This randomized clinical trial evaluates the use of sacubitril/valsartan therapy compared with valsartan alone in US patients with advanced chronic heart failure.
Key Points
Question
What is the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of sacubitril/valsartan in patients with advanced chronic heart failure?
Findings
In this randomized clinical trial including 335 patients with advanced heart failure, the area under the curve for the ratio of N-terminal pro–brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) relative to baseline through 24 weeks of therapy was not significantly different in 167 patients in the sacubitril/valsartan treatment arm compared with 168 patients in the valsartan treatment arm.
Meaning
The findings of this clinical trial showed no difference between sacubitril/valsartan and valsartan with respect to lowering baseline NT-proBNP levels in patients with advanced heart failure.
Abstract
Importance
The use of sacubitril/valsartan is not endorsed by practice guidelines for use in patients with New York Heart Association class IV heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction because of limited clinical experience in this population.
Objective
To compare treatment with sacubitril/valsartan treatment with valsartan in patients with advanced heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction and recent New York Heart Association class IV symptoms.
Design, Setting, and Participants
A double-blind randomized clinical trial was conducted; a total of 335 patients with advanced heart failure were included. The trial began on March 2, 2017, and was stopped early on March 23, 2020, owing to COVID-19 risk.
Intervention
Patients were randomized to receive sacubitril/valsartan (target dose, 200 mg twice daily) or valsartan (target dose, 160 mg twice daily) in addition to recommended therapy.
Main Outcomes and Measures
The area under the curve (AUC) for the ratio of N-terminal pro–brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) compared with baseline measured through 24 weeks of therapy.
Results
Of the 335 patients included in the analysis, 245 were men (73%); mean (SD) age was 59.4 (13.5) years. Seventy-two eligible patients (18%) were not able to tolerate sacubitril/valsartan, 100 mg/d, during the short run-in period, and 49 patients (29%) discontinued sacubitril/valsartan during the 24 weeks of the trial. The median NT-proBNP AUC for the valsartan treatment arm (n = 168) was 1.19 (IQR, 0.91-1.64), whereas the AUC for the sacubitril/valsartan treatment arm (n = 167) was 1.08 (IQR, 0.75-1.60). The estimated ratio of change in the NT-proBNP AUC was 0.95 (95% CI 0.84-1.08; P = .45). Compared with valsartan, treatment with sacubitril/valsartan did not improve the clinical composite of number of days alive, out of hospital, and free from heart failure events. Aside from a statistically significant increase in non–life-threatening hyperkalemia in the sacubitril/valsartan arm (28 [17%] vs 15 [9%]; P = .04), there were no observed safety concerns.
Conclusions and Relevance
The findings of this trial showed that, in patients with chronic advanced heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction, there was no statistically significant difference between sacubitril/valsartan and valsartan with respect to reducing NT-proBNP levels.
Trial Registration
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02816736
Introduction
Treatment with evidence-based medical therapies improves survival, reduces heart failure hospitalizations, and improves quality of life in patients with chronic heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction.1,2,3 However, the evidence supporting the use of medical therapies among patients with advanced heart failure is less robust, given that it may be difficult to reach the target drug doses that are achieved in clinical trials that enroll patients with milder symptoms, and patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class IV heart failure are not often enrolled in phase 3 clinical trials.4,5,6,7 The landmark Prospective Comparison of Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Neprilysin Inhibitor With Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure (PARADIGM-HF) trial reported that, compared with the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor enalapril, sacubitril/valsartan, an angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor, reduced the relative risk of cardiovascular mortality and heart failure hospitalizations by 20% in ambulatory patients with heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction.5
Although the PARADIGM-HF trial enrolled patients with NYHA class II to IV symptoms, more than 99% of the patients had NYHA class II to III symptoms. Accordingly, the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Heart Failure Society of America guidelines restricted their recommendations for the use of sacubitril/valsartan to patients with NYHA class II to III heart failure and provided no guidance with regard to its use in patients with more advanced heart failure.8 The purpose of the LCZ696 in Advanced Heart Failure (LIFE) trial was to provide additional information about the tolerability, safety, and potential efficacy of sacubitril/valsartan in patients with more advanced heart failure who were underrepresented in the PARADIGM-HF trial. The LIFE trial tested the hypothesis that sacubitril/valsartan is superior to valsartan alone in lowering N-terminal pro–brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels in patients with advanced heart failure.
Methods
Study Design
The LIFE trial was a 24-week, prospective, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active comparator phase 4 clinical trial designed to assess the tolerability, safety, and efficacy of sacubitril/valsartan compared with valsartan in patients with advanced chronic heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction and recent NYHA class IV symptoms. The details of the trial design have been reported.9 Trial enrollment began on March 2, 2017; because of the high risk for adverse outcomes associated with COVID-19 infection, trial enrollment was suspended on March 23, 2020. The original protocol and statistical analysis plan (available in Supplement 1) specified randomization and analysis of 400 participants followed up for 24 weeks. The revised statistical analysis plan specified that the primary analysis would be limited to patients randomized on or before December 7, 2019, whose week 12 study visit occurred before March 1, 2020 (n = 335).9 The trial protocol was approved by a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute protocol review committee and monitored by the Heart Failure Network’s Data and Safety Monitoring Board (eAppendix in Supplement 2). The final protocol was approved by the institutional review boards at all 38 US centers that participated. All patients provided written informed consent; participants did not receive financial compensation. Responsibility for the oversight and management of the trial was provided by the LIFE Executive Committee (eAppendix in Supplement 2). Data collection, management, and analyses were performed at the Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, North Carolina. The study protocol (with protocol amendments) and statistical analysis plan are provided in Supplement 1. This study followed the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) reporting guideline.
Participants
The inclusion and exclusion criteria are reported in eTable 1 in Supplement 2. The key entry criteria for defining advanced heart failure included (1) NYHA class IV symptoms, defined as chronic dyspnea or fatigue at rest or with minimal exertion occurring at presentation or in the previous 3 months; (2) a minimum of 3 months of guideline-directed medical therapy for heart failure and/or intolerance to such therapy; (3) ejection fraction less than or equal to 35%; (4) BNP level greater than or equal to 250 pg/mL (1:1 conversion to nanograms per milliliter) or NT-proBNP level greater than or equal to 800 pg/mL; and (5) at least 1 additional objective finding of advanced heart failure (eTable 1 in Supplement 2).
Eligible patients were enrolled and began an unblinded run-in period of 3 to 7 days with sacubitril/valsartan, 24/26 mg (50-mg fixed dose), administered orally twice daily. Participants tolerating the run-in phase were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to receive sacubitril/valsartan twice daily or valsartan twice daily. The initial doses were selected based on guidelines for initiating sacubitril/valsartan and valsartan.9 Patients also received a placebo that resembled either valsartan or sacubitril/valsartan. The study drug was titrated to attempt to reach a target dose of sacubitril/valsartan, 97/103 mg (200-mg fixed dose), twice daily or valsartan, 160 mg, twice daily.9 Dose adjustments of the study drug were performed every 2 weeks by doubling the dose of study medication up to the target or maximally tolerated subtarget dose. In patients with unacceptable adverse effects, the study drug dosage was either reduced or the drug was discontinued. Participants were evaluated at 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks.
Outcomes
The primary efficacy outcome was the area under the curve (AUC) of NT-proBNP levels at 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks compared with the level of NT-proBNP at randomization. For the end point calculation, the NT-proBNP concentrations measured at 2 to 24 weeks were divided by the concentration at randomization. The calculation of the AUC for the ratio of NT-proBNP relative to baseline through 24 weeks of therapy was based on the trapezoidal rule.
The secondary efficacy end point was the number of days the patient was alive, out of the hospital, and free from any of the following outcomes: listing for cardiac transplant, cardiac transplant, implantation of a left ventricular assist device, receipt of continuous inotropic therapy for 7 or more days, or hospitalization for heart failure on 2 or more occasions other than the index admission. The tolerability end points included an analysis through 24 weeks of the last administration of the study drug and the number of patients who developed symptomatic hypotension, worsening kidney function, or hyperkalemia (potassium level ≥5.5 mEq/L [1:1 conversion to millimoles per liter]). Tolerability was also assessed by noting the patients who were able to complete the short open run-in period. Tertiary end points included time-to-event analyses for death from cardiovascular causes or heart failure hospitalization, heart failure hospitalization, death from cardiovascular causes, all-cause death, the number of heart failure hospitalizations, time to first outpatient visit requiring intravenous diuretic therapy, and the number of patients who required continuous inotropic support for at least 1 day or 7 or more days, were listed for, or underwent heart transplantation, received a left ventricular assist device, had a change in baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate or baseline cystatin C level, or had a change in quality-of-life score assessed by the clinical summary score of the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ).
Statistical Analysis
Based on a 2-sample t test with a 2-sided type I error of .05, a sample size of 335 randomized patients was expected to have approximately 79% power to detect a 20% treatment difference (ie, ratio of change) in the AUC of NT-proBNP between sacubitril/valsartan and valsartan. For the primary analysis, missing NT-proBNP values at week 24 were imputed using the last observation carried forward of the most recent postbaseline data. Patients with missing baseline NT-proBNP levels and those without any postbaseline data were excluded. The NT-proBNP AUC for each participant was divided by the number of days used to calculate the AUC value to provide a value similar to the average daily measurement. The primary analysis used a linear regression model and included covariates for the treatment arm, log(baseline NT-proBNP) value, and baseline atrial fibrillation status. A 2-sided P value <.05 was considered significant.
Several sensitivity analyses were conducted for the primary and key secondary end points, including a nonparametric analysis with the patients assigned the worst possible value for death. All analyses were conducted using SAS, version 9.4 software (SAS Institute Inc). Measurements of NT-proBNP were performed at the Biomarker Core Laboratory (University of Vermont) using the Roche Elecsys platform (Roche Diagnostics).
Results
Participants
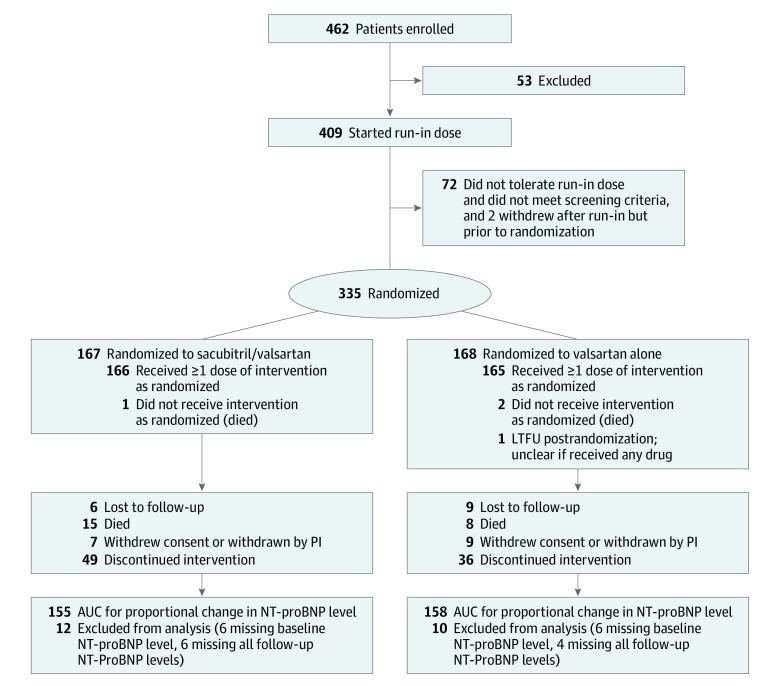
From March 2, 2017, through December 7, 2019, 462 patients with advanced heart failure were screened and provided informed consent at 38 centers. Of these, 53 individuals did not fulfill the entry criteria. Accordingly, 409 patients started the run-in phase with sacubitril/valsartan (median duration, 6 days; IQR, 4.0-7.0). Seventy-two patients (18%) did not tolerate the run-in dose and 2 patients withdrew before randomization. The salient clinical characteristics of the patients who did not tolerate the run-in phase are summarized in eTable 2 in Supplement 2. Patients who did not tolerate the run-in phase had lower systolic blood pressure, higher serum creatinine levels, and had a history of being more intolerant of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, or β-blocker therapy.
A total of 167 patients were randomly assigned to receive sacubitril/valsartan and 168 patients were randomly assigned to receive valsartan (Figure 1). The groups were well balanced, with the exception that there were more patients with ischemic heart disease in the sacubitril/valsartan arm. The mean (SD) age was 59.3 (13.3) years (median, 60; IQR, 52.0-68.0 years). A total of 90 patients (27%) were women and 245 (73%) were men. A total of 127 patients (38%) were Black, 201 patients (60%) were White, and 7 patients (2%) were of other racial or ethnic groups (numbers of specific groups too small to specify). The median duration of heart failure was 4.3 years (IQR, 1.6-10.1) with a mean (SD) ejection fraction of 20.4% (6.5%). A total of 132 patients (39%) experienced at least 1 heart failure hospitalization within 6 months of randomization, 74 patients (22%) had 2 or more heart failure hospitalizations during that period, and 20% were receiving intravenous inotropes at randomization (Table 1; eTable 3 in Supplement 2). The median baseline KCCQ overall score was 51.8 (IQR, 33.8-70.8) and the clinical score was 59.4 (IQR, 40.6-77.4). Patients were receiving recommended guideline-directed medical therapy for heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction (Table 1).
Figure 1. Enrollment, Run-in, Randomization, and Follow-up.
Patients who were randomized and provided informed consent before December 8, 2019, were included. AUC indicates area under the curve; LTFU, lost to follow-up; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro–brain natriuretic peptide; PI, principal investigator.
Table 1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics at Baselinea.
| Characteristic | No. (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sacubitril/valsartan (n = 167) | Valsartan (n = 168) | |
| Age, mean (SD), y | 60.2 (13.4) | 58.3 (13.1) |
| Sex | ||
| Men | 120 (72) | 125 (74) |
| Women | 47 (28) | 43 (26) |
| Racial or ethnic groupb | ||
| Black | 64 (38) | 63 (38) |
| White | 98 (59) | 103 (61) |
| Other | 5 (3) | 2 (1) |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 113.4 (13.6) | 112.4 (16.8) |
| Heart rate, beats/min | 81.4 (15.0) | 81.0 (14.9) |
| BMI | 29.5 (7.5) | 30.3 (7.8) |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dL | ||
| No. | 165 | 166 |
| Mean (SD) | 1.36 (0.40) | 1.36 (0.46) |
| Estimated GFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | ||
| No. | 165 | 166 |
| Mean (SD) | 63.6 (24.3) | 65.7 (25.9) |
| Features of heart failure | ||
| Ischemic cause | 140 (84) | 121 (72) |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction, % | 19.9 (6.2) | 20.9 (6.8) |
| Prior myocardial infarction | 61 (37) | 60 (36) |
| Baseline NT-proBNP, pg/mL | ||
| No. | 161 | 162 |
| Mean (SD) | 3449.6 (6616.2) | 2779.4 (3115.2) |
| Baseline NT-proBNP, pg/mL | ||
| No. | 161 | 162 |
| Median (IQR) | 1921 (1071-3502) | 1818 (929-3415) |
| Baseline NT-proBNP, geometric mean (geometric SD) | 1891.9 (2.8) | 1790.0 (2.6) |
| Ambulatory inotrope use at randomization | 39 (23) | 29 (17) |
| KCCQ overall summary score | ||
| No. | 166 | 167 |
| Mean (SD) | 51.5 (23.6) | 53.5 (23.0) |
| KCCQ clinical summary score | ||
| No. | 166 | 167 |
| Mean (SD) | 57.9 (25.0) | 58.7 (23.4) |
| Baseline NYHA classc | ||
| Id | 3 (2) | 5 (3) |
| II | 38 (23) | 37 (22) |
| III | 67 (40) | 70 (42) |
| IV | 59 (35) | 55 (33) |
| HF hospitalizations within 6 mo before randomization | ||
| ≥1 | 65 (39) | 67 (40) |
| ≥2 | 39 (23) | 35 (21) |
| Medical history | ||
| Hypertension | 118 (71) | 115 (69) |
| TIA or stroke | 22 (13) | 27 (16) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 72 (43) | 80 (48) |
| Diabetes | 74 (44) | 83 (49) |
| Depression | 28 (17) | 29 (17) |
| COPD | 27 (16) | 25 (15) |
| Treatment at randomizatione | ||
| Loop diureticsf | 157 (94) | 155 (92) |
| β-Blocker | 122 (73) | 140 (83) |
| Aldosterone antagonist | 103 (62) | 87 (52) |
| Digoxin | 37 (22) | 30 (18) |
| Hydralazine and nitrates | 17 (10) | 14 (8) |
| ICD or CRT-D | 110 (66) | 107 (64) |
Abbreviations: ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; BMI, body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared); COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CRT-D, cardiac resynchronization therapy with cardioverter-defibrillator; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; HF, heart failure; ICD, implantable cardioverter-defibrillator; KCCQ, Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro–brain natriuretic peptide; NYHA, New York Heart Association; TIA, transient ischemic attack.
SI conversion factors: To convert creatinine to micromoles per liter, multiply by 88.4; NT-proBNP to nanograms per liter, multiply by 1.
There were no significant differences between the 2 groups with respect to baseline characteristics, with the exception of more patients with ischemic heart disease (P < .05) in the sacubitril/valsartan arm compared with the valsartan arm. More details about the baseline characteristics are provided in eTable 3 in Supplement 2.
Racial or ethnic group was reported by the investigators; groups in the other category were too small for specification.
The assessment of NYHA class was not reported for 1 patient in the valsartan treatment arm.
A sensitivity analysis for the change in the area under the curve for NT-proBNP from baseline was performed after removing patients with NYHA class I heart failure (eTable 6 in Supplement 2).
Patients were not receiving an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker at the time of randomization for safety reasons. The prerandomization dose of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin receptor blocker is provided in eTable 3 in Supplement 2.
Doses of pretrial furosemide dose equivalents are provided in the eTable 3 in Supplement 2.
Study Drug Administration and Follow-up
The study drug was discontinued in 49 patients (29%) receiving sacubitril/valsartan and 36 patients (21%) receiving valsartan (P = .10). The median total daily dose was 178.4 mg (IQR, 100.0-331.3 mg) in the sacubitril/valsartan arm and 138.6 mg (IQR, 80.9-263.7) in the valsartan arm; both were 48% of the target dose (Table 2; eFigure 1A in Supplement 2).
Table 2. Primary and Secondary End Pointsa.
| End point | Median (25th to 75th) | R, OR, or difference between groups (95% CI)b | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sacubitril/valsartan (n = 167) | Valsartan (n = 168) | |||
| Primary efficacy end point | ||||
| NT-proBNP AUC, median (IQR) | 1.08 (0.75 to 1.60) | 1.19 (0.91 to 1.64) | 0.95 (0.84 to 1.08) | .45 |
| No. | 155 | 158 | NA | NA |
| Secondary efficacy end points | ||||
| Days alive, out of hospital, and free from HF events, median (IQR)c | 147.0 (9.0 to 164.0) | 157.0 (53.5 to 164.0) | −11.2 (−26.4 to 4.0) | .15 |
| Secondary tolerability end points | ||||
| Last dose of sacubitril/valsartan vs valsartan taken before the end of study, No. (%) | ||||
| 0 vs 0 mgd | 49 (29) | 37 (22) | 1.14 (0.78 to 1.68) | .51 |
| 50 vs 40 mg | 28 (17) | 41 (24) | ||
| 100 vs 80 mg | 33 (20) | 30 (18) | ||
| 200 vs 160 mg | 57 (34) | 60 (36) | ||
| Total daily study drug dose (including those receiving study drug), median (IQR), mg | 178.4 (100.0 to 331.3) | 138.6 (80.9 to 263.7) | NA | NA |
| Hypotension, No. (%)e | 29 (17) | 20 (12) | 1.55 (0.84 to 2.87) | .16 |
| Worsening kidney function, No. (%)f | 7 (4) | 7 (4) | 0.99 (0.34 to 2.91) | .99 |
| Hyperkalemia, No. (%)g | 28 (17) | 15 (9) | 2.05 (1.05 to 4.00) | .04 |
| Disease-related events, No. (%) | ||||
| Dysrhythmiah | 23 (14) | 26 (15) | 0.87 (0.48 to 1.60) | .65 |
| Acute coronary syndromei | 3 (2) | 0 | NA | NA |
| Stroke or transient ischemic attackj | 4 (2) | 1 (1) | 4.10 (0.45 to 37.06) | .14 |
| Angioedema | 0 | 1 (1) | NA | NA |
Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; CV, cardiovascular; HF, heart failure; NA, not applicable; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro–brain natriuretic peptide; OR, odds ratio; R, ratio of change.
SI conversion factor: To convert potassium to millimoles per liter, multiply by 1.
All outcomes were assessed from baseline through 24 weeks.
The AUC data are presented as median (IQR) where a ratio of change; the days alive, out of the hospital, and free from HF events represent a treatment difference; and all of the end points are shown as ORs for sacubitril/valsartan compared with valsartan.
Defined as listing for cardiac transplant (status 1-4), heart transplant, left ventricular assist device implantation, or use of continuous inotropic therapy for 7 days or more, or hospitalization for HF on 2 or more occasions (other than the index admission).
The patient stopped study drug early or therapy with the study drug was never started.
Defined as systolic blood pressure less than or equal to 85 mm Hg.
Defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 20 mL/min/1.73 m2 between randomization and week 24.
Defined as potassium level greater than or equal to 5.5 mEq/L.
Defined as new and clinically significant atrial or ventricular dysrhythmias.
Defined as unstable angina, non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
Defined as cerebrovascular accidents (stroke) or any cause of (hemorrhage, ischemic, embolic) cerebrovascular accident and transient ischemic attack. There were 2 patients in the sacubitril/valsartan arm treatment who experienced a cerebrovascular event 30 days after left ventricular assist device implantation that were censored and not included in this table.
Study Outcomes
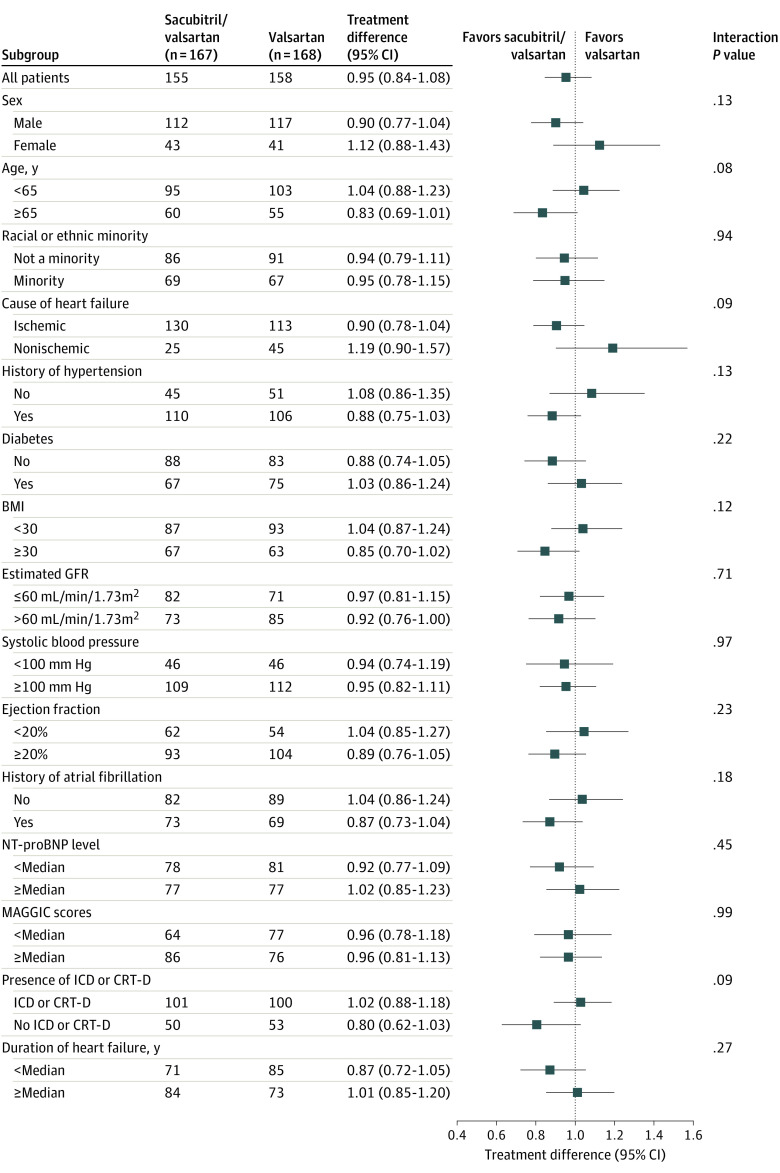
The geometric mean NT-proBNP level compared with baseline remained elevated over 8 weeks of therapy and then decreased below baseline levels in both the sacubitril/valsartan and valsartan treatment arms by week 24 of treatment (Figure 2A). Compared with baseline levels, the median AUC for NT-proBNP was 1.08 (IQR, 0.75-1.60) for the sacubitril/valsartan treatment arm and 1.19 (IQR, 0.91-1.64) for the valsartan treatment arm. The estimated ratio of change for the AUC (primary end point) for sacubitril/valsartan vs valsartan was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.84-1.08; P = .45) (Figure 2B and Table 2; eFigure 2 and eFigure 3 in Supplement 2). There were no informative differences in the AUC for NT-proBNP levels for sacubitril/valsartan compared with valsartan in any of the subgroups that were examined (Figure 3).
Figure 2. Change in N-Terminal Pro–Brain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP) Levels.
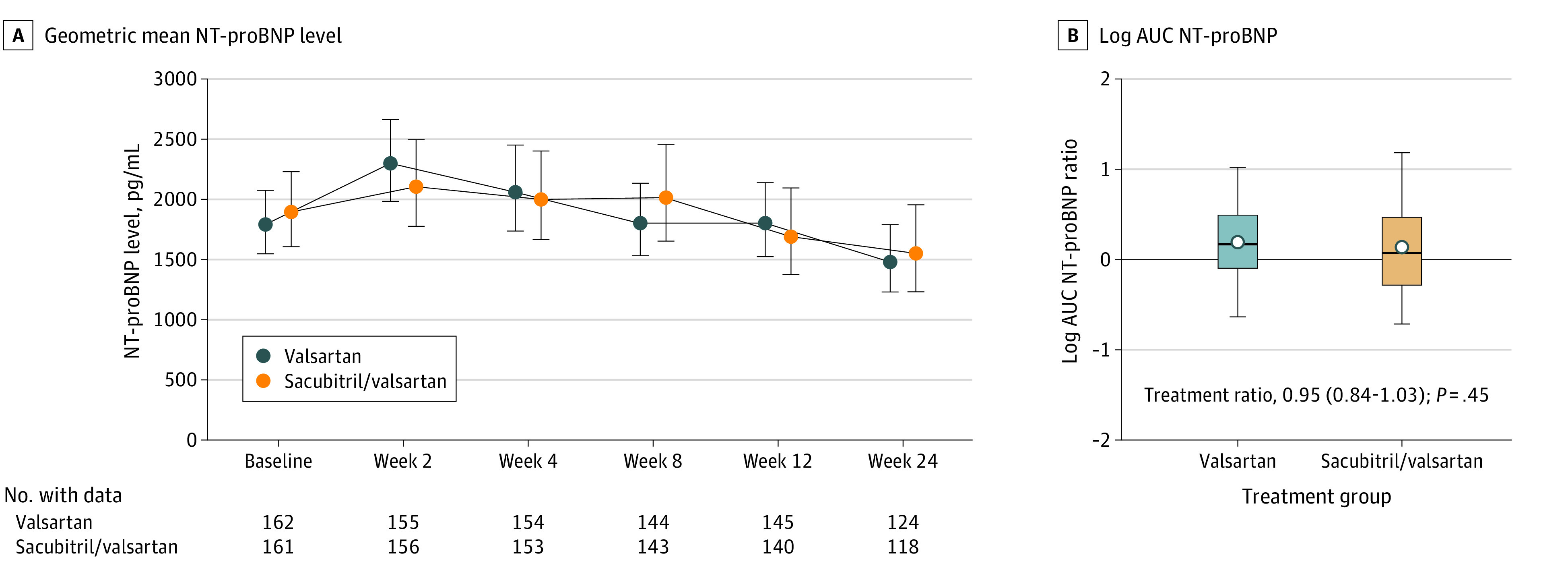
A, The geometric mean NT-proBNP levels remained above baseline values in the sacubitril/valsartan and valsartan treatments arms through 8 weeks of therapy, and then decreased numerically in both treatment arms by 24 weeks. B, The box plots for the log-transformed area under the curve (AUC) (primary end point) were formed by the 25th and 75th percentiles and the line within the box is the median; the error bars indicate the 95% CIs and the data markers indicate the means. Compared with baseline levels, the median AUC of NT-proBNP was 1.19 (IQR, 0.91-1.64) for the valsartan treatment arm and 1.08 (IQR, 0.75-1.60) for the sacubitril/valsartan treatment arm. The estimated ratio of change was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.84-1.08; P = .45) for sacubitril/valsartan vs valsartan. The solid horizontal line reflects the value for no change in NT-proBNP level from baseline. Values above the line indicate an increase in the AUC from baseline, whereas values below the line indicate a decrease in the AUC from baseline. The non–log-transformed data for this figure are presented in eFigure 3 in Supplement 2.
Figure 3. Prespecified Subgroup Analyses.
Point estimates for the ratio of change (sacubitril/valsartan vs valsartan) (95% CI) for the area under the curve of N-terminal pro–brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) relative to baseline (primary end point) among patients in different subgroups. BMI indicates body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared); CRT-D, cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; ICD, implantable cardioverter-defibrillator; and MAGGIC, Meta-analysis Global Group in Chronic Heart Failure.
The secondary efficacy end point of the number of patient-days alive, out of hospital, and without heart failure events was numerically higher (ie, better) in the valsartan arm (median, 157.0; IQR, 53.5-164.0 days) compared with the sacubitril/valsartan arm (median, 147.0; IQR, 9.0-164.0 days). The estimated difference between the 2 groups was −11.2 days (95% CI, −26.4 to 4.0 days; P = .15). The comparable dose of study drug at the last study visit was not significantly different between the 2 groups (Table 2).
There were no informative differences between the sacubitril/valsartan and valsartan treatment arms with respect to the tertiary end points that were examined, including death from cardiovascular causes or hospitalization for heart failure, heart failure hospitalization, death from cardiovascular causes, all-cause death, or the number of patients who received a left ventricular assist device, were listed for or received a heart transplant, had unanticipated use of intravenous diuretics, or required inotropic therapy (eTable 4, eTable 5, and eFigure 4 in Supplement 2).
Safety and Tolerability
There were no differences with respect to the development of symptomatic hypotension or worsening kidney function between the treatment arms, whereas significantly more patients developed hyperkalemia in the sacubitril/valsartan arm (28 [17%]) compared with the valsartan arm (15 [9%]) (P = .04) (Table 2). Furthermore, there were no informative differences in other tolerability or serious adverse events between the treatment arms (Table 2). The number of patients who discontinued the study drug in the sacubitril/valsartan arm compared with the valsartan treatment arm was not significantly different (hazard ratio, 1.36; 95% CI, 0.88-2.09; P = .16) (eFigure 1B in Supplement 2).
A nonparametric sensitivity analysis of the NT-proBNP AUCs that assigned the worst possible value to death did not detect a significant difference between the 2 treatment arms (mean [SD], sacubitril/valsartan, 160.34 [98.01] vs valsartan, 156.66 [84.47]; P = .72) (eTable 6 in Supplement 2). The sensitivity analyses of complete cases, all randomized patients, and patients with compete follow-up (n = 25 did not have complete their 24-week visit before study closure) were qualitatively similar to the primary analysis with respect to the AUC for the proportional change from baseline in NT-proBNP levels and the secondary efficacy end point (eTable 6 in Supplement 2).
Discussion
In patients with advanced heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction who experienced NYHA class IV symptoms within the previous 3 months, we did not detect a statistically significant difference between sacubitril/valsartan and valsartan with respect to reducing NT-proBNP levels. This finding was consistent across most subgroups examined. Although the LIFE trial was underpowered to detect differences in the secondary or tertiary outcomes, we did not observe informative differences between treatment groups across the entire spectrum of outcomes examined, including the secondary end point of patient-days alive and out of the hospital and free from heart failure events, as well as the tertiary outcomes of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization and heart failure hospitalization.
Direct comparisons between the results of the LIFE trial and the PARADIGM-HF trial5 are fraught because of the inherent differences in clinical design and in the intended purpose of the 2 trials. PARADIGM-HF was a large phase 3 clinical trial designed to evaluate clinical outcomes in ambulatory patients with chronic heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction, and NYHA class II to IV symptoms, whereas the LIFE trial was a phase 4 clinical trial designed to evaluate the tolerability and safety of sacubitril/valsartan in a group of sicker patients with more advanced heart failure (eTable 7 in Supplement 2) who were underrepresented (<1%) in the PARADIGM-HF trial. Relevant to this discussion, 18% of the patients who met the enrollment criteria in the LIFE trial could not be randomized because they were unable to tolerate a 100-mg/d dose of sacubitril/valsartan during the run-in phase, 30% of the randomized patients discontinued sacubitril/valsartan during the study, and less than 35% of the patients were receiving the target dose of 400 mg/d of sacubitril/valsartan at the end of the study. In contrast, 100% of the patients in the PARADIGM-HF trial were receiving the target dose of sacubitril/valsartan, 400 mg/d, at the time of randomization; 17.8% of patients discontinued the study drug over a median of 27 months of follow-up; and the mean (SD) dose of sacubitril/valsartan at the end of the study was 375 (71) mg/d.5 Another potentially important difference between the trials is that the active treatment comparator in the LIFE trial was valsartan, whereas enalapril was the active treatment comparator in the PARADIGM-HF trial. Although angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers are considered equivalent treatments for heart failure, these 2 classes of drugs modulate the classic and alternative renin-angiotensin signaling pathways differently.10
With the exception of a statistically significant increase in the incidence of non–life-threatening hyperkalemia in the sacubitril/valsartan arm, there were no other safety concerns. Hyperkalemia was not observed in either the PARADIGM-HF or Comparison of Sacubitril–Valsartan vs Enalapril on Effect on NT-proBNP in Patients Stabilized From an Acute Heart Failure Episode (PIONEER) trials.11 One explanation for the increased incidence of hyperkalemia with sacubitril/valsartan in the LIFE trial is that participants’ blood pressure was lower and kidney function was worse (eTable 7 in Supplement 2). We cannot exclude the possibility that the safety and tolerability of sacubitril/valsartan may have been different than observed if the patients had not undergone a run-in phase with low-dose sacubitril/valsartan.
The observation that the ratio of change in NT-proBNP levels between the sacubitril/valsartan and valsartan treatment arms was not significantly different is consistent with prior experimental and clinical studies that have shown that, in advanced heart failure, chronic excessive stimulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system either overrides or blunts the salutary effects of natriuretic peptide signaling in the heart, vasculature, and kidneys.12,13,14,15,16 Blunting of natriuretic peptide signaling would result in pharmacologic equivalence between an angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor and an angiotensin receptor antagonist. A subgroup analysis of the PARADIGM-HF trial showed that there was a significant treatment interaction with NYHA class (P = .03 [no further data reported]).5 Although there was a decrease in cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization in the sacubitril/valsartan treatment arm compared with the enalapril treatment arm in patients with NYHA class I to II failure, there was no difference between the sacubitril/valsartan and enalapril treatment arms in cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization in the sicker patients with NYHA class III to IV heart failure.5,17
Limitations
The LIFE trial has limitations, including the smaller sample size and relatively short duration compared with contemporary phase 3 trials that predominately enroll patients with NYHA class II to III heart failure. Another limitation is that the reasons for premature discontinuation of study drug were not recorded. Interpreting the results of the LIFE trial also requires a discussion of how the COVID-19 mitigation strategy affected the results. The decrease in the number of randomized patients from the originally planned 400 to 335 nominally reduced the statistical power to detect a 20% treatment difference from 88% to 79%. To account for the patients who did not have the opportunity to complete their 24-week visit before study closure (n = 25), we performed a sensitivity analysis that showed that the proportional change for the ratio of NT-proBNP levels to baseline was directionally consistent with and numerically similar to the value calculated for the primary analysis of 335 patients.
Conclusions
The results of the LIFE trial show there was no difference between sacubitril/valsartan and valsartan with respect to lowering NT-proBNP levels in patients with advanced heart failure. This finding was consistent across most subgroups examined. Moreover, we did not observe clinically important differences between sacubitril/valsartan and valsartan across a spectrum of clinical outcomes in patients with advanced heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction. The interpretation of these results should take into consideration that LIFE is a phase 4 clinical trial and was underpowered to detect differences in clinical outcomes, as well as the understanding that the premature discontinuation of the trial because of the COVID-19 pandemic nominally reduced the statistical power of the trial. These statements notwithstanding, the trial provides additional information that addresses the tolerability and safety of sacubitril/valsartan compared with valsartan in a vulnerable population of patients with severe advanced heart failure in whom medical treatment options are limited.
Trial Protocol
eAppendix. LIFE Trial Members, Investigators, and Committees
eTable 1. Detailed Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
eTable 2. Characteristics of Patients Who Did Not Tolerate Sacubitril/Valsartan During Run-in as Compared With Patients Who Completed Run-in
eTable 3. Additional Patient Characteristics
eTable 4. Tertiary Clinical End Points
eTable 5. Change From Baseline eGFR and Cystatin C Compared With Weeks 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24
eTable 6. Sensitivity Analysis of Complete Cases, All Randomized Patients, Patients With Full Follow-up, and NHYA Class I Patients Excluded
eTable 7. Comparison of Baseline Demographics in LIFE and PARADIGM-HF
eFigure 1. Average Study Drug Dose and Time to Premature Discontinuation of Study Drug
eFigure 2. Ratio of the Change in NT-proBNP Levels for Sacubitril With Valsartan vs Valsartan
eFigure 3. Box and Whisker Plot of the Change in NT-proBNP AUC
eFigure 4. Cardiovascular Death or Heart Failure Hospitalization and Heart Failure Hospitalization
Nonauthor Collaborators. LIFE Investigators
Data Sharing Statement
References
- 1.Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. ; WRITING COMMITTEE MEMBERS; American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines . 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128(16):e240-e327. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829e8776 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2016 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update on new pharmacological therapy for heart failure: an update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68(13):1476-1488. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.05.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, et al. ; ESC Scientific Document Group . 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(27):2129-2200. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ambardekar AV, Kittleson MM, Palardy M, et al. Outcomes with ambulatory advanced heart failure from the Medical Arm of Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support (MedaMACS) registry. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019;38(4):408-417. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2018.09.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McMurray JJ, Packer M, Desai AS, et al. ; PARADIGM-HF Investigators and Committees . Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition versus enalapril in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(11):993-1004. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1409077 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, et al. ; DAPA-HF Trial Committees and Investigators . Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(21):1995-2008. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, et al. ; EMPEROR-Reduced Trial Investigators . Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(15):1413-1424. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022190 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(6):776-803. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.04.025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mann DL, Greene SJ, Givertz MM, et al. ; LIFE Investigators . Sacubitril/valsartan in advanced heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: rationale and design of the LIFE Trial. JACC Heart Fail. 2020;8(10):789-799. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2020.05.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pavo N, Prausmüller S, Spinka G, et al. Myocardial angiotensin metabolism in end-stage heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(14):1731-1743. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.01.052 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Velazquez EJ, Morrow DA, DeVore AD, et al. ; PIONEER-HF Investigators . Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition in acute decompensated heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(6):539-548. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812851 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Díez J. Chronic heart failure as a state of reduced effectiveness of the natriuretic peptide system: implications for therapy. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017;19(2):167-176. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen HH, Schirger JA, Chau WL, et al. Renal response to acute neutral endopeptidase inhibition in mild and severe experimental heart failure. Circulation. 1999;100(24):2443-2448. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.100.24.2443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lee NS, Daniels LB. Current understanding of the compensatory actions of cardiac natriuretic peptides in cardiac failure: a clinical perspective. Card Fail Rev. 2016;2(1):14-19. doi: 10.15420/cfr.2016:4:2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen HH, Burnett JC. Natriuretic peptides in the pathophysiology of congestive heart failure. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2000;2(3):198-205. doi: 10.1007/s11886-000-0069-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tsutamoto T, Kanamori T, Morigami N, Sugimoto Y, Yamaoka O, Kinoshita M. Possibility of downregulation of atrial natriuretic peptide receptor coupled to guanylate cyclase in peripheral vascular beds of patients with chronic severe heart failure. Circulation. 1993;87(1):70-75. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.87.1.70 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Highlights of prescribing information for Entresto (sacubitril and valsartan). Novartis. February 2021. Accessed June 5, 2021. https://www.novartis.us/sites/www.novartis.us/files/entresto.pdf
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Trial Protocol
eAppendix. LIFE Trial Members, Investigators, and Committees
eTable 1. Detailed Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
eTable 2. Characteristics of Patients Who Did Not Tolerate Sacubitril/Valsartan During Run-in as Compared With Patients Who Completed Run-in
eTable 3. Additional Patient Characteristics
eTable 4. Tertiary Clinical End Points
eTable 5. Change From Baseline eGFR and Cystatin C Compared With Weeks 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24
eTable 6. Sensitivity Analysis of Complete Cases, All Randomized Patients, Patients With Full Follow-up, and NHYA Class I Patients Excluded
eTable 7. Comparison of Baseline Demographics in LIFE and PARADIGM-HF
eFigure 1. Average Study Drug Dose and Time to Premature Discontinuation of Study Drug
eFigure 2. Ratio of the Change in NT-proBNP Levels for Sacubitril With Valsartan vs Valsartan
eFigure 3. Box and Whisker Plot of the Change in NT-proBNP AUC
eFigure 4. Cardiovascular Death or Heart Failure Hospitalization and Heart Failure Hospitalization
Nonauthor Collaborators. LIFE Investigators
Data Sharing Statement