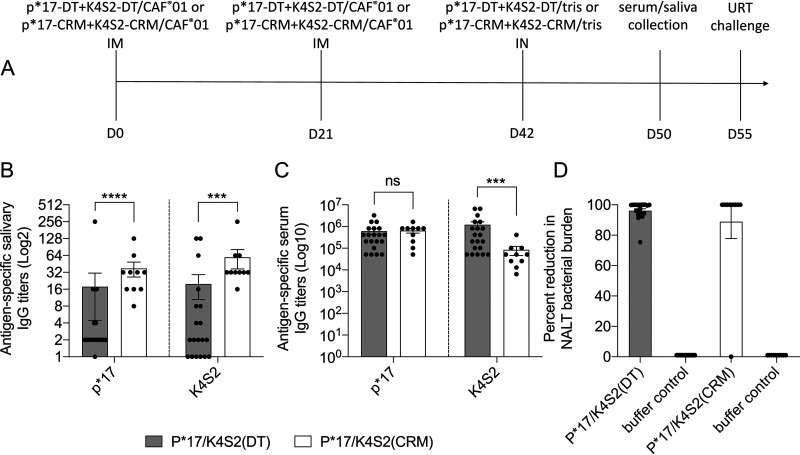
FIG 1.
Immunogenicity and protective efficacy following prime-pull immunization with P*17/K4S2(DT) and P*17/K4S2(CRM). BALB/c mice were immunized via the prime-pull method with P*17/K4S2(DT) (n = 20) or P*17/K4S2(CRM) (n = 9) (day 0 and 21, i.m. with antigen/CAF®01; day 42, i.n. with antigen/Tris) and Tris only (day 0 and 21, i.m. with Tris; day 42, i.n. with Tris). (A) Immunization, sample collection, and challenge timeline. (B and C) Immunogenicity of vaccines. Serum and saliva samples were collected one week post last vaccine boost and antigen-specific antibody levels were measured by ELISA. The endpoint titer was defined as the highest dilution that gave an absorbance of >3 standard deviations above the mean absorbance of negative-control wells. Salivary IgG titers (B) and serum IgG titers (C) for individual mice are shown. Data are mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical comparisons were performed using the Mann-Whitney test in GraphPad Prism 8.1.2: ns, P > 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. (D) Percent reduction in NALT bacterial burden. Mice were challenged intranasally with the covR/S MT S. pyogenes isolate, 5448AP. On day 3 post-infection, all mice were sacrificed and organs harvested for assessment of bacterial load. Percent reduction in NALT bacterial load for each individual mouse in the vaccinated cohort was calculated in comparison to the mean bacterial burden of buffer control cohort. The data are from two independent experiments with either P*17/K4S2(DT) or P*17/K4S2(CRM). The mean bacterial burden (CFU/ml) for the corresponding buffer controls (DT and CRM experiments) were 4.12 × 1012 and 3.95 × 104, respectively. We chose to use a Tris (buffer) control for these experiments; however, preliminary experiments using CAF®01/Tris as a control (2× i.m. injections with CAF®01 and 1× i.n. with Tris) showed that vaccination with P*17/K4S2(CRM) (2× i.m. injections with p*17-CRM+K4S2-CRM/CAF®01 and 1× i.n. with p*17-CRM+K4S2-CRM/Tris) resulted in >88% protection in NALT (judged by colony count reduction).