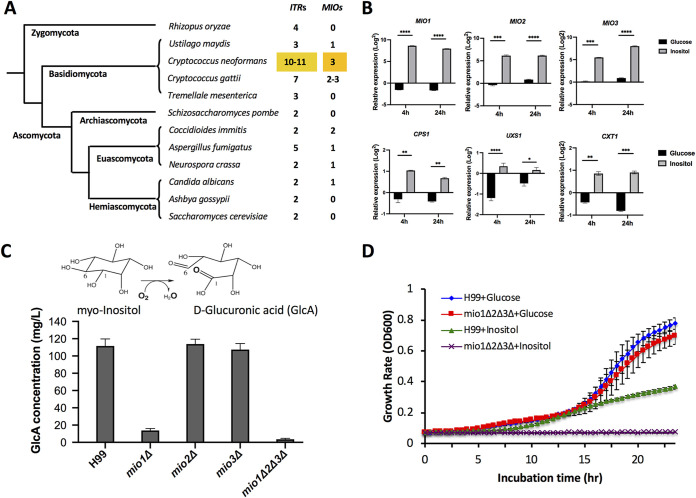
FIG 2.
Genes involved in inositol catabolic pathway were highly induced by inositol. (A) Number of ITR and MIO homologs in different fungal species. (B) Genes involved in the inositol catabolic pathway (MIO, CPS1, UXS1, and CXT1) were highly induced by inositol based on qRT-PCR analysis. qRT-PCR was used to quantify the expression changes of the listed genes in wild-type H99 incubated for 4 h or 24 h in medium containing 1% inositol or 1% glucose compared to YPD culture. The relative expression changes were calculated using the ΔΔCT method. Statistical analysis was done using Student's t test. ****, P < 0.0001; ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05. (C) MIO functions as an inositol oxygenase in C. neoformans. The oxidation reaction to convert myo-inositol to d-glucuronic acid is catalyzed by myo-inositol oxygenase. Mio enzyme activity was analyzed by measuring d-glucuronic acid production in H99 and its mio1Δ, mio2Δ, and mio3Δ single mutants and a mio1Δ2Δ3Δ triple mutant. (D) Growth rates of wild-type H99 and its mio mutants on YNB liquid medium containing either 1% glucose or 1% inositol. The mio1Δ2Δ3Δ triple mutant failed to grow on YNB with inositol as the sole carbon source.