Abstract
The retinoblastoma protein (pRb)/E2F pathway regulates commitment of mammalian cells to replicate DNA. On the other hand, mitogen-stimulated cells deprived of E2F activity can still maintain physiologically relevant levels of cyclin E-dependent kinase activity and gradually enter S phase, suggesting the existence of a DNA synthesis-inducing mechanism parallel to the pRb/E2F axis. Here we show that regulatable ectopic expression of cyclin E or transcriptionally active Myc can rapidly induce DNA synthesis in U2OS-derived cell lines whose E2F activity is blocked by a constitutively active pRb (pRbΔcdk) mutant. The effect of Myc is associated with Cdc25A phosphatase and cyclin E-CDK2 kinase activation and abolished by antagonizing Myc activity with the dominant-negative (dn) MadMyc chimera. Moreover, while abrogation of either endogenous E2F or Myc activity only delays and lowers DNA synthesis in synchronized U2OS cells or rat diploid fibroblasts, concomitant neutralization of both abolishes it. Whereas ectopic Myc and E2F1 rescue the G1/S delay caused by pRbΔcdk (or dnDP1) and MadMyc, respectively, cyclin E or Cdc25A can restore DNA replication even in cells concomitantly exposed to pRbΔcdk and MadMyc. However, coexpression of dnCDK2 neutralizes all of these rescuing effects. Finally, proper transcription of cyclin E and Cdc25A at the G1/S transition requires both Myc and E2F activities, and subthreshold levels of ectopic cyclin E and Cdc25A synergistically restore DNA synthesis in cells with silenced Myc and E2F activities. These results suggest that Myc controls a G1/S-promoting mechanism regulating cyclin E-CDK2 in parallel to the “classical” pRb/E2F pathway.
The “retinoblastoma (Rb) pathway,” comprising Rb protein (pRb) and its immediate upstream regulators, D-cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4 and -6, respectively), INK4 CDK inhibitors (CKIs), and pRb-regulated E2F transcription factors, appears instrumental in regulating homeostatic tissue renewal and preventing neoplastic growth (4, 68). However, it remains to be elucidated whether this pathway represents the only physiological way to commit mammalian somatic cells to DNA replication. In particular, it is unclear whether cyclin E, a powerful inducer of cell cycle progression and DNA synthesis (31, 35, 37, 55), is solely a primary target of the pRb/E2F axis (8, 16, 21, 54), or whether it may also be under the control of a parallel G1/S-regulatory pathway. Compelling evidence exists in Drosophila and mammals for cyclin E being a pivotal downstream mediator of the Rb pathway (15, 22). However, cyclin E is required and rate-limiting for G1/S progression in both Rb-positive and -negative cells (55). Moreover, unlike D-type cyclins, this cyclin can induce S-phase entry and DNA synthesis in mammalian cells deprived of E2F activity by expression of a constitutively active pRb mutant (pRbΔcdk) or of a dominant-negative DP1 mutant, dnDP1 (44). These and other recent reports (29, 39) suggest that cyclin E may play multiple roles in promoting S-phase entry and that at least one of its critical functions is either downstream of or parallel to pRb phosphorylation and independent of E2F activation.
These features render cyclin E a candidate target for a hypothetical G1/S-promoting mechanism different from the Rb pathway. A tissue-specific E2F-independent transcription of cyclin E (16) and the occurrence of S-phase entry despite elimination of E2F-dependent transcriptional activity by dE2F and dDP mutations (62) were detected in Drosophila, raising the possibility that this mechanism may actually exist. Observations that Rb-null fibroblasts or cells functionally deprived of active transrepression mediated by pRb-E2F complexes are still sensitive to serum deprivation (27, 76) are compatible with its presence as well in mammalian cells. More direct evidence comes from our recent work with human U2OS osteosarcoma cells conditionally expressing pRbΔcdk and in diploid rat fibroblasts microinjected with this mutant (47). Indeed, when observed over an extended period of several days, these cells arrest only transiently in G1 despite pRbΔcdk's capability of quantitatively repressing all endogenous E2Fs (44, 47). Although abruptly and severely deprived of cyclin A expression and associated kinase activity, such cells are able to maintain physiologically significant levels of cyclin E mRNA, protein, and associated kinase activity, thereby allowing S-phase entry and DNA replication within 2 days (43, 47). These results, consistent with observations by others in transient experiments (11, 36), suggest the existence of a mitogen-stimulated, G1/S-promoting mechanism capable of inducing DNA synthesis by regulating cyclin E function in parallel to the pRb/E2F pathway. Yet, cells devoid of E2F activity, although able to rereplicate DNA over several days, do not proliferate (47), indicating that the E2F-dependent and -independent pathways triggering DNA synthesis must mutually cooperate to ensure proper progression through somatic cell cycles.
Previous work prompted us to investigate the possibility that c-Myc, as a paradigmatic non-E2F, cell-cycle-related transcription factor (3, 24, 53), is potentially involved in the regulation of this G1/S-promoting pathway parallel to the classical pRb/E2F axis. Myc is promptly induced by mitogens and continuously expressed in cycling cells (3, 24, 26), and its ectopic expression, like that of E2F (34, 46, 72) or cyclin E-CDK2 (13), is able to induce S-phase entry in quiescent cells (reviewed in references 3, 26, 53). Moreover, forced expression of c-Myc is reportedly able to activate cyclin E-CDK2 complexes in quiescent or exponentially growing cells by as-yet-debated mechanisms involving modulation of levels and function of the CKI p27 or increased expression of cyclin E or Cdc25A phosphatase (3, 9, 20, 40, 53, 57, 58). Importantly, the activity of cyclin E-CDK2 is necessary for cell cycle progression induced by conditional Myc alleles (63), is reduced in cells arrested in G1 by a dnMyc allele (5), and is delayed and reduced during the G0/S transition in c-Myc−/− cells (49). Finally, further supporting the idea of c-Myc as an upstream regulator of cyclin E, both c-Myc and cyclin E may overcome a p16-induced cell cycle arrest (1, 44) and uncouple DNA replication from cell cycle progression, leading to genomic instability (18, 41, 52, 69).
However, despite all this work pointing to Myc as an upstream regulator of cyclin E function, the potential involvement of Myc transcriptional activity in the control of a mechanism that may promote G1/S transition and DNA replication independently of E2F activity remains untested. In this respect, given the reported ability of Myc to induce E2F-1 gene expression and activate E2F-2 promoter (40, 67), one may query whether the control of G1/S transition and cyclin E function by Myc transcriptional activity is direct or is mediated by increased E2F activity (3, 53, 72).
To directly address the potential existence of a “parallel” pathway that could commit mammalian cells to DNA replication via cyclin E function and to test whether Myc requires E2F activity for inducing DNA replication and S phase, we have now generated novel inducible U2OS cell lines expressing pRbΔcdk together with cyclin E or with c-Myc. We have also employed functional E2F- and Myc-knockout analyses with U2OS cells and diploid fibroblasts to assess in more detail the independent control of S-phase entry by the activities of these two transcription factors. Our data indicate that Myc plays a critical role in sustaining an E2F-independent, G1/S-promoting mechanism by regulating cyclin E-CDK2 function, which therefore represents a common rate-limiting target of both E2F-dependent and -independent pathways for S-phase entry. We also show that both E2F and Myc activities are required to ensure timely and proper levels of DNA replication and orderly completion of cell cycles.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plasmids.
Hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged, phosphorylation-deficient murine pRb mutant pRbΔcdk (44) was contained in the pBI vector (47), which allows expression of two genes from a bidirectional, tetracycline (TET)-repressible promoter (Clontech). Eleven CDK phosphorylation sites, regulating pRb binding to E2F, c-Abl, and LXCXE-containing proteins, have been mutated to alanine in pRbΔcdk, and the remaining ones do not affect stable inhibition of all E2Fs by this mutant (44, 47). Human cyclin E and c-Myc cDNAs were subcloned into the SalI site of pBI's second polylinker to generate the pBI-HA-RbΔcdk/CycE and pBI-HA-RbΔcdk/Myc vectors, respectively, while the subcloning of c-Myc cDNA into the EcoRV site yielded the pBI-Myc vector. The plasmids pBabePuro, pCMV-CD20, pBI-p16, pCMV-HA-dnDP1 (Δ103–126), and pECE-pRbΔB/X for expression of murine wild-type pRb, and the 6xE2F-luciferase (6xE2F-Luc) reporter, containing six E2F-responsive elements in front of the TATA box, are described elsewhere (44, 45, 47). The Cdc25A cDNA, the kind gift of B. Ducommun, was linked in frame at its N terminus with the HA tag and subcloned into the pBI plasmid by PCR, generating pBI-HA-Cdc25A. The expression vectors pCMV-dnCDK2 (dnK2) (71) and pCMVMadMyc (5) (kindly donated by R. Bernards) and the reporter ODCΔLuc, containing the Myc-responsive region of murine ODC promoter, and its mutant ODCΔLucS-5A (56) (kindly provided by J. L. Cleveland) were used as reported. The reporter M4-Luc, a kind gift of R. N. Eisenman, contains four Myc-responsive E boxes cloned into pGL2-Promoter vector (Promega).
Cell culture and gene transfer.
U2OS-TA, a U2OS human osteosarcoma cell line with stably integrated TET-regulated transcriptional activator (tet-VP16) and a neomycin resistance gene (47), was transfected with the pBI vectors for pRbΔcdk, pRbΔcdk/CycE, pRbΔcdk/c-Myc, or c-Myc along with pBabePuro at a 10:1 ratio. Puromycin-resistant clones were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) containing 10% fetal calf serum, G418 (400 μg/ml), puromycin (1 μg/ml), and TET (2 μg/ml). Derepression of clones by TET removal was performed according to procedures previously published (47). The R12 embryonic diploid fibroblasts expressing tet-VP16 and derived from Rat-1 fibroblasts (44, 47) were maintained in DMEM containing G418.
Calcium-phosphate transfection, electroporation, and microinjection of plasmids were performed as reported previously (44–46).
Flow cytometry and BrdU incorporation.
The procedures for propidium iodide staining of cellular DNA, for immunostaining and sorting of CD20-positive cells, and for DNA analysis were as published previously (47). Stained cells were acquired by the FACSCalibur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson) by using CellQuest software, and the DNA distribution (FL2-A parameter) was analyzed by ModFit software.
For analysis of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation, 106 U2OS-TA or R12 cells were seeded onto 10-cm-diameter dishes. The next day, cells were cotransfected with 1 μg of pCMV-CD20 and the indicated combinations of plasmids and concomitantly synchronized by addition of nocodazole (50 ng/ml) to TET-free medium. Fifteen hours later, nocodazole and transfection precipitate were washed off, and arrested cells were reseeded on coverslips in TET-free medium containing 10% serum and 100 μM BrdU. At the indicated time points after release from nocodazole, cells were immunoreacted with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (MAb), fixed, and eventually at least 300 CD20-positive cells were assayed for BrdU incorporation by double immunostaining as reported previously (45, 46). The counts were highly comparable to those obtained by double labeling with antibodies for BrdU and for the ectopic proteins (not shown).
Immunochemical techniques and kinase and phosphatase assays.
The MAbs used in this study were anti-pRb 245 (Pharmingen) and anti-Myc 9E10 (a kind gift from G. Evan) for immunoblots; anti-HA 12CA5 (44), anti-CD20 (Becton Dickinson), anti-cyclin E HE12 (kindly provided by S. I. Reed), and anti-p16 DCS-50 (45) for immunostaining; anti-cyclin E HE172 (provided by S. I. Reed), anti-cyclin B1 (Transduction Laboratories), and anti-Cdc25A DCS-124 (N. Mailand, J. Falck, C. Lukas, R. Syljuåsen, J. Bartek, and J. Lukas, submitted for publication) for immunoprecipitation; fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled anti-CD20 and anti-BrdU (Becton Dickinson) for fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis and BrdU detection, respectively. Rabbit antisera to the c-Myc C terminus (SC-788) for immunostaining of c-Myc and the chimeric protein MadMyc (MM), and to CDK2 (SC-163) for immunostaining of dnK2, were from Santa Cruz. Immunostaining of cells grown on coverslips and immunoblotting procedures, unless otherwise stated, were as described previously (45, 46). Equal loading of immunoblots was verified by Ponceau-S staining.
Cyclin E-associated kinase activity was assessed as described previously (44) with some modifications. Briefly, cells were harvested at the indicated times after TET removal, pelleted, and incubated for 30-min in 3 to 5 volumes of ice-cold lysis buffer (50 mM HEPES [pH 7.5], 250 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 1 mM dithiothreitol [DTT], 0.1% NP-40, 1 mM NaF, 0.1 mM Na3VO4, 10 mM sodium PPi, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate, 10 μg of leupeptin per ml, 10 μg of aprotinin per ml, 10 μg of pepstatin per ml, 0.1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride) with periodical vigorous vortexing. Cell lysates were centrifuged at 14,000 × g for 10 min to remove insoluble debris, and the supernatants were incubated for 1 h at 4°C with protein G-Sepharose beads (Pharmacia Biotech.) previously equilibrated with lysis buffer. Protein concentrations in the precleared extracts were measured with the Bio-Rad Protein Assay kit. Twenty microliters of preequilibrated beads was then precoated with the HE172 MAb for 90 min at 4°C, washed, and reacted with 200 μg of precleared lysates for 2 h at 4°C in 1 ml of lysis buffer. The resulting immunoprecipitates were washed three times in lysis buffer and twice in kinase buffer (50 mM HEPES [pH 7.5], 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate, 1 mM NaF, 0.1 mM Na3VO4) and then resuspended in 25 μl of kinase buffer containing 2.5 μg of histone H1, 50 μM ATP, and 5 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP (Amersham Life Science) and incubated for 30 min at 30°C. After stopping the kinase reactions by adding 10 μl of 4× Laemmli sample buffer, the reaction products were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (12% polyacrylamide). The gel was Coomassie stained to verify equal loading and dried, and the specific phosphate incorporation into the substrate was quantified by PhosphorImager scanning and ImageQuant software (Molecular Dynamics). The histone H1 kinase activity from U2OS cells incubated with the nonimmunoprecipitating HE12 MAb was used as negative control.
Cdc25A phosphatase activity was indirectly quantified as the capability to activate cyclin B1-CDC2. To generate inactive, Thr14- and Tyr15-phosphorylated cyclin B1-CDC2 complexes, wild-type U2OS cells were cultured in presence of 0.2 μg of adriamycin per ml (Calbiochem) for 24 h (59). Two-hundred micrograms of protein extracts from these cells was used to immunoprecipitate inactivated cyclin B1-CDC2 complexes with anti-cyclin B1 MAb, while Cdc25A was immunoprecipitated in parallel from 1 mg of U2OS-Myc and U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc cell lysates by using the DCS-124 MAb. After three washes in lysis buffer containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors and three washes in cold phosphatase buffer (20 mM Tris [pH 8.3], 150 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA, 0.1% Triton X-100, 5 mM DTT), the beads from the cyclin B1-CDC2 and Cdc25A immunoprecipitates were mixed in a final volume of 50 μl of phosphatase buffer and coincubated for 1 h at 30°C. The reaction was stopped by adding kinase assay buffer and the cyclin B1-CDC2 kinase activity was assayed with histone H1 as a substrate followed by PhosphorImager quantification as described above. The histone H1 kinase activity associated with cyclin B1-CDC2 immunoprecipitates non-coincubated with Cdc25A immunoprecipitates was used as a negative control.
Reporter assays.
The noninvasive in vivo photon emission assay to monitor E2F-dependent transcription was performed and quantified essentially as reported previously (44). Briefly, the synthetic 6xE2F-Luc reporter, which is effectively activated by E2F-1 to -5 and significantly more sensitive than natural E2F-responsive reporters (44), was microinjected (100-μg/ml needle concentration) with an automatic Zeiss AIS micromanipulator system and an Eppendorf microinjector into the nuclei of cells cultured in TET-containing or -free medium. Twenty-four hours later, 1 mM beetle luciferin (Promega) was added to the medium, the injected fields were recovered by grid coordinates, and the emitted photoelectrons were acquired by using a cooled (−30°C) ICCD-567-S/RB EM detector and an ST-138S controller (Princeton Instruments, Inc.) attached to a Zeiss Axiovert 135M microscope with a Fluar ×10 objective. The total acquisition time was 10 min/field. During acquisition, cells were kept in the dark on a 37°C-heated stage in a chamber with a 5% CO2 atmosphere.
To evaluate Myc activity, 1.5 × 106 U2OS-Myc or U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc TET-repressed cells were electroporated with 2 μg of the indicated reporter, 0.5 μg of the internal control pCMV-LacZ, and 5 μg of pCMVMadMyc or empty pCMV and harvested after a 48-h culture in TET-containing or -free medium as indicated. The resulting luciferase and β-galactosidase activities were assayed with a Lumat LB 9501 luminometer (Berthold) and an UltroSpec 2000 spectrophotometer (Pharmacia Biotech.), respectively, following the instructions of the Promega Luciferase Assay System.
RT-PCR.
U2OS-TA cells were synchronized and transfected with CD20, pEGFP-C1 (1 μg; Clontech), and the indicated plasmids according to the procedure described above. CD20-positive cells were isolated with anti-CD20 MAb-coated Dynabeads and a DYNAL Magnetic Particle Concentrator according to the manufacturer's protocol (Dynal A.S.). At least 95% of the cells isolated displayed green fluorescent protein fluorescence. One microgram of RNA, obtained from the CD20-positive cells with a Trizol Reagent kit (Gibco, BRL, Gaithersburg, Md.) was pretreated with DNase and reverse transcribed with Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase (RT) following the supplier's suggestions (Stratagene). For amplification, 1 μl of the RT reactant was mixed in a final volume of 20 μl together with 8 pmol of primer pairs, 0.5 μCi of [α-32P]dCTP (Amersham Life Science), and 25 μM each deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) and amplified with 0.5 U of HotStar Taq DNA polymerase (Qiagen, Inc.) for 20 cycles (denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, annealing at 58°C for 30 s, and extension at 72°C for 60 s). This number of cycles had been previously estimated to be the optimal one for detecting the signal in the linear range. The primer sequences were as follows: cyclin E, 5′-GTTTACCCAAACTCAAC GTGC-3′ (forward) and 5′-CGCAAACTGGTGCAACTTTGG-3′ (reverse); Cdc25A, 5′-CAGCTCATCGACCCAGATGAG-3′ (forward) and 5′-AGCTTGCATCGGTTGTCAAGG-3′ (reverse); and the porphobilinogen deaminase (PBGD) housekeeping gene (12), 5′-CATGTCTGGTAACGGCAATG-3′ (forward) and 5′-AGGGCATGTTCAAGCTCCTT-3′ (reverse). As a control, PCR was performed on RNA samples that had not been reverse transcribed. Amplification products were visualized by PhosphorImager scanning of acrylamide gels and quantified by ImageQuant software.
RESULTS
Characterization of U2OS clones conditionally coexpressing constitutively active pRb and cyclin E.
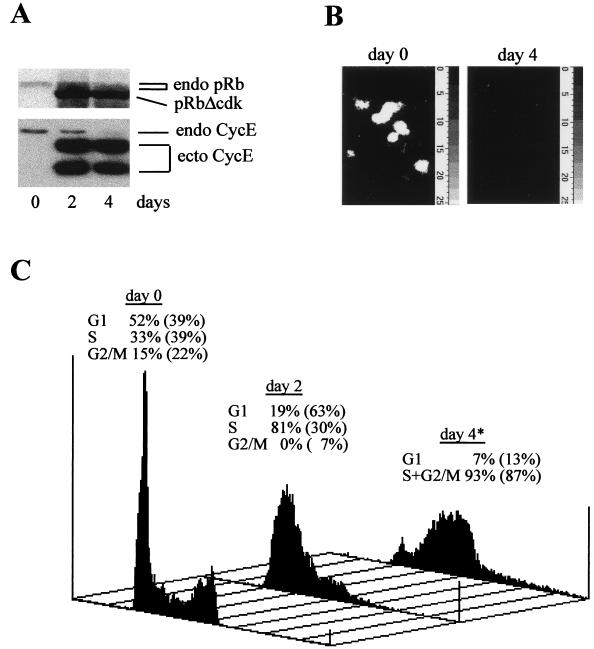
It was shown that cyclin E activity can induce DNA replication without activation of the pRb/E2F pathway (1, 38, 44) and that its persistence at physiologically relevant levels may allow Drosophila or mammalian cells deprived of E2F activity to gradually overcome G1 arrest (47, 62). To extend these findings, we generated U2OS clones coexpressing pRbΔcdk and cyclin E in a TET-repressible manner and compared them with U2OS cells expressing pRbΔcdk alone recently described (43, 47). Basic characterization of a representative U2OS-RbΔcdk/CycE clone is documented in Fig. 1. Immunoblotting and immunofluorescence time course analyses showed no expression of the transgenes in the repressed state and rapid, uniform, and sustained induction of these proteins in more than 90% of cells after TET removal (Fig. 1A and data not shown).
FIG. 1.
Characterization of a representative U2OS clone conditionally coexpressing RbΔcdk with cyclin E (clone B3B4). (A) Protein extracts from cells grown in presence (day 0) or absence of TET for the indicated days were analyzed by immunoblotting with MAbs to pRb and cyclin E. endo, endogenous proteins; pRbΔcdk, phosphorylation-deficient pRb mutant; ecto CycE, ectopic cyclin E. (B) Sustained suppression of endogenous E2F activity by pRbΔcdk. Cells grown with (day 0) or without (day 4) TET were microinjected with the 6xE2F-Luc reporter plasmid and examined 24 h later for reporter activity measured as in vivo photon emission from productively injected cells. The average emission per cell during a 10-min acquisition period was (25 ± 13) × 103 light counts at day 0, whereas no cell luminescence above background was detected at day 4, indicating the complete suppression of endogenous E2F activity. (C) Representative flow-cytometric DNA histograms of U2OS-RbΔcdk/CycE cells grown with (day 0) or without TET for the indicated times. The cell cycle distribution at each time point is indicated above the histograms, and for comparison, the corresponding values of cells carrying pRbΔcdk alone (U2OS-RbΔcdk clone A5) are indicated in parentheses. The asterisk indicates that, at day 4, S and G2/M are represented together because the algorithm was unable to clearly distinguish these two phases. Note the presence of some endoreplication in U2OS-RbΔcdk/CycE after transgene induction. The time course was repeated at least three times with similar results and reproduced in independent clones.
To confirm that the induced proteins were functional, cyclin E-associated kinase activity and the ability of the constitutively active pRbΔcdk mutant to inhibit endogenous E2F activity were examined. Four days after TET removal, cyclin E-associated kinase activity was increased up to sixfold the value in TET-repressed cells, thereby verifying the expected function of this cyclin (data not shown). A quantitative luciferase reporter assay to monitor E2F-dependent transactivation in live cells (44) revealed high luminescence in U2OS-RbΔcdk/CycE cells cultured in TET-containing medium, in sharp contrast to no detectable luciferase activity after induction of the transgenes (Fig. 1B). Similar results were obtained with other independent U2OS-RbΔcdk/CycE clones. Thus, despite the coexistence of increased cyclin E activity, pRbΔcdk was able to prevent any E2F-dependent promoter activation for several days after induction. These data were consistent with those obtained in transient experiments in which luciferase expression, in addition to the artificial 6xE2F, was controlled by the natural, E2F-responsive regions of dihydrofolate reductase, B-Myb, or E2F-1 promoters (44; E. Santoni-Rugiu, J. Lukas, and J. Bartek, unpublished data).
We next analyzed the cell cycle profile of U2OS-RbΔcdk/CycE cells and correlated it with that of U2OS-RbΔcdk cells. The latter, as previously observed (47), displayed a G1 arrest during the first 2 days of induction, followed thereafter by entry and accumulation in S phase (Fig. 1C). In contrast, coinduction of pRbΔcdk and cyclin E completely abolished the transient G1 arrest observed when pRbΔcdk was expressed alone and induced rapid entry into and progression through S phase (Fig. 1C). This effect was essentially confirmed upon microinjection of synchronized or exponentially growing R12 cells with RbΔcdk and cyclin E (44; data not shown). Taken together, our results indicate that cyclin E-associated kinase can induce S phase even in cells deprived of E2F function long term. This implies that a cyclin E-targeting mechanism independent of the pRb/E2F pathway may have G1/S-promoting properties. Cyclin E, however, appeared to be unable to restore productive cell division over an extended period of time, since U2OS-RbΔcdk/cycE cells displayed only limited reappearance of a G1 peak, with the initial ploidy at day 4 remaining largely locked in late S phase with appreciable levels of DNA endoreplication (Fig. 1C). This conclusion was further supported by the lack of mitotic figures or chromatin condensation when these cells were observed by phase-contrast or fluorescence microscopy (not shown). Thus, although transient coexpression of pRbΔcdk and ectopic cyclin E was able to promote completion of one division cycle in U2OS or R12 cells (44), additional critical events controlled by the pRb/E2F pathway (39, 43, 51) are required to ensure orderly progression into G2/M over the long term.
U2OS clones with inducible expression of constitutively active pRb and c-Myc.
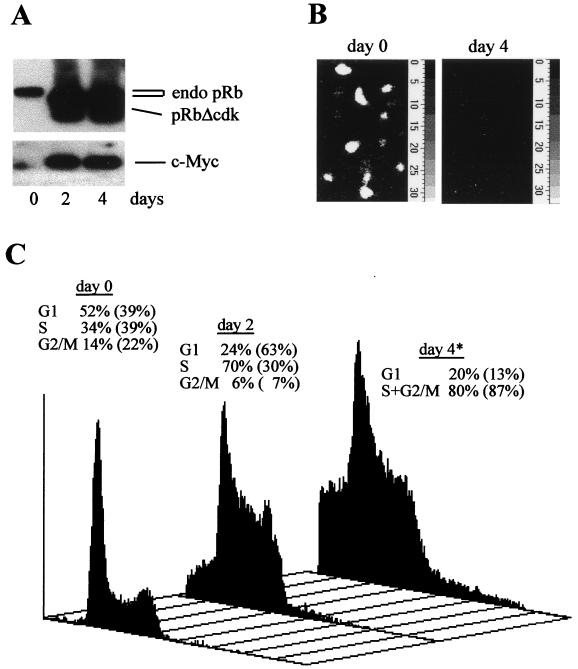
To assess whether c-Myc could mimic the cell cycle effects of cyclin E in cells deprived of E2F activity long term, U2OS clones conditionally coexpressing c-Myc with pRbΔcdk were generated. Expression of the transgenes in U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc clones was strongly induced in a homogenous and sustained manner in more than 90% of the cells after removal of TET (Fig. 2A and data not shown). Since Myc can reportedly induce E2F-1 gene expression and activate the E2F-2 promoter (40, 67) and it is still debated whether certain effects of Myc on the cell cycle, (i.e., induction of cyclin E and Cdc25A) are in fact indirect via increased E2F activity (3, 53, 72), we tested whether Myc was able to regenerate E2F activity in U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc cells. These cells displayed a high level of activity of the 6xE2F-Luc reporter when transgene expression was repressed as opposed to the absence of photon emission above the background after induction (Fig. 2B). Hence, these cells expressed a fully functional pRbΔcdk able to repress E2F activity even in presence of increased levels of active c-Myc (see Fig. 2A and below). This was independently confirmed by the remarkable transcriptional down-regulation of a known E2F target, cyclin A, observed after TET removal (E. Santoni Rugiu, J. Lukas, and J. Bartek, unpublished data).
FIG. 2.
Characterization of U2OS cells conditionally coexpressing c-Myc and pRbΔcdk. (A) Immunoblotting with MAbs to pRb and c-Myc. Expression of the ectopic proteins is tightly repressed in a representative U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc clone (clone A4C7) exposed to TET (day 0), as opposed to the high levels observed during the induction time. endo pRb, endogenous pRb. Endogenous c-Myc migrates as a faint band just below the ectopic one. (B) Endogenous E2F activity examined by in vivo photon emission imaging in cells injected with 6xE2F-Luc reporter before (day 0) or after (day 4) coinduction of transgenes. The average emission per cell during the acquisition period (10 min) was (24 ± 15) × 103 and (0.5 ± 0.3) × 103 light counts at days 0 and 4, respectively. The background value was (0.4 ± 0.2) × 103 light counts. (C) Myc stimulates S-phase entry in cells deprived of E2F activity. Representative flow-cytometric DNA histograms of propidium iodide-stained U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc cells grown with (day 0) or without TET for the indicated times. The cell cycle distribution at each time point is indicated above the histograms. As in Fig. 1C, the numbers in parentheses represent the corresponding distribution of U2OS-RbΔcdk cells at the same time points. The asterisk is as defined in the legend to Fig. 1C. Note the presence of pre-G1 (apoptotic) cells and endoreplication after transgene induction in U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc cells. The time course was reproduced at least three times in this clone and in other independent clones.
Myc can promote S-phase entry and activate cyclin E-associated kinase in the absence of E2F activity.
Having established the model cell line, we investigated whether ectopic Myc expression in cells stably deprived of E2F activity would have effects resembling those caused by exogenous cyclin E. Flow-cytometric analysis of DNA content showed that U2OS-RbΔcdk/CycE and U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc cells behaved very similarly upon long-term induction of the transgenes. Indeed, coinduction of pRbΔcdk and c-Myc rapidly stimulated S-phase entry and persistent DNA replication without, however, being able to significantly restore productive cell division (Fig. 2C). In comparison, induction of c-Myc transgene alone (U2OS-Myc cells) stimulated progression through all phases of the cell cycle (Table 1 and data not shown), in agreement with the idea that Myc plays a role in both G1 and G2 (48, 53) and with the requirement of intact E2F activity for completion of cell division (described above). In U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc cells, we also observed endoreplication and apoptosis after 2 to 3 days of induction (Fig. 2C), consistent with similar effects of Myc in other systems in which cell cycle progression is perturbed (41, 60). The molecular basis underlying the delayed apoptosis is currently under investigation in our laboratory. The absence of apoptosis in U2OS-RbΔcdk, U2OS-RbΔcdk/CycE, and U2OS-Myc cells (reference 47 and this work) suggests that the effect is specific to coexpression of Myc and pRbΔcdk and is unlikely to be caused by activation of CDK2, in line with previous observations (63).
TABLE 1.
MM inhibits Myc-induced S-phase entry in U2OS clonesa
| Cells | % of cells in phase:
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| G0/G1 | S | G2/M | |
| U2OS-Myc + TET | 57 | 32 | 11 |
| U2OS-Myc + TET + MM | 71 | 16 | 13 |
| U2OS-Myc − TET | 35 | 41 | 24 |
| U2OS-Myc − TET + MM | 49 | 33 | 18 |
| U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc + TET | 53 | 35 | 12 |
| U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc + TET + MM | 73 | 15 | 12 |
| U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc − TET | 20 | 74 | 6 |
| U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc − TET + MM | 53 | 39 | 8 |
Each cell cycle profile was evaluated at least three times and in independent clones with similar results. After being electroporated with 5 μg of pCMV or pCMVMadMyc (MM) and 0.5 μg of pCMV-CD20, cells were cultured in TET-containing (+ TET) or TET−free (− TET) medium for 3 days. The cell cycle distribution of CD20-positive cells was analyzed by flow cytometry with CellQuest software and quantified with ModFit software. In preliminary experiments, expression of CD20 did not change the cell cycle profiles of each clone in either the repressed or induced state.
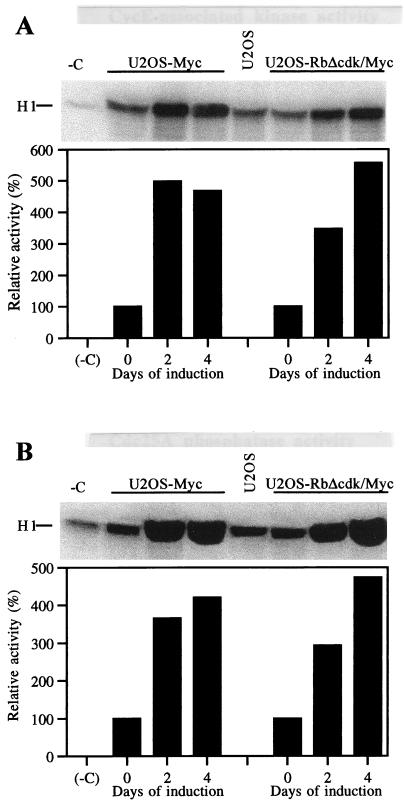
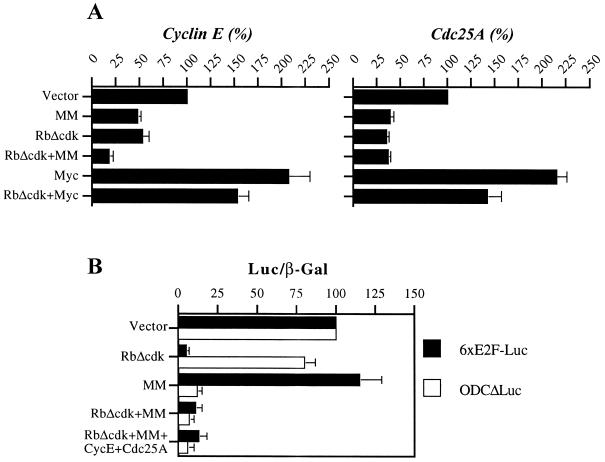
Collectively, our results suggested that c-Myc can promote G1/S transition and DNA replication in the absence of E2F activity, possibly by stimulating cyclin E-CDK2. Validating this assumption, cyclin E-associated kinase activity increased up to approximately fivefold after coinduction of pRbΔcdk and Myc for 4 days (Fig. 3A). Concomitantly, we observed a significant increment of Cdc25A phosphatase activity reaching almost fivefold at day 4 (Fig. 3B). Preliminary experiments demonstrated the absence of intrinsic histone H1 kinase activity in Cdc25A immunoprecipitates throughout the time course of the observation (data not shown), thus confirming the specificity of our findings. Given that Cdc25A is thought to be a downstream target of Myc, capable of activating cyclin E-CDK2 (6, 20), our observations suggest that the stimulation of cyclin E-dependent kinase in U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc cells may be partly mediated by induction of Cdc25A activity. They also indicate that forced Myc expression can significantly induce both enzymatic activities in the absence of E2F activity. In this respect, similar induction levels of cyclin E-associated kinase and Cdc25A phosphatase activities were observed in derepressed U2OS-Myc cells (Fig. 3).
FIG. 3.
Ectopic Myc can induce both cyclin E-associated kinase and Cdc25A phosphatase activities in cells deprived of E2F activity long term. (A) Histone H1 kinase activity coimmunoprecipitated with cyclin E from U2OS-Myc (left) and U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc (right) cell samples isolated at the indicated times after transgene induction. The kinase activity of wild-type, nonclonal U2OS cells is also shown (U2OS lane) for comparison with that of TET-repressed clones (days 0). −C, negative control lane. (B) Cdc25A phosphatase activity in U2OS-Myc (left) and U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc (right) cells harvested at the indicated times after transgene induction. The phosphatase activity was indirectly assessed as cyclin B1-CDC2 kinase activity induced by Cdc25A immunoprecipitates as described in Materials and Methods. Cdc25A activity in TET-repressed clones (days 0) is comparable to that in wild-type U2OS cells (U2OS lane). No detectable histone H1 kinase activity was found associated with Cdc25A immunoprecipitated from either induced or uninduced cells when coincubation with cyclin B1-CDC2 immunocomplexes was omitted (not shown). After quantification, the activities were normalized for the negative control (−C lane) and expressed as percentages relative to those of TET-repressed cells set at 100%. Each panel is representative of three independent experiments with similar results.
MM antagonizes Myc activity and inhibits S-phase entry in U2OS-Myc and U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc clones.
The approach described so far, like previous ones used by others to study Myc function, presented the caveat that the effects caused by forced expression of Myc may not necessarily indicate a faithful transcriptional regulation in vivo. In fact, nonphysiological levels of Myc might be able to overpower endogenous promoter-interacting factors (10, 53). The comparison of parental, Myc-null, and Myc-replaced null Rat-1 fibroblasts recently raised this issue by showing that among several putative target genes examined, only the expression of endogenous cad, gadd45, and c-myc was clearly dependent on Myc (10). Moreover, c-MycS, a naturally occurring c-Myc translational variant lacking ∼100 amino-terminal amino acids of the transactivation domain, can only transrepress and not transactivate Myc targets and yet can elicit proliferation and apoptosis and rescue the phenotype of Myc-null fibroblasts (74). Thus, though ill-defined, the ability of Myc to restrain antiproliferative and differentiation-related genes also appears to be important for Myc biological functions (10, 14, 24, 74). To overcome the problems inherent in Myc overexpression, we chose to further investigate the E2F-independent G1/S control mediated by Myc activity by antagonizing the latter with the chimeric protein MM (5). In this dominant-negative allele, Myc amino acids aa 1 to 263, comprising the highly conserved N-terminal domains necessary for Myc-dependent transactivation, transrepression, and biological activities (14, 26, 74), are substituted for by the transcriptional repression domain of Mad (14, 19, 26). Consequently, MM via its intact DNA binding and dimerization domains binds to the genomic sites normally occupied by c-Myc and actively antagonizes gene regulation by Myc (5).
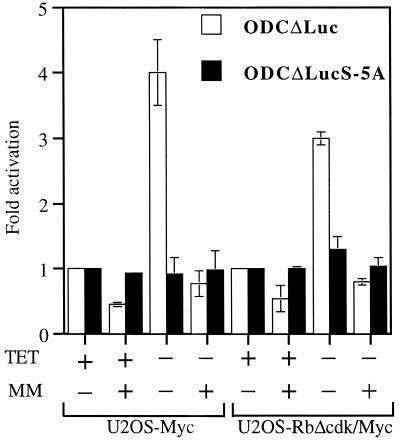
We first verified the ability of MM to effectively inhibit Myc activity by using our U2OS clones (Fig. 4). We observed a seven- to eightfold induction of the synthetic, four-E-box-containing, Myc-responsive reporter M4-Luc (data not shown) and a three- to fourfold activation of the natural, two-E-box-containing, Myc-responsive reporter ODCΔLuc (56) in derepressed U2OS-Myc and U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc cells (Fig. 4). These results were consistent with previously reported levels of promoter transactivation by Myc (10, 14, 26, 56). Importantly, proficient expression of MM (as assessed by immunoblotting of electroporated cell lysates; data not shown) not only halved the basal activity of either reporter in the repressed clones (likely by inhibiting endogenous Myc activity), but also completely abolished their activation when Myc expression was induced (Fig. 4 and data not shown). This indicates that MM can suppress Myc-responsive promoters even when levels of active Myc are increased. In contrast, the mutant ODCΔLucS-5A reporter, in which the two E-boxes are mutated, or a reporter without E-boxes, like Tatab-Luc, showed neither activation in the clones cultured without TET nor inhibition by MM (Fig. 4 and data not shown), indicating the Myc-specific transrepressive effect of MM. We next examined the effects of MM on the cell cycle profiles of our U2OS clones by electroporating them with MM and CD20 and analyzing CD20-positive cells by flow cytometry (Table 1). TET-repressed U2OS-Myc and U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc cells were both arrested in G1 by expression of MM, consistent with the MM-induced G1 arrest observed in NIH 3T3 cells (5). More importantly, MM was also able to effectively antagonize the accelerated S-phase entry in derepressed cells, particularly those from the U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc clone in which it reestablished a profile comparable with that of TET-exposed cells (Table 1). These data supported the notion that c-Myc transcriptional activity is instrumental in controlling a G1/S-promoting “parallel” pathway in cells deprived of E2F activity.
FIG. 4.
Myc transcriptional activity and its inhibition by MM in U2OS-Myc and U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc cells. Cells were electroporated with the indicated reporters plus either empty vector or MM and analyzed for luciferase activity after a 48-h culture in medium with or without TET. For either clone, the basal activity of vector-electroporated, TET-repressed cells was arbitrarily set at 1. Results are expressed as mean luciferase activity normalized to β-galactosidase activity ± standard deviation of three experiments performed in triplicate.
Independent inhibition of DNA synthesis by blocking of endogenous E2F or Myc activities is overcome by cyclin E or Cdc25A.
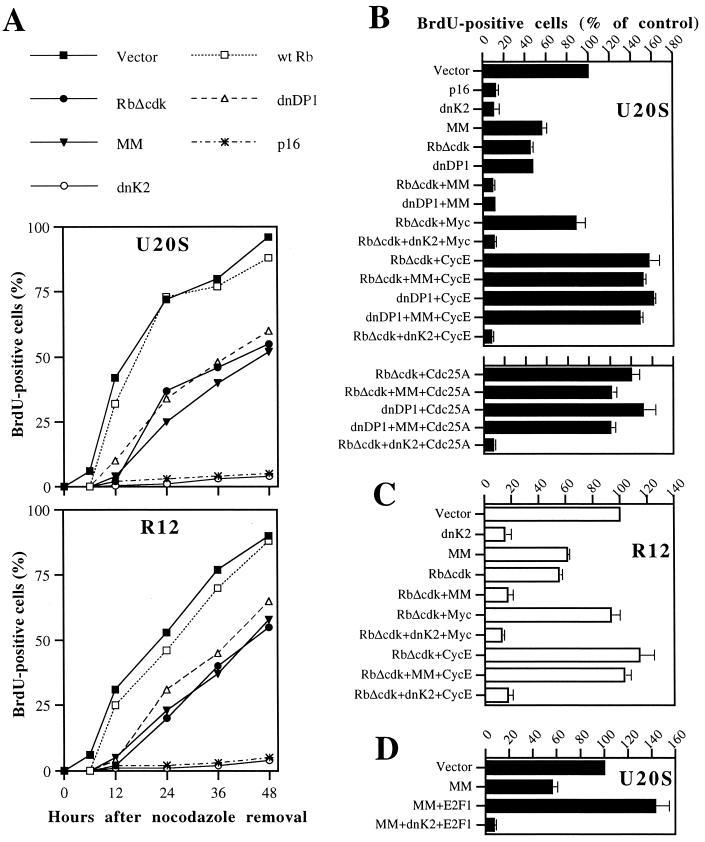
Because MM proved to be such an effective tool for antagonizing Myc activity and cell cycle function, we focused our attention on a system in which we could block either endogenous E2F or Myc activity or both simultaneously and assess the impact on G1/S transition. For this purpose, synchronized U2OS-TA or R12 cells transfected with the plasmids indicated in Fig. 5A were first monitored for 48 h to assess their pattern of BrdU incorporation after nocodazole removal. With this analysis, empty vector-transfected U2OS cells showed evident DNA replication already between 6 and 12 h after nocodazole removal, followed closely by cells transfected with wild-type Rb that is effectively inactivated by endogenous CDKs. Instead, cells productively transfected with RbΔcdk or with dnDP1 initiated DNA synthesis some 12 h later, in accordance with our previous findings that a block of the pRb/E2F pathway can significantly delay but not prevent S-phase entry (47). Importantly, the abrogation of Myc transcriptional activity by MM expression caused a similar delay of DNA synthesis and not permanent arrest, consistent with the prolonged G1 phase of Myc-null cells (48). Also noteworthy is that cells deprived of E2F or Myc activity never reached the levels of DNA synthesis observed in control cells during the 48-h time course. The kinetics of this G1/S delay was entirely reproducible in diploid R12 rat fibroblasts (Fig. 5A, bottom), ruling out cancer-associated as well as species- and cell-type-specific effects. Thus, our results suggested that either activity may suffice for DNA synthesis, but the intactness of both is necessary for timely initiation and proper levels of DNA replication in mammalian cells. In contrast, cells exposed to p16, which imposes a sustained G1 arrest by inhibiting both cyclin D-CDKs and cyclin E-CDK2 (32, 47, 50), virtually never initiated DNA synthesis for the entire time course (Fig. 5A, top). Equivalent prevention of DNA synthesis was observed upon ectopic expression of a dominant-negative CDK2 allele (dnK2), concordant with the idea that cyclin E-CDK2 activity is required for proper initiation of DNA replication (31, 37, 39).
FIG. 5.
E2F and Myc activities cooperate in regulating timing and levels of DNA synthesis by targeting cyclin E-CDK2 activity. (A) The blocking of either E2F or Myc activity delays and lowers but does not prevent DNA synthesis. CD20-positive U2OS or R12 cells expressing the indicated plasmids (wild-type [wt] Rb, RbΔcdk, dnDP1, and p16 at 5 μg; MM and dnK2 at 15 μg), were assayed for BrdU incorporation over 48 h after release from nocodazole arrest. Empty vector was added to a total of 25 μg of DNA/100-mm-diameter dish. A representative example of three comparable experiments is shown. (B and C) Cyclin E and Cdc25A are downstream targets of the E2F- and Myc-dependent pathways for S-phase entry. (B) Cyclin E-induced (top panel) or Cdc25A-induced (bottom panel) rescue of DNA synthesis in U2OS cells deprived of E2F and Myc activities is inhibited by dnK2. CD20-positive cells exposed to the indicated combinations of plasmids (Myc, cyclin E, and Cdc25A at 5 μg; the others as in panel A) were assayed for BrdU labeling 20 h after nocodazole removal. Data, expressed as a percentage of the control, are means ± standard deviations of five experiments. (C) Rescue effect of cyclin E in R12 cells analyzed as in panel B. Experiments with dnDP1 and with Cdc25A are omitted for simplicity. (D) Rescue effect of ectopic E2F1 (5 μg) in U2OS cells devoid of Myc activity is abolished by dnK2. Assay performed as in panel B.
To better judge the importance of each pathway in the initiation of DNA synthesis we examined BrdU incorporation 20 h after nocodazole removal, a time point allowing detection of significant levels of DNA synthesis in control cells and also in those with a block of either transcriptional function. In line with what was seen during the time course, BrdU incorporation was reduced by about 50% in cells exposed to either RbΔcdk, dnDP1, or MM and was minimal in p16- and dnK2-expressing cells, compared to that of vector-transfected cells (Fig. 5B, top panel, and C). Interestingly, BrdU labeling was almost completely abolished by the combined expression of MM with RbΔcdk or dnDP1, arguing for an independent control of DNA synthesis by E2F and Myc activities. Next, we tested the rescue capacity of molecules we had postulated to be involved in the “parallel” pathway's function, with the intent to determine whether cyclin E-CDK2 may be a downstream target. Coexpression of c-Myc with RbΔcdk essentially restored the levels of DNA synthesis exhibited by control cells. This rescue effect of Myc was totally abrogated by dnK2, confirming that Myc-stimulated S-phase entry in cells deprived of E2F activity relies on activation of cyclin E-CDK2 activity (Fig. 3). Consistent with that, cyclin E dramatically rescued the RbΔcdk- or dnDP1-mediated reduction of DNA synthesis, inducing a massive acceleration of S-phase entry that, again, could be entirely inhibited by quenching CDK2 activity with dnK2 (Fig. 5B, top panel). Strikingly, the dramatic rescue by cyclin E was absolutely unaffected by the concomitant blocking of both pathways via MM plus RbΔcdk or dnDP1, meaning that cyclin E-CDK2 is a common downstream target. These conclusions were further corroborated by comparable results in R12 cells (Fig. 5C). It is worth noting that cyclin E overexpression did not affect the stability of pRbΔcdk, dnDP1, or MM or their combination (Fig. 1A and data not shown), ruling out the possibility that the rescue properties of cyclin E were due to artifactual degradation of these mutants. Given our observations that Myc can enhance Cdc25A-associated phosphatase activity in cells devoid of E2F activity (Fig. 3), we also ascertained whether Cdc25A, a potential transcriptional target of both Myc and E2F (20, 72) shown to be required for S-phase entry (28, 33), may have rescue capabilities similar to those of cyclin E. This was the case, because ectopic Cdc25A stimulated massive DNA replication not only in cells deprived of E2F activity by RbΔcdk or dnDP1, but also in those with a concomitant abrogation of Myc activity by MM (Fig. 5B, bottom panel, and data not shown). Furthermore, the rescue properties of Cdc25A were completely neutralized by coexpression of dnK2, suggesting that they depended on CDK2 activity. Finally, ectopic E2F-1 potently rescued the S phase in MM-treated cells (Fig. 5D) and, again, this effect was abolished by coexpression of dnK2, further supporting the notion of a parallel Myc and E2F pathway converging on cyclin E-CDK2.
Both E2F and Myc activities are required for proper cyclin E and Cdc25A gene expression.
To address the issue of whether E2F and Myc transcriptional activities may affect cyclin E-CDK2 activity by regulating cyclin E and/or Cdc25A gene expression, we quantified by RT-PCR the levels of the corresponding mRNAs in synchronized and magnetically isolated cells productively transfected with RbΔcdk, MM, or both. By this technique, we observed that cyclin E RNA levels were decreased by ∼50% in cells expressing either RbΔcdk or MM when compared with control vector-transfected cells, further reduced to less than 20% of control value in cells coexpressing both mutants (Fig. 6A). To rule out that the effect of MM was indirectly due to reduction of E2F activity and/or cell cycle position, we tested the activity of the 6xE2F-Luc reporter in MM-expressing cells. We found no significant change over cells transfected with empty vector, whereas as expected, pRbΔcdk was able to inhibit this reporter and MM repressed ODCΔLuc activity (Fig. 6B). By the same token, pRbΔcdk, but not MM, was able to inhibit the luciferase activity of a reporter containing the E2F-responsive region of the E2F-1 promoter (E. Santoni-Rugiu, J. Lukas, and J. Bartek, unpublished data). These data suggested that E2F and Myc transcriptional activities regulate expression of endogenous cyclin E, at least in part, independently and synergistically. In addition, both RbΔcdk and MM caused a more than 60% reduction of Cdc25A RNA levels, but no further decrease was observed when RbΔcdk and MM were combined (Fig. 6A), implying that other factors may also play a significant role in sustaining Cdc25A transcription. Finally, ectopic expression of c-Myc yielded an approximately twofold induction of either cyclin E or Cdc25A RNA (Fig. 6A) and completely rescued their transcription in cells exposed to pRbΔcdk, increasing almost threefold the levels of these RNAs (Fig. 6A, RbΔcdk versus RbΔcdk+Myc). This confirms that changes in Myc activity may result in modulation of these two genes as well in an E2F-independent manner. All together, our findings indicate that Myc and E2F activities are both required for proper cyclin E and Cdc25A expression during G1/S transition.
FIG. 6.
E2F and Myc activities are both required for proper cyclin E and Cdc25A transcription during G1/S. (A) RNA expression levels in magnetically sorted U2OS cells expressing the indicated plasmids were assessed by RT-PCR 20 h after nocodazole removal. PhosphorImager scans of PCR products were normalized to the PBGD housekeeping gene and quantified by ImageQuant software. Values, expressed as a percentage of the control, are means ± standard deviations of three experiments. (B) MM does not significantly affect endogenous E2F activity in synchronized cells. Cells were synchronized and transfected with 2 μg of 6xE2F-Luc or ODCΔLuc reporter and 0.5 μg of pCMV-LacZ plus the indicated plasmids as in Fig. 5 (except for cyclin E and Cdc25A, used at minimal doses as in Fig. 7). Note that cyclin E and Cdc25A do not reactivate reporter activities in cells coexpressing RbΔcdk and MM. Reporter activities were assayed 20 h after nocodazole removal, normalized for β-galactosidase activity, and expressed as a percentage of the control (vector transfected) cells. Shown are means of two independent experiments in triplicate.
Transcriptional regulation of cyclin E and Cdc25A gene expression is one of the mechanisms by which E2F and Myc activities control G1/S transition.
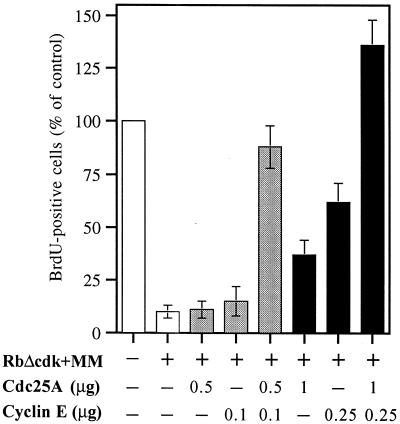
To further emphasize the importance of this issue for DNA replication, we entertained the possibility that even subtle changes in cyclin E and Cdc25A gene expression may have a strong impact on the corresponding CDK2-activating activities. Indeed, endogenous cyclin E and Cdc25A are expressed and their associated enzymatic activities are activated at the same time during the cell cycle (6, 33, 35). Moreover, Cdc25A activity appears to be required for E2F1-induced S phase, and coexpression of cyclin E and Cdc25A, like that of active cyclin E-CDK2, is sufficient to induce S phase in quiescent fibroblasts (13, 72). Thus, we postulated that Myc and E2F activities may govern the mechanism described by Hoffman et al. (28) in which cyclin E or CDK2 phosphorylates and activates Cdc25A, resulting in a positive feedback loop that amplifies the kinase's activity and ensures S-phase entry. We wished to test this cooperative mechanism in our system as well to clarify the powerful induction of DNA synthesis by ectopic cyclin E or Cdc25A in cells deprived of both E2F and Myc activities. To this end, we first determined with pilot titration experiments the minimum amount of cyclin E or Cdc25A cDNA able to restore significant levels of DNA synthesis in synchronized cells cotransfected with RbΔcdk and MM and the subminimal dose unable to do so (not shown). We next demonstrated that cells coexpressing RbΔcdk and MM were able to restore DNA synthesis at levels comparable to those of control cells, when subthreshold amounts of cyclin E (0.1 μg) and Cdc25A (0.5 μg) expression vectors were combined (Fig. 7). Consistent with that, the combination of minimal cyclin E (0.25 μg) and Cdc25A (1 μg) doses produced levels of DNA replication more than twice those observed in cells exposed to either dose alone. Nonetheless, neither this latter combination nor the maximal doses (5 μg) of cyclin E or Cdc25A shown on Fig. 5 were capable of reactivating E2F or Myc reporter activity (Fig. 6B and data not shown). This suggests that the S-phase rescue by these ectopic proteins is independent of E2F or Myc transcriptional activities. Hence, cyclin E and Cdc25A are downstream targets of both pathways, and even relatively small adjustments in their expression orchestrated by either Myc or E2F may well result in amplification of critical G1/S-promoting activities.
FIG. 7.
Synergistic rescue of DNA synthesis by subminimal (gray bars) and minimal (black bars) doses (indicated in micrograms) of Cdc25A and cyclin E expression vectors in U2OS cells deprived of both E2F and Myc activities by coexpression of RbΔcdk and MM. CD20-positive cells were assayed for BrdU labeling 20 h after nocodazole removal. Results, expressed as a percentage of the control (empty vector-transfected cells), are means ± standard deviations of three experiments.
DISCUSSION
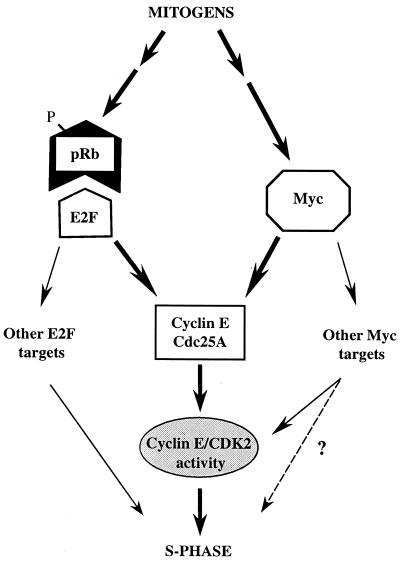
Our current data strongly point to Myc transcriptional activity regulating a cyclin E-targeting mechanism capable of promoting the G1/S transition in parallel with the pRb/E2F pathway in mammalian cells (Fig. 8). By employing novel U2OS-inducible cell lines, we show that ectopic expression of Myc, like that of cyclin E, can rapidly induce S-phase entry and persistent DNA replication in cells deprived of E2F function long term by constitutively active pRb. This effect was not connected with restoration of E2F activity, but was associated with increased Myc activity and abolished by antagonizing the latter with the dnMM mutant. Hence Myc, like the putative downstream target cyclin E, can perform G1/S-promoting functions independent of E2F activity. This property was associated with induction of cyclin E-dependent kinase and Cdc25A phosphatase activities, implying that control of cyclin E and Cdc25A by Myc is not necessarily consequential to increased E2F activity (3, 53). Cyclin E- and cyclin A-CDK2 complexes are likely targets for Cdc25A activity in vivo (6; Mailand et al., submitted). However cyclin A is not expressed, and cyclin A-associated kinase is silenced in cells deprived of E2F activity (43, 47), even when Myc is induced (Santoni-Rugiu et al., unpublished data). Thus, the similar temporal induction patterns of Cdc25A phosphatase and cyclin E-CDK2 activities in derepressed U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc cells suggest that, in this context, Cdc25A may contribute to cyclin E-CDK2 activation.
FIG. 8.
Schematic model of cyclin E-associated kinase activity as an integrative convergence point for the regulation of G1/S transition by the “classic” pRb/E2F and the “parallel” Myc-dependent pathways in mammalian cells (thick arrows). Mitogenic signals lead to inactivation of pRb and release of E2F and to activation of Myc. The resulting transcriptional activities may independently contribute to cyclin E and Cdc25A expression, thereby inducing cyclin E-CDK2 activity, which stimulates DNA synthesis (see text for details). This model appears to be part of a more complex setting in which E2F may further control the S phase by inducing other downstream targets involved in DNA replication (Cdc6, MCM1 to MCM7, cyclin A, etc.), whereas Myc may control cyclin E-CDK2 activity also indirectly through functional inactivation of CKIs (thin arrows). The role played by Myc downstream targets other than cyclin E and Cdc25A in S-phase induction remains to be defined (dotted arrow). Also, the possibility that E2F and Myc stimulate each other's expression and activity cannot be ruled out.
Although the impact of the G1/S “parallel” pathway with respect to other stages of cell cycle remains to be further explored, we found that coinduction of either Myc or cyclin E with pRbΔcdk was unable to restore productive cell division over an extended period of time. Thus, even in presence of activated cyclin E-associated kinase, the intactness of E2F activity appears essential for the orderly completion of mammalian cell cycle, in accord with a role for the pRb/E2F pathway extending beyond the control of G1/S transition (see, for instance, references 11, 39, 43, and 51).
To elucidate in more detail the existence of parallel Myc and E2F pathways for S-phase entry, we developed a system to block endogenous E2F and/or Myc activity and assess the impact on G1/S transition in synchronized cells. By this approach, we have shown in different cell types that blocking either of these activities significantly delays and lowers, but does not prevent, DNA replication, while the concurrent blocking of both activities virtually abolishes it. These findings support the concept of an independent role of Myc and E2F activities in controlling the G1/S transition and suggest that they are both necessary to cooperatively allow timely and proper initiation of DNA synthesis in mammalian cells (Fig. 8). This independent but apparently synergistic control of S-phase entry depends on the capacity to activate cyclin E-CDK2 kinase. Indeed, the data from U2OS-RbΔcdk/CycE (Fig. 1) and U2OS-RbΔcdk/Myc (Fig. 2) cells and from transiently transfected cells (Fig. 5B and C) indicate that both cyclin E and Myc can strongly induce DNA replication in cells deprived of E2F activity. This property of Myc and cyclin E is nullified by the expression of a dnK2 allele. Moreover, while ectopic E2F-1 potently rescues S phase in cells deprived of Myc activity, cyclin E and Cdc25A are able to dramatically overcome the abrogation of DNA synthesis due to a concomitant block of both Myc- and E2F-dependent pathways. Again, the rescue capabilities of E2F-1 or Cdc25A are completely neutralized by dnK2. Collectively, these results indicate that cyclin E-CDK2 activity is a common rate-limiting target of both transcriptional pathways for entry into S phase.
Our findings are supported by the previous observation that activation of cyclin E-dependent kinase by Myc requires transcription and depends on dimerization and DNA binding sites of Myc (70). They are also consistent with Myc's ability to abrogate a G1 arrest induced by wild-type pRb (23) and with the fact that serum growth factors, potent activators of the pRb/E2F pathway, synergize with ectopic Myc in activating cyclin E-CDK2 kinase in arrested fibroblasts (70). By the same token, cyclin D1 and Myc collaborate in lymphomagenesis of transgenic mice (7, 42). Finally, ectopic Ras and Myc reportedly cooperate in inducing cyclin E-CDK2 activity and S-phase entry in quiescent cells (40). This was ascribed to a combined effect of Rb pathway control by Ras, Myc-induced E2F-1 gene activation, and modulation of p27 and Cdc25A levels by Myc and Ras signaling (3, 40). The present work argues, though, that E2F activity is not strictly necessary for Myc-induced cyclin E activation and S-phase entry.
Previous experiments suggest that ectopic Myc may stimulate cyclin E-CDK2 and S-phase entry via direct induction of cyclin E or Cdc25A gene transcription or via functional inactivation of p27 (see the introduction). These mechanisms might also be operating in cells deprived of E2F activity. Indeed, our results indicate that the independent and synergistic control of S-phase entry by Myc and E2F activities relies, at least in part, on the transcriptional regulation of cyclin E and Cdc25A gene expression. In particular, repression of either E2F or Myc activity approximately halved cyclin E and Cdc25A transcription levels in synchronized cells. The effect of MM was not caused indirectly by reduced E2F activity, since MM expression did not significantly affect the activity of E2F-responsive reporters in these cells. Furthermore, ectopic Myc increased cyclin E and Cdc25A RNA levels by more than twofold (Fig. 6A, Myc) and approximately tripled the levels present in cells deprived of E2F activity (Fig. 6A, RbΔcdk+Myc). Thus, Myc and E2F activities play, at least in part, independent roles in regulating cyclin E and Cdc25A expression at the G1/S transition. In addition, suppression of both activities by RbΔcdk+MM caused a further, marked decrease of cyclin E transcription, indicating that such a regulation is synergistic. All together, our data therefore argue against the possibility that Myc may induce cyclin E gene expression only indirectly by increasing E2F activity (3, 53, 58). Cdc25A RNA levels, instead, do not further decline upon coexpression of MM and pRbΔcdk, possibly because other transcriptional factors may contribute to Cdc25A transcription. Supporting this hypothesis, binding sites for multiple transcription factors have been recently identified in a human Cdc25A promoter region (72). Observations in Myc-null cells have suggested that Myc makes a contribution of approximately twofold to Cdc25A gene activation and only during early phases of growth factor stimulation (10). However, the contribution and possible compensation by E2F or other transcription factors to Cdc25A expression in Myc-null cells have not been examined, although compensatory increases in critical Myc targets are considered possible in this experimental model (14). In any case, our data indicate that both Myc and E2F activities are required for proper cyclin E and Cdc25A expression during G1/S transition and suggest that this could have a strong impact on critical G1/S-promoting activities associated with cyclin E and Cdc25A. Indeed, we show that these two proteins can effectively cooperate in reestablishing DNA synthesis in cells devoid of both E2F and Myc activities, even when expressed in amounts unable to do it on their own. This is presumably due to a positive feedback loop between cyclin E-CDK2 and its activator Cdc25A (28). Thus, even relatively small adjustments of cyclin E and Cdc25A gene expression induced by changes in E2F or Myc activity may be critical for the decision to enter the S phase.
Further work will elucidate alternative mechanisms of cyclin E-CDK2 control by E2F-dependent and -independent pathways. However, our current findings may have important implications for cancer treatment, because they suggest that limiting E2F activity in Myc-overexpressing cells may not suffice to halt DNA replication and therefore the risk of genomic instability. In this regard, a potent growth suppressor like transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) inhibits transcription of both E2F and Myc (2, 66, 73), and the down-regulation of Myc also occurs in cells lacking pRb function and yet leads to significant cell cycle arrest (2, 75). On the other hand, despite the plethora of TGF-β inhibitory effects on cell cycle progression (2, 30, 61, 73), overexpression of Myc, like that of E2F (66), renders cells in culture or in transgenic animals resistant to this cytokine, even when the expression of CKIs and pRb is preserved (2, 17, 64, 65, 73). Depending on the cellular context, this may be achieved through functional inactivation of p27 (3, 9, 53, 57), prevention of p15 induction (73), or transcriptional control of CDK2 activators (references 20 and 58 and this work). This is relevant for those human cancers in which increased expression of TGF-β and increased expression of Myc are frequent and early events (see references 14 and 25 and references herein). In these cases, Myc activation may allow neoplastic cells to initially counteract TGF-β and induce unscheduled DNA replication, increasing the risk of additional genetic defects necessary for tumor progression.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank R. Bernards, J. L. Cleveland, B. Ducommun, R. N. Eisenman, G. Evan, A. Fattey, K. Helin, and S. I. Reed for providing important reagents; C. S. Sørensen for critical reading of the manuscript; and K. Holm and C. Lindeneg for technical assistance.
This work was supported by grants from the Danish Cancer Society, the Human Frontier Science Programme, and the Danish Medical Research Council.
REFERENCES
- 1.Alevizopoulos K, Vlach J, Hennecke S, Amati B. Cyclin E and c-Myc promote cell proliferation in the presence of p16INK4a and hypophosphorylated retinoblastoma family proteins. EMBO J. 1997;16:5322–5333. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alexandrow M G, Moses H L. Transforming growth factor β and cell cycle regulation. Cancer Res. 1995;55:1452–1457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Amati B, Alevizopoulos K, Vlach J. Myc and the cell cycle. Front Biosci. 1998;3:250–268. doi: 10.2741/a239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bartek J, Bartkova J, Lukas J. The retinoblastoma protein pathway and the restriction point. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:805–814. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Berns K, Hijmans E M, Bernards R. Repression of c-Myc responsive genes in cycling cells causes G1 arrest through reduction of cyclin E/CDK2 kinase activity. Oncogene. 1997;15:1347–1356. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Blomberg I, Hoffmann I. Ectopic expression of Cdc25A accelerates the G1/S transition and leads to premature activation of cyclin E- and cyclin A-dependent kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:6183–6194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.9.6183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bodrug S E, Warner B J, Bath M L, Lindeman G J, Harris A W, Adams J M. Cyclin D1 transgene impedes lymphocyte maturation and collaborates in lymphomagenesis with the myc gene. EMBO J. 1994;13:2124–2130. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Botz J, Zerfass-Thome K, Spitkovsky D, Delius H, Vogt B, Eilers M, Hatzigeorgiou A, Jansen-Dürr P. Cell cycle regulation of the murine cyclin E gene depends on an E2F binding site in the promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:3401–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.7.3401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bouchard C, Thieke K, Maier A, Saffrich R, Hanley-Hyde J, Ansorge W, Reed S, Sicinski P, Bartek J, Eilers M. Direct induction of cyclin D2 by Myc contributes to cell cycle induction and sequestration of p27. EMBO J. 1999;18:5321–5333. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.19.5321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bush A, Mateyak M, Dugan K, Obaya A, Adachi S, Sedivy J, Cole M. c-myc null cells misregulate cad and gadd45 but not other proposed c-Myc targets. Genes Dev. 1998;12:3797–3802. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.24.3797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chew Y P, Ellis M, Wilkie S, Mittnacht S. pRB phosphorylation mutants reveal role of pRB in regulating S phase completion by a mechanism independent of E2F. Oncogene. 1998;17:2177–2186. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chretien S, Dubart A, Beaupain D, Raich N, Grandchamp B, Rosa J, Goossens M, Romeo P H. Alternative transcription and splicing of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene result either in tissue-specific or in housekeeping expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Connell-Crowley L, Elledge S J, Harper J W. G1 cyclin-dependent kinases are sufficient to initiate DNA synthesis in quiescent human fibroblasts. Curr Biol. 1998;8:65–68. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dang C V. c-Myc target genes involved in cell growth, apoptosis, and metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:1–11. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Duronio R J, Brook A, Dyson N, O'Farrell P H. E2F-induced S phase requires cyclin E. Genes Dev. 1996;19:2505–2513. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.19.2505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Duronio R J, O'Farrell P H. Developmental control of the G1 to S transition in Drosophila: cyclin E is a limiting downstream target of E2F. Genes Dev. 1995;12:1456–1468. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.12.1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Factor V, Kao C-Y, Santoni-Rugiu E, Woitach J T, Jensen M R, Thorgeirsson S S. Constitutive expression of mature transforming growth factor β1 in the liver accelerates hepatocarcinogenesis in transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1997;57:2089–2095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Felsher D W, Bishop J M. Transient excess of Myc activity can elicit genomic instability and tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:3940–3944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Foley K P, Eisenman R N. Two MAD tails: what the recent knockouts of Mad1 and Mxi1 tell us about the MYC/MAX/MAD network. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1423:M37–M47. doi: 10.1016/s0304-419x(99)00012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Galaktionov K, Chen X, Beach D. Cdc25 cell-cycle phosphatase as a target of c-myc. Nature. 1996;382:511–517. doi: 10.1038/382511a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Geng Y, Eaton E N, Picon M, Roberts J M, Lundberg A S, Gifford A, Sardet C, Weinberg R A. Regulation of cyclin E transcription by E2Fs and retinoblastoma protein. Oncogene. 1996;12:1173–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Geng Y, Whoriskey W, Park M Y, Bronson R T, Medema R H, Li T, Weinberg R A, Sicinski P. Rescue of cyclin D1 deficiency by knockin cyclin E. Cell. 1999;97:767–777. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80788-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Goodrich D W, Lee W H. Abrogation by c-myc of G1 phase arrest induced by RB protein but not by p53. Nature. 1992;360:177–179. doi: 10.1038/360177a0. . (Erratum, 360:491.) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Grandori C, Eisenman R N. Myc target genes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:177–181. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(97)01025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.He T-C, Sparks A B, Rago C, Hermeking H, Zawel L, da Costa L T, Morin P J, Vogelstein B, Kinzler K W. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science. 1998;281:1509–1512. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5382.1509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Henriksson M, Lüscher B. Proteins of the Myc network: essential regulators of cell growth and differentiation. Adv Cancer Res. 1996;68:109–182. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60353-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Herrera R E, Sah V P, Williams B O, Mäkelä T P, Weinberg R A, Jacks T. Altered cell cycle kinetics, gene expression, and G1 restriction point regulation in Rb-deficient fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:2402–2407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.5.2402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hoffmann I, Draetta G, Karsenti E. Activation of the phosphatase activity of human cdc25A by cdk2-cyclin E dependent phosphorylation at the G1/S transition. EMBO J. 1994;13:4302–4310. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06750.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hua X H, Newport J. Identification of a preinitiation step in DNA replication that is independent of origin recognition complex and cdc6, but dependent on cdk2. J Cell Biol. 1998;140:271–281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.140.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Iavarone A, Massagué J. Repression of the CDK activator Cdc25A and cell-cycle arrest by cytokine TGF-β in cells lacking p15. Nature. 1997;387:417–422. doi: 10.1038/387417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jackson P K, Chevalier S, Philippe M, Kirschner M W. Early events in DNA replication require cyclin E and are blocked by p21CIP1. J Cell Biol. 1995;130:755–769. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.4.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jiang H, Chou H S, Zhu L. Requirement of cyclin E-Cdk2 inhibition in p16INK4a-mediated growth suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:5284–5290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.9.5284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jinno S, Kuto S, Nagata A, Igarashi M, Kanaoka Y, Nojima H, Okayama H. Cdc25A is a novel phosphatase functioning early in the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1994;13:1549–1556. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06417.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Johnson D G, Schwarz J K, Cress W D, Nevins J R. Expression of transcription factor E2F1 induces quiescent cells to enter S phase. Nature. 1993;13:349–352. doi: 10.1038/365349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Keyomarsi K, Herliczek T W. The role of cyclin E in cell proliferation, development and cancer. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 1997;3:171–191. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5371-7_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Knudsen E S, Buckmaster C, Chen T T, Feramisco J R, Wang J Y. Inhibition of DNA synthesis by RB: effects on G1/S transition and S-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1998;15:2278–2292. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.15.2278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Krude T, Jackman M, Pines J, Laskey R A. Cyclin/cdk-dependent initiation of DNA replication in a human cell-free system. Cell. 1997;88:109–119. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81863-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Leng X, Connell-Crowley L, Goodrich D, Harper J W. S-phase entry upon ectopic expression of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases in the absence of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Curr Biol. 1997;7:709–712. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Leone G, DeGregori J, Jakoi L, Cook J G, Nevins J R. Collaborative role of E2F transcriptional activity and G1 cyclin-dependent kinase activity in the induction of S phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:6626–6631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Leone G, DeGregori J, Sears R, Jakoi L, Cook J G, Nevins J R. Myc and Ras collaborate in inducing accumulation of active cyclin E/Cdk2 and E2F. Nature. 1997;387:422–426. doi: 10.1038/387422a0. . (Erratum, 387:932.) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Li Q, Dang C V. c-Myc overexpression uncouples DNA replication from mitosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:5339–5351. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.8.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lovec H, Grzeschiczek A, Kowalski M B, Möroy T. Cyclin D1/bcl-1 cooperates with myc genes in the generation of B-cell lymphoma. EMBO J. 1994;13:3487–3495. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lukas C, Sørensen C S, Kramer E, Santoni-Rugiu E, Lindeneg C, Peters J-M, Bartek J, Lukas J. Accumulation of cyclin B1 requires E2F and cyclin A-dependent rearrangement of the anaphase-promoting complex. Nature. 1999;401:815–818. doi: 10.1038/44611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lukas J, Herzinger T, Hansen K, Moroni M C, Resnitzky D, Helin K, Reed S I, Bartek J. Cyclin E-induced S phase without activation of the pRb/E2F pathway. Genes Dev. 1997;11:1479–1492. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.11.1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lukas J, Parry D, Aagaard L, Mann D J, Bartkova J, Strauss M, Peters G, Bartek J. Retinoblastoma-protein-dependent cell cycle inhibition by the tumor suppressor p16. Nature. 1995;375:503–506. doi: 10.1038/375503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lukas J, Petersen B O, Holm K, Bartek J, Helin K. Deregulated expression of E2F family members induces S-phase entry and overcomes p16INK4A-mediated growth suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:1047–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lukas J, Sørensen C S, Lukas C, Santoni-Rugiu E, Bartek J. p16INK4a, but not constitutively active pRb, can impose a sustained G1 arrest: molecular mechanisms and implications for oncogenesis. Oncogene. 1999;18:3930–3935. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mateyak M K, Obaya A J, Adachi S, Sedivy J M. Phenotypes of c-Myc-deficient rat fibroblasts isolated by targeted homologous recombination. Cell Growth Differ. 1997;8:1039–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mateyak M K, Obaya A J, Sedivy J M. c-Myc regulates cyclin D-Cdk4 and -Cdk6 activity but affects cell cycle progression at multiple independent points. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:4672–4683. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.7.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.McConnell B B, Gregory F J, Stott F J, Hara E, Peters G. Induced expression of p16INK4a inhibits both CDK4- and CDK2-associated kinase activity by reassortment of cyclin-CDK inhibitor complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:1981–1989. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.3.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Meraldi P, Lukas J, Fry A M, Bartek J, Nigg E. Centrosome duplication in mammalian somatic cells requires E2F and Cdk2/cyclin A. Nat Cell Biol. 1999;1:88–93. doi: 10.1038/10054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mumberg D, Haas K, Möroy T, Niedenthal R, Hegemann J H, Funk M, Müller R. Uncoupling of DNA replication and cell cycle progression by human cyclin E. Oncogene. 1996;13:2493–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Obaya A J, Mateyak M, Sedivy J M. Mysterious liaisons: the relationship between c-Myc and the cell cycle. Oncogene. 1999;18:2934–2941. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ohtani K, DeGregori J, Nevins J R. Regulation of the cyclin E gene by transcription factor E2F1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:12146–12150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.26.12146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ohtsubo M, Theodoras A M, Schumacher J, Roberts J M, Pagano M. Human cyclin E, a nuclear protein essential for the G1-to-S phase transition. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15:2612–2624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Packham G, Cleveland J L. Induction of ornithine decarboxylase by IL-3 is mediated by sequential c-Myc-independent and c-Myc-dependent pathways. Oncogene. 1997;15:1219–1232. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Pérez-Roger I, Kim S H, Griffiths B, Sewing A, Land H. Cyclins D1 and D2 mediate Myc-induced proliferation via sequestration of p27Kip1 and p21Cip1. EMBO J. 1999;18:5310–5320. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.19.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Pérez-Roger I, Solomon D L C, Sewing A, Land H. Myc activation of cyclin E/Cdk2 kinase involves induction of cyclin E gene transcription and inhibition of p27Kip1 binding to newly formed complexes. Oncogene. 1997;14:2373–2381. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Poon R Y C, Jiang W, Toyoshima H, Hunter T. Cyclin-dependent kinases are inactivated by a combination of p21 and Thr-14/Tyr-15 phosphorylation after UV-induced DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:13283–13291. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.22.13283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Prendergast G C. Mechanisms of apoptosis by c-Myc. Oncogene. 1999;18:2967–2987. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Reynisdóttir I, Polyak K, Iavarone A, Massagué J. Kip/Cip and Ink4 Cdk inhibitors cooperate to induce cell cycle arrest in response to TGF-β genes. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1831–1845. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.15.1831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Royzman I, Whittaker A J, Orr-Weaver T L. Mutations in Drosophila DP and E2F distinguish G1-S progression from an associated transcriptional program. Genes Dev. 1997;15:1999–2011. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.15.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rudolph B, Zwicker J, Saffrich R, Henglein B, Müller R, Ansorge W, Eilers M. Activation of cyclin dependent kinases by Myc mediates transcriptional activation of cyclin A, but not apoptosis. EMBO J. 1996;15:3065–3076. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Santoni-Rugiu E, Jensen M R, Thorgeirsson S S. Disruption of the pRb/E2F pathway and inhibition of apoptosis are major oncogenic events in liver constitutively expressing c-myc and transforming growth factor α. Cancer Res. 1998;58:123–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Santoni-Rugiu E, Jensen M R, Factor V, Thorgeirsson S S. Acceleration of c-myc-induced hepatocarcinogenesis by co-expression of transforming growth factor (TGF)-α in transgenic mice is associated with TGF-β1 signaling disruption. Am J Pathol. 1999;154:1693–1700. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65425-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Schwarz J K, Bassing C H, Kovesdi I, Datto M B, Blazing M, George S, Wang X F, Nevins J R. Expression of the E2F1 transcription factor overcomes type β transforming growth factor-mediated growth suppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:483–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sears R, Ohtani K, Nevins J R. Identification of positively and negatively acting elements regulating expression of the E2F2 gene in response to cell growth signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:5227–5235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.9.5227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Sherr C J. Cancer cell cycles. Science. 1996;274:1672–1677. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5293.1672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Spruck C H, Won K-A, Reed S I. Deregulated cyclin E induces chromosome instability. Nature. 1999;410:297–300. doi: 10.1038/45836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Steiner P, Philipp A, Lukas J, Godden-Kent D, Pagano M, Mittnacht S, Bartek J, Eilers M. Identification of a Myc-dependent step during the formation of active G1 cyclin-cdk complexes. EMBO J. 1995;14:4814–4826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00163.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.van den Heuvel S, Harlow E. Distinct roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in cell cycle control. Science. 1993;262:2050–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8266103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Vigo E, Müller H, Prosperini E, Hateboer G, Cartwright P, Moroni M C, Helin K. CDC25A phosphatase is a target of E2F and is required for efficient E2F-induced S phase. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:6379–6395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.9.6379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Warner B J, Blain S W, Seoane J, Massagué J. Myc downregulation by transforming growth factor β required for activation of the p15Ink4b G1 arrest pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:5913–5922. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.9.5913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Xiao Q, Claassen G, Shi J, Adachi S, Sedivy J, Hann S. Transactivation-defective c-MycS retains the ability to regulate proliferation and apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1998;12:3803–3808. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.24.3803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Zentella A, Weis F M B, Ralph D A, Laiho M, Massagué J. Early gene responses to transforming growth factor-β in cells lacking growth-suppressive RB function. Mol Cell Biol. 1991;11:4952–4958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Zhang H S, Postigo A, Dean D C. Active transcriptional repression by the Rb-E2F complex mediates G1 arrest triggered by p16INK4a, TGFβ, and contact inhibition. Cell. 1999;97:53–61. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80714-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]