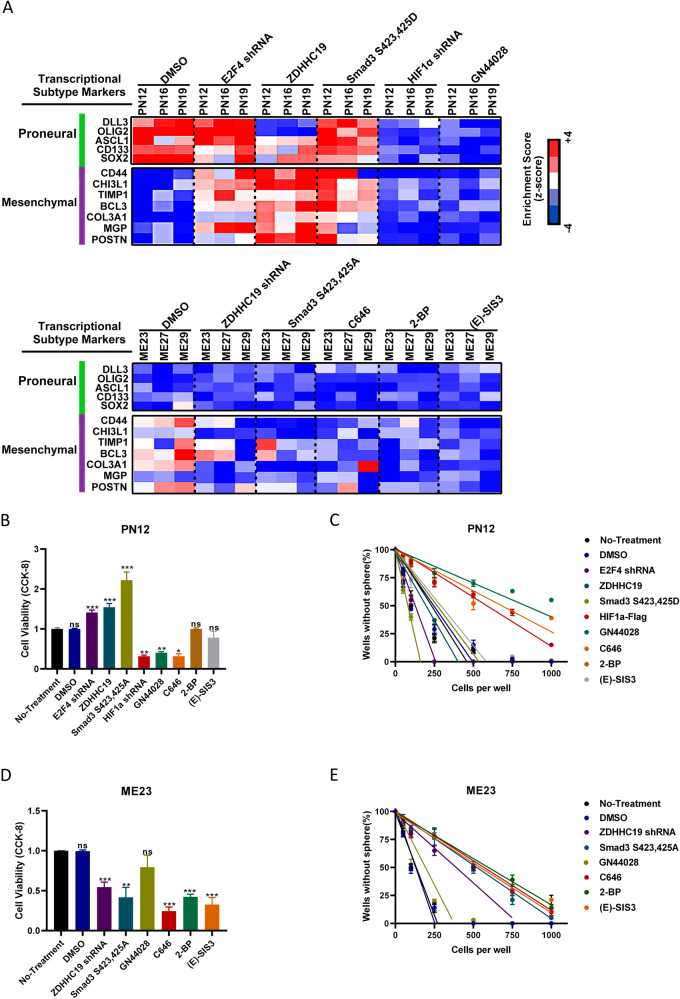
Fig. 4. Inhibition of HIF-1α or Smad3 could reduce cell viability and self-renewal in the proneural and mesenchymal subtypes of GSCs.
A Heatmap showing molecular subtype marker expression in proneural GSCs (PN12, PN16, and PN19), mesenchymal GSCs (ME23, ME27, and ME29), and proneural (or mesenchymal) GSCs infected with the indicated plasmids or shRNA or treated with the indicated inhibitors. HIF-1α inhibitor, GN44028, 12.5 μM. Palmitoylation inhibitor, 2-BP, 100 μM. Smad3 inhibitor, (E)-SIS3, 20 μM. EP300 inhibitor, C646, 15 μM. Z-scores were calculated from the △Ct values obtained in the quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis. B Viability of proneural PN12 GSCs transfected with the indicated plasmids or shRNA or treated with GN44028, C646, 2-BP, or (E)-SIS3 for 48 h. C A serial dilution assay was used to determine the self-renewal capacity of PN12 GSCs transfected with the indicated plasmids or shRNA or treated with GN44028, C646, 2-BP, or (E)-SIS3. D Viability of mesenchymal ME23 GSCs transfected with the indicated plasmids or shRNA or treated with GN44028, C646, 2-BP, or (E)-SIS3 for 48 h. E A serial dilution assay was used to determine the self-renewal capacity of ME23 GSCs transfected with the indicated plasmids or shRNA or treated with GN44028, C646, 2-BP, or (E)-SIS3. GSCs glioblastoma stem cells, HIF-1α hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha.