Abstract
We report the case of a 61-year-old man who had presented with acute unilateral limb swelling. Computed tomography venography and duplex ultrasound demonstrated compression of the right common femoral vein by a common femoral vein adventitial cyst. Before intervention, the patient had developed an acute deep vein thrombosis of the right common femoral vein and great saphenous vein. Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated concern for synovial connection. After 6 months of anticoagulation therapy, the patient underwent adventitial cyst excision with ligation of the hip joint articular connection. At 4 months postoperatively, the patient was symptom free without cyst recurrence. The findings from the present case support the synovial theory for adventitial cystic disease.
Keywords: Adventitial cystic disease, Femoral vein, Synovial cyst, Venous thrombosis
Adventitial cystic disease (ACD) is a rare etiology of peripheral arterial occlusive disease and venous disease. ACD is characterized by the formation of mucinous cysts with the adventitia of arteries and veins, which can lead to various signs or symptoms depending on the location and degree of luminal obstruction. Most often, it affects the popliteal artery, leading to intermittent claudication.1 Several theories exist regarding the origin of adventitial cysts; however, our center previously identified a synovial connection in 17% of the reported cases.1, 2, 3 The present case is unique owing to involvement of the femoral vein and identification of a joint communication in support of the synovial origin theory. We have provided a review of the available literature on venous involvement in ACD. The patient provided written informed consent for the report of his case.
Case report
A 61-year-old man with no pertinent medical history had presented to an outside institution with a 9-day history of right lower extremity edema after prolonged air travel. Duplex ultrasound and computed tomography venography demonstrated compression of the right common femoral vein by an adventitial cyst, without evidence of venous thrombosis.
After car travel en route to obtain a second opinion at our institution, he had noted worsening edema, now involving the thigh, and was subsequently evaluated in the emergency department. A repeat ultrasound scan confirmed the presence of the cystic mass and demonstrated an acute deep vein thrombosis of the right common femoral vein and great saphenous vein. He had no personal or familial history of thrombotic events.
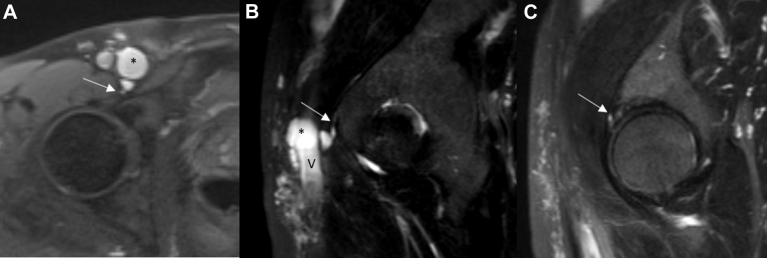
On examination, the patient had palpable pedal pulses and right lower extremity edema from the ankle to the thigh, without varicosities or skin changes. No palpable lymphadenopathy or masses were present in the groin. Anticoagulation was initiated, and thigh-high graduated compression stockings rated at 30 to 40 mm Hg were placed. A repeat ultrasound scan at 6 months demonstrated recanalization of the common femoral and saphenous veins with chronic post-thrombotic changes. Magnetic resonance venography demonstrated a 3-cm cyst anteromedial to the right common femoral vein that was compressing the lumen and another 1.2-cm cyst posterior to the vein and communicating to the hip joint (Figs 1 and 2). A labral tear was identified on the magnetic resonance venogram (Fig 1, C), which possibly contributed to formation of the adventitial cyst.
Fig 1.
T2-weighted magnetic resonance venogram images. A, Axial cut demonstrating the joint connection (arrow) to the cyst (asterisk). B, Sagittal cut demonstrating the joint connection (arrow), the main cyst (asterisk), and caudal common femoral vein (V). C, The origin of the labral tear (arrow).
Fig 2.
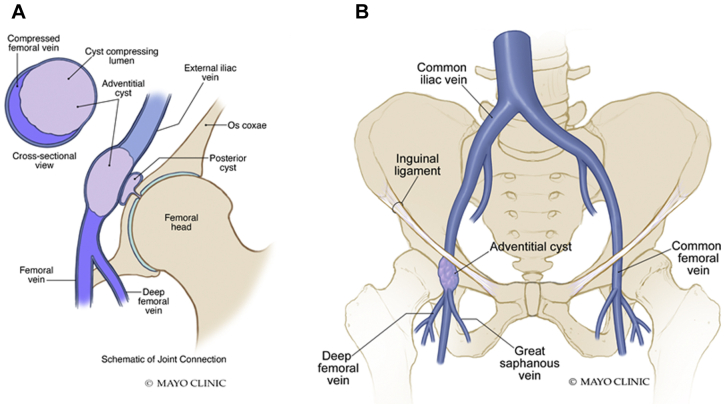
A, Illustration demonstrating compression of the vein lumen by the cyst with a connection to the hip joint capsule. B, Schematic diagram demonstrating the location of the adventitial cyst caudal to the inguinal ligament but cephalad to the saphenofemoral junction.
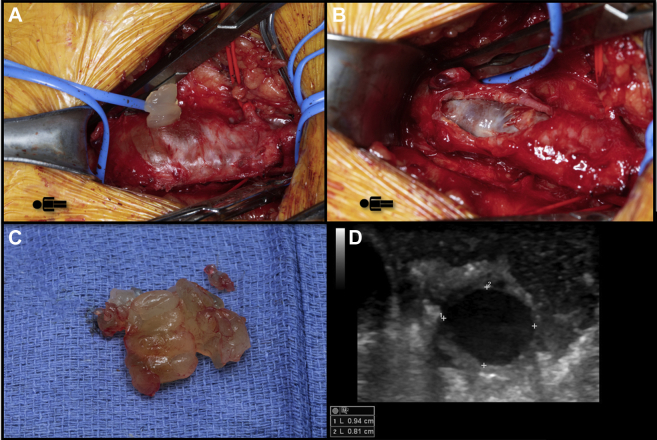
A shared decision was made for operative intervention owing to the risk of recurrent thrombosis. The patient underwent open right common femoral vein cyst excision (Fig 3, A-C) and ligation of the connection to the hip joint. Intraoperative ultrasound confirmed the normal caliber of the common femoral vein without compression at completion (Fig 3, D). Histopathologic examination of the specimen demonstrated features consistent with cystic adventitial disease. The patient had an uneventful postoperative course and was discharged to home on postoperative day 1. He continued taking rivaroxaban for 1 month, followed by a further 6 months of aspirin monotherapy. At the 4-month follow-up visit, his symptoms had completely resolved, and duplex ultrasound demonstrated no evidence of cyst recurrence.
Fig 3.
Intraoperative photographs of the adventitial cyst before (A) and after (B) cyst excision. C, Photograph of cyst contents. D, Select transverse view of the common femoral vein on intraoperative ultrasound demonstrating full expansion after cyst excision.
Discussion
A 61-year-old man with a venous adventitial cyst causing compression and thrombosis of the right common femoral vein was successfully treated with cyst excision and ligation of the connection with the hip joint. Venous reconstruction was not undertaken, because complete expansion of the common femoral vein had occurred after cyst removal and the joint connection was identified and ligated.
The articular origin theory of ACD has been supported by previous reports identifying a connection between a synovial joint and an adjacent adventitial cyst.2,4 This joint connection arises from a feeding vessel, which serves as a conduit for synovial fluid. As demonstrated in the present patient, the joint connection can be visualized with preoperative imaging in select cases.5 We investigated the literature to determine the incidence of joint connections in patients with ACD of the venous system.
A review of the literature identified 64 studies reporting 72 cases of ACD of the venous system (Appendix). The common femoral vein (65%) was the most commonly affected location, followed by the external iliac (18%) and popliteal (7%) veins (Table I). Additionally, ACD involving the brachiocephalic vein, basilic vein, an autogenous brachiocephalic fistula, posterior tibial vein, and small and great saphenous veins was identified.4,6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 The mean age at presentation was 47.8 years (range, 5-75 years), 39 of the patients were men (54%), and the disease process was localized to the left side in 42 patients (58%). Medical comorbidities were infrequently reported, with five patients (7%) having a history of venous thromboembolism (Table I). Symptoms that indicated the need for intervention included limb swelling in most patients (85%), a palpable mass in 28%, limb pain in 15%, varices in 7%, and paresthesia in 6%. Three patients were asymptomatic, two with the finding of a painless mass and one with the cyst incidentally identified by imaging studies. ACD was initially misdiagnosed as deep vein thrombosis in 13 patients (18%) and treated with anticoagulation. To assist in the diagnosis, ultrasound (68%) and computed tomography (63%) were the most commonly used imaging modalities. A connection between the cyst and an adjacent joint space was identified in 12 patients (17%), and the connection was ligated intraoperatively in 5 patients. No recurrences were reported after ligation of the connection to the joint capsule.
Table I.
Patient demographics and presentation
| Variable | Mean ± SD (range) or No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 47 ± 14 (5-75) |
| Male sex | 39 (54) |
| Left sided | 42 (58) |
| Location | |
| Common femoral vein | 47 (65) |
| External iliac vein | 13 (18) |
| Popliteal vein | 5 (7) |
| Short saphenous vein | 2 (3) |
| Basilic vein | 1 (1) |
| Brachiocephalic vein | 1 (1) |
| Brachiocephalic AVF | 1 (1) |
| Posterior tibial vein | 1 (1) |
| Great saphenous vein | 1 (1) |
| Comorbidity | |
| History of VTE | 5 (7) |
| Tobacco use | 3 (4) |
| Hypertension | 5 (7) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 1 (1) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1 (1) |
| AAA | 2 (3) |
| Coronary artery disease | 1 (1) |
| Presenting symptoms and signs | |
| Swelling | 61 (85) |
| Pain | 11 (15) |
| Palpable mass | 20 (28) |
| Varices | 5 (7) |
| Paresthesia | 4 (6) |
| Asymptomatic | 3 (4) |
| Claudication | 2 (3) |
| Bruit | 1 (1) |
| Joint stiffness | 1 (1) |
| Weakness | 1 (1) |
| Abdominal pain/nausea | 1 (1) |
AAA, Abdominal aortic aneurysm; AVF, arteriovenous fistula; VTE, venous thromboembolism.
The initial interventions for treatment of the adventitial cyst are detailed in Table II, with 16 patients undergoing reintervention for recurrence. Recurrence was observed in all 10 patients for whom cyst aspiration with or without sclerosant was the primary treatment, with surgical excision or resection the final successful treatment in 9 patients. In one patient treated with aspiration, recurrent aspiration and injection of sclerosant was successful through 18 months of follow-up.12 Simple cyst drainage was the primary treatment in two patients. Both patients developed recurrence and were treated with cyst excision. Cyst excision with or without patch venoplasty was the primary treatment in 47 patients. Four patients had developed recurrence after excision and underwent repeat excision (two patients), interposition graft (one patient), or aspiration with sclerosant (one patient). Interposition grafting with a prosthetic graft or autologous vein conduit was performed in 10 patients without recurrence. A stent placed in the external iliac vein to treat one patient was complicated by in-stent thrombosis.13 The mean follow-up after intervention was 11 months (range, 1-48 months). Surveillance imaging was obtained for 40 patients (56%), a limitation of the reported rates of recurrence in our review. Recurrence was identified within 6 months of the primary intervention in all cases.
Table II.
Summary of initial treatment and associated recurrence rate with each intervention
| Initial treatment | Patients, No. (%) | Recurrence, No. (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CE, all cases | 47 (65) | 4 (9) |
| CE without reconstruction | 41 (57) | 2 (5) |
| CE with patch venoplasty | 5 (7) | 2 (40) |
| Laparoscopic CE | 1 (1) | 0 (0) |
| CA, all cases | 10 (14) | 10 (100) |
| CA without sclerosant | 9 (13) | 9 (100) |
| CA with injection of sclerosant | 1 (1) | 1 (100) |
| VR, all cases | 12 (17) | 0 (0) |
| VR with prosthetic interposition graft | 7 (10) | 0 (0) |
| VR with vein interposition graft | 3 (6) | 0 (0) |
| VR with simple ligation | 2 (3) | 0 (0) |
| Cyst drainage | 2 (3) | 2 (100) |
| Venous stent | 1 (1) | 0 (0)a |
CA, Cyst aspiration; CE, cyst excision; VR, venous resection.
The adventitial cyst was never excised or aspirated and was complicated by stent thrombosis.
Conclusions
We have presented an unusual case of ACD of the common femoral vein with associated thrombosis and identification of a connection with the hip joint on preoperative imaging. The patient was successfully treated with cyst excision and ligation of the joint communication. Similar to previous reports, a connection to a joint space was identified in 17% of patients with ACD of the veins.1, 2, 3 Surgical treatment with cyst excision or venous resection had a low rate of recurrence of 7%. Previous reviews of ACD have reported similar recurrence rates with surgical treatment.1,14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23 Simple cyst drainage or cyst aspiration resulted in unacceptably high rates of cyst recurrence when reported. Repeat imaging after intervention is warranted to monitor for cyst recurrence.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the assistance of Omar Itani, MD, and Jesse Chait, DO, MS.
From the Society for Clinical Vascular Surgery
Footnotes
Author conflict of interest: none.
The editors and reviewers of this article have no relevant financial relationships to disclose per the Journal policy that requires reviewers to decline review of any manuscript for which they may have a conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Desy N.M., Spinner R.J. The etiology and management of cystic adventitial disease. J Vasc Surg. 2014;60 doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.04.014. 235-45.e1-e11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Spinner R.J., Desy N.M., Agarwal G., Pawlina W., Kalra M., Amrami K.K. Evidence to support that adventitial cysts, analogous to intraneural ganglion cysts, are also joint-connected. Clin Anat. 2013;26:267–281. doi: 10.1002/ca.22152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Levien L.J., Benn C.-A. Adventitial cystic disease: a unifying hypothesis. J Vasc Surg. 1998;28:193–205. doi: 10.1016/s0741-5214(98)70155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mentha C. [Mucoid degeneration of the veins] Presse Med. 1963;71:2205–2206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Spinner R.J., Edwards P.K., Amrami K.K. Application of three-dimensional rendering in joint-related ganglion cysts. Clin Anat. 2006;19:312–322. doi: 10.1002/ca.20292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sonobe A., Kato H., Mathis B.J., Tsukada T., Matsubara M., Sakamoto H. Surgical resection of an adventitial cyst of the right brachiocephalic vein. Ann Thorac Surg. 2020;110:e201–e203. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2020.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Vasconcelos R.S., Cherubim C.A.F., França F.M.P., D'Allacqua E.L., Dalio M.B., Joviliano E.E. Doença cística da adventícia na veia basílica: relato de caso. J Vasc Bras. 2016;15:245–249. doi: 10.1590/1677-5449.002616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Betanco-Peña A., Córdova-Quintal P., Lecuona-Huet N., Campero-Urcullo A., León-Rey C., Rodríguez-López E. Quiste de adventicia, localización inusual. Rev Mex Angiol. 2016;44:81–83. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yoshii S., Ikeda K., Murakami H. Cystic, myxomatous adventitial degeneration of a saphenous vein. J Vasc Surg. 1998;27:780–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lie J.T., Jensen P.L., Smith R.E. Adventitial cystic disease of the lesser saphenous vein. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1991;115:946–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Leafblad N.D., Wilson T.J., Amrami K.K., Turner N.S., Spinner R.J. Cystic adventitial disease of the tibial vein arising from the subtalar joint: a case report. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;58:377–380. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2018.08.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Johnson J.M., Kiankhooy A., Bertges D.J., Morris C.S. Percutaneous image-guided aspiration and sclerosis of adventitial cystic disease of the femoral vein. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009;32:812–816. doi: 10.1007/s00270-009-9581-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Priya S., Steigner M. Images in vascular medicine: cystic adventitial disease involving external iliac vein: a rare cause of unilateral limb swelling. Vasc Med. 2018;23:86–87. doi: 10.1177/1358863X17747513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen Y., Sun R., Shao J., Li Y., Liu C. A contemporary review of venous adventitial cystic disease and three case reports. Phlebology. 2015;30:11–16. doi: 10.1177/0268355513516948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bascone C., Iqbal M., Narh-Martey P., Szuchmacher M., Cicchillo M., Krishnasastry K.V. Venous adventitial cystic disease: a review of 45 cases treated since 1963. Int J Vasc Med. 2016;2016:5287697. doi: 10.1155/2016/5287697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lun Y., Zhang J., Jiang H., Xu D., Sun J., Wang S. Treatment options for venous cystic adventitial disease: a case report and literature review. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020;64:413.e1–413.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2019.10.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu P., Yan B., Zhang Y., Yan J., Ma C., Wang G. Cystic adventitial disease of femoral vein presenting as enlarging lower limb swelling and pain: two case reports and review of the literature. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18:3563–3567. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schaeffer J.S., Davis C.A., Shakhnovich I. Incidental finding of adventitial cystic disease of the common femoral vein: case report and review of the literature. J Vasc Ultrasound. 2016;40:83–86. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wu X., Lun Y., Jiang H., Gang Q., Duan Z., Xin S. Cystic adventitial disease of the common femoral vessels: report of 2 cases and literature review. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2014;48:325–328. doi: 10.1177/1538574413518616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mousa A.Y., Alhalbouni S., Abu-Halimah S., Gill G., Sadek B., Nanjundappa A. Cystic adventitial disease of the common femoral vein: a case report and review of the literature. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2013;47:569–572. doi: 10.1177/1538574413497110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Paravastu S.C., Regi J.M., Turner D.R., Gaines P.A. A contemporary review of cystic adventitial disease. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2012;46:5–14. doi: 10.1177/1538574411419377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dix F.P., McDonald M., Obomighie J., Chalmers N., Thompson D., Benbow E.W. Cystic adventitial disease of the femoral vein presenting as deep vein thrombosis: a case report and review of the literature. J Vasc Surg. 2006;44:871–874. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2006.05.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Paty P.S.K., Kaufman J.L., Koslow A.R., Chang B.B., Leather R.P., Shah D.M. Adventitial cystic disease of the femoral vein: a case report and review of the literature. J Vasc Surg. 1992;15:214–217. doi: 10.1067/mva.1992.30555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Appendix. Case Reports included in literature review
Supplementary References
- 1.Ann J.H., Kim J.H., Byun S.S., Kang J.M., Kim H.S., Choi H.Y. Percutaneous ethanol sclerotherapy for recurrent adventitial cystic disease of external iliac vein after surgical treatment: a case report. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2015;73:384–388. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Annetts D.L., Graham A.R. Cystic degeneration of the femoral vein: a case report. Br J Surg. 1980;67:287–288. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800670419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Betanco-Peña A., Córdova-Quintal P., Lecuona-Huet N., Campero-Urcullo A., León-Rey C., Rodríguez-López E. Quiste de adventicia, localización inusual. Rev Mex Angiol. 2016;44:81–83. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cai T.Y., Loa J. Multimodal imaging demonstrating adventitial cystic disease of the common femoral vein. ANZ J Surg. 2021;91:E330–E331. doi: 10.1111/ans.16363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chen Y., Sun R., Shao J., Li Y., Liu C. A contemporary review of venous adventitial cystic disease and three case reports. Phlebology. 2015;30:11–16. doi: 10.1177/0268355513516948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cho K., Shin T.B. A case of adventitial cystic disease of the femoral vein [in Korean] J Korean Soc Vasc Surg. 2005;21:186–189. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cho S.H., Shin H.W., Lee Y.G., Koo M.J. Adventitial cystic disease of the left external iliac vein: a case report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2005;53:285–288. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Desjardins J.F., Turlin B., Kerdiles Y., Ledu J., Clément B. Cystic degeneration of the femoral vein. Lancet. 1997;349:1000. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)62898-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dix F.P., McDonald M., Obomighie J., Thompson D., Benbow E.W., Smyth J.V. Cystic adventitial disease of the femoral vein presenting as deep vein thrombosis: a case report and review of the literature. J Vasc Surg. 2006;44:871–874. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2006.05.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Frileux C., Le Baleur A., Uzan E. Obstruction of the iliac vein by mucoid cyst: successful result of surgical excision. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1979;20:517–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fukui S., Paraskevas N., Lafaurie C., Soury P., Gigou J., Petit M.D. Cystic formation compressing the femoral vein: synovial hip joint or adventitial cyst. EJVES Extra. 2004;8:1–4. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fukumoto Y. A case of lower extremity swelling due to iliac vein stenosis caused by hip joint ganglion. Jpn J Vasc Surg. 2017;26:217–220. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fyfe N.C., Silcocks P.B., Browse N.L. Cystic mucoid degeneration in the wall of the femoral vein. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1980;21:703–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gasparis A.P., Wall P., Ricotta J.J. Adventitial cystic disease of the external iliac vein presenting with deep venous thrombosis: a case report. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2004;38:273–276. doi: 10.1177/153857440403800313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gomez-Ferrer F. Cystic degeneration of the wall of the femoral vein. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1966;7:162–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Guo F., Guo Y. Cystic adventitial disease of the common femoral vein: a case report. Vascular. 2020;28:489–493. doi: 10.1177/1708538120915297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hach-Wunderle V., Präve F., Hanschke D., Gruss J.D., Hach W. Die zystische Adventitiadegeneration der Venen. Gefässchirurgie. 2003;8:125–130. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Higami S., Ueda T., Sakakibara Y., Tohyama A., Harada H., Kurita T. Laparoscopically resected venous adventitial cystic disease that was difficult to distinguish from an ovarian tumor. Journal UOEH. 2020;42:51–55. doi: 10.7888/juoeh.42.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Howard E., Benson R., Day C., Gwynn B. Cystic adventitial disease of the common femoral vein. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017 doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-219818. bcr2017219818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ikeda M., Fujimori Y., Tankawa H., Iwata H. Compression syndrome of the popliteal vein and artery caused by popliteal cyst. Angiology. 1984;35:245–251. doi: 10.1177/000331978403500407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Iwasaki A., Furukawa K., Nakamura E., Nakamura K. Adventitial cystic disease of the common femoral vein misdiagnosed as deep vein thrombosis. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2018;27:312–313. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivy052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jayaraj A., Shalhub S., Deubner H., Starnes B.W. Cystic adventitial disease of the common femoral vein. Ann Vasc Surg. 2011;25:558.e9–558.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2010.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Johnson J.M., Kiankhooy A., Bertges D.J., Morris C.S. Percutaneous image-guided aspiration and sclerosis of adventitial cystic disease of the femoral vein. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009;32:812–816. doi: 10.1007/s00270-009-9581-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jones D.W., Rezayat C., Winchester P., Karwowski J.K. Adventitial cystic disease of the femoral vein in a 5-year-old boy mimicking deep venous thrombosis. J Vasc Surg. 2012;55:522–524. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.06.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kim E., Lamb K.M., Whisenhunt A.K., Ayad M., Farber J., DiMuzio P. Venous cystic adventitial disease of the common femoral vein. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2014;2:194–196. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2013.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim Y.K., Chun H.J., Hwang J.K., Kim J.I., Kim S.D., Park S.-C. Adventitial cystic disease of the common femoral vein presenting as deep vein thrombosis. Asian J Surg. 2016;39:178–181. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2013.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kwun W.-H., Suh B.-Y. Adventitial cystic disease of common femoral vein. J Korean Surg Soc. 2011;80(Suppl 1):S75–S79. doi: 10.4174/jkss.2011.80.Suppl1.S75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lavarde G. [Adventitial colloid degeneration of the popliteal vein] J Chir (Paris) 1972;103:31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Leafblad N.D., Wilson T.J., Amrami K.K., Turner N.S., Spinner R.J. Cystic adventitial disease of the tibial vein arising from the subtalar joint: a case report. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;58:377–380. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2018.08.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Leiva-Hernando L., Arroyo-Bielsa A., Porto-Rodríguez J., Montero-Mendizábal R.F., Gil-Sales J., Gesto-Castromil R. Compresión de la vena femoral asociada a quistes intra y extravasculares: a propósito de dos casos. Angiología. 2007;59:67–72. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lie J.T., Jensen P.L., Smith R.E. Adventitial cystic disease of the lesser saphenous vein. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1991;115:946–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liu P., Yan B., Zhang Y., Yan J., Ma C., Wang G. Cystic adventitial disease of femoral vein presenting as enlarging lower limb swelling and pain: two case reports and review of the literature. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18:3563–3567. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lun Y., Zhang J., Jiang H. Treatment options for venous cystic adventitial disease: a case report and literature review. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020;64:413.e1–413.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2019.10.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Maldonado-Fernández N., Lopez-Espada C., Moreno-Escobar J., Martinez-Gámez J., Rodriguez-Morata A., García-Róspide V. Recurring adventitial cyst in the left external iliac vein. EJVES Extra. 2004;8:10–14. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Matsubara J., Ban I., Nakata Y. [Cystic adventitia degeneration of the external iliac vein] Vasa. 1978;7:443–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mentha C. [Mucoid degeneration of the veins] Presse Med. 1963;71:2205–2206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Michaelides M., Papas S., Pantziara M., Ioannidis K. High spatial resolution MRI of cystic adventitial disease of the iliofemoral vein communicating with the hip joint. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2014;37:271–274. doi: 10.1007/s00270-013-0645-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Morizumi S., Suematsu Y., Gon S., Shimizu T., Iwai T. Adventitial cystic disease of the femoral vein. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010;24:1135.e5–1135.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2010.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Motaganahalli R.L., Smeds M.R., Harlander-Locke M.P., Lawrence P.F., Fujimura N., DeMartino R.R. A multi-institutional experience in adventitial cystic disease. J Vasc Surg. 2017;65:157–161. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.08.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mousa A.Y., Alhalbouni S., Abu-Halimah S., Gill G., Sadek B., Nanjundappa A. Cystic adventitial disease of the common femoral vein: a case report and review of the literature. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2013;47:569–572. doi: 10.1177/1538574413497110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nakata H., Fukuda I. Cystic adventitial degeneration of popliteal vein: report of a case. Jpn J Vasc Surg. 2003;12:549–552. [Google Scholar]
- 42.O'Loghlen S., Hall G.J., Zeiadin N., Milne L., Mussari B. Adventitial cystic disease of the common femoral vein-a rare mimic of deep venous thrombosis: a case report. Ann Intern Med. 2016;165:75–76. doi: 10.7326/L15-0532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.O'Neill J.S., Drury R.A., Bliss B.P. Cystic myxomatous degeneration of the femoral vein. Eur J Vasc Surg. 1987;1:359–361. doi: 10.1016/s0950-821x(87)80065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ohta T., Hirai M., Matsubara J., Shionoya S., Iwata H. Cystic adventitial degeneration of the ilio-femoral artery and vein. Vasc Surg. 1984;18:119–126. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Park K.M., Park Y.J., Yang S.S., Kim Y.W. Two cases of adventitial cystic disease of the external iliac vein. EJVES Extra. 2013;26:e34–e35. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Paty P.S.K., Kaufman J.L., Koslow A.R., Chang B.B., Leather R.P., Shah D.M. Adventitial cystic disease of the femoral vein: a case report and review of the literature. J Vasc Surg. 1992;15:214–217. doi: 10.1067/mva.1992.30555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Priya S., Steigner M. Images in vascular medicine: cystic adventitial disease involving external iliac vein: a rare cause of unilateral limb swelling. Vasc Med. 2018;23:86–87. doi: 10.1177/1358863X17747513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rog C.J., French B., Kobayashi E., Tan S.L. Cystic adventitial disease of the common femoral vein successfully treated with resection, synthetic graft reconstruction, and fistula creation. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020;64:408.e1–408.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2019.09.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sakamoto A., Tanaka K., Matsuda S., Harimaya K., Nakamura T., Oda Y. Adventitial cystic disease of the popliteal vein: report of a case. Surg Today. 2006;36:1098–1100. doi: 10.1007/s00595-006-3296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schaeffer J.S., Davis C.A., Shakhnovich I. Incidental finding of adventitial cystic disease of the common femoral vein: case report and review of the literature. J Vasc Ultrasound. 2016;40:83–86. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Schraverus P., Dulieu J., Mailleux P., Coulier B. Cystic adventitial disease of the popliteal vein: report of a case. Acta Chir Belg. 1997;97:90–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Scott M.F., Gavin T., Levin S. Venous cystic adventitial disease presenting as an enlarging groin mass. Ann Vasc Surg. 2014;28:489.e15–489.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2013.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Seo J.Y., Chung D.J., Kim J.H. Adventitial cystic disease of the femoral vein: a case report with the CT venography. Korean J Radiol. 2009;10:89–92. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2009.10.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sonobe A., Kato H., Mathis B.J., Tsukada T., Matsubara M., Sakamoto H. Surgical resection of an adventitial cyst of the right brachiocephalic vein. Ann Thorac Surg. 2020;110:e201–e203. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2020.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sugimoto T., Yamamoto K., Tanaka S., Saitou N., Kikuchi C., Motohashi S. Adventitial cystic disease of the femoral vein: report of a case. Surg Today. 2004;34:286–288. doi: 10.1007/s00595-003-2676-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Suzuki K., Miyazawa Y., Nishida K. Cystic adventitial degeneration of the femoral vein: report of a case [in Japanese] Angiology. 2002;42:207–211. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Tinelli G., Montanari F., Minelli F., De Nigris F., Sica S., Tshomba Y. Long-term follow-up of adventitial cyst surgical excision in external iliac vein. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Techn. 2020;6:320–323. doi: 10.1016/j.jvscit.2020.04.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Vasconcelos R.S., Cherubim C.A.F., França F.M.P., D'Allacqua E.L., Dalio M.B., Joviliano E.E. Doença cística da adventícia na veia basílica: relato de caso. J Vasc Bras. 2016;15:245–249. doi: 10.1590/1677-5449.002616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Vidoedo J., Cruz A., Pinto J.A., Maia M., Vasconcelos J. [An uncommon cause of lower limb oedema—case report] Rev Port Cir Cardiotorac Vasc. 2015;22:175–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wu X., Jiang B., Lun Y., Xia Q., Han Y., Liu Z. Venous occlusion due to cystic adventitial degeneration of the common femoral vein. Vasa. 2013;42:461–464. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Wu X., Lun Y., Jiang H., Gang Q., Duan Z., Xin S. Cystic adventitial disease of the common femoral vessels: report of 2 cases and literature review. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2014;48:325–328. doi: 10.1177/1538574413518616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yoshii S., Ikeda K., Murakami H. Cystic, myxomatous adventitial degeneration of a saphenous vein. J Vasc Surg. 1998;27:780–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Yu J., Lu C., Pan X., Li W. Cystic adventitial disease of the common femoral vein: a case report. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2016;5:231–234. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2016.01038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Zhang Z.G., Zhang Y., Liu H.Y., Song Y.L., Li X.Q., Wang B.H. [Cystic adventitial degeneration of left external iliac vein: report of a case] Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2008;37:715–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]