Abstract
A novel Gram-stain negative, aerobic, halotolerant, motile, rod-shaped, predatory bacterium ASxL5T, was isolated from a bovine slurry tank in Nottinghamshire, UK using Campylobacter hyointestinalis as prey. Other Campylobacter species and members of the Enterobacteriaceae were subsequently found to serve as prey. Weak axenic growth on Brain Heart Infusion agar was achieved upon subculture without host cells. The optimal growth conditions were 37 °C, at pH 7. Transmission electron microscopy revealed some highly unusual morphological characteristics related to prey availability. Phylogenetic analyses using 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that the isolate was related to members of the Oceanospirillaceae family but could not be classified clearly as a member of any known genus. Whole genome sequencing of ASxL5T confirmed the relationship to members the Oceanospirillaceae. Database searches revealed that several ASxL5T share 16S rRNA gene sequences with several uncultured bacteria from marine, and terrestrial surface and subsurface water. We propose that strain ASxL5T represents a novel species in a new genus. We propose the name Venatorbacter cucullus gen. nov., sp. nov. with ASxL5T as the type strain.
Subject terms: Ecology, Evolution, Microbiology
Introduction
A predatory bacterium is one that demonstrates the ability to pursue and kill other living bacteria to obtain biosynthetic materials and energy1. This is distinct from the universal recycling of the nutrients from dead microorganisms and from parasitic interactions where bacteria form close associations with their hosts without killing them. Predatory bacteria have evolved diverse life cycles to exploit abundant food sources in the niches where they are found, for example in marine habitats2. They are a taxonomically diverse group connected only by their unique bactericidal life cycle1. Examples of predatory bacteria are found in several different phyla including: Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes and Chloroflexi3. However, the most well-studied predatory bacteria are, Bdellovibrio and Bdellovibrio-and-like organisms (BALOs4). Predatory bacteria are promising sources of new bioactive compounds and antimicrobials5.
Predatory bacteria are suggested to enhance microbial diversity, and have positive effects on ecosystem health, productivity, and stability6. Despite these positive attributes, there are few studies of new predatory bacteria because of difficulties in culturing the bacteria, and the need for careful observation of cellular interactions in order to understand their complex lifecycles. This information is not readily available from in silico analysis.
In an era of increased antimicrobial resistance novel strategies such as the use of bacteriophage and predatory bacteria, that target bacterial pathogens, are being investigated7,8. The ASxL5T bacterium was isolated from cattle slurry collected from the University of Nottingham Dairy Centre, Nottinghamshire, in 2019 using techniques for phage isolation9. The aim of the investigation was to isolate organisms that had potential as biocontrol agents. Campylobacter hyointestinalis, a zoonotic pathogen that is increasingly associated with enteric disease in humans10, was prevalent in the slurry and was used as a target host.
Results
ASxL5T is a predatory bacterium with unusual cell morphology
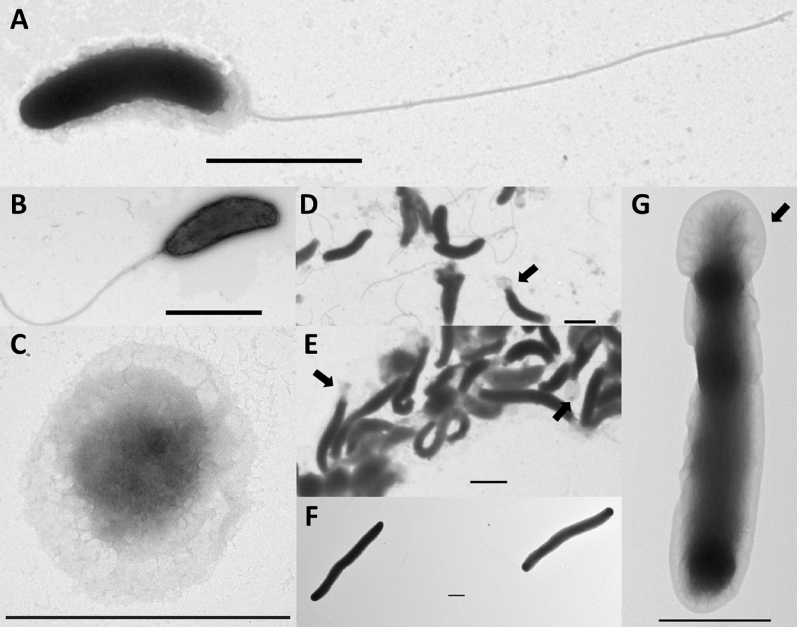
The ASxL5T bacterium was isolated from bovine slurry due to the observation that it formed plaques on C. hyointestinalis lawns similar to those produced by bacteriophage. It was an unexpected finding because part of the phage isolation procedure involved filtration through a 0.2 µm filter designed to remove bacterial cells. Microscopic examination of the material extracted from the plaques revealed small Gram-stain negative curved rod-shaped bacteria that did not accumulate polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB). Axenic culture was achieved independent of prey cells on rich solid media such as Brain Heart Infusion agar (BHI) and Blood agar (BA), with weak growth that improved on subculture using heavy inocula. Growth occurred equally well under microaerobic (7% v/v oxygen) and atmospheric oxygen conditions but not in an anaerobic atmosphere. Colonies were small reaching 2 mm in diameter after 72 h and were beige, translucent, circular, convex and shiny. Standard biochemical tests were hampered as ASxL5T could not be reliably cultured in liquid medium suggesting a complex life cycle with possible dependence on biofilm formation. However, plate suspensions demonstrated ASxL5T was aerobic, oxidase and catalase positive and able to tolerate 5% NaCl. ASxL5T was resistant to streptomycin 10 µg, but sensitive to all other antibiotics tested. The ASxL5T bacterial cells were examined by TEM (Fig. 1). When grown without prey cells on BA, the ASxL5T cells were small, curved bacteria with an average length of 1.63 μm (± 0.4) and width of 0.37 μm (± 0.08), with a single long (up to 5 μm) polar flagellum. Approximately 1.6% of cells appeared to have a width of less than 0.2 μm, which would allow passage through a filtration device. An unusual structural extension resembling a cowl (latin cucullus), was observed at the apex of some cells (see arrows in Fig. 1D,E,G). This appeared to be composed of excess outer membrane, possibly due to a rapid reduction in size of the periplasmic envelope, with the outer membrane remaining intact, giving a “baggy” appearance. Prolonged incubation of ASxL5T without nutrients (in PBS), at 4 °C, resulted in most, but not all, of the cells exhibiting coccal morphology (Fig. 1C). When ASxL5T was grown for 48 h with C. jejuni as prey, the mean cell sizes were significantly longer and narrower, than cells grown without host (Table 1 and Fig. 1E). In contrast when ASxL5T was grown for 48 h with E. coli as prey, the mean cell sizes were longer and wider than when grown without prey (Table 1), and the cell length was variable, often showing filamentation (Fig. 1F). ASxL5T cells showed a complete absence of flagella when incubated for 48 h with either C. jejuni or E. coli as prey. Observations of the variation in cell size according to presence, absence, and type of prey of ASxL5T are summarised in Table 1.
Figure 1.
TEM of ASx5LT showing: (A) ASx5LT showing long polar flagellum; (B) typical ASx5LT cell; (C) coccal ASx5LT cell following prolonged incubation without nutrients; (D) group of ASx5LT cells showing unusual apical structure indicated with arrow; (E) group of ASx5LT cells incubated with Campylobacter prey showing increased cell length compared with those grown without prey (D) also showing apical structures; (F) large filamentous aflagellate, ASx5LT cells, following incubation with E. coli prey; (G) single ASx5LT cell following incubation with E. coli showing unusual apical structure. Bar represents 1 μm.
Table 1.
Variation in size of ASx5LT with presence, absence, and prey type determined from TEM images.
| Growth condition (48 h at 37 °C) | Mean cell dimensions | Difference from BA (ANOVA p-value) |
|---|---|---|
| Grown on BA | ||
| Length | 1.63 µm (± 0.42) | |
| Width | 0.37 µm (± 0.08) | |
| Incubated with C. jejuni | ||
| Length | 2.09 µm (± 0.69) | 0.0003 |
| Width | 0.30 µm (± 0.06) | 4 × 10–15 |
| Incubated with E. coli | ||
| Length | 4.99 µm (± 2.45) | 0.00016 |
| Width | 0.63 µm (± 0.11) | 2 × 10–15, |
The genome sequence of ASxL5T reveals a relationship with marine bacteria
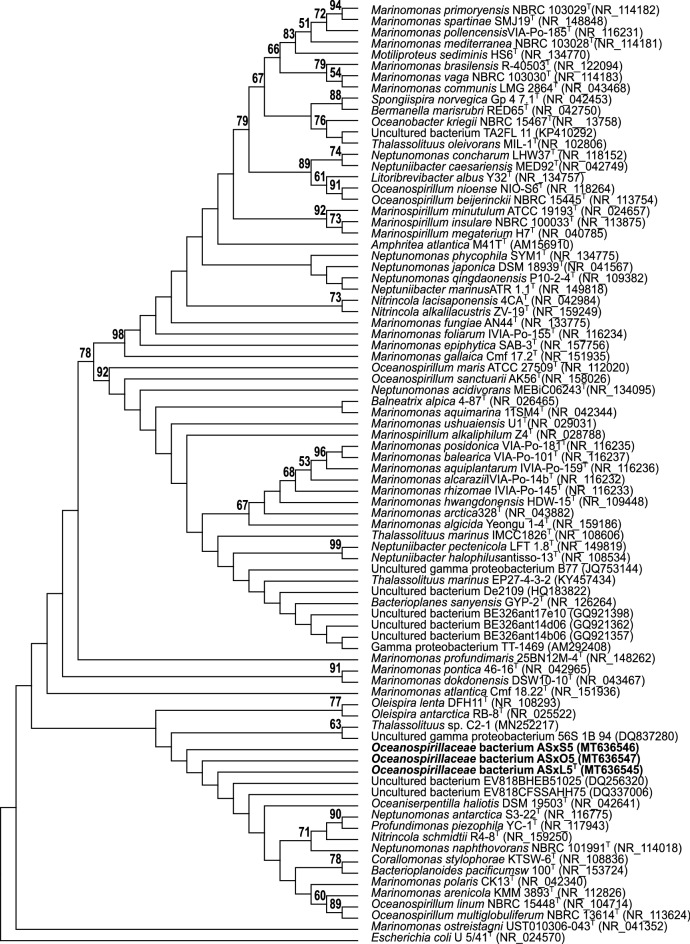
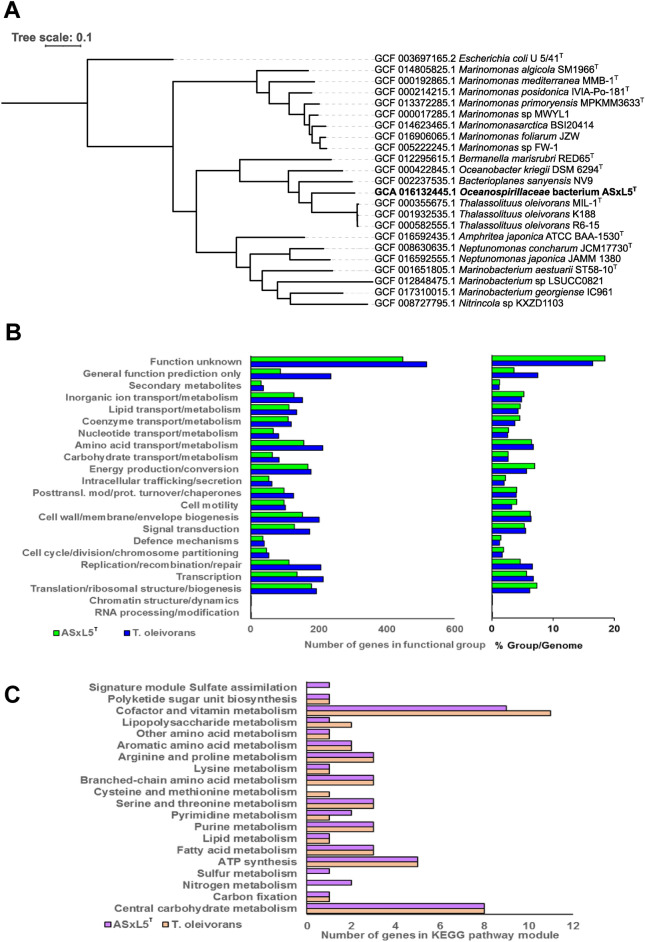
Determination of the 16S rRNA gene sequence (accession number MT636545.1) enabled database searches to establish the sequence resembled those in the class Gammaproteobacteria and were most closely aligned with marine bacteria in the family Oceanospirillaceae (Fig. 2) with members of the genera Thalassolituus and Oceanobacter the nearest relatives. The 16S rRNA gene sequences were notably diverged from predatory bacteria belonging to the family Bdellovibrionaceae (Deltaproteobacteria). The pairwise alignments for B. bacteriovorus HD100T (type strain, DSM 50701) and B. bacteriovorus DM11A were 48.4% and 47.7% identity, and for B. exovorus JSS 46.7% identity. The ASxL5T bacterium had 3 copies of the 16S rRNA genes with two being identical to each other and the third differing by 3 bases. Two further predatory bacterial isolates from the same location with similar morphology and phenotypic characteristics (ASx5S and ASx5O; 16S rRNA gene accession numbers MT636546.1 and MT636547.1 respectively) were not identical, but clustered with ASxL5T and uncultured bacterial database sequences, separate from other genera in the Oceanospirillaceae (Fig. 2). The whole genome sequence of ASxL5T was determined and deposited in the NCBI database under the accession number CP046056. The genome of ASxL5T consisted of a single circular chromosome of 2,831,152 bp with a G + C ratio of 56.1%. The genome sequence contained 2653 CDSs (total), of which 2567 were predicted to encode proteins, and of these 1596 could be assigned a putative function (60.2%). The genome contained 67 RNA encoding genes comprising of 9 rRNAs (3 each 5S, 16S and 23S) together with 57 tRNAs. The genomic characteristics of ASxL5T were compared to the available genomes of the type strains of the closest relatives identified from the 16S rRNA gene sequences (Table 2). All available Thalassolituus genomes were compared with ASxL5T using amino acid identity (AAI). The closest available genome sequence (incomplete) determined by AAI was that of Thalassolituus sp. C2-1 (accession NZ_VNIL01000001). This strain was isolated from a deep-sea sediment of the Mariana Trench, but no phenotypic information regarding this strain is available for comparison at present. This organism has a much larger genome at 4.36 Mb compared to 2.82 Mb for ASxL5T. The average genome size for a member of the order Oceanospirillales is approximately 4.16 Mb (± 1.1; n = 92 complete reference genomes surveyed from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/assembly), so the genome of ASxL5T is quite small compared to other members of the order. A genome-based estimated maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree (Fig. 3A) was generated with GToTree 1.5.54 utilizing aligned and concatenated amino acid sequences of 172 single-copy genes specific to Gammaproteobacteria 11–18. This analysis demonstrated a close relationship to Thalassolituus, Bacterioplanes, and Oceanobacter genera. However, these data indicate that ASxL5T is distinct from its relatives in the Oceanospirillaceae for which genomic sequence data are available.
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree using 16S rRNA gene sequences highlighting the position of ASxL5T, ASxO5 and ASxS5strains (emboldened) relative to uncultured and strains of marine bacteria genera within the family Oceanospirillaceae. Genbank accession numbers follow the strain name in parenthesis. Sequences were aligned using ClustalW and the phylogenic relationship inferred using the Maximum Likelihood method with the Tamura-Nei model, with 1000 bootstrap replicates, within the MEGA X program. Numbers on branches indicate bootstrap replicate values greater than 50%. Escherichia coli U/541T was used as an outgroup.
Table 2.
Genomic comparison of ASx5LT with type strains of related genera.
| Genome | Accession no. | Genome size (Mb) | G + C ratio | 16S RNA identity | AF | ANI | AAI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASxL5T | CP046056 | 2.82 | 56.1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Thalassolituus oleivorans MIL-1T | HF680312 | 3.9 | 46.6 | 95.03 | 0.421 | 71.86 | 67.61 |
| Bacterioplanes sanyensis KCTC 32220T | BMYY01000001 | 3.83 | 53.4 | 94.64 | 0.394 | 72.87 | 66.78 |
| Oceanobacter kriegii DSM 6294T | NZ_AUGV00000000 | 4.5 | 55.3 | 94.14 | 0.327 | 74.10 | 53.78 |
| Marinomonas communis DSM 5604T | ASM436330v1 | 3.85 | 44.9 | 90.56 | 0.124 | 67.40 | 45.67 |
| Oceanospirullum linum ATCC 11336T | MTSD02000001 | 3.78 | 49.13 | 90.21 | 0.153 | 69.20 | 52.34 |
AF alignment fraction, ANI average nucleic acid identity, AAI amino acid identity.
Figure 3.
(A) Genome-based phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of Oceanospirillaceae bacterium ASxL5T to closest relatives in the Oceanospirillaceae family with E. coli U 5/41T as an outgroup. (B) Functional class distribution of predicted genes according to the clusters of orthologous groups (COG) of proteins of ASx5LT compared to T. oleivorans MIL-1T. Left panel shows the number of genes per functional COG category for each genome. The right panel shows the percentage of the genome that each functional COG group comprises. (C) Analysis of complete KEGG (Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes) module pathways for ASxL5T compared to T. oleiverans MIL-1T.
Examination of the component genes present in the ASxL5T genome using the KEGG database19 revealed metabolic pathways typical of an aerobic Gammaproteobacterium. ASxL5T contains a total of 75 genes assigned to bacterial motility proteins, including those involved in chemotaxis, flagella assembly and type IV pilus systems. Within the last category 9 out of 10 genes are responsible for twitching motility in a range of other organisms. The genome of ASxL5T contained the complete ectoine biosynthesis pathway involved in the protective response to osmotic stress20, as might be expected for a halophilic organism. The genome also contains the complete pathways for many cofactors and vitamins including the riboflavin synthesis pathway. Hydrocarbon utilization pathways were incomplete although a gene for alkane 1-monooxygenase (alkB2) was present in ASxL5T. Homologues of genes identified as largely responsible for hydrocarbon degradation in T. oleiverans MIL-1T21 such as TOL_2658 (alkB) and TOL_2772 (alcohol dehydrogenase) were notably absent in the genome sequence of ASxL5T. A comparison of the distribution of genes in COG categories for ASxL5T with T. oleiverans MIL-1T is presented in Fig. 3B. Overall, the smaller genome of ASxL5T contained proportionally less genes from each COG category compared to the larger related genomes. When the number of genes in each functional category are expressed as a percentage of the genome, differences were noted in the percentage of genes in the translation, ribosomal structure, and biogenesis categories together with the energy production and conversion functional categories, which comprise a greater percentage of the ASxL5T genome than the same groups present in the T. oleiverans MIL-1T genome. In contrast, T. oleivorans MIL-1T has a greater percentage of genes within the replication, recombination and repair, and transcription categories compared to the ASxL5T genome. Interestingly the greatest difference in the contents of each of the functional categories for the two genomes was the number of unknown genes present in ASxL5T (Fig. 3B). KEGG module enrichment analysis was carried out where each KEGG module represents a collection of manually defined functional units used for annotation and the biological interpretation of genome sequence data. A comparison of the distribution of genes in complete KOG module pathways for ASxL5T with T. oleiverans MIL-1T is presented in Fig. 3C. This analysis indicates that while ASxL5T has complete pathways for sulfur and nitrogen metabolism but T. oleiverans MIL-1T does not. In contrast T. oleiverans MIL-1T has a complete pathway for cysteine and methionine metabolism that is incomplete in ASxL5T. Accordingly, ASxL5T has a signature module (defined as a set of genes that can be used as a phenotypic marker such metabolic capacity or pathogenicity; https://www.genome.jp/kegg/module.html) for sulfate assimilation that is absent in T. oleiverans MIL-1T. Comparison of the gene content of ASxL5T with a list of genes suggested to be indicative of a predatory lifestyle3 was inconclusive. Whilst the waaL gene which encodes a ligase associated with linking O-antigen polysaccharide to the core was present in the ASxL5T genome (but is common in many Gram-negative bacteria), a tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) gene that may include a 60 amino acid region common in predatory bacteria22, was absent. Additional predatory signature genes included those that encode enzymes involved in the mevalonate pathway isoprenoid biosynthesis3 were also absent from the genome of ASxL5T. The transcriptional regulator gene gntR was noted to be absent in the predator group examined3, but three gntR-like genes could be identified in ASxL5T.
Phenotypic comparison with related bacteria
The phenotypic characteristics of ASxL5T are summarised in Table 3 and compared to the phenotypic characteristics reported in the literature for related genera23–27. Isolates from T. marinus, T. olevorans, B. sanyensis and Oceanobacter kriegii are motile, halotolerant, oxidase positive rods, but have few other phenotypic characteristics in common with ASxL5T. The average pH of the oceans is 8.1 (https://ocean.si.edu/ocean-life/invertebrates/ocean-acidification#section_77), a feature reflected in the basic pH survival range of T. marinus, T. olevorans, B. sanyensis and O. kriegii. ASxL5T is adapted to a greater pH range (4–9) typical of non-marine species. The phenotypic characteristics of Thalassolituus sp. C2-1.are unknown. The growth temperature range of ASxL5T was generally wider than the marine strains (4–42 °C), although some but not all isolates of T. marinus were thermotolerant. Further phenotypic characterisation was hampered by the inability to grow ASxL5T in broth medium. Using API 20E tests with material scraped from BA plates, ONPG, arginine dihydrolase, lysine decarboxylase, ornithine decarboxylase, citrate utilisation, urease, tryptophan deaminase, gelatin hydrolase, tests were all negative, whilst indole, acetoin and H2S were not produced. Carbohydrates that were not fermented included: glucose, mannose, inositol, sorbitol, rhamnose, sucrose, melibiose, amygdalin and arabinose. The cellular fatty acid profiles of strain ASxL5T compared to published related reference strains are shown in Table 4. The predominant cellular fatty acids were C16 : 1ω6c and/or C16 : 1ω7c, C16:0, and C18:1 ω9. Hydroxy fatty acids C12:0 3-OH and C10:0 3-OH were also present. The proportion of C16:0 was higher in ASxL5T than the reported values for related genera. In contrast, there was a reduced proportion of C18 : 1ω7c and/or C18 : 1 ω6c in ASxL5T compared to that reported for T. marinus IMCC1826T T. oleivorans MIL-1T and O. kriegii DSM 6294T but not detected in B. sanyensis KCTC 32220T. A comparison to the fatty acid profiles of ASxL5T with ASxLS revealed minor differences in quantities of individual fatty acids between the two strains, which is consistent with the genomic DNA sequences that they belong to the same species. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) granules were not detected using the Sudan Black test.
Table 3.
Phenotypic characteristics of ASx5LT and closest relatives.
| Characteristic | ASxL5T | T. marinus | T. oleivorans | B. sanyensis | O. kriegii | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth temperature (°C) | 42 | + | V | − | + | − |
| 37 | + | V | − | + | NK | |
| 25 | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 4 | + | V | + | − | − | |
| Catalase | + | + | V | + | + | |
| Oxidase | + | + | + | + | + | |
| PHB accumulation | − | − | − | + | + | |
| pH range | 4–9 | 6–9 | 7.5–9 | 6–10 | 5–9 | |
| Salt tolerance (%) | 0.5–5 | 0.5–5 | 0.5–5 | 1–10 | NK | |
| Cell shape | CR | CR | CR | SR | SR | |
| Mean cell dimensions (μm) | Length | 1.6–2a | 1.2–2.5 | 1.2–3.1 | 2.1–2.8 | 2.6–3.6 |
| Width | 0.3–0.4 | 0.4–0.5 | 0.25–0.77 | 0.5–0.6 | 0.8–1.2 |
Table 4.
Fatty acid analysis of ASx5LT and closest relatives.
| Fatty acid | ASxL5T | T. marinus IMCC1826T | T. oleivorans MIL-1T | B. sanyensis KCTC 32220T | O. kriegii DSM 6294T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10 : 0 | 2.3 | Trb | 1.2 | tr | tr |
| C12 : 0 | 2.3 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 8.6 | 21.2 |
| C14 : 0 | 1.9 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 1 | – |
| C16 : 0 | 25.3 | 14 | 13.3 | 13.2 | 13.4 |
| C18 : 0 | 2.0 | – | 2.5 | – | – |
| C17 : 1ω8c | 1.3 | 1.2 | – | 3.8 | – |
| C10 : 0 3-OH | 2.3 | 3.7 | 3.6 | 4 | 11.2 |
| C12 : 1 3-OH | 4.7 | 6.3 | 6.5 | 2.9 | 6.7 |
| Summed featuresa | |||||
| 3 | 40.6 | 48 | 45.4 | 40.7 | 26.8 |
| 8 | 5.7 | 21.1 | 22.6 | – | 20.7 |
aSummed features represent groups of two fatty acids that could not be separated by GLC with the MIDI system. Summed feature 3 is C16 : 1ω6c and/or C16 : 1ω7c; summed feature 8 is C18 : 1ω7c and/or C18 : 1ω6c.
btr, trace (< 1.0%). Data for reference strains were obtained from a literature survey23–27.
ASxL5T preys on Campylobacter species and other Gram-stain negative hosts
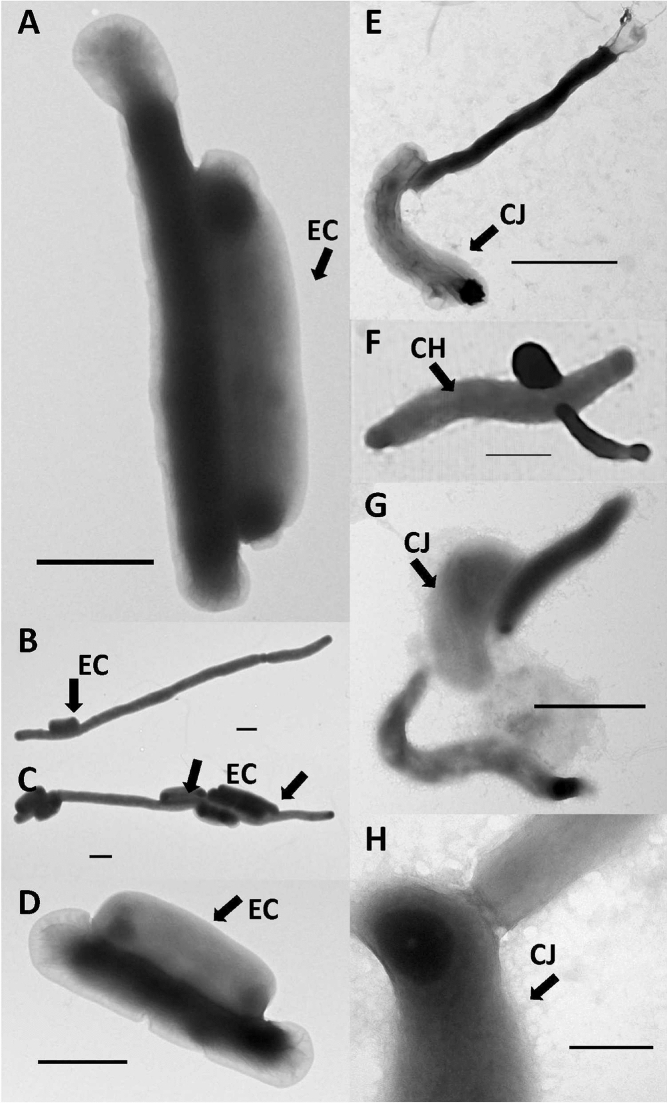
The predatory activity of the ASxL5T bacterium was investigated to determine the prey range. The bacterium was able to form plaques on Campylobacter species including: C. hyointesinalis 11608T, C. jejuni PT14, C. jejuni 12662, C. jejuni NCTC 11168T; C. coli NCTC 12667; C. helveticus NCTC 12472; C. lari NCTC 11458 and C. upsaliensis NCTC 11541T. Testing of a wider selection of Gram-stain negative and Gram-stain positive bacteria, using cultures listed in the Host Range Determination section of Methods, revealed that ASxL5T could also form plaques on Escherichia coli NCTC 86, Citrobacter freundii NCTC 9750T and Klebsiella oxytoca 11466. TEMs of the interaction with E. coli NCTC 86 are shown in Fig. 4A–D whilst the interaction with C. jejuni PT14 and C. hyointestinalis S12 are shown in Fig. 4E–H. The attack mechanism appeared to differ between the prey types tested, with one or more E. coli cells becoming attached to each ASxL5T cell, positioned laterally along the extended cell before adsorption. In contrast ASxL5T appeared to attach to campylobacters via a single contact point, often with the predator cell apex, making contact near the Campylobacter cell apex (Fig. 4H).
Figure 4.
TEM of ASx5LT interacting with prey showing: (A–D) with E. coli prey; (E–H) with C. jejuni prey. (A) typical cell ASx5LT attached to a single E. coli (EC) cell; (B) filamentous ASx5LT attached to single EC cell; (C) filamentous ASx5LT cells attached to multiple EC cells; (D) smaller ASx5LT cell attached to a single E. coli (EC) cell; (E) single ASx5LT cell attached to a C. jejuni (CJ) cell; (F) ASx5LT attacking a C. hyointestinalis (CH) cell; (G) two ASx5LT cells attacking a CJ cell; (H) close view of attachment point of ASx5LT, close to apex of the CJ cell (bar 0.2 μm). Bar represents 1 μm in (A–G).
Discussion
Predatory bacteria have evolved to exploit abundant prey sources. It is becoming apparent that they are widespread in many different environments. The ASxL5T bacteria was able to be isolated from slurry using phage isolation methods because of the narrow dimensions of members of the population. The genomic relatedness of ASxL5T to members of the marine bacterial family Oceanospirillaceae was surprising, even though the organism was halotolerant being able to grow on 5% salt containing medium. Water quality analysis of the slurry revealed the sodium chloride level to be less than 0.1%. The slurry is therefore far from a marine environment—geographically and chemically. The presence of three related, but non-identical isolates from the same source, provided evidence that these predators were thriving in this non-marine environment. Moreover, microbiome analysis (data files available from https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/browser/view/PRJEB38990) revealed identical 16S rRNA gene sequences to be in the top 50 most abundant operational taxonomic units (OTUs) in the slurry over several sampling intervals. Several uncultured bacteria were identified in the Genbank database that had similar 16S rRNA gene sequences to the ASxL5T bacterium. These sequences together with those of ASxL5T, ASxS5 and ASxO5 appeared to represent a distinct clade separated from Thalassolituus and Oceanobacter (Fig. 2). Three of the uncultured bacteria (GQ921362, GQ921357 and GQ921396) were all isolated from fracture water, from a depth of 1.3 km in a South African gold mine in 2009, while a further two (DQ256320 and DQ337006) were obtained from subsurface water (also in South Africa) in 2005. The most closely related 16S rRNA gene sequence relative to ASxL5T is a partial 16S rRNA gene sequence that was obtained from enrichment culture of sandy sediment, obtained from a beach in Northern France in 2006 (accession number AM29240828). A further closely related 16S rRNA gene sequence from an uncultured bacterium, HQ183822.1, was obtained from a collection pool leached from a municipal landfill site in China29. Clearly the ASxL5T bacteria is not highly represented in taxonomic databases but it is likely that these sequences from uncultured bacteria represent similar organisms to ASxL5T, which are distributed worldwide, often in challenging environments. The closest relatives to ASxL5T from whole genome phylogenetic analysis were: Thalassolituus sp. C2-1, T. marinus, T. oleivorans. and O. kriegii23–27. Thalassolituus are members of the marine obligate hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria (OHCB) and are prevalent in marine and terrestrial environments often becoming dominant following incidents of hydrocarbon pollution30,31. Oceanobacter are not members of the OHCB group but are isolated from marine environments32.
The phenotypic data indicate that ASxL5T is a novel species and a member of a previously unrecognised genus within the family Oceanospirillaceae. There are at present no unambiguous criteria for assignment of a newly isolated strain into a new genus. Attempts have been made to identify a universal genus boundary, for example that based on the genomic percentage of conserved proteins (POCP), with a suggested cut off value of 50% identity to reference strains33. Others have suggested using AAI values, which have an advantage over POCP in that they can be obtained from incomplete genomes34. The authors suggested that a strain is a representative of a different genus if the AAI value is less than 74% when compared with the type strain of the type species. The type genus in the family Oceanospirillaceae, is Oceanospirillum and the type strain is O. linum ATCC 11336T. The AAI value between ASxL5T and O. linum ATCC 11336T is 54.34% and between ASxL5T and T. oleivorans MIL-1T (genus type strain) is 67.61% indicating that ASxL5T represents a novel genus distinct from Thalassolituus. Using the 16S rRNA gene sequences as the taxonomic criteria with a suggested genus delimitation boundary of 94.5%35 would potentially place ASxL5T within the genus Thalassolituus exhibiting a 16S rRNA sequence identity of 95.03% with T. oleivorans MIL-1T and 96.17% to T. marinus IMCC1826T. However, it would also be placed in the Bacterioplanes genus with a 16S rRNA gene identity with B. sanyensis NV9 of 94.64% illustrating that the use of a single gene such as the16S rRNA gene, can lead to arbitrary taxonomic assignments. Another suggested method uses both ANI and genome alignment fraction (AF) to examine the clustering of data points from all the type and non-type strains of existing genera36. The authors suggest the use of a genus demarcation boundary in conjunction with the estimated genus inflection point that is specific to the taxon that is being analyzed. However, without sufficient complete genome sequences from Thalassolituus isolates it is not possible to determine whether ASxL5T belongs to the Thalassolituus genus by this method. The whole genomic phylogenic tree should be interpreted with discretion due to the limited availability of complete genome sequences to carry out the analysis and secondly methods for whole genome comparison do not account for the substantial difference in the sizes of the genomes being compared. They measure the similarity of core single-copy genes that are conserved between related genera but do not take into account the very large number of genes which are not present in the much smaller genome of ASxL5T. Clearly ASxL5T and the group including Thalassolituus, Oceanobacter and Bacterioplanes have a common ancestor, but evolution has taken a different path resulting in genome reduction, possibly as an adaption to a predatory lifestyle. This contrasts with T. oleivorans MIL-1T that is 28% larger, and which has evolved under different environmental pressures to utilise hydrocarbons23,30. An interesting comparison can be made to obligate intracellular parasites and symbionts such as Rickettsia, Chlamydia and Buchnera which have genome sizes of approximately 1 Mb, having undergone significant evolutionary genome degradation as the ability to exploit host-cell metabolites leads to gene loss37. An evolutionary change from a marine chemolithotroph to predatory lifestyle could result in a similar genome size reduction. COG and KEGG analysis highlighted global differences in the numbers of genes devoted to specific functions and in the genomic pathways between ASxL5T and T. oleivorans MIL-1T and are not due to the extensive acquisition of mobile genetic elements. The difference in the G + C ratios for the whole genomes of ASxL5T of 56.1% and T. oleivorans MIL-1T of 46.6% is also indictive of genus separation.
Examination of the coding content of the ASxL5T genome provided functional insights into the phenotypic characteristics. The presence of genes that encode type IV pili (Tfp) are of particular interest as these facilitate cell movement referred to as social gliding or twitching without flagella over surfaces. Tfp are reported to have other functions including predation, pathogenesis, biofilm formation, natural DNA uptake, auto‐aggregation of cells and development38. That the ASxL5T genome contains 18 genes encoding diguanylate cyclase (enzyme that catalyses the conversion of 2 guanosine triphosphate to 2 diphosphate and cyclic di-GMP) and 6 genes encoding the corresponding diguanylate cyclase phosphodiesterase (catalyses the degradation of cyclic di-GMP to guanosine monophosphate) is of interest because cyclic-di-GMP is an important second messenger involved in processes that include biofilm development and detachment, motility, cellular attachment and virulence39,40. It should also be noted that in Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus cyclic-di-GMP has been shown to control the switch between free-living and predatory lifestyles41.
Most research into predatory bacteria has centred on Bdellovibrio, Bdellovibrio-like organisms and Myxocococcus species. These and other known examples of predatory bacteria form a taxonomically diverse group. Despite this diversity, a group of signature protein families that reflect the phenotypes of 11 known predatory bacteria have been identified3,22. However, only the gene encoding O-antigen ligase (waaL) was identified, which is notably prevalent in Gram-negative bacteria. This form of analysis was not helpful for the assignment of ASxL5T as a predator, likely because of the novel attack strategies it employs. The availability of more diverse predatory bacterial genomes will enable the development of finer resolution analyses that take into account evidence of functional and environmental differences between group members. Examples of predatory bacteria not included in this analysis include Cupriavidus necator42 and members of the Bradymonabacteria43 as more predatory taxa are established as researchers investigate different microbial communities.
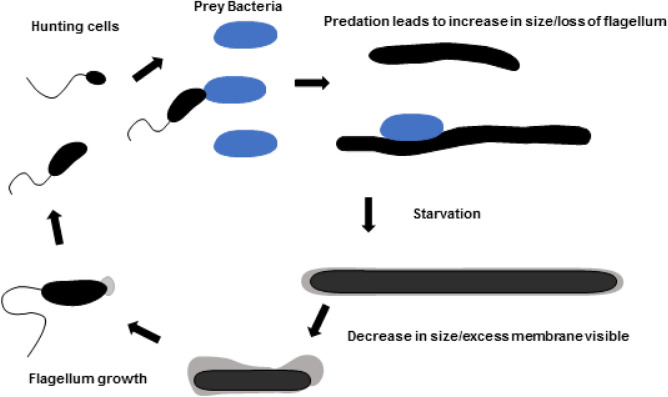
The most remarkable features of the ASxL5T bacterium as captured by TEM images, are its unique flexible morphologies that facilitate interactions with prey bacteria. The type of interaction observed is different from other predatory bacteria and has not been identified or reported previously. A proposed predatory life cycle of ASxL5T is shown in Fig. 5. There are few examples in the literature of similar apical structures to those we report here, but these include those of Terasakiispira papahanaumokuakeensis an Oceanospirillaceae bacterium, that shows occasional apical enlargement44, and the Alphaproteobacteria, Terasakiella pusilla previously in the genus Oceanospirillum, that exhibits what are described as “polar membranes”45. The presence of coccal forms in older cultures is a frequent observation particularly for bacteria with curved morphology, such as Vibrio, Campylobacter and Helicobacter46–48, which probably represents a degenerative state. Further work is required to elucidate the precise life cycle of the ASxL5T bacterium. to determine how it traps and feeds on its prey, and whether its genome encodes bioactive compounds that can be exploited for medicinal or biotechnological purposes.
Figure 5.
Proposed life cycle of the ASxL5T bacterium.
Description of Venatorbacter gen. nov. Venatorbacter (Ven.a.tor, ba’c.ter, L. composed of venator from L. n. venator, ‘hunter’ and Gr. n. bacter, ‘a rod’. Venatorbacter, ‘a hunting rod’. Cells are aerobic, halotolerant, curved Gram-stain negative, motile rods. Catalase and oxidase activities are positive. Does not accumulate PHB. Growth is obtained at a range of temperatures from 4 to 42 °C. The pH range of 4–9 is unusual in the Oceanospirillaceae as most are intolerant of acid pH. The major fatty acids are C16 : 1ω6c and/or C16 : 1ω7c, C16:0, and C18:1 ω9; C12:0 3-OH and C10:0 3-OH are found as hydroxy fatty acids. Growth does not occur in broth medium. The DNA G + C content is 56.1 mol%. Members of this genus exhibit predatory behaviour with Campylobacter species and members of the Enterobacteriaceae. The phylogenetic position of the genus is in the family.
Oceanospirillaceae in the class Gammaproteobacteria. The type species is Venatorbacter cucullus.
Description of Venatorbacter cucullus sp. nov. Venatorbacter cucullus (cu'cull.us.; L. n. cucullus meaning cowl).
In addition, the description features of the genus, cells are of 1.63 µm in length by 0.37 µm wide when grown on BA or BHI. Colonies on BHI agar are small reaching 2 mm in diameter after 72 h. They are beige, translucent, circular, convex and shiny. Members of the species can use E. coli, Klebsiella spp. Campylobacter spp. and several other Gram-stain negative bacteria as prey.
The type strain ASxL5T was isolated in Nottinghamshire UK from bovine slurry and is deposited at National Collection of Type Cultures (UK): accession number NCTC 14397 and the Netherlands Culture Collection of Bacteria (NCCB) accession number NCCB 100775. The complete genome sequence of ASxL5T has been deposited at Genbank under accession CP046056.
Methods
Isolation and phenotypic characterisation of ASx5LT
The ASxL5T bacterium was isolated from cattle slurry using a technique for phage isolation9,49. The slurry was diluted in 1:9 (w/v) in SM buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl [pH 7.5], 0.1 M NaCl, 8 mM MgSO4·7H2O, and 0.01% gelatine; Sigma Aldrich, Gillingham,UK) then incubated at 4 °C for 24 h with slow rotation to elute the predator into the buffer. The suspension was centrifuged at 3000g for 3 min. The supernatant was collected and subjected to a second centrifugation step for 5 min at 13,000g. The supernatant was then passed through a 0.45 µm membrane filter (Minisart; Sartorius, Gottingen, Germany) and a 0.2 µm membrane filter (Minisart) to remove any remaining bacterial cells. ASxL5T was able to pass through these filters. Soft agar lawns of an isolate of C. hyointestinalis S12, (NCBI accession number CP040464) from the same slurry, were prepared using standard techniques49. The filtered slurry was dispensed as 10 µl droplets in triplicate, on each of these host cell plates and allowed to dry. The plates were incubated at 37 °C under microaerobic conditions (5% O2, 5% H2, 10% CO2, and 80% N2) in microaerobic jars for 48 h. Visible plaques obtained were extracted into SM buffer and transferred to fresh lawns of C. hyointestinalis S12 to propagate the lytic organism further. Once it was established that a bacterium was responsible for the lytic plaques rather than a bacteriophage, attempts were made to cultivate the organism independently from the host and characterize it further. Weak growth that improved on subculture was obtained on Brain Heart Infusion Agar (BHI; CM1136, Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) and Horse Blood Agar No 2 (BA; CM0271 Oxoid) with 5% v/v defibrinated horse blood (TCS Biosciences Lt, Buckingham, UK, added) by aerobic incubation at 37 °C. Antimicrobial sensitivity testing was performed using the disk diffusion methods in accordance with the National Committee for Clinical Standards guidelines50. BHI agar incubated aerobically at 37 °C using discs with the following antibiotics (Oxoid): amoxycillin and clavulanic acid 30 µg; cefotaxime 30 µg; streptomycin 10 µg; ciprofloxacin 5 µg; ceftazidime 30 µg nalidixic acid 30 µg; imipenem 10 µg; azithromycin 15 µg; chloramphenicol 30 µg; cefoxitin 30 µg; tetracycline 30 µg; nitrofurantoin 300 µg; aztreonam 30 µg; ampicillin 10 µg; cefpodoxime 10 µg; trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 25 µg. Salt tolerance was established by cultivation aerobically at 37 °C on BHI agar plates to which additional NaCl was added to give a range of concentrations up to 10% w/v. The pH range was determined by cultivation aerobically at 37 °C on BHI agar plates where the pH range had been adjusted to be between 4 and 9 with either sterile HCl or sterile NaOH, and the target pH verified before pouring the plates. For cellular fatty acid analysis, ASxL5T was cultured on BHI agar for 3 days, aerobically at 37 °C. The cellular fatty acids were extracted, prepared, and analysed according to the standard protocol of MIDI (Sherlock Microbial Identification System, version 6.10) by FERA Science Ltd, (York, UK).
Microscopy
For TEM, ASxL5T was cultured aerobically by spreading uniformly on BA for 24 h at 37 °C and harvested into 1 ml of 3% (v/v) glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M cacodylate buffer, fixed for 1 h at room temperature then centrifuged at 10,000g for 3 min. The pellet was then re-suspended gently into 600 μl of 0.1 M cacodylate buffer. The fixed ASxL5T suspension was transferred onto Formvar/carbon film on copper 200 mesh grids. The bacteria stained with 0.5% (w/v) uranyl acetate for 1 min and examined by TEM using a TEI Tecnai G2 12 Biotwin microscope. The predator prey interaction was also examined by TEM as described above combining equal numbers of prey and predator in NZCYM broth (BD Difco™, Fisher Scientific UK Ltd, Loughborough) and incubating for 48 h at 37 °C, under microaerobic conditions for Campylobacter or aerobic conditions for E. coli. Prey and predatory bacteria were examined independently to establish any changes in cell morphology arising as a consequence of predation. Light microscopy for PHB accumulation was carried out using the Sudan Black method51.
Host range determination
Overnight cultures of ASxL5T were grown by spreading growth on BHI or BA plates using a sterile swab. The ASxL5T cells were collected and suspended in MRD (CM0733, Oxoid) and then placed at 4 °C for 7 days, to starve the cells. NCTC reference or laboratory stock bacteria cultures were inoculated into BHI broth or Nutrient Broth No 2 (CM007, Oxoid), incubated overnight, centrifuged at 13,000g and re-suspended in MRD to an OD600 of 0.4. The cultures were: Bacillus subtilis NCTC 3610T, Citrobacter freundii NCTC 9750T, Enterobacter aerogenes NCTC 10006T, Enterococcus faecalis NCTC 775T, Escherichia coli NCTC 86, Klebsiella oxytoca 11466, Leuconostoc mesenteroides NCTC 10817, Listeria monocytogenes NCTC 4885, Paenibacillus macerans NCTC 6355T, Providencia stuartsii NCTC 10318, Pseudomonas fluorescens SMDL, Rhodococcus hoagie NCTC 1621T, Salmonella enterica Montevideo NCTC 5747, Serratia liquefaciens NCTC 10861, Staphylococcus aureus NCTC 8532T, Streptococcus pneumoniae NCTC 7465T, Yersinia enterocolitica NCTC 10460. Campylobacter hosts were incubated microaerobically at 37 °C on BA plates and then suspended in NZCYM broth. Campylobacter hosts tested were: C. coli 12667 NCTC, C. jejuni 12662, C. jejuni PT14, C. jejuni NCTC 11168T, C. helveticus NCTC 12472, C. lari NCTC 11458, C. upsaliensis NCTC 11541T, C. hyointestinalis NCTC 11608T. Cells were collected in MRD, centrifuged at 13,000g and re-suspended in MRD to an OD600 of 0.4. An aliquot of 0.5 ml of the suspensions was added to 5 ml aliquots of molten NZCYM top agar (0.6% agar) and poured on to 1.2% NZCYM baseplates. Once set and dried, serial dilutions of ASxL5T were dispensed as 20 µl droplets in triplicate onto each lawn plate. The incubation temperature and atmosphere were dependent on the test bacteria’s requirements.
16S rRNA gene and whole genome sequence determination
DNA was prepared from bacterial isolates using GenElute™ Bacterial Genomic DNA Kit (Sigma Aldridge). PCR amplification of 16S rRNA gene and sequence determination of the product using dye-terminator chemistry (Eurofins Value Read Service, Germany) was carried out using standard methods. The sequences were compared with other 16S rRNA gene sequences using the BLAST-N program to identify and collect closely related species. These were aligned using ClustalW within the MEGA X program52. Phylogenetic trees were reconstructed using MEGA X using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the Tamura-Nei model53 with 1000 bootstrap replications54. DNA for whole genome sequencing was extracted using the PureLink™ Genomic DNA Kit (Fisher Scientific, Loughborough, UK). The genome sequence of ASxL5T was determined using a combination of Illumina MiSeq consisting of 250 bp paired-end reads using libraries prepared from the Nextera tagmentation kit, and long reads of 2 to 20 kb from the PacBio (Pacific Biosciences) platform performed at the Nu-Omics DNA Sequencing Research Facility, Northumbria University. The genome was assembled using CLC Genomics Workbench 12.0.3 (Qiagen, Aarhus, Denmark). ASxL5T cultures were deposited at National Collection of Type cultures (UK) and the Netherlands Culture Collection of Bacteria (NCCB). Genomes of related organisms used for comparisons were: Thalassolituus oleivorans MIL-1T (accession HF680312, complete); Bacterioplanes sanyensis KCTC 32220T (accession BMYY01000001, incomplete); Oceanobacter kriegii DSM 6294T (accession NZ_AUGV00000000, incomplete); Marinomonas communis DSM 5604T (accession ASM436330v1, incomplete), Oceanospirullum linum ATCC 11336T (accession MTSD02000001, incomplete) and Thalassolituus sp. C2-1 (accession NZ_VNIL01000001, incomplete). The alignment fraction (AF) and average nucleic acid identity (ANI) were determined using the JGI Genome Portal36 hosted at https://img.jgi.doe.gov//cgi-bin/mer/main.cgi?section=ANI&page=pairwise. Amino acid identities (AAI) were determined using the method of Rodriguez-R & Konstantinidis55. An estimated maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree was generated with GToTree 1.5.5411–18. Input genomes representing available reference genomes were selected from reference genera identified as related to ASxL5T from the 16S rRNA phylogeny. The tree was annotated using the Interactive Tree Of Life online tool, (https://itol.embl.de/). Functional annotation and analysis of the ASxL5T genome was carried out using KEGG (Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes) module enrichment assignment using the BlastKOALA KEGG online tool19. The distribution of COG categories (clusters of orthologous groups) was determined using the eggNOG-mapper online tool56.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank R.W.A Park for his guidance in writing the manuscript. This work was supported by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council [Grant number BB/I024585/1], UK.
Author contributions
I.F.C. conceived the experiments, A.S., P.L.C., D.M. and N.C. conducted the experiments, I.F.C., A.S., P.L.C. and N.C. analysed the results, and the manuscript drafted by P.L.C., A.S. and I.F.C. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Code availability
Accession code: Genome sequence of ASxL5T CP046056.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Ahmed Saeedi, Nicola J. Cummings, Ian F. Connerton and Phillippa L. Connerton.
References
- 1.Pérez J, Moraleda-Muñoz A, Marcos-Torres FJ, Muñoz-Dorado J. Bacterial predation: 75 years and counting! Environ. Microbiol. 2016;18:766–779. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Linares-Otoya L, et al. Diversity and antimicrobial potential of predatory bacteria from the Peruvian coastline. Mar. Drugs. 2017;15:E308. doi: 10.3390/md15100308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pasternak Z, et al. By their genes ye shall know them: Genomic signatures of predatory bacteria. ISME J. 2013;7:756–769. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2012.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sockett RE. Predatory lifestyle of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 2009;63:523–539. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.091208.073346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Korp J, Vela Gurovic MS, Nett M. Antibiotics from predatory bacteria. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016;12:594–607. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.12.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Johnke J, Fraune S, Bosch TCG, Hentschel U, Schulenburg H. Bdellovibrio and like organisms are predictors of microbiome diversity in distinct host groups. Microb. Ecol. 2020;79:252–257. doi: 10.1007/s00248-019-01395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Vila J, Moreno-Morales J, Ballesté-Delpierre C. Current landscape in the discovery of novel antibacterial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hobley L, et al. Dual predation by bacteriophage and Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus can eradicate Escherichia coli prey in situations where single predation cannot. J. Bacteriol. 2020;202:e00629-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00629-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.El-Shibiny A, Connerton PL, Connerton IF. Enumeration and diversity of campylobacters and bacteriophages isolated during the rearing cycles of free-range and organic chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005;71:1259–1266. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.3.1259-1266.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wilkinson DA, et al. Updating the genomic taxonomy and epidemiology of Campylobacter hyointestinalis. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:2393. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20889-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee MD. GToTree: A user-friendly workflow for phylogenomics. Bioinformatics. 2019;35:4162–4164. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eddy SR. Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011;10:e1002195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Edgar RC. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004;5:113. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Capella-Gutiérrez S, Silla-Martínez JM, Gabaldón T. TrimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1972–1973. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hyatt D, LoCascio PF, Hauser LJ, Uberbacher EC. Gene and translation initiation site prediction in metagenomic sequences. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:2223–2230. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shen, W. & Xiong, J. TaxonKit: A cross-platform and efficient NCBI taxonomy toolkit. bioRxiv. (Accessed 1 June 2021); https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/513523v1 (2019).
- 17.Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP. FastTree 2—Approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS One. 2010;5:e9490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tange, O. GNU Parallel. (Accessed 1 June 2021); https://zenodo.org/record/1146014#.YOHaiJhKiUk (2018).
- 19.Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28:27–30. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Czech L, et al. Role of the extremolytes ectoine and hydroxyectoine as stress protectants and nutrients: Genetics, phylogenomics, biochemistry, and structural Analysis. Genes (Basel). 2018;9:E177. doi: 10.3390/genes9040177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gregson BH, Metodieva G, Metodiev MV, Golyshin PN, McKew BA. Differential protein expression during growth on medium versus long-chain alkanes in the obligate marine hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium Thalassolituus oleivorans MIL-1. Front. Microbiol. 2018;9:3130. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pasternak Z, Ben Sasson T, Cohen Y, Segev E, Jurkevitch E. A new comparative-genomics approach for defining phenotype-specific indicators reveals specific genetic markers in predatory bacteria. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0142933. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yakimov MM, et al. Thalassolituus oleivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel marine bacterium that obligately utilizes hydrocarbons. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004;54:141–148. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang Y, Yu M, Liu Y, Yang X, Zhang XH. Bacterioplanoides pacificum gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from seawater of South Pacific Gyre. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016;66:5010–5015. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bowditch RD, Baumann L, Baumann P. Description of Oceanospirillum kriegii sp. nov. and O. jannaschii sp. nov. and assignment of two species of Alteromonas to this genus as O. commune comb. nov. and O. vagum comb. nov. Curr. Microbiol. 1984;10:221–229. doi: 10.1007/BF01627259. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dong C, Chen X, Xie Y, Lai Q, Shao Z. Complete genome sequence of Thalassolituus oleivorans R6-15, an obligate hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacterium from the Arctic Ocean. Stand Genom. Sci. 2014;9:893–901. doi: 10.4056/sigs.5229330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Choi A, Cho J-C. Thalassolituus marinus sp. nov., a hydrocarbon utilizing marine bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013;63:2234–2238. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.046383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Alain K, Harder J, Widdel F, Zengler K. Anaerobic utilization of toluene by marine alpha- and gammaproteobacteria reducing nitrate. Microbiology. 2012;158:2946–2957. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.061598-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liu J, Wu W, Chen C, Sun F, Chen Y. Prokaryotic diversity, composition structure, and phylogenetic analysis of microbial communities in leachate sediment ecosystems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011;91:1659–1675. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yakimov MM, Timmis KN, Golyshin PN. Obligate oil-degrading marine bacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007;18:257–266. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2007.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.McKew BA, et al. Efficacy of intervention strategies for bioremediation of crude oil in marine systems and effects on indigenous hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2007;9:1562–1571. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Satomi M, Kimura B, Hamada T, Harayama S, Fujii T. Phylogenetic study of the genus Oceanospirillum based on 16S rRNA and gyrB genes: emended description of the genus Oceanospirillum, description of Pseudospirillum gen. nov., Oceanobacter gen. nov. and Terasakiella gen. nov. and transfer of Oceanospirillum jannaschii and Pseudomonas stanieri to Marinobacterium as Marinobacterium jannaschii comb. nov. and Marinobacterium stanieri comb. no. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002;52:739–747. doi: 10.1099/00207713-52-3-739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Qin QL, et al. A proposed genus boundary for the prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J. Bacteriol. 2014;196:2210–2215. doi: 10.1128/JB.01688-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nicholson AC, et al. Division of the genus Chryseobacterium: Observation of discontinuities in amino acid identity values, a possible consequence of major extinction events, guides transfer of nine species to the genus Epilithonimonas, eleven species to the genus Kaistella, and three species to the genus Halpernia gen. nov., with description of Kaistella daneshvariae sp. nov. and Epilithonimonas vandammei sp. nov. derived from clinical specimens. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020;70:4432–4450. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.003935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yarza P, et al. Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014;12:635–645. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Barco RA, et al. A genus definition for Bacteria and Archaea based on a standard genome relatedness index. MBio. 2020;11:e02475-192020. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02475-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Andersson JO, Andersson SG. Insights into the evolutionary process of genome degradation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1999;9:664–671. doi: 10.1016/S0959-437X(99)00024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wall D, Kaiser D. Type IV pili and cell motility. Mol. Microbiol. 1999;32:1–10. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jenal U, Malone J. Mechanisms of cyclic-di-GMP signaling in bacteria. Ann. Rev. Genet. 2006;40:385–407. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.40.110405.090423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dow JM, Fouhy Y, Lucey JF, Ryan RP. The HD-GYP domain, cyclic di-GMP signaling, and bacterial virulence to plants. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2006;19:1378–1384. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-19-1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hobley L, et al. Discrete cyclic di-GMP-dependent control of bacterial predation versus axenic growth in Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8:e1002493. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Seccareccia I, Kovács ÁT, Gallegos-Monterrosa R, Nett M. Unraveling the predator-prey relationship of Cupriavidus necator and Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol. Res. 2016;192:231–238. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2016.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mu DS, et al. Bradymonabacteria, a novel bacterial predator group with versatile survival strategies in saline environments. Microbiome. 2020;8:1262020. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00902-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zepeda VK, et al. Terasakiispira papahanaumokuakeensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a gammaproteobacterium from Pearl and Hermes Atoll, Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015;65:3609–3617. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.000438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Terasaki Y. Transfer of five species and two subspecies of Spirillum to other genera (Aquaspirillum and Oceanospirillum), with emended descriptions of the species and subspecies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1979;29:130–144. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Baker DA, Park RW. Changes in morphology and cell wall structure that occur during growth of Vibrio sp. NCTC4716 in batch culture. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1975;86:12–28. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ng LK, Sherburne R, Taylor DE, Stiles ME. Morphological forms and viability of Campylobacter species studied by electron microscopy. J. Bacteriol. 1985;164:338–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.338-343.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Reshetnyak VI, Reshetnyak TM. Significance of dormant forms of Helicobacter pylori in ulcerogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017;23:4867–4878. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Loc Carrillo C, et al. Bacteriophage therapy to reduce Campylobacter jejuni colonization of broiler chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005;71:6554–6563. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.11.6554-6563.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Methods for determining bactericidal activity of antimicrobial agents; approved guideline M26-A. Clin. Lab. Stand. Inst. 1999;19:7. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Legat A, Gruber C, Zangger K, Wanner G, Stan-Lotter H. Identification of polyhydroxyalkanoates in Halococcus and other haloarchaeal species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010;87:1119–1127. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2611-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018;35:1547–1549. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tamura K, Nei M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993;10:512–526. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution. 1985;39:783–791. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT. Bypassing cultivation to identify bacterial species. Microbe. 2014;9:111–118. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Huerta-Cepas J, et al. Fast genome-wide functional annotation through orthology assignment by eggNOG-mapper. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017;34:2115–2122. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Accession code: Genome sequence of ASxL5T CP046056.