectomy. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2018;28:735–40. doi: 10.1177/1120672117747010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Macher T, Haberle H, Wachter J, Thannhauser C, Aurich H, Pham DT. Trabecular microbypass stents as minimally invasive approach after conventional glaucoma filtration surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2018;44:50–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2017.10.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Best UP, Domack H, Schmidt V, Khalifa M. [Microinvasive glaucoma surgery-Efficacy of trabecular stents in combined interventions:A clinical study on 65 eyes] Ophthalmologe. 2019;116:771–9. doi: 10.1007/s00347-018-0824-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Arriola-Villalobos P, Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Diaz-Valle D, Morales-Fernandez L, Fernandez-Perez C, Garcia-Feijoo J. Glaukos iStent inject (R) trabecular micro-bypass implantation associated with cataract surgery in patients with coexisting cataract and open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension:A long-term study. J Ophthalmol. 2016;2016:1056573. doi: 10.1155/2016/1056573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hengerer FH, Auffarth GU, Riffel C, Conrad-Hengerer I. Prospective, non-randomized, 36-month study of second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents with phacoemulsification in eyes with various types of glaucoma. Ophthalmol Ther. 2018;7:405–15. doi: 10.1007/s40123-018-0152-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Alnawaiseh M, Muller V, Lahme L, Merte RL, Eter N. Changes in flow density measured using optical coherence tomography angiography after istent insertion in combination with phacoemulsification in patients with open-angle glaucoma. J Ophthalmol. 2018;2018:2890357. doi: 10.1155/2018/2890357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Clement CI, Howes F, Ioannidis AS, Shiu M, Manning D. One-year outcomes following implantation of second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents in conjunction with cataract surgery for various types of glaucoma or ocular hypertension:Multicenter, multi-surgeon study. Clin Ophthalmol. 2019;13:491–9. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S187272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Salimi A, Lapointe J, Harasymowycz P. One-year outcomes of second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents (iStent Inject) implantation with cataract surgery in different glaucoma subtypes and severities. Ophthalmol Ther. 2019;8:563–75. doi: 10.1007/s40123-019-00214-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Neuhann R, Neuhann T. Second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stent implantation:Retrospective analysis after 12- and 24-month follow-up. Eye Vis (Lond) 2020;7:1. doi: 10.1186/s40662-019-0169-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ioannidis AS, Toteberg-Harms M, Hamann T, Hodge C. Refractive outcomes after trabecular micro-bypass stents (iStent Inject) with cataract extraction in open-angle glaucoma. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020;14:517–24. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S239103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hooshmand J, Rothschild P, Allen P, Kerr NM, Vote BJ, Toh T. Minimally invasive glaucoma surgery:Comparison of iStent with iStent inject in primary open angle glaucoma. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019;47:898–903. doi: 10.1111/ceo.13526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Manning D. Real-world case series of iStent or iStent inject trabecular micro-bypass stents combined with cataract surgery. Ophthalmol Ther. 2019;8:549–61. doi: 10.1007/s40123-019-00208-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Guedes RAP, Gravina DM, Lake JC, Guedes VMP, Chaoubah A. One-year comparative evaluation of iStent or iStent inject Implantation combined with cataract surgery in a single center. Adv Ther. 2019;36:2797–810. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01067-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Guedes RAP, Gravina DM, Lake JC, Guedes VMP, Chaoubah A. Intermediate results of iStent or iStent inject implantation combined with cataract surgery in a real-world setting:A longitudinal retrospective study. Ophthalmol Ther. 2019;8:87–100. doi: 10.1007/s40123-019-0166-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.American Academy of Ophthalmology. ICD-10 Glaucoma Reference Guide:Glaucoma Stage Definitions 2015. Available from: https://www.aao.org/Assets/5adb14a6-7e5d-42ea-af51-3db772c4b0c2/636713219263270000/bc-2568-update-icd-10-quick-reference-guides-glaucoma-final-v2-color-pdf?inline=1 .
- 40.Gonnermann J, Bertelmann E, Pahlitzsch M, Maier-Wenzel AB, Torun N, Klamann MK. Contralateral eye comparison study in MICS &MIGS:Trabectome (R) vs. Stent inject (R) Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017;255:359–65. doi: 10.1007/s00417-016-3514-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.