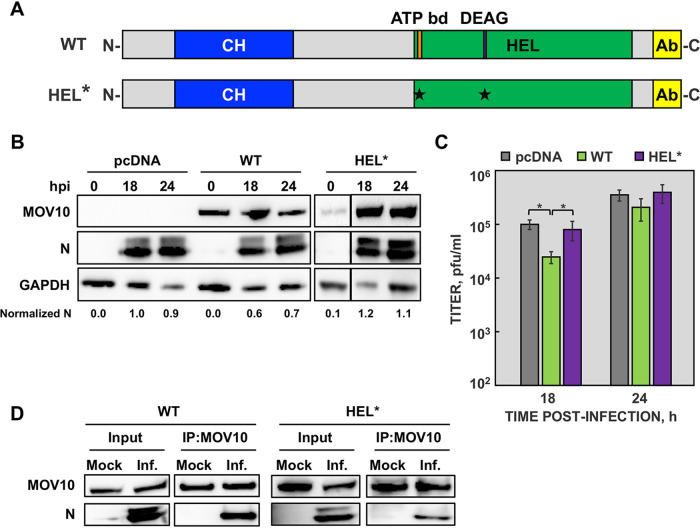
FIG 7.
MOV10 helicase activity is required for its antiviral function. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type (WT) and helicase mutant (HEL*) MOV10 proteins. CH, CH-rich domain; HEL, helicase domain; ATP bd, ATP binding motif; DEAG, conserved DEAG box; Ab, domain recognized by MOV10 antibody. The asterisks indicate the point mutations introduced. (B) MOV10-KO cells were transfected with an empty plasmid or plasmids expressing either WT or HEL* proteins and infected with MERS-CoV at an MOI of 1 for 18 and 24 hpi. MOV10 and N protein accumulation in cytoplasmic extracts was detected by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Numbers under the blots indicate the estimated levels of N protein, normalized to GAPDH levels and relative to pcDNA-transfected cells at 18 hpi. (C) Virus titers were measured at the indicated time points, from infected MOV10-KO cells previously transfected with an empty plasmid (gray) or plasmids expressing either WT (green) or HEL* (purple) proteins. The values are means from three independent infections; error bars represent SD. *, P < 0.05. (D) MOV10-KO cells were transfected with plasmids expressing either WT or HEL* proteins and then infected with MERS-CoV at an MOI of 0.1. At 20 hpi, cell lysates were obtained and immunoprecipitated with anti-MOV10 antibody. MOV-10 and MERS-CoV N protein were detected by Western blotting.