Abstract
Covid-19-related encephalitis is a heterogeneous syndrome characterized by a combination of clinical, laboratory, and imaging features related to inflammation of the brain, where the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is presumably the causative agent. We reported a case of Covid-19-related encephalitis presenting with neuropsychiatric symptoms, including intense agitation. Reverse-transcriptase polymerase-chain-reaction in cerebrospinal fluid was positive for SARS-CoV-2. Our case expands the literature about neurologic manifestations of Covid-19 and emphasizes the possibility of prominent behavioral symptoms as the initial manifestation.
Keywords: Covid-19-related encephalitis, SARS-CoV-2 infection, Neuropsychiatric symptoms, Agitation
1. Introduction
Covid-19, the infection caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has a range of typical clinical manifestations, including cough, fever, myalgias, gastrointestinal symptoms, and anosmia (Gandhi et al., 2020). Several neurologic manifestations have been described since late 2019, when a global pandemic started, increasing the burden of the disease (Asadi-pooya, 2020; Chen et al., 2021; Hassett et al., 2020). Neuropsychiatric manifestations have also been described, including a range of psychopathologies such as depression, anxiety, psychosis, suicidal ideation, insomnia, and delirium (Nalleballe et al., 2020; Taquet et al., 2021). Uncommon presentations of Covid-19 with encephalitis were recently reported (Pilotto et al., 2021), including limbic encephalitis (Bhagat et al., 2021; Chiveri et al., 2021). We report Covid-19-related encephalitis, confirmed by reverse-transcriptase polymerase-chain-reaction (RT-PCR) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), presenting with severe agitation.
2. Case report
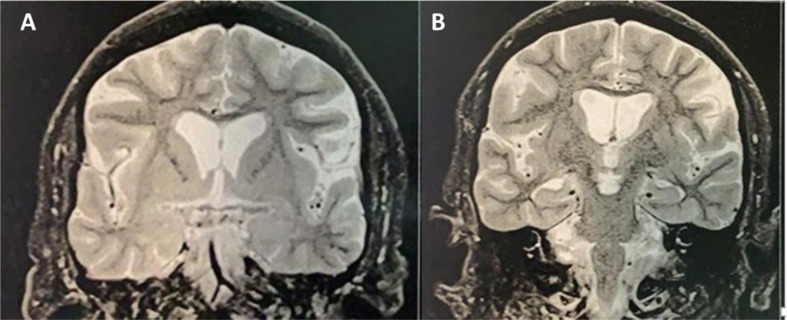
A 52-year-old man was present in an outpatient neurologic office with a 3-day history of acute onset cognitive impairment characterized by impaired attention, forgetfulness, and difficulties with word-finding. Concomitantly, he developed aggressiveness and psychomotor agitation. He also had a new-onset generalized tonic-clonic seizure. He had contact with family members infected with Covid-19 in the previous 15 days. His past medical history was unremarkable. During the evaluation, the patient became agitated, with increased aimless motor activity and verbal and physical aggressiveness. He was unconcerned about the use of a facemask and became distressed when confronted by his family. During the office evaluation, he needed to be restricted to avoid aggression toward the physician. In-hospital investigation with 1.5T MRI revealed a normal-appearance brain imaging (including medial temporal lobe and other limbic structures - Fig. 1 ). CSF analysis showed a mild lymphocytic pleocytosis. CSF RT-PCR was positive for SARS-CoV-2 (Table 1 ). The electroencephalogram was normal. After a few days, cognitive impairment and neuropsychiatric features progressed. The patient evolved to a decreased level of consciousness. He developed dyspnea with rapid evolution to severe respiratory failure due to lung injury. The patient died due to pulmonary complications after three days of intensive care unit admission (10 days after the beginning of his illness). An autopsy was not performed.
Fig. 1.
T2-weighted coronal MRI at the level of amygdalae (A) and hippocampal formations (B) showing typical appearing limbic structures.
Table 1.
Cerebrospinal fluid panel results.
| Parameter | Result | Reference value |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Colorless | Colorless |
| Aspect | Clear | Clear |
| Total proteins | 60 mg/dl | Adults: 15–45 mg/dl Adults >60 anos: 15–60 mg/dl |
| Albumin | 22 mg/dl | 10–30 mg/dl |
| Glucose | 53 mg/dl | 50–80 mg/dl |
| Chlorides | 117 mmol/L | 115–130 mmol/l |
| LDH | 21 U/L | 0–25 U/L |
| Glutamine | 17 mg/dl | 15–20 mg/dl |
| Leukocytes | 8/μl | 0–5U/μl |
| Differential cytology | Lymphocytes: 50% Monocytes: 12% Neutrophils: 4% |
Lymphocytes: 60% ± 20% Monocytes: 30% ± 15% Neutrophils: 2% ± 4% |
| Opening pressure | 120 | 100–180 |
| Cellularity | 8 cells/mm3 | 0-4 cells/mm3 |
| Virus | Sars-Cov-2 Positive | Negative |
| Mycobacteria | Negative | Negative |
| Fungi | Negative | Negative |
| Protozoa | Negative | Negative |
| Spirochetes | Negative | Negative |
3. Discussion
We reported a case of encephalitis due to Covid-19 with positive CSF RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2, in which agitation was the first symptom.
Encephalitis is characterized by a combination of clinical, laboratory, and imaging features related to brain inflammation (Graus et al., 2016). Proposed criteria for possible autoimmune encephalitis might be used as a guide for more general encephalitis and includes: 1) subacute onset (rapid progression of fewer than three months) of working memory deficits (short-term memory loss), altered mental status (defined as decreased or altered level of consciousness, lethargy, or personality change) or psychiatric symptoms; and 2) at least one of the following: new focal central nervous system (CNS) findings; seizures not explained by a previously known seizure disorder; CSF pleocytosis (white blood cell count of more than five cells per mm³; MRI features suggestive of encephalitis (Graus et al., 2016). According to this proposal, our patient fulfilled the criteria for possible encephalitis.
The involvement of the central nervous system in SARS-CoV-2 is associated with a large spectrum of clinical syndromes, including encephalitis (Asadi-pooya, 2020; Hassett et al., 2020; Pilotto et al., 2021). In agreement with our case, most cases of encephalitis reported in a series of patients had normal MRI imaging (Pilotto et al., 2021). Despite significant neuropsychiatric symptomatology (agitation), neuroimaging was unremarkable in our case. However, normal imaging does not exclude CNS involvement of the SARS-CoV-2. Moreover, this clinical-radiologic paradox is frequently seen in the neurologic manifestations of COVID-19 (Jegatheeswaran et al., 2021; Kremer et al., 2020).
Different from most cases of the same authors, our patient showed a positive CSF RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2. Even with CNS involvement, positive CSF RT-PCR appears to be rare through the spectrum of CNS involvement of Covid-19 (Lewis et al., 2021; Placantonakis et al., 2020). However, CSF RT-PCR is the gold standard to detected CNS involvement in Covid-19 (Bellon et al., 2020).
SARS-CoV-2 affects the brain through different mechanisms, including direct brain invasion inducing systemic pro-inflammatory cytokines that surpass the blood-brain barrier (cytokine storm). Also, neurotransmitter system dysfunction, brain vascular injury, thrombotic events, and neuronal damage are possible pathophysiologic events. All mechanisms may be associated with a myriad of neuropsychiatric symptoms (Boldrini et al., 2021). The finding of positive CSF RT-PCR in our patient is consistent with CNS direct invasion. Several mechanisms have been proposed, including penetration of the olfactory mucosa and transsynaptic migration along the olfactory tract, inflammation-induced breakdown of the blood-brain barrier or entrance via monocytes ("Trojan-horse" mechanism), or via circumventricular organs (midline structures around the third and fourth ventricles, where the capillaries have a wall devoid of the blood-brain barrier (Boldrini et al., 2021; Paterson et al., 2020; Zubair et al., 2020).
Limbic system involvement probably occurs even in mild to moderate Covid-19 (Douaud et al., 2021). Limbic encephalitis was also reported (Bhagat et al., 2021; Chiveri et al., 2021). Proposed diagnostic criteria for limbic encephalitis require abnormal medial temporal lobe imaging (Graus et al., 2016), which was not present in the reported patient. Therefore, our case cannot be label as “limbic encephalitis. Nevertheless, the severe agitation presented by our patient possibly indicated the involvement of the limbic system (Cummings et al., 2015), even without imaging abnormalities in the limbic system, and is in line with other neuropsychiatric manifestations reported in the literature.
4. Conclusion
Covid-19 related encephalitis is a heterogeneous syndrome characterized by a combination of clinical, laboratory, and imaging features related to brain inflammation, where the SARS-CoV-2 is presumably the causative agent. As the pandemic persists and the number of infected subjects increases, knowledge about CNS involvement of the SARS-CoV-2 also increases. Our case report of COVID-19-related encephalitis presenting with prominent neuropsychiatric symptoms (agitation) and a positive CSF RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 expands the literature about the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and CNS involvement.
Author statements
Marco Orsini: Conceptualization, Methodology; Data curation, Writing- Original draft preparation. Fábio Porto: Conceptualization, Methodology; Writing- Original draft,Writing- Reviewing and Editing. Jacqueline Fernandes do Nascimento: Writing- Original draft preparation.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psycom.2021.100004.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following is the Supplementary data to this article:
References
- Asadi-pooya A.A., et al. Central nervous system manifestations of COVID-19: a systematic review. J Neurol Sci. 2020 Jun 15. 2020;413:116832. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.116832. Epub 2020 Apr 11. PMID: 32299017; PMCID: PMC7151535. Elsevier 215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellon M., Schweblin C., Lambeng N., Cherpillod P., Vazquez J., Lalive P.H., Schibler M., Deffert C. Cerebrospinal fluid features in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) positive patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020 doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhagat R., Kwiecinska B., Smith N., Peters M., Shafer C., Palade A., Sagi V. New-onset seizure with possible limbic encephalitis in a patient with COVID-19 infection: a case report and review. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Reports. 2021;9:1–7. doi: 10.1177/2324709620986302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldrini M., Canoll P.D., Klein R.S. How COVID-19 affects the brain. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021 doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.0500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Laurent S., Onur O.A., Kleineberg N.N., Fink G.R., Schweitzer F., Warnke C. A systematic review of neurological symptoms and complications of COVID-19. J. Neurol. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-10067-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiveri L., Verrengia E., Muscia F., Nuzzaco G., Raimondi E., Vecchio E., Bompane D., Mazzone A., Fociani P., Corbellino M., Prelle A. Limbic encephalitis in a COVID-19 patient? J. Neurovirol. 2021:2–4. doi: 10.1007/s13365-021-00971-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J., Mintzer J., Brodaty H., Sano M., Banerjee S., Devanand D.P., Gauthier S., Howard R., Lanctôt K., Lyketsos C.G., Peskind E., Porsteinsson A.P., Reich E., Sampaio C., Steffens D., Wortmann M., Zhong K. Agitation in cognitive disorders: international Psychogeriatric Association provisional consensus clinical and research definition. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2015 doi: 10.1017/S1041610214001963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douaud G., Lee S., Alfaro-Almagro F., Arthofer C., Wang C., Lange F., Andersson J.L.R., Griffanti L., Duff E., Jbabdi S., Taschler B., Winkler A., Nichols T.E., Collins R., Matthews P.M., Allen N., Miller K.L., Smith S.M. Brain imaging before and after COVID-19 in UK biobank. medRxiv. 2021 [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi R.T., Lynch J.B., del Rio C. Mild or moderate Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;383:1757–1766. doi: 10.1056/nejmcp2009249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graus F., Titulaer M.J., Balu R., Benseler S., Bien C.G., Cellucci T., Cortese I., Dale R.C., Gelfand J.M., Geschwind M., Glaser C.A., Honnorat J., Höftberger R., Iizuka T., Irani S.R., Lancaster E., Leypoldt F., Prüss H., Rae-Grant A., Reindl M., Rosenfeld M.R., Rostásy K., Saiz A., Venkatesan A., Vincent A., Wandinger K.P., Waters P., Dalmau J. A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:391–404. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00401-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassett C.E., Gedansky A., Migdady I., Bhimraj A., Uchino K., Cho S.M. Neurologic complications of COVID-19. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. Off. 2020;87:729–734. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jegatheeswaran V., Chan M.W.K., Chakrabarti S., Fawcett A., Chen Y.A. Neuroimaging findings of hospitalized Covid-19 patients: a Canadian retrospective observational study. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2021 doi: 10.1177/08465371211002815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer S., Lersy F., Anheim M., Merdji H., Schenck M., Oesterlé H., Bolognini F., Messie J., Khalil A., Gaudemer A., Carré S., Alleg M., Lecocq C., Schmitt E., Anxionnat R., Zhu F., Jager L., Nesser P., Mba Y.T., Hmeydia G., Benzakoun J., Oppenheim C., Ferré J.C., Maamar A., Carsin-Nicol B., Comby P.O., Ricolfi F., Thouant P., Boutet C., Fabre X., Forestier G., de Beaurepaire I., Bornet G., Desal H., Boulouis G., Berge J., Kazémi A., Pyatigorskaya N., Lecler A., Saleme S., Edjlali-Goujon M., Kerleroux B., Constans J.M., Zorn P.E., Mathieu M., Baloglu S., Ardellier F.D., Willaume T., Brisset J.C., Caillard S., Collange O., Mertes P.M., Schneider F., Fafi-Kremer S., Ohana M., Meziani F., Meyer N., Helms J., Cotton F. Neurologic and neuroimaging findings in patients with COVID-19: a retrospective multicenter study. Neurology. 2020 doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000010112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A., Frontera J., Placantonakis D.G., Lighter J., Galetta S., Balcer L., Melmed K.R. Cerebrospinal fluid in COVID-19: a systematic review of the literature. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021 doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2021.117316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalleballe K., Reddy Onteddu S., Sharma R., Dandu V., Brown A., Jasti M., Yadala S., Veerapaneni K., Siddamreddy S., Avula A., Kapoor N., Mudassar K., Kovvuru S. Spectrum of neuropsychiatric manifestations in COVID-19. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020;88:71–74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.06.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R.W., Brown R.L., Benjamin L., Nortley R., Wiethoff S., Bharucha T., Jayaseelan D.L., Kumar G., Raftopoulos R.E., Zambreanu L., Vivekanandam V., Khoo A., Geraldes R., Chinthapalli K., Boyd E., Tuzlali H., Price G., Christofi G., Morrow J., McNamara P., McLoughlin B., Lim S.T., Mehta P.R., Levee V., Keddie S., Yong W., Trip S.A., Foulkes A.J.M., Hotton G., Miller T.D., Everitt A.D., Carswell C., Davies N.W.S., Yoong M., Attwell D., Sreedharan J., Silber E., Schott J.M., Chandratheva A., Perry R.J., Simister R., Checkley A., Longley N., Farmer S.F., Carletti F., Houlihan C., Thom M., Lunn M.P., Spillane J., Howard R., Vincent A., Werring D.J., Hoskote C., Jäger H.R., Manji H., Zandi M.S. The emerging spectrum of COVID-19 neurology: clinical, radiological and laboratory findings. Brain. 2020 doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilotto A., Masciocchi S., Volonghi I., Crabbio M., Magni E., De Giuli V., Caprioli F., Rifino N., Sessa M., Gennuso M., Cotelli M.S., Turla M., Balducci U., Mariotto S., Ferrari S., Ciccone A., Fiacco F., Imarisio A., Risi B., Benussi A., Premi E., Focà E., Caccuri F., Leonardi M., Gasparotti R., Castelli F., Zanusso G., Pezzini A., Padovani A., Masciocchi S., Volonghi I., Crabbio M., Del Zotto E., Magni E., De Giuli V., Caprioli F., Rifino N., Sessa M., Gennuso M., Cotelli M.S., Turla M., Balducci U., Mariotto S., Ferrari S., Ciccone A., Fiacco F., Guindani M., Imarisio A., Risi B., Benussi A., Poli L., Gipponi S., Filosto M., Premi E., Gamba M., Caratozzolo S., Cristillo V., Libri I., Cola F.S. di, Piccinelli S.C., Cortinovis M., Scalvini A., Baldelli E., Locatelli M., Benini M., Gazzina S., Chiari E., Odolini S., Focà E., Caccuri F., Caruso A., Leonardi M., Ambrosi C., Pinelli L., Gasparotti R., Gerevini S., Ciceri E.F.M., Zanusso G., Ferraro B., Volta G.D., Pezzini A., Padovani A. Clinical presentation and outcomes of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-related encephalitis: the ENCOVID multicenter study. J. Infect. Dis. 2021 doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Placantonakis D.G., Aguero-Rosenfeld M., Flaifel A., Colavito J., Inglima K., Zagzag D., Snuderl M., Louie E., Frontera J.A., Lewis A. SARS-CoV-2 is not detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of encephalopathic COVID-19 patients. Front. Neurol. 2020;11:1–7. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.587384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taquet M., Luciano S., Geddes J.R., Harrison P.J. Bidirectional associations between COVID-19 and psychiatric disorder: retrospective cohort studies of 62354COVID -19cases in the USA. The Lancet Psychiatry. 2021 doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30462-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubair A.S., McAlpine L.S., Gardin T., Farhadian S., Kuruvilla D.E., Spudich S. Neuropathogenesis and neurologic manifestations of the coronaviruses in the age of coronavirus disease 2019: a review. JAMA Neurol. 2020 doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.