Correction to: Cancer Cell Int (2015) 22:607 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-015-0195-z
Following the publication of the original article [1], we were notified of an error in Fig. 5.
Both incorrect and corrected Fig. 5 are presented in this erratum. The revision does not affect the results and conclusions of the article.
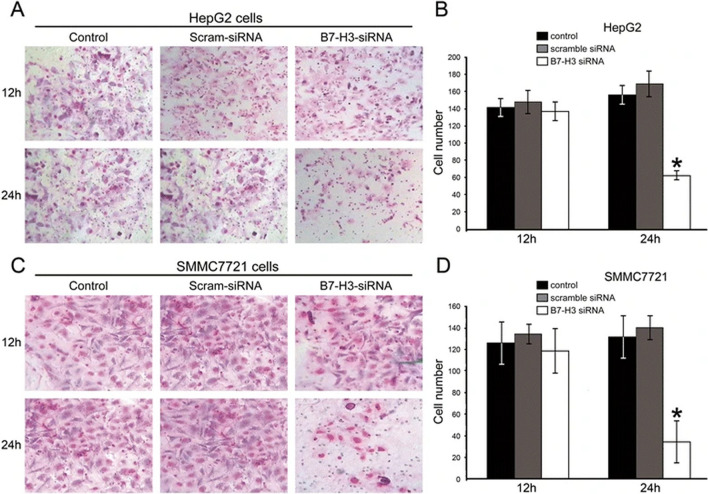
Originally published Fig. 5.
B7-H3 siRNA interference effects on HepG2 (A-B) and SMMC7721 (C-D) cell invasion by transwell chamber assay. Representative photographs of invasive HepG2 and SMMC7721 cells on the membrane, all the experiments were repeated for three times (magnification, 200×)
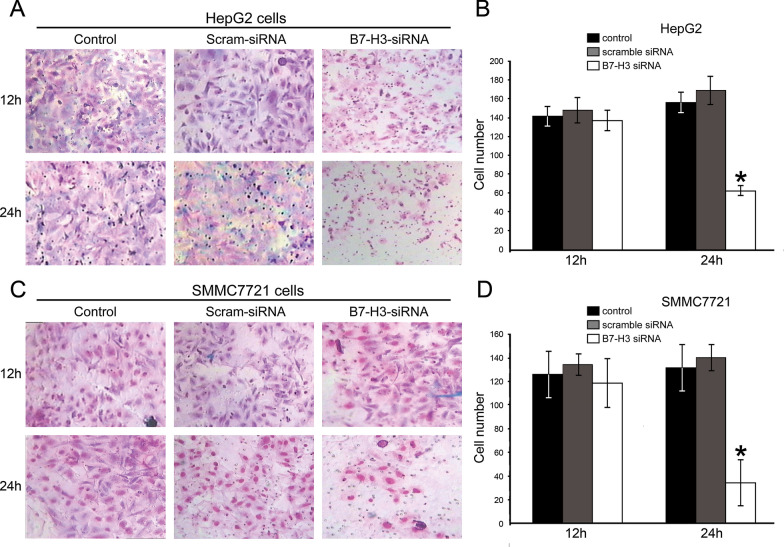
Corrected Fig. 5.
B7-H3 siRNA interference effects on HepG2 (A, B) and SMMC7721 (C, D) cell invasion by transwell chamber assay. Representative photographs of invasive HepG2 and SMMC7721 cells on the membrane, all the experiments were repeated for three times (magnification, × 200)
The original article has been corrected.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Reference
- 1.Kang F, Wang L, Jia H, Li D, Li H, Zhang Y, Sun D. B7-H3 promotes aggression and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via JAK2/STAT3/Slug signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2015;22:607. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0195-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]