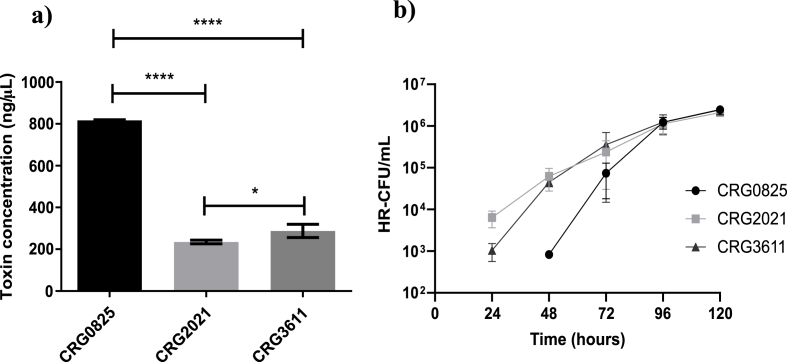
Fig. 2.
Toxin and sporulation profiles of R20291 derivatives. The three derivatives of R20291 were assessed for a) Their ability to produce and secrete toxin through a combined ELISA for TcdA and TcdB on sterile-filtered 72 h supernatants b) Their ability to form heat-resistant endospores (heat-resistant colony forming units HR-CFU/mL) across six time-points between 0 and 120 h. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical significance according to One-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnet's multiple comparison test (P = ∗<0.05; ∗∗∗∗<0.0001).