Figure 1.
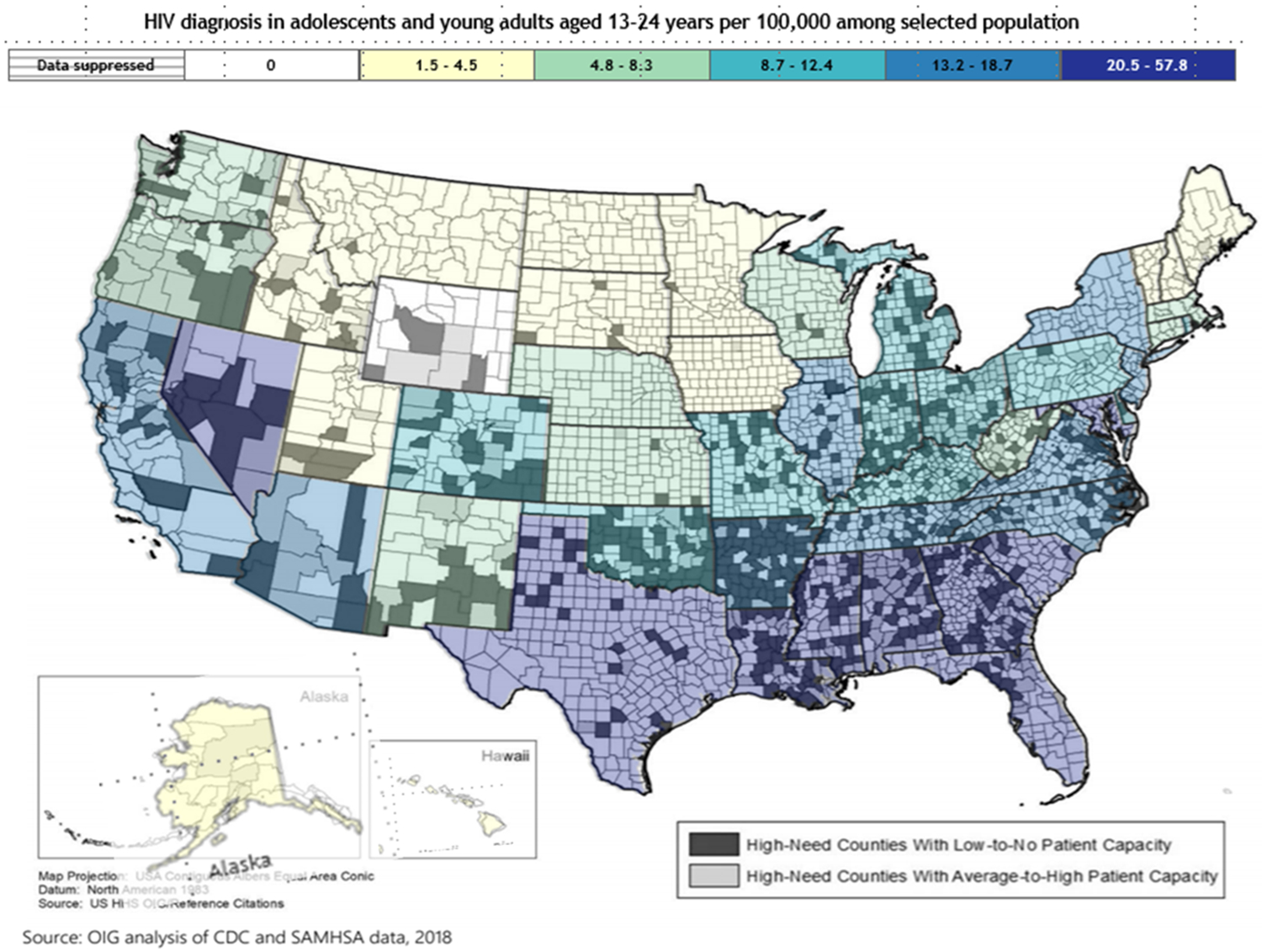
The overlap of HIV in adolescents and young adults aged 13-24 years and areas of high opioid misuse but low access to care.
The overlap of HIV in adolescents and young adults aged 13-24 years and areas of high opioid misuse but low access to MOUD.
This figure illustrates the geographic overlap of states with high rates of HIV diagnosis among adolescents and young adults aged 13-24 years in 2018[1] with counties with high need of opioid treatment based on high indicators of opioid misuse in that county[2, 3]. Counties were further delineated by whether the county had high or low capacity to provide MOUD treatment to people with OUD in 2018[2]. Patient capacity was determined by number of X-waivered providers present in a county and surrounding area.
