Abstract
This study was conducted to evaluate the effect of pyridoxine on the development of hair follicles in Rex rabbits and the underlying molecular mechanism. Two hundred 3-month-old Rex rabbits were randomly divided into 5 groups and fed diets supplemented with 0, 5, 10, 20, or 40 mg/kg pyridoxine. The hair follicle density on the dorsal skin and the gene and protein expression levels of components of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB or Akt), Wnt, Notch and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signalling pathways were measured. In addition, free hair follicles were isolated from Rex rabbits and cultured with pyridoxine in vitro to measure hair shaft growth. Furthermore, dermal papilla cells (DPC) were isolated from the skin of Rex rabbits and cultured with pyridoxine in vitro to measure the gene and protein expression levels of components of the PI3K/Akt, Wnt, Notch and BMP signalling pathways. The results showed that the addition of dietary pyridoxine significantly increased the total follicle density, secondary follicle density, and secondary-to-primary ratio (S/P, P < 0.05), that the growth ratio of hair stems was promoted by pyridoxine in basic culture medium, and that the growth length of tentacle hair follicles cultured in the pyridoxine group was longer than that in the control group (P < 0.05). In addition, pyridoxine changed the DPC cycle progression and promoted cell proliferation, and appropriate concentrations of pyridoxine (10 and 20 μmol/L) significantly inhibited cell apoptosis (P < 0.05). Pyridoxine significantly affected the gene expression of components of the PI3K/Akt, Wnt and Notch signalling pathways in the skin and DPC of Rex rabbits (P < 0.05), increased the levels of phosphorylated catenin beta 1 (CTNNB1) and Akt, and decreased the level of phosphorylated glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK-3β) (P < 0.05). Therefore, the molecular mechanism by which pyridoxine promotes hair follicle density in Rex rabbits probably occurs through activation of the PI3K/Akt, Wnt and Notch signalling pathways, prolonging hair follicle growth and delaying the onset of telogen.
Keywords: Hair follicle development, Pyridoxine, Rex rabbit, Dermal papilla cell
1. Introduction
Hair follicles are part of the skin epithelium in vertebrates and are characterized by periodic growth during adult life (Millar, 2002). Many different cells and signalling pathways interact with each other to regulate hair follicle development. Dermal papilla cells (DPC), hair matrix cells, inner root sheath cells, and outer root sheath cells are important cellular components of hair follicles and participate in hair follicle development (Fuchs, 2007; Driskell et al., 2011; Chi et al., 2013). Moreover, many studies have reported that different signalling pathways, such as the Wnt, Notch, bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) pathways, participate in hair follicle development (Kulessa et al., 2000; Foitzik et al., 2000; Su et al., 2008; Demehri and Kopan, 2009; Lin et al., 2015, Zhang et al., 2016). The Notch signalling pathway interacts with the BMP signalling pathway, which can inhibit the Wnt signalling pathway by regulating β-catenin (Demehri and Kopan, 2009). Signal exchange between hair follicle stem cells and DPC is the key to initiating the next hair follicle cycle (Wu et al., 2010, Woo et al., 2013).
Vitamins are trace organic resources that must be obtained from food to maintain normal physiological function, and they play important roles in animal growth, metabolism and development. Vitamin B6 is a general term for pyridine compounds, including pyridoxine, pyridoxal, pyridoxine and their phosphate forms; it was discovered almost one century ago (György, 1956; Hellmann and Mooney, 2010; Kraemer et al., 2012; Eggersdorfer et al., 2012), and it is the active form of pyridoxal-5′-phosphate (PLP), which serves as a cofactor for a wide variety of proteins and enzymes (Jansonius, 1998; Christen and Mehta, 2001; Eliot and Kirsch, 2004; Phillips, 2015). According to reports, PLP functions as a cofactor of more than 160 enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of amino acids (John, 1995; Eliot and Kirsch, 2004; Percudani and Peracchi, 2009). The formation of fur on animal skin requires a large amount of protein and sulfur-containing amino acids, but there are few studies on the molecular mechanism by which pyridoxine regulates hair follicle morphogenesis in Rex rabbits. In other words, the molecular mechanism by which pyridoxine participates in regulating hair follicle development is not clear. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of pyridoxine on hair follicle development in vivo and in vitro, and the molecular mechanism was preliminarily discussed.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Animals, free hair follicles, DPC and experimental design
2.1.1. Animals, feeding and experimental design in feeding
Two hundred 3-month-old Rex rabbits with similar body weights were randomly assigned to 1 of 5 diets, with 40 rabbits in each experimental diet group. The experimental diet formula composition and nutritional level met the recommended nutrient requirements for juvenile rabbits (NRC 1977, Table 1), and the following 5 concentrations of pyridoxine were added to the experimental diets: 0, 5, 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg (98% pyridoxine hydrochloride, Jiangxi Tyson Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China; as-fed basis). At the end of the 60-d feeding trial (53-d experimental period and a 7-d adjustment period), 8 rabbits per dietary group (4 males and 4 females) with body weights close to that of the average body weight of the group were bled by cardiac puncture. After shearing, the middle part of the back skin were collected with cryopreservation tube, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C for mRNA and protein expression analysis.
Table 1.
Composition and nutrient levels of the experimental diet (%, dry matter basis).
| Ingredients | Content | Nutrient levels2 | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 15.0 | Digestible energy, MJ/kg | 11.42 |
| Barley grain | 10.0 | Crude protein | 18.00 |
| Wheat bran | 12.0 | Ether extract | 3.10 |
| Soybean meal | 10.0 | Crude fibre | 19.41 |
| Sunflower meal | 8.0 | Crude ash | 13.06 |
| Peanut vine straws | 30.0 | Calcium | 1.08 |
| Rice hull powder | 10.0 | Phosphorus | 0.48 |
| Premix1 | 5.0 | Lysine | 0.67 |
| Total | 100.0 | Methionine | 0.30 |
The premix provided the following per kilogram of diet, vitamin A: 10,000 IU; vitamin D3: 2,000 IU; vitamin E: 50 mg; vitamin K3: 2.5 mg; choline chloride: 400 mg; thiamine: 5 mg; riboflavin: 10 mg; nicotinic acid: 20 mg, pantothenic acid: 50 mg; folic acid: 2.5 mg; cobalamin: 1 mg; Fe: 100 mg; Zn: 50 mg; Cu: 40 mg; Mn: 30 mg; I: 0.5 mg; Se: 0.05 mg; calcium hydrogen phosphate: 1.5 g; sodium chloride: 5 g; lysine: 1.5 g; methionine: 1.5 mg; the rest is miscellaneous meal carrier complement.
Digestible energy was calculated according to “Tables of feed composition and nutritive values in China (The 20th revised edition, 2009), Institute of animal science of CAAS (Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019)”, while the others were measured values.
2.1.2. Free hair follicle culture in vitro and experimental design in organ
The whisker hair follicles from 30-d-old Rex rabbits were used in this study to establish organ cultures. Small skin pieces (1 cm2) of whisker were excised from Rex rabbits as previously described in mice (Ouji et al., 2007). Tentacle hair follicles were divided into 6 groups, with 10 follicles in each group. The extracted hair follicles were placed in 24-well plates. The concentrations of pyridoxine (Solarbio, China) in basic culture medium were 0, 10, 20, 40, 80 and 160 μmol/L, and suspended culture was carried out at 31 °C and 5% CO2. The basic culture medium composition was Williams E medium (Sigma–Aldrich, USA), 2 mmol/L L-glutamine (Sigma–Aldrich, USA), 10 μg/mL insulin (Sigma–Aldrich, USA), 10 ng/mL hydrocortisone (Sigma–Aldrich, USA), 100 U/mL penicillin (Solarbio, China), and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Solarbio, China). The medium was changed every 2 d. The growth length of the fur wool stem was measured every 24 h from the beginning of follicle culture (0 to 144 h).
2.1.3. Isolation and culture of DPC and experimental design in cell
DPC were isolated from median skin of back pieces from 30-d-old Rex rabbits and cultured according to previously reported methods (Liu et al., 2020a). Third-generation DPC were inoculated at 104 cells/mL in a 6-well plate, with 2 mL of cell suspension per well. After the cells were allowed to adhere for 24 h, the culture medium was removed, and Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM, Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific) containing 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific) with pyridoxine (Solarbio, China) concentrations of 0, 10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 μmol/L was added, with 6 replicate wells for each concentration. After 72 h, the cells were collected, and the effects of pyridoxine on the cell proliferation rate, cell cycle progression and apoptosis were evaluated. The gene expression of components of the PI3K/Akt, Wnt, Notch and BMP signalling pathways and the levels of phosphorylated Akt, catenin beta 1 (CTNNB1) and GSK-3β were also detected.
2.2. Determinations and analyses
2.2.1. Chemical analysis of the experimental diets
Dry matter (DM, 934.01), crude protein (CP, 954.01), ether extract (EE, 920.39) crude fibre (CF, 932.09) and ash (942.05) were measured according to Association of Official Analytical Chemists ((AOAC International 2005)) procedures. The CP content and EE were determined using a Kjeltec Auto 1030 Analyser and Soxtec 1043, respectively (FOSS Tecator AB, Höganäs, Sweden). The calcium and phosphorus contents were determined by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-EMS; Optima 8000, PerkinElmer, USA). The lysine and methionine contents in the feed were analysed using an automatic amino acid analyser (Basic L-8900, Japan) as a reference (Liu et al., 2017). The DM intakes for each rabbit were calculated according to total dry matter intakes divided by total experimental days.
2.2.2. Assessment of the proliferation, cell cycle progression and apoptosis of DPC
The effect of pyridoxine on proliferation was measured by thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide (MTT; Solarbio, China), and cell cycle progression and apoptosis were measured by PI/RNase standing buffer (BD Biosciences, cat: 550825) and PE Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit I (BD Biosciences, cat: 559763), respectively, using flow cytometry (BD Accuri C6, BD). The results were analysed with ModFit LT 5.0 software (Verity Software House, USA).
2.2.3. Total RNA extraction and real-time PCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted from skin tissues or DPC with RNAiso reagent (TaKaRa, Japan) according to a reference (Liu et al., 2017). The PCR primers used in this study (Table 2) were designed using a Premier 5.0 Software and synthesized by Ruibo Biological Engineering Co., Ltd. (Qingdao, China). For quantitative RT-PCR analysis of mRNA, 1 μg of total RNA was used to synthesize cDNA with a Transcriptor First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Roche Diagnostics GmbH Mannheim, Germany). PCR amplification was performed using Fast Start Universal SYBR Green Master Mix (Roche Diagnostics GmbH Mannheim, Germany). The relative mRNA expression levels were calculated using the arithmetic formula 2−△△Ct (LiLivak and Schmittgen, 2001).
Table 2.
Information of primers.
| Gene | Accession number | Primer sequence (5′-3′) | Product length, bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inppl1 | NM_017349797 | F: CAGAGCACGAGAACCGCATCAG | 199 |
| R: AGCCGCAGGATGTCCAGGTAG | |||
| Inpp4b | NM_008267416 | F: TCCTAAGAGCACAGCGGAGAGC | 195 |
| R: GCTGCCTTCACTGCCACCATC | |||
| Frk | XM_008263392 | F: CAAGCGATGGCCTCTGTGTCAG | 195 |
| R: CTGCTACTGGAGTGGTGTTGTTCC | |||
| Phlda3 | XM_002717603 | F: GCGGCGGCGAGATTGACTTC | 101 |
| R: CTGGATGGCCTGCTGGTTCTTG | |||
| Wnt10b | NM_002711076 | F: TGTGCCATCCCTCTTCCTTA | 150 |
| R: GGCTCCACCTCTAACTTCTGC | |||
| CTNNB1 | DQ786777 | F: TTCTTGGGACTCTTGTTCAGC | 122 |
| R: CACTTGGCACACCATCATCT | |||
| GSK-3β | NM_001146156 | F: ATCCATGTCTCCCTGTCCAC | 119 |
| R: TTTCCTCTTCCCACTCCTGA | |||
| DKK1 | NM_001082737 | F: ATTCCAACGCCATCAAGAAC | 163 |
| R: CCACACTCCTCGTCCTCTGT | |||
| Notch1 | XM_011518717 | F: TGCGAGACCAACATCAACGAGTG | 94 |
| R: TCAGGCAGAAGCAGAGGTAGGC | |||
| JAG1 | XM_018261778 | F: TGGAGGAGGACGACATGGACAAG | 176 |
| R: CATCCGATTGAGGCTCTGTGCTG | |||
| Hes1 | XM_002716517 | F: CCAGATCAACGCCATGACCTATCC | 200 |
| R: ACACCTTAGCCGCCTCTCCAG | |||
| Hes5 | NM_008253710 | F: AGACCGCATCAACAGCAGCATC | 105 |
| R: ATCTCCAGGATGTCCGCCTTCTC | |||
| BMP2 | XM_001082650 | F: GACATCCTGAGCGAGTTCGAGTTG | 113 |
| R: CGGCGGTACAAGTCCAGCATG | |||
| BMP4 | NM_001195723 | F: CTAAGCATCACCCACAGCGG | 163 |
| R: CAGTCATTCCAGCCCACGTC | |||
| TGF-β1 | NM_008249704 | F: 5′- CCGTTTCTTTCGTGGGATAC | 108 |
| R: GGTAAGGGAGGAGGGTCTCA | |||
| GAPDH | NM_001082253 | F: TGCCACCCACTCCTCTACCTTCG | 118 |
| R: CGAAGGTAGGGATGGGTGGCA |
Inppl1 = inositol polyphosphate phosphatase like 1; F = forward primer; R = reverse primer; Frk = fyn-related kinase; Phlda3 = pleckstrin homology like domain family A member 3; CTNNB1 = catenin beta 1; GSK-3β = glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; DKK1 = dickkopf-1; JAG1 = Jagged1; BMP = bone morphogenetic protein; TGF-β1 = transforming growth factor-β; GAPDH = glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
2.2.4. Western blotting
Total protein was extracted from skin tissues or DPC using a radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer (Beyotime, China), and the protein concentrations were determined using a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Beijing Kangwei Century Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China). The extracted proteins (50 ng/sample) were solubilized in 40 mL of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) loading buffer (Solarbio, China) and then resolved by electrophoresis (Bio-Rad, Richmond, USA) on 12.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) gels prior to electrophoretic transfer to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore, Billerica, USA). Standard markers for protein molecular masses were purchased from Thermo (USA). The membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk in PBS (Solarbio, China) at 4 °C overnight and incubated with a 1:1,000 dilution primary antibodies (tubulin AT819, Beyotime, China; phospho-CTNNB1-S552 pAb, Abcam, US; phospho-GSK3B–S9 pAb, Abcam, US; phospho-AKT1-S473 pAb, Abcam, US; or noggin (NOG) polyclonal antibody, Abcam, US). The membranes were then washed with Tris-buffered saline containing Tween (TBST; Solarbio, China) and incubated with a 1:3000 dilution of a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG antibody (Beyotime, China) at 37 °C for 1 h. The proteins were visualized using Beyo ECL reagents (Beyotime, China) as the reference (Liu et al., 2020b). The intensity of the bands was quantified with a Pro Plus 6.0 Biological Image Analysis System.
2.3. Statistical analysis
All the data were analysed by one-way ANOVA with SAS software (SAS version 8e; SAS Institute, Cary. NC, USA) to determine the significance of differences in the effects of the pyridoxine treatments on the responses among the various groups, Duncan's test was used for multiple comparisons. The data are shown as the means and root mean errors (RMSE), and P < 0.05 was regarded as statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of dietary pyridoxine supplementation on hair follicle development in rex rabbits
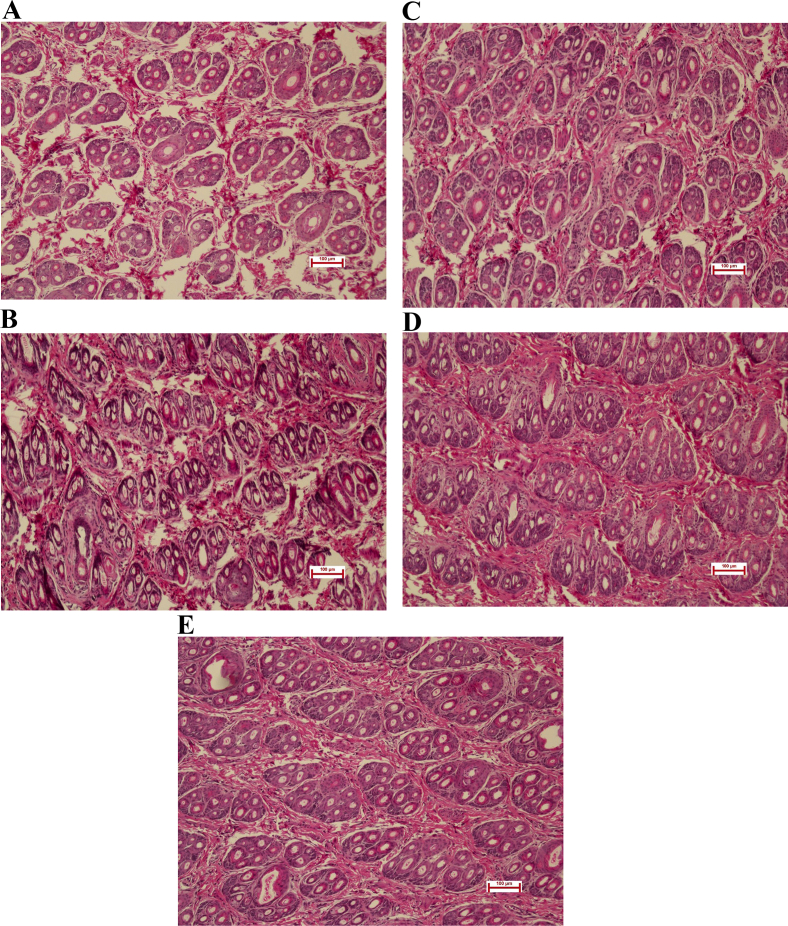
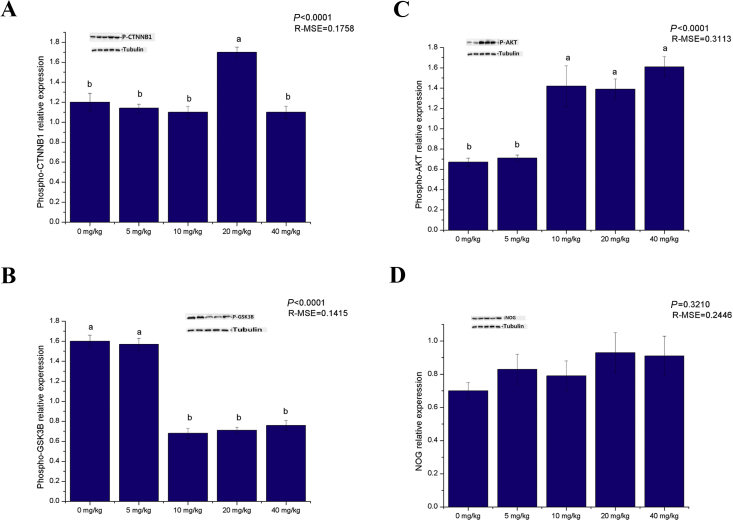
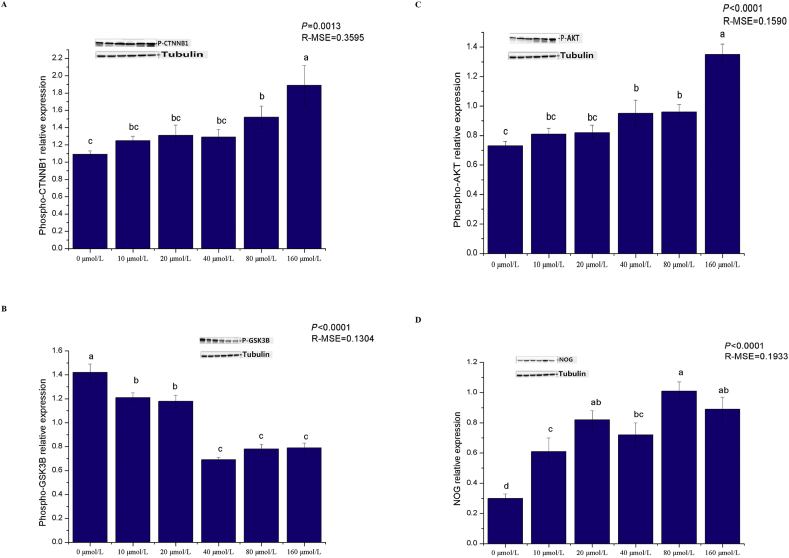
Dietary pyridoxine supplementation significantly affected dry matter intakes, total follicle density, secondary follicle density and the secondary-to-primary ratio (S/P, P < 0.05). With increasing levels of supplementation, the dry matter intakes and follicle density first increased and then decreased, and maximum values were observed in the 20 mg/kg group (Table 3; Fig. 1). Dietary pyridoxine supplementation increased the gene expression of inositol polyphosphate phosphatase like 1 (Inppl1), a component of the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. The expression Wnt10b and CTNNB1, components of the Wnt signalling pathway, was increased and the expression of GSK-3β, a component of the Wnt signalling pathway, was decreased by dietary pyridoxine supplementation (P < 0.05). Pyridoxine promoted the gene expression of Notch1, Hes1 and Hes5, components of the Notch signalling pathway (P < 0.05). There was no effect on the gene expression of BMP2, BMP4 or transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β1), which are components of the BMP signalling pathway (P > 0.05; Table 4). Pyridoxine increased the levels of phosphorylated CTNNB1 and Akt and decreased the level of phosphorylated GSK-3β (P < 0.05; Fig. 2).
Table 3.
Effects of pyridoxine on dry matter intakes and hair follicle density of Rex rabbit1.
| Item | Pyridoxine level, mg/kg |
RMSE | P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 40 | |||
| Dry matter intakes, g/d | 128.47c | 129.24bc | 131.81b | 134.58a | 130.50bc | 31.301 | 0.001 |
| Total hair follicle density, count/mm2 | 258.83b | 286.22b | 318.50ab | 395.71a | 338.92b | 64.795 | 0.002 |
| Primary hair follicle density, count/mm2 | 14.77 | 17.00 | 15.23 | 14.38 | 14.90 | 3.513 | 0.604 |
| Secondary hair follicle density, count/mm2 | 244.07c | 269.21bc | 302.98bc | 381.33a | 324.02ab | 65.240 | 0.002 |
| Secondary-to-primary ratio (S/P) | 17.13b | 16.48b | 21.42ab | 28.63a | 22.54ab | 8.363 | 0.044 |
a, b, c Within a row, means with different superscript letters are significantly different (P < 0.05).
Data represent means and root mean error (RMSE), n = 40 for dry matter intakes, and n = 8 for hair follicle density.
Fig. 1.
Effects of dietary pyridoxine supplemented level on hair follicle density of Rex rabbit. (A) Pyridoxine were supplemented 0 mg/kg; (B) pyridoxine were supplemented 5 mg/kg; (C) pyridoxine were supplemented 10 mg/kg; (D) pyridoxine were supplemented 20 mg/kg; (E) pyridoxine were supplemented 40 mg/kg. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Table 4.
Effects of pyridoxine on gene expression of signal pathway of Rex rabbit1.
| Gene | Pyridoxine level, mg/kg |
RMSE | P-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 40 | ||||
| PI3K/Akt signal pathway | ||||||||
| Inppl1 | 1.00b | 0.96b | 1.59ab | 2.00a | 1.47ab | 0.541 | 0.014 | |
| Inpp4b | 1.00 | 1.17 | 1.26 | 1.29 | 1.14 | 0.270 | 0.391 | |
| Frk | 1.00 | 1.24 | 1.35 | 1.33 | 1.33 | 0.283 | 0.201 | |
| Phlda3 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 1.09 | 1.15 | 1.02 | 0.346 | 0.896 | |
| Wnt signal pathway | ||||||||
| Wnt10b | 1.00b | 0.93b | 0.84b | 2.73a | 1.22b | 0.951 | 0.011 | |
| CTNNB1 | 1.00b | 0.67b | 0.65b | 1.63a | 1.10b | 0.380 | 0.001 | |
| GSK-3β | 1.00a | 0.76ab | 0.74ab | 0.43bc | 0.40c | 0.261 | 0.003 | |
| DKK1 | 1.00 | 1.17 | 1.14 | 1.06 | 0.98 | 0.333 | 0.804 | |
| Notch signal pathway | ||||||||
| Notch1 | 1.00b | 1.07b | 1.14b | 2.14a | 1.20b | 0.597 | 0.016 | |
| JAG1 | 1.00 | 1.33 | 1.48 | 1.97 | 1.50 | 0.814 | 0.374 | |
| Hes1 | 1.00c | 1.06c | 2.23b | 3.36a | 1.28c | 0.524 | <0.001 | |
| Hes5 | 1.00b | 1.03b | 1.85b | 3.73a | 2.21b | 1.184 | 0.003 | |
| BMP signal pathway | ||||||||
| BMP2 | 1.00 | 0.68 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.404 | 0.697 | |
| BMP4 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 0.443 | 0.788 | |
| TGF-β1 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 1.03 | 1.21 | 0.93 | 0.464 | 0.816 | |
Inppl1 = inositol polyphosphate phosphatase like 1; Frk = fyn-related kinase; Phlda3 = pleckstrin homology like domain family A member 3; CTNNB1 = catenin beta 1; GSK-3β = glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; DKK1 = dickkopf-1; JAG1 = Jagged1; BMP = bone morphogenetic protein; TGF-β1 = transforming growth factor-β.
a,b,c Within a row, means with different superscript letters are significantly different (P < 0.05).
Data represent means and root mean error (RMSE), n = 8 for per group.
Fig. 2.
Effects of pyridoxine on expression of hair follicle-related proteins of Rex rabbit. (A) Phospho-catenin beta 1 (p-CTNNB1); (B) phospho-glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (p-GSK-3β); (C) phospho-Akt (p-Akt); (D) noggin (NOG) protein. Data represent means ± standard error and root mean error (R-MSE), n = 8 for per group. a, b, c Bars with different letters means significantly different (P < 0.05).
3.2. Effects of pyridoxine on the growth of hair follicles from rex rabbits
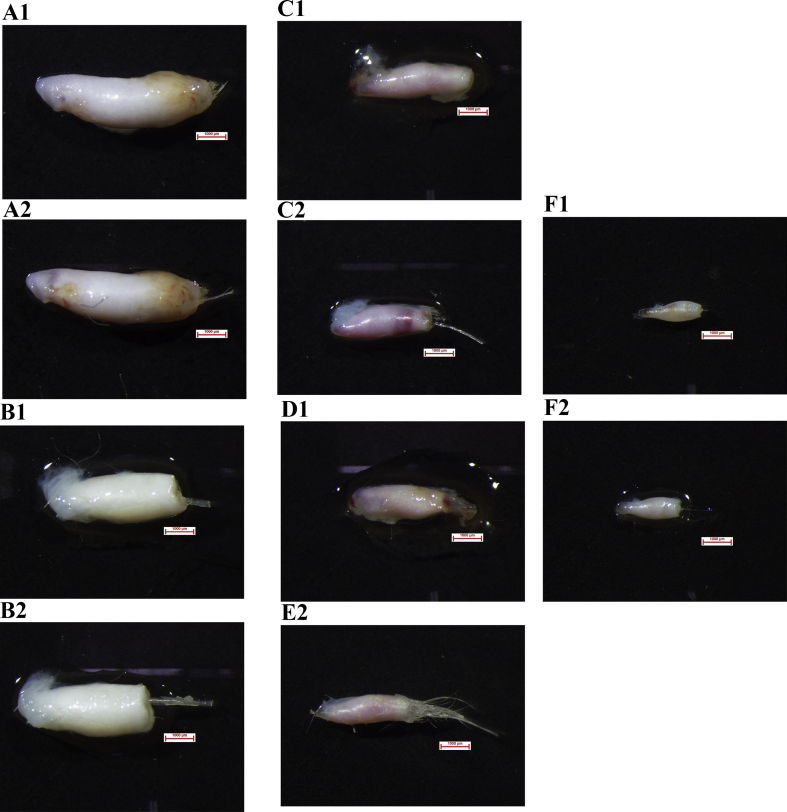
To investigate the effects of pyridoxine on hair follicles growth, the whisker hair follicles were separated from 30-d-old Rex rabbits. The results showed that the hair follicles of Rex rabbit tentacles cultured in vitro grew at an average rate of 3.89 μm/d for 144 h, and the growth rate was faster in the early stage than in the late stage (Table 5). The growth rate of whisker hair stems was promoted by the addition of pyridoxine to the culture medium. The length of Rex rabbit tentacle hair follicles cultured for 144 h reached 36.15 μm in the 80 μmol/L pyridoxine group, with the fastest growth rate of 6.03 μm/d, which was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05; Fig. 3; Table 5). Therefore, pyridoxine could promote hair growth and delay hair follicle degeneration and death in Rex rabbits.
Table 5.
Effects of pyridoxine on the growth of free hair follicles in vitro1.
| Item | Pyridoxine concentration, μmol/L |
RMSE | P-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 80 | 160 | |||
| 0 to 24 h, μm | 7.20b | 7.14b | 7.11b | 7.30b | 9.13a | 5.67c | 0.693 | <0.001 |
| 24 to 48 h, μm | 5.78d | 6.52bc | 6.74b | 7.19b | 9.08a | 6.00cd | 0.743 | <0.001 |
| 48 to 72 h, μm | 3.38c | 2.85c | 3.23c | 4.69a | 5.08a | 4.11b | 0.625 | <0.001 |
| 72 to 96 h, μm | 2.53c | 2.68c | 3.08c | 3.79b | 4.38a | 3.02c | 0.590 | <0.001 |
| 96 to 120 h, μm | 2.35d | 2.71cd | 3.15bc | 3.89a | 4.18a | 3.72ab | 0.639 | <0.001 |
| 120 to 144 h, μm | 2.10c | 2.50c | 3.05b | 4.03a | 4.29a | 3.21b | 0.517 | <0.001 |
| Total length, μm | 23.33d | 24.39cd | 26.37c | 30.88b | 36.15a | 25.72c | 2.203 | <0.001 |
| Growth ratio, μm/d | 3.89d | 4.07cd | 4.40c | 5.15b | 6.03a | 4.29c | 0.367 | <0.001 |
a, b, c Within a row, means with different superscript letters are significantly different (P < 0.05).
Data represent means and root mean error (RMSE), n = 10 for per group.
Fig. 3.
Effects of pyridoxine on the growth of hair follicles (20× magnification). (A) Pyridoxine were supplemented 0 μmol/L, A1 and A2 represent 0 and 144 h in vitro culture, respectively; (B) pyridoxine were supplemented 10 μmol/L, B1 and B2 represent 0 and 144 h in vitro culture, respectively; (C) pyridoxine were supplemented 20 μmol/L, C1 and C2 represent 0 and 144 h in vitro culture, respectively; (D) pyridoxine were supplemented 40 μmol/L, D1 and D2 represent 0 and 144 h in vitro culture, respectively; (E) pyridoxine were supplemented 80 μmol/L, E1 and E2 represent 0 and 144 h in vitro culture, respectively; (F) pyridoxine were supplemented 160 μmol/L, F1 and F2 represent 0 and 144 h in vitro culture, respectively. Scale bars = 1,000 μm.
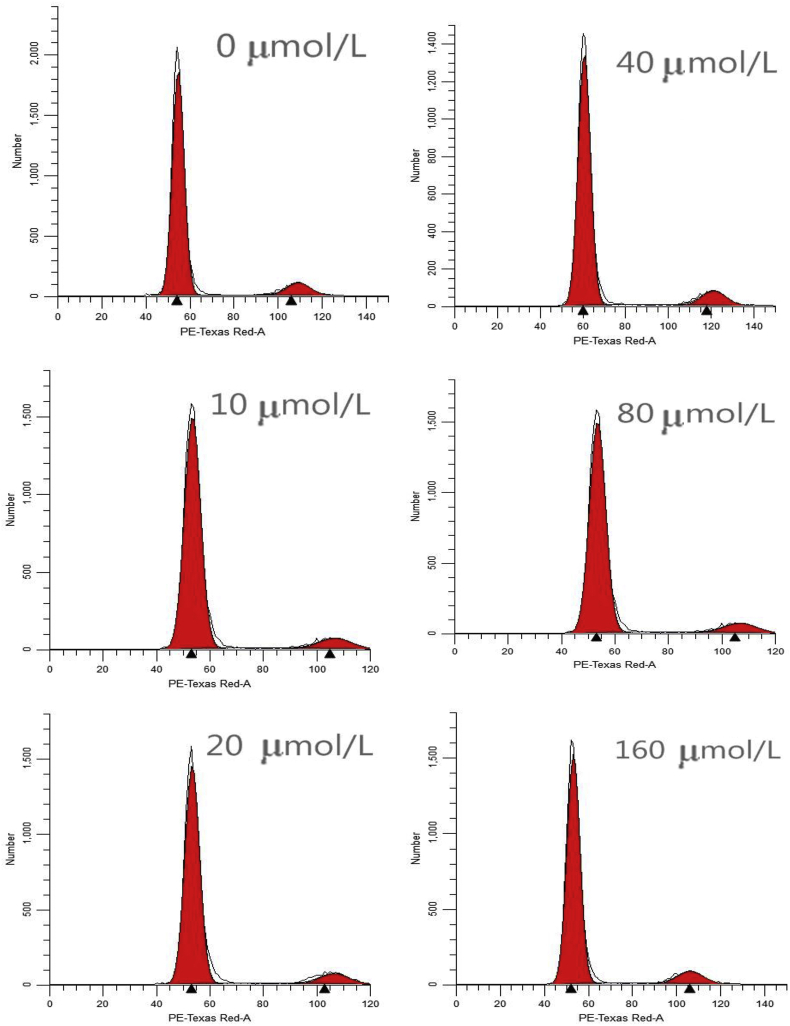
3.3. Effects of pyridoxine on DPC from rex rabbits
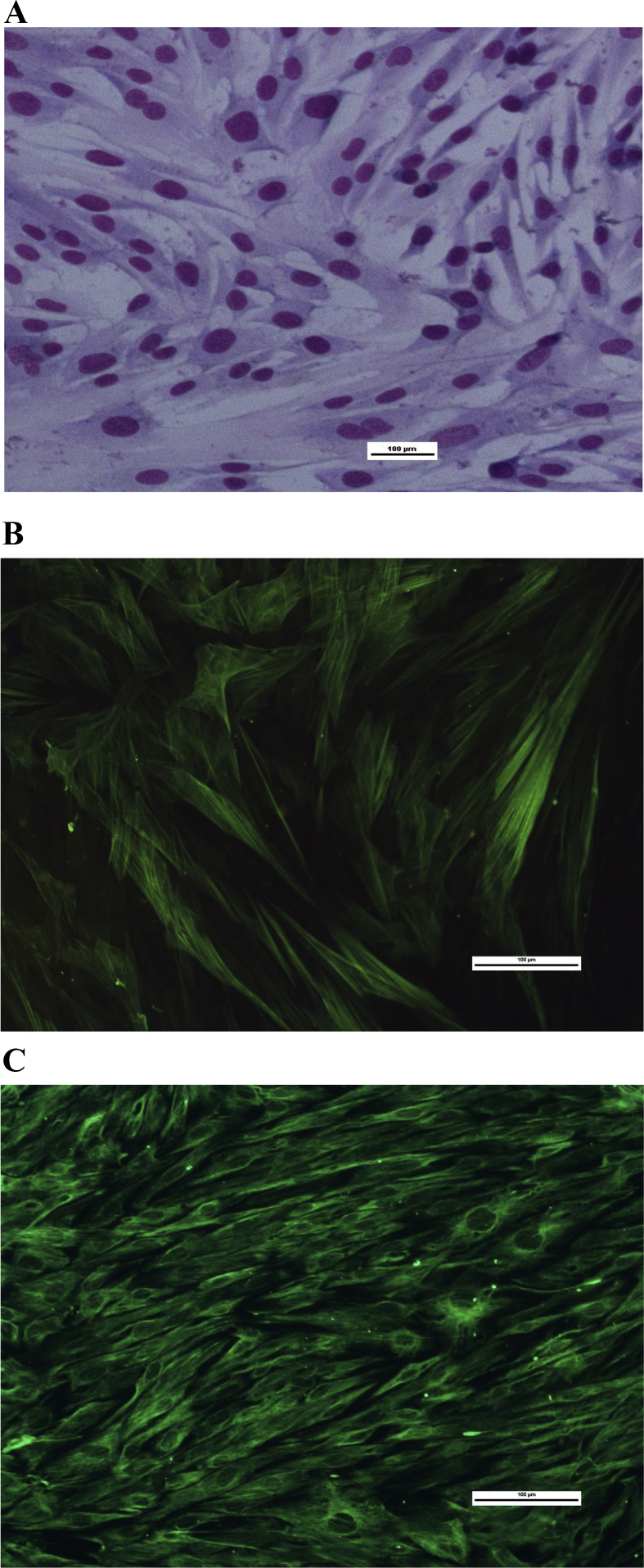
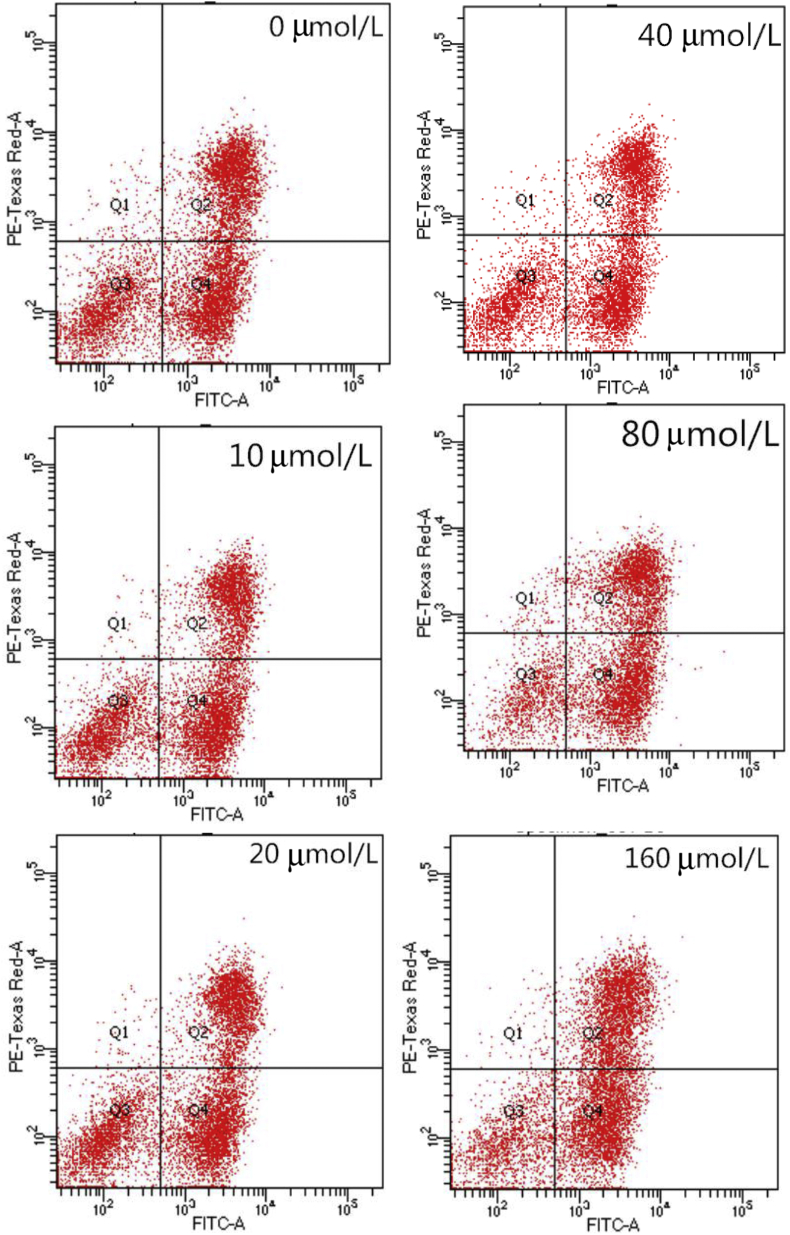
To investigate the effects of pyridoxine on hair follicle development, DPC were isolated from 30-d-old Rex rabbits, and these cells were identified by Giemsa staining (Fig. 4A) and by immunofluorescence analysis of the protein expression of α smooth muscle actin (α-SMA; Fig. 4B) and versican (Fig. 4C). The results of the cell proliferation experiment showed that the optical density (OD) values of the 160 μmol/L pyridoxine group were lower than those of the other groups (P < 0.05), and the cell cycle progression of the pyridoxine group was different from that of the control group (Fig. 5). The proportion of cells in the resting state/first gap (G0/G1) phase in the pyridoxine group was lower than that in the control group (P < 0.05), and the proportion of cells in the second gap/mitosis (G2/M) phase in the pyridoxine group was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). Pyridoxine at appropriate concentrations (10 and 20 μmol/L) significantly inhibited cell apoptosis (P < 0.05), but pyridoxine at high concentrations (80 and 160 μmol/L) significantly promoted cell apoptosis (P < 0.05; Fig. 6 and Table 6). Pyridoxine promoted the gene expression of Inppl1, Inpp4b and pleckstrin homology like domain family A member 3 (Phlda3), which are components of the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway (P < 0.05), and Wnt10b and CTNNB1, which are components of the Wnt signalling pathway, and inhibited the expression of dickkopf-1 (DKK1) (P < 0.05). The expression of Notch1, Jagged1 (JAG1), Hes1 and Hes5, components of the Notch signalling pathway, was increased by pyridoxine (P < 0.05), and the gene expression of BMP2, BMP4 and TGF-β1, components of the BMP signalling pathway, was not affected by pyridoxine (P > 0.05; Table 7). Pyridoxine promoted the phosphorylation of CTNNB1 and Akt and the protein expression of NOG, inhibiting GSK-3β phosphorylation (P < 0.05; Fig. 7).
Fig. 4.
Identification of dermal papilla cells (DPC) from Rex rabbit. DPC were isolated form 30-d-old Rex rabbit and cultured in vitro. The third generation of DPC were characterized by giemsa staining to observe (A) the cell metamorphosis (100× magnification), and by immunofluorescence technique for (B) the expression of α smooth muscle actin (α-SMA; 200× magnification), by immunofluorescence technique for (C) the expression of versican (200× magnification). Scale bars = 100 μm.
Fig. 5.
Effects of pyridoxine on cell cycle of dermal papilla cells (DPC).
Fig. 6.
Effects of pyridoxine on cell apoptosis of dermal papilla cells (DPC).
Table 6.
Effects of pyridoxine on proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis of dermal papilla cells (DPC)1.
| Item | Pyridoxine concentration, μmol/L |
RMSE | P-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 80 | 160 | |||
| Proliferation of DPC | ||||||||
| Optical density (OD) value | 0.59ab | 0.65a | 0.52b | 0.52b | 0.63ab | 0.34c | 0.111 | <0.001 |
| Cell cycle of DPC, % | ||||||||
| Resting state/first gap (G0/G1) | 92.09a | 91.08b | 89.49c | 89.92c | 89.61c | 89.50c | 33.641 | <0.001 |
| Synthesis (S) | 1.99 | 1.12 | 1.87 | 2.02 | 1.83 | 0.86 | 0.729 | 0.072 |
| Second gap/mitosis (G2/M) | 5.91c | 7.80b | 8.64b | 8.06b | 8.55b | 9.52a | 0.609 | <0.001 |
| Apoptosis of DPC, % | ||||||||
| Early apoptotic ratio (Q4) | 36.34a | 31.86b | 31.66b | 34.95ab | 37.88a | 38.39a | 3.170 | 0.001 |
| Later apoptotic ratio (Q2) | 33.21bc | 32.53c | 31.40c | 36.11a | 37.65a | 39.13a | 3.115 | <0.001 |
| Total apoptosis ratio (Q4 + Q2) | 69.55b | 64.39c | 63.06c | 71.06b | 75.53a | 77.51a | 4.250 | <0.001 |
a, b, c Within a row, means with different superscript letters are significantly different (P < 0.05).
Data represent means and root mean error (RMSE), n = 8 for per group.
Table 7.
Effects of pyridoxine on gene expression of signal pathway of dermal papilla cells (DPC)1.
| Gene | Pyridoxine concentration, μmol/L |
RMSE | P-value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 80 | 160 | |||
| PI3K/Akt signal pathway | ||||||||
| Inppl1 | 1.00c | 3.46a | 3.55a | 2.93ab | 1.54bc | 1.60bc | 1.361 | 0.001 |
| Inpp4b | 1.00b | 3.91a | 2.24ab | 1.31b | 1.94b | 1.20b | 1.732 | 0.018 |
| Frk | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.98 | 0.71 | 1.14 | 0.79 | 0.382 | 0.231 |
| Phlda3 | 1.00c | 1.68b | 1.87ab | 1.67b | 1.42bc | 2.27a | 0.503 | <0.001 |
| Wnt signal pathway | ||||||||
| Wnt10b | 1.00b | 1.12b | 1.51ab | 2.54a | 2.22a | 2.03ab | 0.957 | 0.012 |
| CTNNB1 | 1.00c | 2.50a | 2.20ab | 2.60a | 1.29bc | 1.51abc | 1.073 | 0.017 |
| GSK-3β | 1.00 | 1.67 | 1.86 | 1.64 | 1.83 | 1.79 | 0.636 | 0.094 |
| DKK1 | 1.00a | 0.51b | 0.52b | 0.16c | 0.51b | 0.47b | 0.453 | 0.002 |
| Notch signal pathway | ||||||||
| Notch1 | 1.00c | 2.82ab | 2.75ab | 2.66ab | 1.66bc | 3.42a | 1.278 | 0.006 |
| JAG1 | 1.00b | 3.17a | 3.26a | 2.60a | 2.66a | 3.08a | 0.860 | <0.001 |
| Hes1 | 1.00c | 1.12bc | 0.92c | 0.91c | 1.89a | 1.39b | 0.356 | <0.001 |
| Hes5 | 1.00c | 1.65ab | 1.75ab | 1.87a | 1.27bc | 1.26bc | 0.453 | 0.002 |
| BMP signal pathway | ||||||||
| BMP2 | 1.00 | 1.17 | 0.95 | 0.75 | 1.10 | 0.89 | 0.403 | 0.369 |
| BMP4 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 1.15 | 0.84 | 1.22 | 1.06 | 0.465 | 0.585 |
| TGF-β1 | 1.00 | 1.24 | 1.09 | 1.19 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.459 | 0.575 |
Inppl1 = inositol polyphosphate phosphatase like 1; Frk = fyn-related kinase; Phlda3 = pleckstrin homology like domain family A member 3; CTNNB1 = catenin beta 1; GSK-3β = glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; DKK1 = dickkopf-1; JAG1 = Jagged1; BMP = bone morphogenetic protein; TGF-β1 = transforming growth factor-β.
a, b, c Within a row, means with different superscript letters are significantly different (P < 0.05).
Data represent means and root mean error (RMSE), n = 8 for per group.
Fig. 7.
Effects of pyridoxine on expression of hair follicle-related proteins of dermal papilla cells (DPC). (A) Phospho-catenin beta 1 (p-CTNNB1); (B) phospho-glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (p-GSK-3β); (C) phospho-Akt (p-Akt); (D) noggin (NOG) protein. Data represent means ± standard error and root mean error (R-MSE), n = 8 for per group. a, b, c Bars with different letters means significantly different (P < 0.05).
4. Discussion
Pyridoxine, a form of vitamin B6, serves as a cofactor for enzymes that participate in amino acid metabolism (Jansonius, 1998; Christen and Mehta, 2001; Eliot and Kirsch, 2004; Phillips 2015). Dietary pyridoxine supplementation levels could increase the feed intake of growing Rex rabbits, and the appetite genes of melanocortin 4 receptor and corticotropin-releasing hormone in paraventricular nuclei and peptide YY in duodenum are involved in the pyridoxine-caused hyperphagia (Liu et al., 2015, 2017). Adequate nutrition with higher feed intake could increase the density of hair follicles (Zhu et al., 2020). In this study, dietary pyridoxine supplementation levels increased the dry matter intakes and density of hair follicles of growing Rex rabbits. DPC have potential therapeutic value for the treatment of hair loss and are able to induce the de novo formation of hair follicle structures in both the follicular and a follicular epidermis (Jahoda et al., 1984, Kollar, 1970, Oliver, 1970). The PI3K/Akt signalling pathway can activate the Wnt signalling pathway by increasing the phosphorylation of β-catenin and inhibiting the phosphorylation of GSK-3β (Lin et al., 2015). DKK1 can inhibit the phosphorylation of β-catenin, regulate the Wnt signalling pathway and lead to hair follicle regression (Greco et al., 2009). However, when the Notch receptor is bound by its ligands, it can activate hair follicle stem cells and then promote the progression of hair follicles from the resting stage to the growing stage (Demehri and Kopan, 2009). The BMP signalling pathway is involved in embryonic skin appendage organ morphogenesis and postnatal hair follicle growth (Kulessa et al., 2000). The BMP2 and BMP4 genes inhibit hair follicle development and are associated with maintaining hair follicle quiescence (Su et al., 2008). Noggin acts as an inhibitor of the BMP signalling pathway, and abnormal Noggin expression leads to follicular enlargement (Zhang et al., 2006). The Notch signalling pathway interacts with the BMP signalling pathway, which can inhibit the Wnt signalling pathway by regulating β-catenin (Demehri and Kopan, 2009). In the present study, pyridoxine significantly affected the gene expression of the PI3K/Akt, Wnt, Notch and BMP signalling pathways in skin tissues and DPC of Rex rabbits, promoted the phosphorylation of CTNNB1 and Akt, and inhibited the phosphorylation of GSK-3β. Therefore, the molecular mechanism by which pyridoxine promotes hair follicle density in Rex rabbits probably occurs through the activation of the PI3K/Akt, Wnt and Notch signalling pathways, prolonging hair follicle growth and delaying the onset of telogen.
5. Conclusion
The molecular mechanism by which pyridoxine promotes hair follicle density in Rex rabbits probably occurs through the activation of the PI3K/Akt, Wnt and Notch signalling pathways, prolonging hair follicle growth and delaying the onset of telogen.
Author contributions
G. Liu and F. Li performed the experiments. G. Cheng, S. Gao and L. Bai conceived the project idea, designed the study and supervised the project. G. Cheng and H. Sun raised the rabbits and conducted the animal experiments. G. Liu, Y. Zhang, S. Li, Y. Zhu and C. Wang performed the laboratory work. G. Liu analyses the data and wrote the manuscript. All the listed authors have read the manuscript and agreed to all of the contents.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, and there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the content of this paper.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972594), Earmarked Fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (CARS-43-B-1), the Thoroughbred Project from Shandong Government (2017LZN008), Shandong Province Modern Agricultural Technology System Innovation Team (SDAIT-21), and Funds of Shandong “Double Tops” Programme (SYL2017YSTD11).
Footnotes
Peer review under responsibility of Chinese Association of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine.
References
- AOAC International . 18th ed. Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Maryland, USA: 2005. Official methods of analyses. [Google Scholar]
- Chi W., Wu E., Morgan B.A. Dermal papilla cell number specifies hair size, shape and cycling and its reduction causes follicular decline. Development. 2013;140:1676–1683. doi: 10.1242/dev.090662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences . 20th ed. Institute of Animal Science of CAAS (Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences); 2009. Tables of feed composition and nutritive values in China. [Google Scholar]
- Christen P., Mehta P.K. From cofactor to enzymes. The molecular evolution of pyridoxal-5′-phosphate-dependent enzymes. Chem Rec. 2001;1:436–447. doi: 10.1002/tcr.10005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demehri S., Kopan R. Notch signalling in bulge stem cells is not required for selection of hair follicle fate. Development. 2009;136(6):891–896. doi: 10.1242/dev.030700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driskell R.R., Clavel C., Rendl M., Watt F.M. Hair follicle dermal papilla cells at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:1179–1182. doi: 10.1242/jcs.082446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggersdorfer M., Laudert D., Letinois V. One hundred years of vitamins - a success story of the natural sciences. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012;51:12960–12990. doi: 10.1002/anie.201205886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliot A.C., Kirsch J.F. Pyridoxal phosphate enzymes: mechanistic, structural, and evolutionary considerations. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:383–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.074021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foitzik K., Lindner G., Mueller-Roever S., Maurer M., Botchkareva N., Botchkarev V. Control of murine hair follicle regression (catagen) by TGF-beta1 in vivo. Faseb J. 2000;14:752–760. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.14.5.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E. Scratching the surface of skin development. Nature. 2007;445:834–842. doi: 10.1038/nature05659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greco V., Chen T., Rendl M., Schober M., Pasolli H.A., Stokes N. Two-step mechanism for stem cell activation during hair regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- György P. The history of vitamin B6. Am J Clin Nutr. 1956;4:313–317. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/4.4.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellmann H., Mooney S. Vitamin B6: a molecule for human health? Molecules. 2010;15:442–459. doi: 10.3390/molecules15010442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahoda C.A., Horne K.A., Oliver R.E. Induction of hair growth by implantation of cultured dermal papilla cells. Nature. 1984;311:560–562. doi: 10.1038/311560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansonius J.N. Structure, evolution and action of vitamin B6-dependent enzymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998;8:759–769. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(98)80096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John R.A. Pyridoxal phosphate dependent enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1248:81–96. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(95)00025-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollar E.J. The induction of hair follicles by embryonic dermal papillae. J Invest Dermatol. 1970;55:374–378. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12260492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer K., Semba R.D., Eggersdorfer M., Schaumberg D.A. Introduction: the diverse and essential biological functions of vitamins. Ann Nutr Metab. 2012;61:185–191. doi: 10.1159/000343103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulessa H., Turk G., Hogan B.L. Inhibition of Bmp signalling affects growth and differentiation in the anagen hair follicle. EMBO J. 2000;19(24):6664–6674. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.24.6664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiLivak K.J., Schmittgen T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 -ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C., Chen X., Li H., Cai B., Liu Y., Zhang H. Expression of Wnt/β–catenin signalling, stem-cell markers and proliferating cell markers in rat whisker hair follicles. J Mol Histol. 2015;46(3):233–240. doi: 10.1007/s10735-015-9616-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G., Zhao N., Zhu Y., Liu L., Liang C., Li F. Effects of dietary vitamin B6 supplementation levels on production performance and vitamin B6 metabolism of growing Rex rabbits. Chin J Anim Nutr. 2015;27(7):2292–2299. [Google Scholar]
- Liu G.Y., Wu Z.Y., Zhu Y.L., Liu L., Li F.C. Effects of dietary vitamin B 6 on the skeletal muscle protein metabolism of growing rabbits. Anim Prod Sci. 2017;57:2007–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu G., Bai L., Li S., Liu H., Zhu Y., Sun H. Isolation, culture and growth characteristics of dermal papilla cells from Rex rabbits. Tissue Cell. 2020;65:101348. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2020.101348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G., Li S., Liu H., Zhu Y., Bai L., Sun H. The functions of ocu-miR-205 in regulating hair follicle development in Rex rabbits. BMC Dev Biol. 2020;20(8):1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12861-020-00213-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L., Wang H., Sun H., Fu C., Liu H., Sun Y. Effects of pyridoxine on selected appetite regulating peptides mRNA expression in hypothalamic PVN/ARC nuclei and gastrointestinal tract tissues. Adv Biosci Biotechnol. 2017;8(9):273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Millar S.E. Molecular mechanisms regulating hair follicle development. J Invest Dermatol. 2002;118:216–225. doi: 10.1046/j.0022-202x.2001.01670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NRC . 2nd revised edn. National Academy of Science, National Research Council; Washington, DC: 1977. Nutrient requirements of domestic animals, no.9. Nutrient requirements of rabbits. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver R.F. The induction of hair follicle formation in the adult hooded rat by vibrissa dermal papillae. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1970;23:219–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouji Y., Yoshikawa M., Moriya K., Ishizaka S. Effects of Wnt-10b on hair shaft growth in hair follicle cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;359:516–522. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percudani R., Peracchi A. The B6 database: a tool for the description and classification of vitamin B6-dependent enzymatic activities and of the corresponding protein families. BMC Bioinf. 2009;273(10):1–8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R.S. Chemistry and diversity of pyridoxal-5′-phosphate dependent enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1854:1167–1174. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.12.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su R., Li J., Zhang W., Yin J., Zhao J., Chang Z. Expression of BMP2 in the skin and hair follicle from different stage in Inner Mongolia cashmere goat. Sci Agric Sin. 2008;23:559–563. [Google Scholar]
- Woo C., Eleanor W., Bruce A. Morgan dermal papilla cell number specifies hair size, shape and cycling and its reduction causes follicular decline. Development. 2013;140:1676–1683. doi: 10.1242/dev.090662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Sun Q., Guo X., Liu H. hMSCs possess the potential to differentiate in to CDP cells in vivo and in vitro. Cell Biol Int Rep. 2010;19(2) doi: 10.1042/CBR20120003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., He X., Tong W., Johnson T., Wiedemann M. Bone morphogenetic protein signalling inhibits hair follicle anagen induction by restricting epithelial stem/progenitor cell activation and expansion. Stem Cell. 2006;24:2826–2839. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2005-0544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y., Wu Z., Liu H., Liu G., Li F. Methionine promotes the development of hair follicles via the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in Rex rabbits. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr. 2020;104:379–384. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Nan W., Wang S., Zhang T., Si H., Wang D. Epidermal growth factor promotes proliferation of dermal papilla cells via Notch signalling pathway. Biochimie. 2016;127:10–18. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]