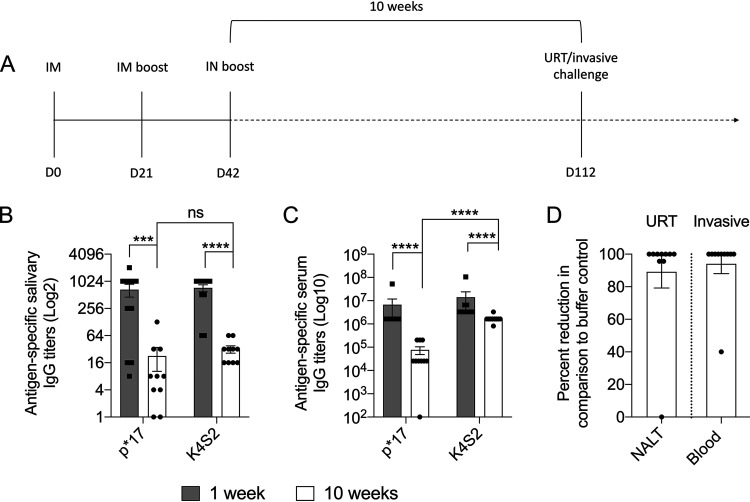
FIG 4.
Longevity of immune responses 10 weeks following prime-pull immunization with P*17/K4S2(DT). BALB/c mice were immunized using the prime-pull immunization regimen with P*17/K4S2(DT) or 10 mM Tris buffer (buffer control). (A) Immunization and challenge timeline. (B and C) Longevity of vaccine-induced Ig response. Serum and saliva samples were collected 10 weeks after the last vaccine boost and antigen-specific IgG levels in saliva (B) and serum (C) were measured by ELISA. The endpoint titer was defined as the highest dilution that gave an absorbance of >3 standard deviations above the mean absorbance of negative control wells. Data for n = 10 mice as mean ± SEM are shown. Statistical comparisons were performed using a Mann-Whitney test (ns, P > 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001). (D) Assessment of longevity of vaccine-induced protective immunity. Mice were challenged intranasally or via the skin with covR/S MT S. pyogenes isolate 5448AP. Mice were sacrificed and percent reduction for each individual mouse in the vaccinated cohort was calculated in comparison to the mean of the buffer control cohort. Percent reduction in NALT bacterial burden (day 3) and percent reduction in blood bacterial burden (day 6) following URT and skin challenge infections, respectively, are shown (D). The mean bacterial burden (CFU/ml) for corresponding buffer controls (for the URT and invasive infections) were 5.7 × 102 and 4 × 102, respectively.