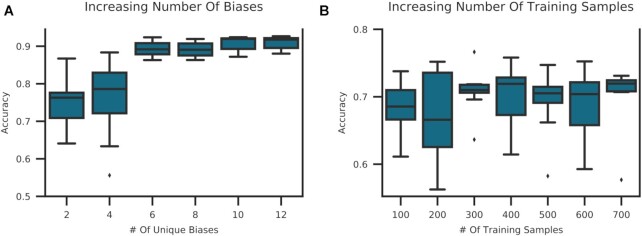
Figure 4.
: Increasing bias vs increasing sample size in training data. (A) An MLP Ssmall for sample source prediction on SRA data was trained by randomly sampling an increasing number of SRA studies per class. Each study was subsampled to 50 samples. Studies were drawn from all SRA studies with n > 100 for either sample source tissue or cell line. (B) To differentiate the effect of increased bias vs increased sample size, the same model was trained by randomly subsampling the largest available SRA study per class. At each step an additional 50 samples were added to the training set per class. Models were run with 10 different seeds and the mean sample accuracy was computed. Box plots are produced by 10 random sampling iterations and show the the minimum, the maximum, the sample median, and the first and third quartiles. We observe a positive correlation between training data diversity and accuracy.