Abstract
Depression is the leading cause of disability worldwide, making antidepressant drugs the most used psychiatric drugs in the USA. Withdrawal effects and rebound symptoms frequently occur after the reduction and/or discontinuation of these drugs. Although these phenomena have been investigated with respect to the clinical symptomatology, no studies have systematically investigated the effects of withdrawal/rebound on general cognition. We present a novel framework based on the idea of allostatic adaptation, which allows to predict how different antidepressants likely impair different cognitive processes as a result of withdrawal and rebound effects. This framework relies on the assumptions that the type of cognitive impairments evoked by an antidepressant is determined by the targeted neurotransmitter systems, while the severity of deficits depends on its half-life. Our model predicts that the severity of detrimental cognitive withdrawal and rebound effects increases with a shorter half-life of the discontinued antidepressant drug. It further proposes drug-specific effects: antidepressants mainly targeting serotonin should primarily impair aversive and emotional processing, those targeting norepinephrine should impair the processing of alerting signals, those targeting dopamine should impair motivational processes and reward processing, and those targeting acetylcholine should impair spatial learning and memory. We hope that this framework will motivate further research to better understand and explain cognitive changes as a consequence of antidepressant discontinuation.
Key words: antidepressants, withdrawal, rebound, allostatic adaptation, cognitive deficits
Introduction
Around 300 million people, or 4.4% of the global population, are estimated to be diagnosed with depression 1 . Depression is the leading cause of disability worldwide, with numbers continuously increasing, especially in lower-income countries 1 , resulting in very high healthcare costs 2 . As a consequence of the recent COVID-19 pandemic, approximately 4 times as many individuals reported depressive symptoms in the US in June 2020, as compared to the previous year (24.3 vs. 6.5%) 3 . Other countries, such as Germany 4 5 6 , China 7 , and Iran 8 seem to follow the same trend.
To date, most national guidelines recommend pharmacotherapy for severely depressed individuals, and a recent meta-analysis has shown that a combination of psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy is most efficient for patients with moderate depression 9 . This, as well as the wide indication of “antidepressants” for other disorders (see below), makes antidepressant drugs the most used psychiatric drugs in the USA, with 12% of US adults reporting to take them 10 . This varies in Europe (average of 7.2%), ranging from 15.7% in Portugal to 2.7% in Greece 11 . In Germany, the use of antidepressants has slowly increased 12 from 3.3% in 2008 to 5.0% in 2017 (derived from federal statistical data available on https://de.statista.com/infografik/16707/verordnungen-von-antidepressiva-in-deutschland/). Further adding to this, antidepressants are also prescribed to treat other conditions like anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and bulimia 13 . In addition to the side effects of taking antidepressants, withdrawal effects (i. e., adverse reactions when ceasing to take a drug) and rebound symptoms (i. e., re-surfacing of depressive symptoms to a greater extent than before starting the medication) seem to frequently occur after their reduction and/or discontinuation 14 . As the brain tries to “compensate” the pharmacologic upregulation of neurotransmission by further physiological downregulation, these alterations drive patients even further away from a “baseline” point of optimal functioning 15 .
It is crucial to correctly diagnose these phenomena because withdrawal and rebound symptoms can easily be mistaken for true relapse or recurrence of the original depression. While withdrawal symptoms are usually relatively short-lasting (typically a few hours to a few weeks until complete recovery), rebound symptoms may persist for much longer and last for several months 16 . In 1998, the antidepressant discontinuation syndrome (ADS) was defined to account for withdrawal effects 17 . Rosenbaum et al. 18 suggested the Discontinuation-Emergent Signs and Symptoms Checklist (DESS), which is an ADS symptom list comprising a total of 48 symptoms. Chouinard and Chouinard 16 further elaborated on this and suggested 3 different types of syndromes in a DSM-like type of classification: Type 1 (withdrawal: new symptoms with a peak of 26–96 hours after discontinuation, usually disappearing after a maximum of 6 weeks), Type 2 (rebound: the return of original symptoms, more intense, same peak and duration), and Type 3 (persistent withdrawal disorder: symptoms of new mental disorders, appearing after 24 hours to 6 weeks, may last for months, difficult to distinguish from a relapse) 16 . The likelihood of withdrawal symptoms increases with higher doses of antidepressants 14 19 20 21 and with a shorter half-life of the respective drug 14 18 22 . Relapse data in discontinuation studies and animal data measuring neurotransmission 23 further suggest that the stronger the effect of the drug on monoaminergic neurotransmission, the higher the likelihood of relapse. While antidepressant tapering (i. e., gradually reducing the dose) does not necessarily prevent withdrawal and rebound phenomena, it may reduce their severity 24 25 . The frequency of withdrawal symptoms is difficult to estimate (numbers range between 10 and 70% 22 ), as there is currently no agreement on the diagnostic instruments used to measure occurrence and severity. However, the group of Giovanni Fava has recently suggested a diagnostic interview for withdrawal syndromes 26 . Although the incidence of withdrawal symptoms is debated, discontinuation of antidepressants is a frequent phenomenon, which should be reflected in the frequency of withdrawal symptoms, in particular as most patients discontinue without medical supervision: After 1 month of treatment, around one-quarter of patients have already discontinued their antidepressants, and after 6 months, the number rises to nearly two-thirds 27 28 29 .
Many initial prescribers, in particular non-psychiatrists, do not seem to be sufficiently aware of possible withdrawal symptoms. As a consequence many, if not most, patients are not informed about this possible consequence of discontinuation when starting their antidepressant medication 30 31 1 . This is particularly relevant as antidepressants seem to be no more effective than placebos when prescribed for less severe cases of depression 32 . The most recent discussions of the withdrawal syndromes have focused on their existence, incidence, diagnostics, or management. The clinical picture of withdrawal symptoms for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) has been nicely described with the acronym FINISH (Flu-like symptoms, Insomnia, Nausea, Imbalance, Sensory disturbances, and Hyperarousal) 14 16 22 . Yet, most of these publications mainly focus on the serotonergic system. In this article, we chose to take a different approach by focusing on cognitive symptoms during and after withdrawal and by considering the potential functional role of different involved neurotransmitters. Importantly, such cognitive (dys)functions might also be of considerable clinical importance even though their prevalence is commonly underestimated in depression. In a recent survey, over 90% of patients suffering from depression stated to experience cognitive problems in their daily living activities. Yet, only 50% of those patients had ever been asked about cognitive dysfunction by a healthcare professional 33 . So far, only a single study 34 has investigated the effects of the abrupt and brief discontinuation of SSRI antidepressant treatment on cognitive function. It observed that both depressive symptoms and self-reported failures in perception, memory, and motor function increased during discontinuation and were most severe in patients taking paroxetine (as compared to those patients taking fluoxetine, sertraline, or citalopram). While all of the antidepressant medications investigated in this study were SSRIs, it is noteworthy that the SSRI with the shortest half-life accounted for the most severe worsening of both depressive and cognitive complaints during discontinuation. Despite the current lack of further studies on this topic, identifying and targeting cognitive dysfunctions caused by the discontinuation of antidepressants is crucial given that biases in cognitive processes such as attention and memory may not only be associated with depressive symptoms, but they have actually been shown to predict patients’ vulnerability for the first onset and recurrence of depression 35 . Likewise, the decision to invest effort has been shown to be linked to prospective relapse risk after antidepressant discontinuation 36 , thus further highlighting the importance of cognitive markers (like effort-related decision-making) in predicting relapse risk. In sum, we deem it of utmost importance to shed more light on potential cognitive deficits caused by the discontinuation of antidepressants, as targeting such potential deficits might reduce or delay relapse rates and enhance the productivity of patients in working environments 37 38 .
In the following, we will outline different types of antidepressants and their effects on different families of neurotransmitter transporters, the potential allostatic mechanisms underlying withdrawal and rebound effects, and how the different neurotransmitter systems targeted by antidepressants affect cognitive processes. We argue that as a consequence of withdrawal and rebound effects, cognitive deficits are likely to develop depending on a) the type of antidepressants and the neurotransmitters affected by them and b) the half-life of the antidepressants used. Taking into account both of these factors, we propose a novel framework, which is based on the idea of allostatic adaptation and allows to predict how the different antidepressants are likely to impair cognitive processes as a result of withdrawal and rebound effects ( Fig. 1 ).
Fig. 1 a.
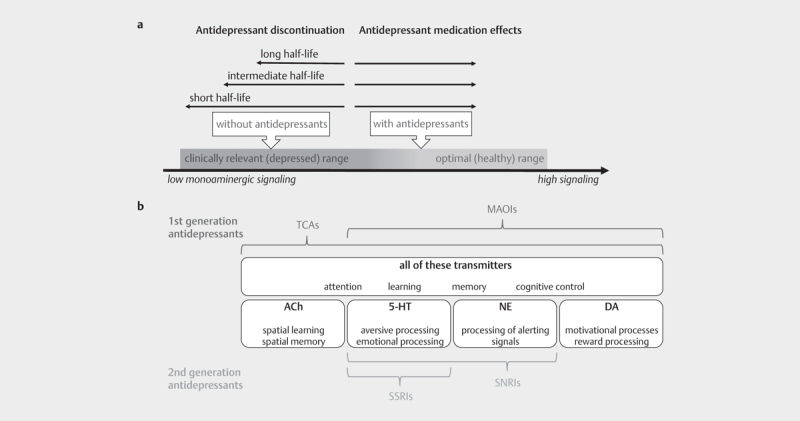
Illustration of the suggested shift in monoaminergic signaling underlying withdrawal and rebound effects. Please note that antidepressants with a short half-life are expected to cause more severe dysregulation (i. e., deficient monoaminergic signaling) and thus more severe cognitive deficits upon their discontinuation. b. Illustration of the antidepressant drug types and the different neurotransmitters that they affect. The first generation of antidepressants (TCAs and MAOIs) affects a broad spectrum of neurotransmitters, whereas the second generation of antidepressants (SSRIs and SNRIs) has a more selective effect. The targeted neurotransmitters also determine the range of cognitive deficits that are likely to develop as a result of withdrawal and rebound effects triggered by drug discontinuation.
Antidepressants affect different neurotransmitter systems: A very short overview
The first generation of antidepressants (tricyclic antidepressants [TCAs] and monoamine oxidase inhibitors [MAOIs]) was introduced in the 1950s and served as evidence to formulate the monoamine hypothesis of depression 39 , which suggests that a lack of monoamines and/or monoaminergic signaling fosters depression. In the 1980s, the second generation of antidepressants (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors [SSRIs] and serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors [SNRIs]) hit the market and revolutionized the pharmacological therapy for depression 39 . Due to their improved tolerability and safety profile, the second generation has largely replaced the use of the first generation of antidepressants in treatment 40 . However, it should not go unmentioned that there are also other, more recently developed multimodal antidepressants such as vortioxetine, which increases both serotonergic and acetylcholinergic signaling and is receiving increasing attention as an add-on therapy in patients with SSRI-resistant depression, and might also benefit cognition 41 . Aside from the monoamine hypothesis, alterations in glutamate receptors, neuronal plasticity, GABAergic transmission, stress/hypothalamic pituitary adrenal(HPA)-axis, and neuroinflammation have also been suggested to contribute to depressive symptoms and thus provide potential alternative targets for pharmacological intervention 42 . While the research on glutamate receptors and other hypotheses is promising, alternative treatments like ketamine administration are still in too early stages to be considered a validated and established approach in the treatment of depression as of yet 42 . As most patients are therefore still prescribed primarily monoaminergic antidepressants, we will mainly focus on this class of antidepressants in this article. Moreover, even if the mechanism of effects on mood might be related to other processes than monoaminergic neurotransmission, discontinuation of standard antidepressants will nevertheless cause mononaminergically-mediated withdrawal effects, as their effects on those neurotransmitters are strong and undisputed. Over the next section, we will briefly sketch the essential pharmacodynamics of the first and second generation of antidepressants, as well as vortioxetine, to establish an understanding of their shared and different pharmacological properties ( Fig. 1b ).
First-generation antidepressants
TCAs
Tricyclic antidepressants block serotonin and norepinephrine transporters, thus increasing the synaptic levels of serotonin (5-HT) and norepinephrine (NE). They further act as potent antihistamines and anticholinergics, showing a high affinity for antagonizing the α adrenoreceptor and the H1 and H2 histamine receptors, as well as the muscarinic acetylcholine (ACh) receptors 43 .
MAOI
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors inhibit the activity of 1 or both monoamine oxidase enzymes (MAO-A and MAO-B). As these enzymes are responsible for metabolizing monoaminergic neurotransmitters like dopamine (DA), NE, and 5-HT, MAOIs increase the availability of those neurotransmitters in the brain 43 .
Second-generation antidepressants
SSRIs
SSRIs increase the extracellular level of 5-HT by limiting its reabsorption (reuptake) into the presynaptic cell. This makes more 5-HT available to bind to the postsynaptic receptor 44 .
SNRIs
SNRIs bind to 5-HT and NE transporters, thus increasing the extracellular levels of 5-HT and NE 45 .
Newly developed multimodal antidepressants
Newly developed multimodal antidepressants, such as vortioxetine, target both 5-HT1A receptors and the serotonin transporter (SERT) 42 , and among other effects, facilitate the release of ACh 46 .
In sum, the first and second generation of antidepressants share similar mechanisms of action on monoamines, but while the former impact a broad spectrum of neurotransmitters, the latter have more selective/specific effects on only 1 or 2 tightly interrelated neurotransmitter systems 47 .
Mechanisms of Action of Withdrawal and Rebound Effects
In this section, we discuss the potential mechanisms of action underlying withdrawal and rebound effects ( Fig. 1a ). In this context, 2 interesting hypotheses have been proposed: the allostatic adaptation account 48 and the oppositional tolerance model 49 . Both are based on the assumption that monoamines underlie homeostatic control, but they differ in their assumptions on whether or not this control can be maintained during depression and/or the intake and discontinuation of monoaminergic medication 23 .
All pharmacoactive compounds produce neuroadaptation (i. e., physiological changes that serve to maintain homeostasis and take place as a result of using drugs) 50 . As a consequence of this neuroadaptation, a new homeostatic point is set, so when the drugs are abruptly discontinued, this induces disruption of the homeostasis 48 . This disruption is thought to cause withdrawal and rebound effects, and the deeper the drug-induced disruption of the homeostasis, the stronger the withdrawal and rebound effects will be 48 . For antidepressants, at least 4 weeks of drug intake appear to be required for withdrawal and rebound effects to occur after discontinuation, suggesting that this is long enough for antidepressants to change allostatic adaptation 51 . Such disrupted homeostasis can lead to a hyper-responsive serotonergic system 14 . Indeed, several antidepressants do not only block the 5-HT and NE transporters but also cause a decrease (and not a counter-regulatory increase) in these transporters when taken long-term 52 53 54 .
In contrast to this 23 , adaptationist hypotheses such as the oppositional tolerance account 49 suggest that homeostatic mechanisms are properly functioning in most depressive patients but that oppositional tolerance arises with protracted antidepressant use, where oppositional forces trigger monoamine levels to alter/perturb their equilibrium levels when medication use is discontinued. As depressive symptoms are modulated by monoamines, this overshoot triggers a potential re-emergence of depressive symptoms, which is proportional to the perturbational effect of the protracted antidepressant use.
Notably, a meta-analysis of antidepressant discontinuation studies supports the notion that the relapse risk after antidepressant discontinuation is positively associated with the drug’s enhancing effects on monoamine concentrations in the brain 23 . Based on this, Andrews et al. 23 deemed it more likely that withdrawal and rebound effects are the result of oppositional tolerance 49 .
Antidepressant types are likely to determine which cognitive processes will be impaired by withdrawal and rebound effects
In this section, we outline the link between the neurotransmitters modulated by antidepressants (i. e., 5-HT, NE, DA, ACh) and specific cognitive deficits that may be produced by withdrawal and rebound effects (see Fig. 1b ).
The monoamines most consistently linked to depression are 5-HT and the catecholamines NE and DA. Monoamines coordinate many important biological processes like sleep, circadian rhythm, body temperature, appetite, pain, and motor activity, but they also regulate higher brain functions like cognitive processes 55 . The high density of monoaminergic and cholinergic projections in the midbrain nuclei, hippocampus, substantia nigra, and prefrontal cortex 56 57 highlights their anatomical and neurochemical affiliation with brain regions most commonly linked to cognitive processes. Pharmacological challenges, patients, and animal studies have consistently demonstrated that these neurotransmitters have overlapping and interactive effects in driving attention, memory, and learning. Importantly, all of these cognitive functions are known to be dysfunctional in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases, in which these neurotransmitters are affected (e. g., schizophrenia, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s disease) 58 59 60 61 62 . Even though there is a large functional overlap between monoamines 60 62 and ACh 58 , these neurotransmitter systems are differently affected by different antidepressant drug types and seem to partly subserve different cognitive functions ( Fig. 1b ). DA, NE, and 5-HT are important for cognitive control (i. e., the way we control our thoughts and goal-directed behavior, including core executive functions) 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 .
5-HT is also likely involved in processing aversive and emotional information, even if that effect might not be uniquely restricted to this neurotransmitter system 60 . Enhancing 5-HT levels boosts the processing of positive emotional information both in healthy controls and patients with severe depression, indicating that enhancing a positive bias might be the prerequisite for patients being able to start the cognitive restructuring of their symptoms 72 .
NE seems to be particularly relevant for the processing of attentional control 73 and to have a crucial role in the maintenance of attentional biases 74 . The NE system has further been suggested to underlie impairments in disengaging attention from mood-congruent material, which is typical of depressive patients 75 .
DA has a predominant, but not exclusive, effect on motivational control and reward learning (i. e., how we process rewards to choose the most adaptive response to the environment) 76 . Notably, reward processing appears to be dysfunctional in depression, and this has been linked to abnormal phasic striatal dopamine signaling, which is crucial for reinforcement learning and for an optimal allocation of effort to obtain rewards 77 .
ACh seems to have a major, but not exclusive, role in spatial learning and spatial memory 58 78 . ACh has been linked to deficits typical of depressive patients in how information about the external environmental space is acquired, stored, organized, and used 79 .
Lastly, the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate plays a major role in learning and neuronal plasticity 42 80 , while the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA plays a major role in response selection and the regulation of cognition, emotion, and memory 42 81 82 83 . Patients with depression have been shown to suffer from impaired neuroplasticity due to changes in glutamatergic signaling 42 80 84 as well as reduced CNS levels of GABA 42 85 .
So far, we found no studies that systematically investigated the effects of withdrawal/rebound on general cognition. Regarding the potential specific cognitive deficits produced by the discontinuation of the different antidepressant types, we expect SSRIs, by their selective effect on 5-HT, to mainly induce impairments in the processing of aversive and emotional information (besides attention, learning, memory, and cognitive control). As a consequence of their selective effect on both 5-HT and NE, SNRIs are likely to cause similar changes as SSRIs, but with deficits extending to the processing of alerting signals, as this function depends on NE. Regarding the first generation of antidepressants, MAOIs should exert deficits comparable to SNRIs, but they should additionally encompass motivational and reward processing. Further, we hypothesize TCAs to broaden their impairments even further than MAOIs and also affect spatial learning and spatial memory when discontinued. Lastly, newly developed multimodal antidepressants, such as vortioxetine, are known to exert procognitive effects via ACh 86 , and, consequently, should negatively affect spatial learning and spatial memory when discontinued.
In sum, we suggest that due to the differences in the functional neurotransmitter systems targeted by different antidepressants, it should be possible to determine which cognitive processes will be most likely impaired by withdrawal and rebound effects.
The severity of the cognitive deficits triggered by withdrawal and rebound effects are likely to depend on the half-life of the antidepressants
In this section, we argue that similar to what is known about the clinical symptoms and irrespective of the antidepressant types / the targeted neurotransmitter systems, the severity of the cognitive deficits caused by withdrawal and rebound effects are likely to depend on the half-life (i. e., plasma elimination time) of the antidepressants. For clinical symptoms of SSRI discontinuation, it is well-known that paroxetine (which has a very short half-life) is much more likely to induce withdrawal symptoms than drugs like fluoxetine (which has a very long half-life) 17 87 . Matching this hypothesis, it has indeed been reported that the abrupt interruption of paroxetine intake caused significantly more cognitive deficits than the interruption of fluoxetine intake, and the deficits were reportedly only reversed after the reinstatement of the treatment 34 . The onset of withdrawal and rebound symptoms are likely to happen around 3 – 5 half-lives after discontinuation 88 , and the shorter the half-life of the antidepressants, the more severe the withdrawal and rebound symptoms are expected to be 14 . Based on the idea that the affected neurotransmitter systems will not only be relevant for specific clinical symptoms but also for cognitive withdrawal effects, we propose a correlation: The more severe the clinical withdrawal and rebound symptoms, the stronger the expected cognitive impairments will be ( Fig. 1a ). In the case of longer half-life, such as for the SSRI drug fluoxetine (better known as Prozac) 17 87 and the SNRI drug milnacipran (commercialized under the name Savella and MilnaNeurax), we hypothesize mild withdrawal and rebound symptoms 89 , which should translate into subtle cognitive deficits. Many of the most used antidepressants show intermediate half-lives, such as the SSRI drug citalopram (better known as Celexa), sertraline (sold under the brand name Zoloft), and the SNRI drug duloxetine (known as Cymbalta). Given their intermediate half-life, we expect them to display moderate withdrawal and rebound symptoms 20 90 91 , which should on average trigger more cognitive impairments than drugs with a long half-life. In contrast, antidepressants with a short half-life like MAOIs 92 and TCAs 93 , the SNRI drug venlafaxine (commercialized as Effexor) 25 94 , and the SSRI drug paroxetine (better known as Paxil and Seroxat) 95 , should be associated with strong withdrawal and rebound symptoms, which are most likely to produce severe cognitive impairments, as compared to substances with a longer half-life.
In sum, we expect the half-life of antidepressants to predict the severity of the cognitive impairments triggered by withdrawal and rebound effects: the shorter the half-life, the more severe the cognitive deficits. It is for empirical research to determine whether this is true and if there are also long-term cognitive deficits like they have been described for clinical symptoms.
Conclusions
Worldwide, antidepressant drugs are the most prescribed and sold psychiatric drugs, which are used to not only treat depression, but also anxiety, OCD, and PTSD. Considering that antidepressants are also commonly prescribed for milder symptoms, even though their use in minor depression has been shown to yield no advantage over placebos in alleviating clinical symptoms 32 96 , it is crucial to question whether the negative effects (withdrawal and rebound effects) are outweighing the limited potential positive effects in mild cases. Keeping in mind that intact cognitive functioning is a reliable predictor known to prevent relapses, we present a comprehensive novel framework based on the idea of allostatic adaptation, which details how withdrawal and rebound effects might potentially cause cognitive deficits. The framework proposes that the type of cognitive impairment is likely to be determined by the neurotransmitter systems targeted by the specific antidepressants and that the severity of the deficits will depend on the half-life of the antidepressants used. Given that the field of withdrawal and rebound effects produced by antidepressants is still under-investigated, we hope that this framework will motivate new research to better understand and explain cognitive changes as a consequence of antidepressant discontinuation, as well as their contribution to relapses of depression. Therefore, prospective cohort studies that take different antidepressant types into account should also provide evidence for causal relationships between antidepressant discontinuation and cognitive deficits, as well as their role in relapses.
Funding Statement
Funding: This work was supported by a research grant from 100 Talent Grant of the Province of Shandong, China, to LSC, WZ, and CB
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Read 30 reported that in a recent online survey of 867 people from 31 countries who used antidepressants, only “six people (0.7 %) recalled being told anything about withdrawal, dependence or addiction by the initial prescriber.”
References
- 1.Depression and other common mental disorders: global health estimates 2017; Im Internet: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254610/WHO-MSD-MER-2017.2-eng.pdf
- 2.Welch C A, Czerwinski D, Ghimire B.Depression and costs of health care Psychosomatics 200950392–401.doi:10.1176/appi.psy.50.4.392 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Czeisler MÉ.Mental health, substance use, and suicidal ideation during the COVID-19 Pandemic—United States, June 24–30, 2020. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020 69: doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6932a1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Benke C, Autenrieth L K, Asselmann E.Lockdown, quarantine measures, and social distancing: associations with depression, anxiety and distress at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic among adults from Germany Psychiatry Res 2020293113462doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Munk AJ L, Schmidt N M, Alexander N.Covid-19—beyond virology: potentials for maintaining mental health during lockdown PLoS One 202015e0236688doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0236688 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schwinger M, Trautner M, Kärchner H [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Yan T, Zhizhong W, Jianzhong Z.Depressive and anxiety symptoms among people under quarantine during the COVID-19 epidemic in China: A cross-sectional study Front Psychiatry 202112566241doi10.3389/fpsyt.2021.566241 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Moayed M S, Vahedian-Azimi A, Mirmomeni G.A survey of psychological distress among the community in the COVID-19 epidemic: A cross-sectional study Adv Exp Med Biol 20211321253–260.doi:10.1007/978-3-030-59261-5_22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cuijpers P, Noma H, Karyotaki E.A network meta-analysis of the effects of psychotherapies, pharmacotherapies and their combination in the treatment of adult depression World Psychiatry 20201992–107.doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20701 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moore T J, Mattison D R.Adult utilization of psychiatric drugs and differences by sex, age, and race JAMA Intern Med 2017177274–275.doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.7507 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lewer D, O’Reilly C, Mojtabai R.Antidepressant use in 27 European countries: associations with sociodemographic, cultural and economic factors Br J Psychiatry 2015207221–226.doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.114.156786 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lohse M J, MüCller-Oerlinghausen B.Psychopharmaka. Arzneiverordnungs-Report 2018 Schwabe U, Paffrath D, Ludwig W-D, Klauber J.Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2018733–761.doi:10.1007/978-3-662-57386-0_41 [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bandelow B, Sher L, Bunevicius R.Guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder in primary care Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract 20121677–84.doi:10.3109/13651501.2012.667114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Henssler J, Heinz A, Brandt L.Antidepressant withdrawal and rebound phenomena Dtsch Arztebl Int 2019116355–361.doi:10.3238/arztebl.2019.0355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Seger D.Cocaine, metamfetamine, and MDMA abuse: the role and clinical importance of neuroadaptation Clin Toxicol (Phila) 201048695–708.doi:10.3109/15563650.2010.516263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chouinard G, Chouinard V-A.New classification of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor withdrawal PPS 20158463–71.doi:10.1159/000371865 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zajecka J, Fawcett J, Amsterdam J.Safety of abrupt discontinuation of fluoxetine: a randomized, placebo-controlled study J Clin Psychopharmacol 199818193–197.doi:10.1097/00004714-199806000-00003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rosenbaum J F, Fava M, Hoog S L.Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor discontinuation syndrome: A randomized clinical trial Biol Psychiatry 19984477–87.doi:10.1016/s0006-3223(98)00126-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Baldwin D S, Montgomery S A, Nil R.Discontinuation symptoms in depression and anxiety disorders Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 20071073–84.doi:10.1017/S1461145705006358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Markowitz J S, DeVane C L, Liston H L.An assessment of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor discontinuation symptoms with citalopram Int Clin Psychopharmacol 200015329–333.doi:10.1097/00004850-200015060-00003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Perahia D G, Kajdasz D K, Desaiah D.Symptoms following abrupt discontinuation of duloxetine treatment in patients with major depressive disorder J Affect Disord 200589207–212.doi:10.1016/j.jad.2005.09.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Fava G A, Gatti A, Belaise C.Withdrawal symptoms after selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor discontinuation: A systematic review PPS 20158472–81.doi:10.1159/000370338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Andrews P, Kornstein S, Halberstadt L
- 24.Horowitz M A, Taylor D.Tapering of SSRI treatment to mitigate withdrawal symptoms Lancet Psychiatry 20196538–546.doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(19)30032-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ninan P T, Musgnung J, Messig M.Incidence and timing of taper/posttherapy-emergent adverse events following discontinuation of desvenlafaxine 50 mg/d in patients with major depressive disorder Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 201517doi:10.4088/PCC.14m01715 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cosci F, Chouinard G, Chouinard V-A.The diagnostic clinical interview for drug withdrawal 1 (DID-W1) – new symptoms of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) or serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRI): Inter-rater reliability Riv Psichiatr 20185395–99.doi:10.1708/2891.29158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kim K-H, Lee S-M, Paik J-W.The effects of continuous antidepressant treatment during the first 6 months on relapse or recurrence of depression J Affect Disord 2011132121–129.doi:10.1016/j.jad.2011.02.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Milea D, Guelfucci F, Bent-Ennakhil N.Antidepressant monotherapy: a claims database analysis of treatment changes and treatment duration Clin Ther 2010322057–2072.doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.11.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Vlahiotis A, Devine S T, Eichholz J.Discontinuation rates and health care costs in adult patients starting generic versus brand SSRI or SNRI antidepressants in commercial health plans J Manag Care Pharm 201117123–132.doi:10.18553/jmcp.2011.17.2.123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Read J.How common and severe are six withdrawal effects from, and addiction to, antidepressants? The experiences of a large international sample of patients Addict Behav 2020102106157doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.106157 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guy A, Brown M, Lewis S.The ‘patient voice’: patients who experience antidepressant withdrawal symptoms are often dismissed, or misdiagnosed with relapse, or a new medical condition Ther Adv Psychopharmacol 2020102.045125320967183E15doi:10.1177/2045125320967183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Barbui C, Cipriani A, Patel V.Efficacy of antidepressants and benzodiazepines in minor depression: Systematic review and meta-analysis Br J Psychiatry 201119811–16.doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.109.076448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Clark Health Communications exploring cognitive dysfunction in people with depression « Savanta ComRes Im Internet: https://comresglobal.com/polls/clark-health-communications-exploring-cognitive-dysfunction-in-people-with-depression/ Stand 16: 03 2021
- 34.Hindmarch I, Kimber S, Cockle S M.Abrupt and brief discontinuation of antidepressant treatment: Effects on cognitive function and psychomotor performance Int Clin Psychopharmacol 200015305–318.doi:10.1097/00004850-200015060-00001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gotlib I H, Joormann J.Cognition and depression: Current status and future directions Annu Rev Clin Psychol 20106285–312.doi:10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.121208.131305 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Berwian I M, Wenzel J G, Collins AG E.Computational mechanisms of effort and reward decisions in patients with depression and their association with relapse after antidepressant discontinuation JAMA Psychiatry 202077513–522.doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.4971 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lam R W, Kennedy S H, McIntyre R S. Cognitive dysfunction in major depressive disorder: Effects on psychosocial functioning and implications for treatment. Can J Psychiatry. 2014;59:649–654. doi: 10.1177/070674371405901206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.McIntyre R S, Cha D S, Soczynska J K.Cognitive deficits and functional outcomes in major depressive disorder: Determinants, substrates, and treatment interventions Depress Anxiety 201330515–527.doi:10.1002/da.22063 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.López-Muñoz F, Alamo C.Monoaminergic neurotransmission: the history of the discovery of antidepressants from 1950s until today Curr Pharm Des 2009151563–1586.doi:10.2174/138161209788168001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Carvalho A F, Sharma M S, Brunoni A R.The safety, tolerability and risks associated with the use of newer generation antidepressant drugs: A critical review of the literature PPS 201685270–288.doi:10.1159/000447034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.De Berardis D, Fornaro M, Anastasia A.Adjunctive vortioxetine for SSRI-resistant major depressive disorder: A “real-world” chart review study Braz J Psychiatry 202042317–321.doi:10.1590/1516-4446-2019-0690 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dale E, Bang-Andersen B, Sánchez C.Emerging mechanisms and treatments for depression beyond SSRIs and SNRIs Biochem Pharmacol 20159581–97.doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2015.03.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Feighner J P.Mechanism of action of antidepressant medications J Clin Psychiatry 1999604–11.discussion 12–13 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sangkuhl K, Klein T, Altman R.Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) Pathway Pharmacogenet Genomics 200919907–909.doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e32833132cb [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Shelton R C.Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors Handb Exp Pharmacol 2019250145–180.doi:10.1007/164_2018_164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Perini G, Cotta Ramusino M, Sinforiani E.Cognitive impairment in depression: recent advances and novel treatments Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2019151249–1258.doi:10.2147/NDT.S199746 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Iversen L.Neurotransmitter transporters and their impact on the development of psychopharmacology Br J Pharmacol 2006147S82–S88.doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706428 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Heinz A, Daedelow L S, Wackerhagen C.Addiction theory matters—why there is no dependence on caffeine or antidepressant medication Addict Biol 202025e12735doi:10.1111/adb.12735 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fava G A, Offidani E.The mechanisms of tolerance in antidepressant action Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2011351593–1602.doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.07.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Shaham Y, Hope B T.The role of neuroadaptations in relapse to drug seeking Nat Neurosci 200581437–1439.doi:10.1038/nn1105-1437 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hohagen F, Winkelmann G, Rasche-Rüchle H. Combination of behaviour therapy with fluvoxamine in comparison with behaviour therapy and placebo. Results of a multicentre study. Br J Psychiatry. 1998:71–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kittler K, Lau T, Schloss P.Antagonists and substrates differentially regulate serotonin transporter cell surface expression in serotonergic neurons Eur J Pharmacol 201062963–67.doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.12.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mirza N R, Nielsen EØ, Troelsen K B.Serotonin transporter density and anxiolytic-like effects of antidepressants in mice Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 200731858–866.doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.01.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Benmansour S, Altamirano A V, Jones D J.Regulation of the norepinephrine transporter by chronic administration of antidepressants Biol Psychiatry 200455313–316.doi:10.1016/s0006-3223(03)00676-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Libersat F, Pflueger H-J.Monoamines and the orchestration of behavior BioScience 20045417–25.doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2004)054[0017:MATOOB]2.0.CO;2 [Google Scholar]
- 56.Felten D L, Sladek J R.Monoamine distribution in primate brain V. Monoaminergic nuclei: Anatomy, pathways and local organization Brain Res Bull 198310171–284.doi:10.1016/0361-9230(83)90045-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Li X, Yu B, Sun Q.Generation of a whole-brain atlas for the cholinergic system and mesoscopic projectome analysis of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons PNAS 2018115415–420.doi:10.1073/pnas.1703601115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Blokland A.Acetylcholine: a neurotransmitter for learning and memory? Brain Res Rev 199521285–300.doi:10.1016/0165-0173(95)00016-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Borodovitsyna O, Flamini M, Chandler D.Noradrenergic nodulation of cognition in health and disease. Neural Plast 2017; 2017: doi:10.1155/2017/6031478 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 60.Cools R, Nakamura K, Daw N D.Serotonin and dopamine: Unifying affective, activational, and decision functions Neuropsychopharmacol 20113698–113.doi:10.1038/npp.2010.121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Guiard B P, El Mansari M, Merali Z.Functional interactions between dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine neurons: An in-vivo electrophysiological study in rats with monoaminergic lesions Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 200811625–639.doi:10.1017/S1461145707008383 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ranjbar-Slamloo Y, Fazlali Z.Dopamine and noradrenaline in the brain; overlapping or dissociate functions? Front Mol Neurosci 202012doi:10.3389/fnmol.2019.00334 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Aznar S, Hervig ME-S.The 5-HT2A serotonin receptor in executive function: Implications for neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases Neurosci Biobehav Rev 20166463–82.doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.02.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Bensmann W, Roessner V, Stock A-K.Catecholaminergic modulation of conflict control depends on the source of conflicts Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 201821901–909.doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyy063 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bensmann W, Zink N, Arning L.The presynaptic regulation of dopamine and norepinephrine synthesis has dissociable effects on different kinds of cognitive conflicts Mol Neurobiol 2019568087–8100.doi:10.1007/s12035-019-01664-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Beste C, Domschke K, Falkenstein M.Differential modulations of response control processes by 5-HT1A gene variation Neuroimage 201050764–771.doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.11.067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Beste C, Domschke K, Radenz B.The functional 5-HT1A receptor polymorphism affects response inhibition processes in a context-dependent manner Neuropsychologia 2011492664–2672.doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2011.05.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Beste C, Heil M, Domschke K.The relevance of the functional 5-HT1A receptor polymorphism for attention and working memory processes during mental rotation of characters Neuropsychologia 2010481248–1254.doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.12.025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Floresco S B, Magyar O.Mesocortical dopamine modulation of executive functions: beyond working memory Psychopharmacology 2006188567–585.doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0404-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Xing B, Li Y-C, Gao W-J.Norepinephrine versus dopamine and their interaction in modulating synaptic function in the prefrontal cortex Brain Res 20161641217–233.doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2016.01.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Zink N, Bensmann W, Arning L.The role of DRD1 and DRD2 receptors for response selection under varying complexity levels: implications for metacontrol processes Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 201922747–753.doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyz024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Harmer C J.Serotonin and emotional processing: does it help explain antidepressant drug action? Neuropharmacology 2008551023–1028.doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.06.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Schwarz L A, Luo L.Organization of the locus coeruleus-norepinephrine system Current Biology 201525R1051–R1056.doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.09.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ehlers M R, Todd R M.Genesis and maintenance of attentional biases: the role of the locus coeruleus-noradrenaline system. Neural Plast. 2017 2017: doi:10.1155/2017/6817349 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 75.De Raedt R, Koster EH W, Joormann J.Attentional control in depression: a translational affective neuroscience approach Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2010101–7.doi:10.3758/CABN.10.1.1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bromberg-Martin E S, Matsumoto M, Hikosaka O.Dopamine in motivational control: rewarding, aversive, and alerting Neuron 201068815–834.doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Whitton A E, Treadway M T, Pizzagalli D A.Reward processing dysfunction in major depression, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia Curr Opin Psychiatry 2015287–12.doi:10.1097/YCO.0000000000000122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Winkler J, Suhr S T, Gage F H.Essential role of neocortical acetylcholine in spatial memory Nature 1995375484–487.doi:10.1038/375484a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Dagytė G, Den Boer J A, Trentani A.The cholinergic system and depression Behav Brain Res 2011221574–582.doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2010.02.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Sanacora G, Treccani G, Popoli M.Towards a glutamate hypothesis of depression: An emerging frontier of neuropsychopharmacology for mood disorders Neuropharmacology 20126263–77.doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.07.036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Möhler H.Role of GABAA receptors in cognition Biochem Soc Trans 2009371328–1333.doi:10.1042/BST0371328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Yildiz A, Quetscher C, Dharmadhikari S.Feeling safe in the plane: neural mechanisms underlying superior action control in airplane pilot trainees—a combined EEG/MRS study Hum Brain Mapp 2014355040–5051.doi:10.1002/hbm.22530 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Steenbergen L, Sellaro R, Stock A-K.Aminobutyric acid (GABA) administration improves action selection processes: A randomised controlled trial Sci Rep 2015512770doi:10.1038/srep12770 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 84.Duman R S. Pathophysiology of depression and innovative treatments: Remodeling glutamatergic synaptic connections. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2014;16:11–27. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2014.16.1/rduman. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Pehrson A L, Sanchez C.Altered γ-aminobutyric acid neurotransmission in major depressive disorder: A critical review of the supporting evidence and the influence of serotonergic antidepressants Drug Des Devel Ther 20159603–624.doi:10.2147/DDDT.S62912 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Blumberg M J, Vaccarino S R, McInerney S J.Procognitive effects of antidepressants and other therapeutic agents in major depressive disorder: A systematic review. J Clin Psychiatry. 2020 81: doi:10.4088/JCP.19r13200 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 87.Michelson D, Amsterdam J, Apter J.Hormonal markers of stress response following interruption of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor treatment Psychoneuroendocrinology 200025169–177.doi:10.1016/s0306-4530(99)00046-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Montgomery D.European College of Neuropsychopharmacology. ECNP Consensus Meeting March 2000. Guidelines for investigating efficacy in GAD Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 20021281–87.doi:10.1016/s0924-977x(01)00147-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Saxe P A, Arnold L M, Palmer R H.Short-term (2-week) effects of discontinuing milnacipran in patients with fibromyalgia Curr Med Res Opin 201228815–821.doi:10.1185/03007995.2012.677418 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Hartford J, Kornstein S, Liebowitz M.Duloxetine as an SNRI treatment for generalized anxiety disorder: results from a placebo and active-controlled trial Int Clin Psychopharmacol 200722167–174.doi:10.1097/YIC.0b013e32807fb1b2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Sir A, D’Souza R F, Uguz S.Randomized trial of sertraline versus venlafaxine XR in major depression: efficacy and discontinuation symptoms J Clin Psychiatry 2005661312–1320.doi:10.4088/jcp.v66n1015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Gahr M, Schönfeldt-Lecuona C, Kölle M A.Withdrawal and discontinuation phenomena associated with tranylcypromine: A systematic review Pharmacopsychiatry 201346123–129.doi:10.1055/s-0032-1333265 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Charney D S, Heninger G R, Sternberg D E.Abrupt discontinuation of tricyclic antidepressant drugs: evidence for noradrenergic hyperactivity Br J Psychiatry 1982141377–386.doi:10.1192/bjp.141.4.377 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Montgomery S A, Huusom AK T, Bothmer J.A randomised study comparing escitalopram with venlafaxine XR in primary care patients with major depressive disorder Neuropsychobiology 20045057–64.doi:10.1159/000078225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Kaufman M J, Henry M E, Frederick BdeB.Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor discontinuation syndrome is associated with a rostral anterior cingulate choline metabolite decrease: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging study Biol Psychiatry 200354534–539.doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(02)01828-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Kirsch I, Deacon B J, Huedo-Medina T B.Initial severity and antidepressant benefits: A meta-analysis of data submitted to the food and drug administration PloS Medicine 20085e45doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


