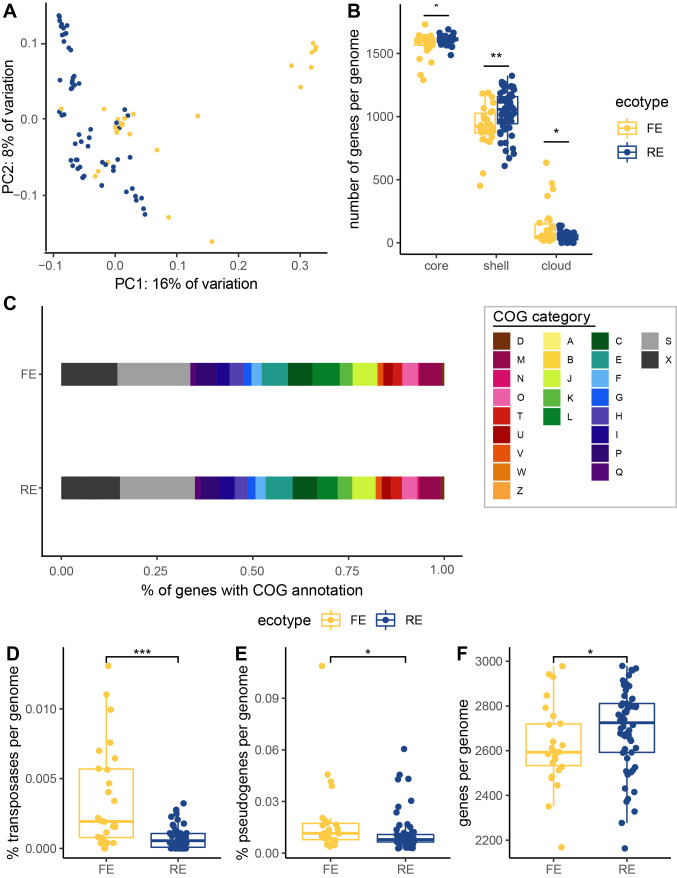
FIG 4.
Structural differences between the genomes of FE and RE Psychrobacter strains. (A) The first two axes of a PCoA of a gene presence-absence matrix of all of the included accessions, colored by ecotype. (B) Pangenome categories. (C) Proportions of the average genome of each ecotype devoted to each cluster of orthologous genes (COG) category. Cellular processing and signaling: [D] cell cycle control cell division, chromosome partitioning; [M] cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; [N] cell motility; [O] posttranslational modification, protein turnover, and chaperones; [T] signal transduction mechanisms; [U] intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; [V] defense mechanisms; [W] extracellular structures; [Y] nuclear structure; [Z] cytoskeleton. Information storage and processing: [A] RNA processing and modification; [B] chromatin structure and dynamics; [J] translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; [K] transcription; [L] replication, recombination, and repair. Metabolism: [C] energy production and conversion; [E] amino acid transport and metabolism; [F] nucleotide transport and metabolism; [G] carbohydrate transport and metabolism; [H] coenzyme transport and metabolism; [I] lipid transport and metabolism; [P] inorganic ion transport and metabolism; [Q] secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism. Poorly characterized: [S] function unknown, [X] not in COG database. (D) Percent of genes that are transposases. (E) Percent of genes per genome that are predicted to be pseudogenes. (F) Number of genes per genome. Means were compared using the Wilcoxon rank sum test. *, P value less than 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0005.