Abstract
Background
Infections caused by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRPA) have been on the rise worldwide, and delayed active antimicrobial therapy is associated with high mortality. However, few studies have evaluated increases in P. aeruginosa infections with antimicrobial resistance and risk factors for such antimicrobial resistance in Korea. Here, we analyzed changes in antimicrobial susceptibility associated with P. aeruginosa bacteremia and identified risk factors of antimicrobial resistance.
Methods
The medical records of patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia who were admitted to a tertiary hospital between January 2009 and October 2020 were retrospectively reviewed. Antibiotic resistance rates were compared among the time periods of 2009–2012, 2013–2016, and 2017–2020 and between the intensive care unit (ICU) and non-ICU setting. Empirical antimicrobial therapy was considered concordant, if the organism was susceptible to antibiotics in vitro, and discordant, if resistant.
Results
During the study period, 295 patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia were identified. The hepatobiliary tract (26.8%) was the most common primary site of infection. The rates of carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa (CRPA), MDRPA, and extensively drug-resistant P. aeruginosa (XDRPA) were 24.7%, 35.9%, and 15.9%, respectively. XDRPA showed an increasing trend, and CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA were also gradually increasing in non-ICU setting. Previous exposure to fluoroquinolones and glycopeptides and urinary tract infection were independent risk factors associated with CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA. Previous exposure to carbapenems was an independent risk factor of CRPA. CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA were associated with discordant empirical antimicrobial therapy.
Conclusion
The identification of risk factors for antimicrobial resistance and analysis of antimicrobial susceptibility might be important for concordant empirical antimicrobial therapy in patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacteremia, Multidrug Resistance, Risk Factors
Graphical Abstract
INTRODUCTION
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an important pathogen in healthcare-associated infections, particularly P. aeruginosa bacteremia, which is associated with high rates of mortality and morbidity.1,2 The 30-day mortality rate associated with P. aeruginosa bacteremia ranges from 39% to 41%,3,4 and delayed active antimicrobial therapy can lead to worse outcomes.3,5,6,7
In the United States, 6,700 cases in 2013 and 32,600 cases in 2017 of multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa (MDRPA) infection were reported in hospitalized patients8,9; thus, increasing antibiotic resistance in P. aeruginosa among hospitalized patients is a major public health issue.10 In particular, infections caused by MDRPA or extensively drug-resistant P. aeruginosa (XDRPA) are a therapeutic challenge in terms of early active antibiotic use because effective antibiotics are limited.6,11 Thus, an analysis of antimicrobial susceptibility and the identification of risk factors for antimicrobial resistance might be important for early treatment initiation with active antibiotics in patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia.
The report of the Korea Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (KARMS) showed that the rate of carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa (CRPA) increased from 2010 (24.3%) to 2015 (41.0%) in sputum, urine, and wound specimens from general hospitals, and the rate of MDRPA was 18.2% in 2016.12 The report of the Korea Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (Kor-GLASS) showed that the rates of MDRPA and XDRPA were 14.7% and 10.7% in blood specimens from general hospitals.13 However, KARMS results included several types of specimens in which infection and colonization were indistinguishable, and the data collection methods of Kor-GLASS and KARMS are different, and thus, it is difficult to evaluate the increase in MDRPA infections. Several studies have assessed risk factors for antibiotic-resistant P. aeruginosa in specific populations from different countries.14,15,16,17 In Korea, Lee et al.18 reported that carbapenem exposure is a risk factor for P. aeruginosa resistant only to carbapenems, and Joo et al.19 reported that ceftazidime, piperacillin, and imipenem resistance in P. aeruginosa is associated with indwelling urinary catheter and prior exposure to fluoroquinolone based on 2006–2009 data. However, there is no recent clinical study of the risk factors for antibiotic-resistant P. aeruginosa or MDRPA infections in Korea. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to analyze the antimicrobial susceptibility trends in P. aeruginosa bacteremia in a tertiary hospital and evaluate the risk factors associated with antibiotic-resistant P. aeruginosa and their outcomes.
METHODS
Study population and data collection
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia admitted to Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, South Korea, from January 2009 to October 2020. The study hospital is a university-affiliated and tertiary hospital with 850 beds, four different intensive care units (ICUs) with 56 beds, and one hematopoietic stem cell transplantation unit. Patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia who had a confirmed diagnosis based on microbiological laboratory results were included in the study. Patients less than 18 years of age were excluded from the analysis. Demographic and clinical characteristics, such as age; sex; underlying diseases; Charlson comorbidity index score; stay in the ICU; hospital stay or healthcare within 30 days before P. aeruginosa bacteremia; prior surgery within 90 days before P. aeruginosa bacteremia; previous exposure (≥ 1 day) to any antimicrobials within 90 days before P. aeruginosa bacteremia; colonization with multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs), including carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE), extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing bacteria, multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus; use of medical devices (central venous catheter, ventilator, or indwelling urinary catheter) before bacteremia; polymicrobial infection; primary site of infection; antimicrobial therapy; length of hospital stay; presentation with septic shock; and 30-day mortality were obtained from medical records.
Our first aim was to evaluate whether clinically important CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA bacteremia were increased in a tertiary hospital. We presented antimicrobial susceptibility results for the period from 2009 to 2020, and since it was relatively small annual data from a single center, we compared the results by dividing them into three groups at 4-year intervals to analyze the trend in antibiotic susceptibility (i.e., 2009–2012, 2013–2016, and 2017–2020). Moreover, we compared the antibiotic resistance rates in P. aeruginosa bacteremia in ICU and non-ICU settings. Our second aim was to evaluate risk factors associated with antibiotic resistance in P. aeruginosa bacteremia and their outcomes. In addition, to identify the difference in mortality according to the antibiotic-resistant strain, we performed an additional evaluation of patients who did not show polymicrobial bacteremia, received active antimicrobial therapy during their hospital stay, and were hospitalized for more than 5 days after the onset of bacteremia.
Microbiological methods
Blood culture was performed using the automated BACTEC FX system (Becton Dickinson, Sparks, MD, USA) or a BacT/Alert 3D system (bioMérieux, Marcy l'Etoile, France). Bacterial identification and antimicrobial susceptibility tests were performed using the Vitek II automated system (bioMérieux). The results of the antimicrobial susceptibility test were interpreted based on the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines, and all the results were re-evaluated based on the revised CLSI guidelines.20 Intermediate susceptibility was defined as being non-susceptible.10
Definitions
P. aeruginosa bacteremia was defined as isolation of the organism from at least one bottle of blood culture grown using samples from patients with symptoms and signs of infection. In the case of patients with recurrent P. aeruginosa bacteremia during hospitalization, only the first P. aeruginosa bacteremia episode for each patient was included in the study. Polymicrobial bacteremia was defined as either the growth of one or more different microorganisms from blood culture in which P. aeruginosa was identified or the growth of species other than P. aeruginosa in two or more separate blood cultures within the same case.21 Colonization with MDROs was defined as a positive rectal swab, nasal swab, urine, sputum, and other clinical specimens, and polymicrobial bacteremia and other infections were excluded. Healthcare-associated infection was defined as confirmed P. aeruginosa bacteremia in patients who had been hospitalized for more than 48 hours or in patients with a history of hospitalization or healthcare such as outpatient chemotherapy or dialysis within 1 month.22,23 The primary site of infection was defined by documented or presumed clinical signs, laboratory findings, and radiologic findings according to National Healthcare Safety Network surveillance definitions.24 Gastrointestinal system infections were classified as gastrointestinal tract and hepatobiliary tract, and respiratory tract infections included both non-ventilator-associated pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia. Neutropenia was defined as an absolute neutrophil count of less than 500 cells/mm3. Septic shock was defined as sepsis with persisting hypotension and requiring vasopressor therapy needed to maintain mean arterial pressure at ≥ 65 mmHg despite adequate fluid resuscitation.25
Antimicrobial categories were classified as aminoglycosides (amikacin, gentamicin), antipseudomonal carbapenems (imipenem, meropenem), antipseudomonal cephalosporins (ceftazidime, cefepime), antipseudomonal penicillin with β-lactamase inhibitors (piperacillin-tazobactam, ticarcillin-clavulanic acid), fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin), monobactams (aztreonam), and polymyxins (colistin). Antimicrobial-resistant P. aeruginosa was categorized as follows: 1) CRPA when resistance or intermediate resistance was confirmed with one or more carbapenems having antipseudomonal activity (e.g., imipenem or meropenem) as per CLSI guidelines5,20; 2) MDRPA when the organism was not susceptible to one or more agents in at least three antimicrobial categories; 3) XDRPA when the organism was not susceptible to at least one agent in all but two or fewer antimicrobial categories; and 4) pandrug-resistant P. aeruginosa (PDRPA) when the organism was not susceptible to all antimicrobial categories.26
Active antimicrobial therapy was defined as antibiotics demonstrated to be active in vitro against blood isolates of P. aeruginosa during the treatment period.5 Concordant empirical antimicrobial therapy was defined as active antimicrobial therapy administered less than or equal to 48 hours after obtaining blood culture samples. Discordant empirical antimicrobial therapy was defined as active antimicrobial therapy not administered within 48 hours after obtaining blood culture samples.27,28
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics, version 26.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). All continuous variables are summarized as medians and interquartile ranges (IQRs), and categorical variables are described using frequencies and percentiles. Categorical variables were compared using Pearson's χ2 tests or Fisher's exact tests, whereas noncategorical variables were tested using Mann-Whitney tests. Multivariable analysis was performed for variables that had a P value less than 0.05 in univariable analysis. Risk factors for antibiotic resistance in P. aeruginosa bacteremia were evaluated using logistic regression analysis. The risk factors of 30-day mortality were analyzed using cox proportional hazard regression. Results with P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Ethics statement
The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board (IRB) of Inje University Busan Paik Hospital (IRB number: 2020-11-003), and the need for informed consent was waived owing to the retrospective nature of the study.
RESULTS
Antimicrobial susceptibility trends in P. aeruginosa bacteremia
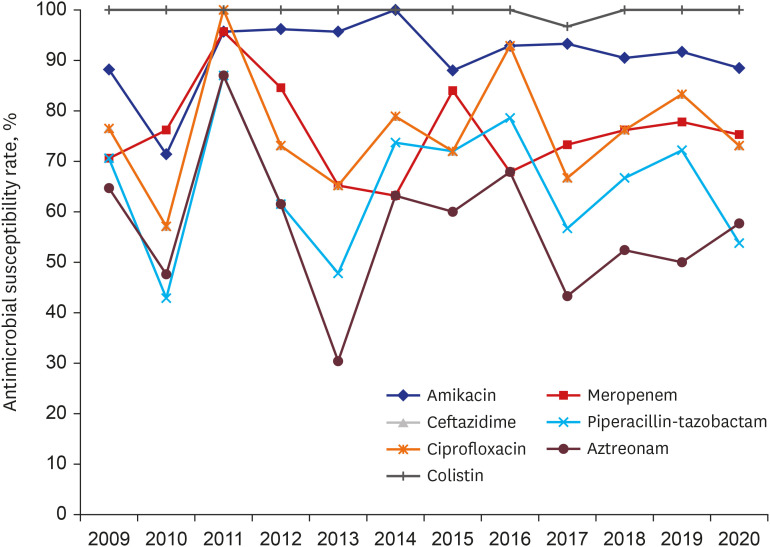
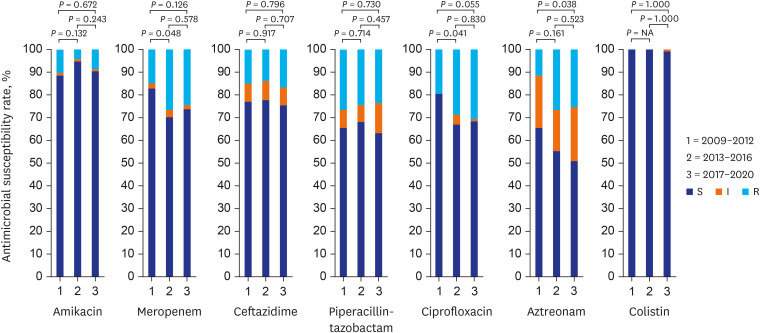
During the study period, 295 patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia were identified. Antimicrobial susceptibility results are shown in Figs. 1 and 2. Among isolates, 213 (72.2%) showed non-susceptibility to one or more antibiotics. The susceptibility rate of P. aeruginosa to only colistin and amikacin was more than 90% (Table 1). The susceptibility rates for meropenem (P = 0.048) and ciprofloxacin (P = 0.041) were significantly decreased during 2013–2016 compared with those during 2009–2012 (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1. Annual antimicrobial susceptibility trends in P. aeruginosa bacteremia.
Fig. 2. Results of antimicrobial susceptibility in P. aeruginosa bacteremia for 2009–2012, 2013–2016, and 2017–2020. The P value was a comparison between susceptible and non-susceptible.
NA = not applicable, S = susceptible, I = intermediate, R = resistant.
Table 1. Antimicrobial susceptibility rates in P. aeruginosa bacteremia.
| Characteristics | Total (n = 295) | 2009–2012 (n = 87) | 2013–2016 (n = 94) | 2017–2020 (n = 114) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amikacin | 269 (91.2) | 77 (88.5) | 89 (94.7) | 103 (90.4) | 0.316 |
| Gentamicin | 246 (83.4) | 75 (86.2) | 82 (87.2) | 89 (78.1) | 0.147 |
| Imipenem | 220 (74.6) | 71 (81.6) | 65 (69.1) | 84 (73.7) | 0.151 |
| Meropenem | 222 (75.3) | 72 (82.8) | 66 (70.2) | 84 (73.7) | 0.131 |
| Cefepime | 228 (77.3) | 68 (78.2) | 76 (80.9) | 85 (74.6) | 0.551 |
| Ceftazidime | 226 (76.6) | 67 (77.0) | 73 (77.7) | 86 (75.4) | 0.926 |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 193 (65.4) | 57 (65.5) | 64 (68.1) | 72 (63.2) | 0.758 |
| Ticarcillin-clavulanate | 99 (33.6) | 23 (26.4) | 37 (39.4) | 39 (34.2) | 0.181 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 211 (71.5) | 70 (80.5) | 63 (67.0) | 78 (68.4) | 0.087 |
| Aztreonam | 167 (56.6) | 57 (65.5) | 52 (55.3) | 58 (50.8) | 0.111 |
| Colistin | 294 (99.7) | 87 (100) | 94 (100) | 113 (99.1) | 1.000 |
Values are presented as number of patients (%).
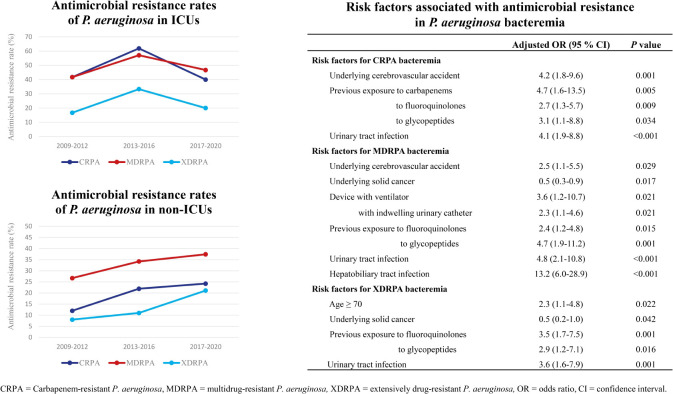
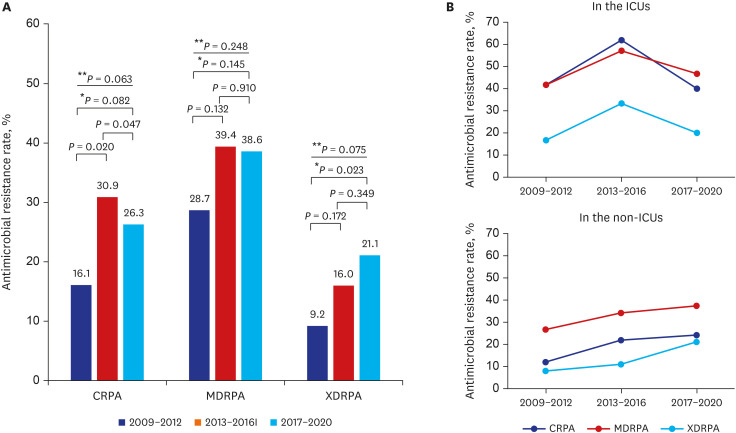
The rates of CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA were 24.7% (73/295), 35.9% (106/295), and 15.9% (47/295), respectively. Among MDRPA and XDRPA, CRPA was identified as 65 (61.3%) and 43 (91.5%) cases, respectively. PDRPA was not identified. There was one colistin-resistant strain, but it was susceptible to anti-pseudomonal cephalosporines and carbapenems, and further evaluation was not performed. The rates of CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA in the ICU were higher than those in non-ICU settings (CRPA: 50% vs. 19.8%, P < 0.001; MDRPA: 50% vs. 33.2%, P = 0.026; and XDRPA: 25% vs. 14.2%, P = 0.061). The XDRPA rate was significantly increased during 2017–2020 compared with that during 2009-2012 (P = 0.023; Fig. 3). During 2017–2020, the antibiotic resistance rates in the ICU decreased compared to 2013–2016, whereas those in the non-ICU setting gradually increased over time.
Fig. 3. Antimicrobial resistance trends in P. aeruginosa bacteremia. (A) Antimicrobial resistance rates in P. aeruginosa bacteremia. (B) Comparison of antibiotic resistance rates of the ICUs vs. the non-ICUs setting.
CRPA = carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa, MDRPA = multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa, XDRPA = extensively drug-resistant P. aeruginosa, ICU = intensive care unit.
*Comparison between 2009–2013 and 2017–2020; **Comparison of the three groups.
Clinical characteristics of patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia
The median age of 295 patients was 68 years (IQR, 60–76 years; Table 2). Among all patients, 245 (83.1%) had healthcare-associated infection, 221 (74.9%) had a history of antibiotic exposure within 90 days, and 155 (52.5%) patients had solid cancer. Of the patients with solid cancer, 9 (5.8%) were being followed after remission, 31 (20%) were hospitalized for cancer diagnosis, and 76 (49.0%) were receiving chemotherapy. The hepatobiliary tract (26.8%) was the most common primary site of infection, followed by the respiratory (23.4%) and urinary (16.9%) tracts. Fifty (16.9%) patients had polymicrobial bacteremia, and the common primary site of infection were the hepatobiliary tract (16/50, 32.0%) and central venous catheter (10/50, 20.0%). Of 79 patients with hepato-biliary tract infection, 55 (69.6%) had undergone endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (37/79, 46.8%) or percutaneous drainage (18/79, 22.8%). Of 50 patients with urinary tract infection, 30 (60%) were catheter-associated urinary tract infections.
Table 2. Clinical characteristics, treatment, and outcomes in patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia.
| Characteristics | Total (n = 295) | CRPA (n = 73) | Non-CRPA (n = 222) | P | MDRPA (n = 106) | Non-MDRPA (n = 189) | P | XDRPA (n = 47) | Non- XDRPA (n = 248) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yrs | 68 (60–76) | 72 (60–77) | 68 (60–75) | 0.078 | 72 (61–77) | 67 (57–75) | 0.041 | 73 (65–79) | 68 (58–75) | 0.005 | |
| Male sex | 197 (66.8) | 53 (72.6) | 144 (64.9) | 0.223 | 73 (68.9) | 124 (65.6) | 0.568 | 34 (72.3) | 163 (65.7) | 0.377 | |
| Underlying diseases or conditions | |||||||||||
| Cardiovascular disease | 30 (10.2) | 10 (13.7) | 20 (9.0) | 0.250 | 10 (9.4) | 20 (10.6) | 0.754 | 6 (12.8) | 24 (9.7) | 0.597 | |
| Cerebrovascular accident | 40 (13.6) | 19 (26.0) | 21 (9.5) | < 0.001 | 21 (19.8) | 19 (10.1) | 0.019 | 13 (27.7) | 27 (10.9) | 0.002 | |
| Chronic kidney disease | 24 (8.1) | 6 (8.2) | 18 (8.1) | 0.976 | 8 (7.5) | 16 (8.5) | 0.782 | 6 (12.8) | 18 (7.3) | 0.240 | |
| COPD or chronic lung disease | 7 (2.4) | 2 (2.7) | 5 (2.3) | 0.812 | 2 (1.9) | 5 (2.6) | 1.000 | 2 (4.3) | 5 (2.0) | 0.309 | |
| Dementia | 14 (4.7) | 3 (4.1) | 11 (5.0) | 1.000 | 5 (4.7) | 9 (4.8) | 0.986 | 4 (8.5) | 10 (4.0) | 0.250 | |
| Diabetes | 84 (28.5) | 23 (31.5) | 61 (27.5) | 0.508 | 35 (33.0) | 49 (25.9) | 0.195 | 19 (40.4) | 65 (26.2) | 0.048 | |
| Heart failure | 14 (4.7) | 2 (2.7) | 12 (5.4) | 0.353 | 4 (3.8) | 10 (5.3) | 0.556 | 2 (4.3) | 12 (4.8) | 1.000 | |
| Hypertension | 112 (38.0) | 30 (41.1) | 82 (36.9) | 0.525 | 43 (40.6) | 69 (36.5) | 0.491 | 23 (48.9) | 89 (35.9) | 0.091 | |
| Liver disease | 12 (4.1) | 2 (2.7) | 10 (4.5) | 0.737 | 4 (3.8) | 8 (4.2) | 1.000 | 0 (0.0) | 12 (4.8) | 0.225 | |
| Solid cancer | 155 (52.5) | 30 (41.1) | 125 (56.3) | 0.024 | 47 (44.3) | 108 (57.1) | 0.035 | 15 (31.9) | 140 (56.5) | 0.002 | |
| Hematologic malignancy | 26 (8.8) | 10 (13.7) | 16 (7.2) | 0.090 | 10 (9.4) | 16 (8.5) | 0.778 | 6 (12.8) | 20 (8.1) | 0.297 | |
| Immunosuppressive therapy | 102 (34.6) | 20 (27.4) | 82 (36.9) | 0.137 | 24 (22.6) | 78 (41.3) | 0.001 | 12 (25.5) | 90 (36.3) | 0.155 | |
| Neutropenia | 54 (18.3) | 10 (13.7) | 44 (19.8) | 0.241 | 13 (12.3) | 41 (21.7) | 0.045 | 7 (14.9) | 47 (19.0) | 0.509 | |
| Transplantation | 7 (2.4) | 3 (4.1) | 4 (1.8) | 0.261 | 3 (2.8) | 4 (2.1) | 0.705 | 2 (4.3) | 5 (2.0) | 0.309 | |
| CCI score | 5 (4–8) | 5 (3–7) | 5 (4–8) | 0.181 | 5 (3–7) | 5 (4–8) | 0.118 | 5 (3–7) | 5 (4–8) | 0.167 | |
| CCI score ≥ 5 | 170 (57.6) | 37 (50.7) | 133 (59.9) | 0.166 | 56 (52.8) | 114 (60.3) | 0.212 | 24 (51.1) | 146 (58.9) | 0.321 | |
| Healthcare-associated infection | 245 (83.1) | 67 (91.8) | 178 (80.2) | 0.022 | 93 (87.7) | 152 (80.4) | 0.108 | 42 (89.4) | 203 (81.9) | 0.209 | |
| Previous surgery within 90 days | 66 (22.4) | 18 (24.7) | 48 (21.6) | 0.589 | 21 (19.8) | 45 (23.8) | 0.429 | 10 (21.3) | 56 (22.6) | 0.844 | |
| Any antibiotic exposure within 90 days | 221 (74.9) | 61 (83.6) | 160 (72.1) | 0.049 | 87 (82.1) | 134 (70.9) | 0.034 | 38 (80.9) | 183 (73.8) | 0.306 | |
| Aminoglycosides | 14 (4.7) | 8 (11.0) | 6 (2.7) | 0.004 | 9 (8.5) | 5 (2.6) | 0.023 | 6 (12.8) | 8 (3.2) | 0.013 | |
| 3rd/4th generation cephalosporins | 152 (51.5) | 44 (60.3) | 108 (48.6) | 0.085 | 64 (60.4) | 88 (46.6) | 0.023 | 26 (55.3) | 126 (50.8) | 0.570 | |
| Anti-pseudomonal penicillins | 49 (16.6) | 19 (26.0) | 30 (13.5) | 0.013 | 23 (21.7) | 26 (13.8) | 0.079 | 10 (21.3) | 39 (15.7) | 0.348 | |
| Carbapenems | 42 (14.2) | 30 (41.1) | 12 (5.4) | < 0.001 | 28 (26.4) | 14 (7.4) | < 0.001 | 15 (31.9) | 27 (10.9) | < 0.001 | |
| Fluoroquinolones | 66 (22.4) | 33 (45.2) | 33 (14.9) | < 0.001 | 36 (34.0) | 30 (15.9) | < 0.001 | 22 (46.8) | 44 (17.7) | < 0.001 | |
| Metronidazole | 46 (15.6) | 16 (21.9) | 30 (13.5) | 0.086 | 21 (19.8) | 25 (13.2) | 0.135 | 11 (23.4) | 35 (14.1) | 0.107 | |
| Clindamycin | 13 (4.4) | 8 (11.0) | 5 (2.3) | 0.004 | 7 (6.6) | 6 (3.2) | 0.236 | 5 (10.6) | 8 (3.2) | 0.039 | |
| Glycopeptides | 40 (13.6) | 27 (37.0) | 13 (5.9) | < 0.001 | 27 (25.5) | 13 (6.9) | < 0.001 | 14 (29.8) | 26 (10.5) | < 0.001 | |
| Linezolid | 8 (2.7) | 4 (5.5) | 4 (1.8) | 0.093 | 4 (3.8) | 4 (2.1) | 0.464 | 1 (2.1) | 7 (2.8) | 1.000 | |
| Tigecycline | 7 (2.4) | 5 (6.8) | 2 (0.9) | 0.004 | 5 (4.7) | 2 (1.1) | 0.102 | 1 (2.1) | 6 (2.4) | 1.000 | |
| Colistin | 7 (2.4) | 5 (6.8) | 2 (0.9) | 0.004 | 5 (4.7) | 2 (1.1) | 0.102 | 1 (2.1) | 6 (2.4) | 1.000 | |
| Colonization with MDROs | |||||||||||
| CRE | 4 (1.4) | 2 (2.7) | 2 (0.9) | 0.239 | 3 (2.8) | 1 (0.5) | 0.134 | 1 (2.1) | 3 (1.2) | 0.502 | |
| ESBL | 27 (9.4) | 10 (13.7) | 17 (7.7) | 0.120 | 10 (9.4) | 17 (9.0) | 0.900 | 4 (8.5) | 23 (9.3) | 1.000 | |
| MRAB | 16 (5.4) | 8 (11.0) | 8 (3.6) | 0.016 | 9 (8.5) | 7 (3.7) | 0.082 | 2 (4.3) | 14 (5.6) | 1.000 | |
| MRSA | 5 (1.7) | 1 (1.4) | 4 (1.8) | 1.000 | 1 (0.9) | 4 (2.1) | 0.658 | 0 (0) | 5 (2.0) | 1.000 | |
| VRE | 19 (6.4) | 13 (17.8) | 6 (2.7) | < 0.001 | 12 (11.3) | 7 (3.7) | 0.011 | 5 (10.6) | 14 (5.6) | 0.200 | |
| ICU stay | 48 (16.3) | 24 (32.9) | 24 (10.8) | < 0.001 | 24 (22.6) | 24 (12.7) | 0.026 | 12 (25.5) | 36 (14.5) | 0.061 | |
| Devices during time at risk | |||||||||||
| Central venous catheter | 107 (36.3) | 34 (46.6) | 73 (32.9) | 0.035 | 36 (34.0) | 71 (37.6) | 0.537 | 19 (40.4) | 88 (35.5) | 0.518 | |
| Ventilator | 29 (9.8) | 13 (17.8) | 16 (7.2) | 0.008 | 18 (17.0) | 11 (5.8) | 0.002 | 7 (14.9) | 22 (8.9) | 0.192 | |
| Indwelling urinary catheter | 100 (33.9) | 37 (50.7) | 63 (28.4) | < 0.001 | 51 (48.1) | 49 (25.9) | < 0.001 | 24 (51.1) | 76 (30.6) | 0.007 | |
| Shock on the first day of bacteremia | 84 (28.5) | 21 (28.8) | 63 (28.4) | 0.949 | 31 (29.2) | 53 (28.0) | 0.826 | 14 (29.8) | 70 (28.2) | 0.828 | |
| Primary site of infection | |||||||||||
| Hepato-biliary tract | 79 (26.8) | 19 (26.0) | 60 (27.0) | 0.867 | 42 (39.6) | 37 (19.6) | < 0.001 | 13 (27.7) | 66 (26.6) | 0.882 | |
| Gastrointestinal tract | 19 (6.4) | 3 (4.1) | 16 (7.2) | 0.424 | 4 (3.8) | 15 (7.9) | 0.162 | 2 (4.3) | 17 (6.9) | 0.748 | |
| Respiratory tract | 69 (23.4) | 13 (17.8) | 56 (25.2) | 0.194 | 18 (17.0) | 51 (27.0) | 0.051 | 10 (21.3) | 59 (23.8) | 0.709 | |
| Urinary tract | 50 (16.9) | 22 (30.1) | 28 (12.6) | 0.001 | 25 (23.6) | 25 (13.2) | 0.023 | 16 (34.0) | 34 (13.7) | < 0.001 | |
| Central venous catheter | 39 (13.2) | 11 (15.1) | 28 (12.6) | 0.591 | 10 (9.4) | 29 (15.3) | 0.150 | 4 (8.5) | 35 (14.1) | 0.357 | |
| Skin and soft tissue | 12 (4.1) | 2 (2.7) | 10 (4.5) | 0.508 | 3 (2.8) | 9 (4.8) | 0.547 | 1 (2.1) | 11 (4.1) | 0.698 | |
| Surgical site | 2 (0.7) | 0 (0) | 2 (0.9) | 1.000 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (1.1) | 0.538 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.8) | 1.000 | |
| Primary bloodstream | 25 (8.5) | 3 (4.1) | 22 (9.9) | 0.123 | 4 (3.8) | 21 (11.1) | 0.030 | 1 (2.1) | 24 (9.7) | 0.147 | |
| Polymicrobial bacteremia | 50 (16.9) | 11 (15.1) | 39 (17.6) | 0.622 | 15 (14.2) | 35 (18.5) | 0.337 | 5 (10.6) | 45 (18.1) | 0.209 | |
| Invasive drainage procedures | 62 (21.0) | 13 (17.8) | 49 (22.1) | 0.438 | 30 (28.3) | 32 (16.9) | 0.021 | 10 (21.3) | 52 (21.0) | 0.962 | |
| Active antimicrobial therapy | 244 (82.7) | 54 (74.0) | 190 (85.6) | 0.023 | 77 (72.6) | 167 (88.4) | 0.001 | 34 (72.3) | 210 (84.7) | 0.040 | |
| Concordant empirical antimicrobial therapy | 181 (61.4) | 25 (34.2) | 156 (70.3) | < 0.001 | 36 (34.0) | 145 (76.7) | < 0.001 | 15 (31.9) | 166 (66.9) | < 0.001 | |
| Single antibiotics | 151 (51.2) | 23 (31.5) | 128 (57.7) | 34 (32.1) | 117 (61.9) | 14 (29.8) | 137 (55.2) | ||||
| Combination antibiotics | 30 (10.2) | 2 (2.7) | 28 (12.6) | 2 (1.9) | 28 (14.8) | 1 (2.1) | 29 (11.7) | ||||
| Duration of active antibiotics, days | 8 (1–15) | 7 (0–14) | 8 (2–14) | 0.172 | 7 (0–14) | 8 (2–15.5) | 0.072 | 8 (0–15) | 8 (2–14.8) | 0.207 | |
| Length of hospital stay after bacteremia, days | 10 (4–18) | 12 (5–23) | 10 (5–18) | < 0.001 | 10 (5–17) | 9 (4–18) | 0.213 | 11 (5–22) | 9 (4–17.5) | 0.204 | |
| 30-day mortality | 80 (27.1) | 22 (30.1) | 58 (26.1) | 0.504 | 28 (35.0) | 52 (27.5) | 0.839 | 14 (29.8) | 66 (26.6) | 0.654 | |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%).
CRPA = carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa, MDRPA = multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa, XDRPA = extensively drug-resistant P. aeruginosa, COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, CCI = Charlson comorbidity index, MDRO = multidrug-resistant organism, CRE = carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, ESBL = extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing bacteria, MRAB = multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, MRSA = methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, VRE = vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, ICU = intensive care unit.
A total of 244 (82.7%) patients received active antimicrobial therapy, and 181 (61.4%) patients received concordant empirical antimicrobial therapy (Table 2). Patients with septic shock received more carbapenem therapy as empirical antimicrobial therapy than patients without shock (28.6% vs. 15.6%, P = 0.011). CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA were significantly more frequent in patients who had underlying cerebrovascular accidents, those with an indwelling urinary catheter, and those exposed to aminoglycosides, carbapenems, fluoroquinolones, and glycopeptides. Moreover, CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA were significantly associated with discordant empirical antimicrobial therapy. Of XDRPA, 21.2% (10/47) were nursing hospital-associated infections.
Risk factors associated with antimicrobial resistance in P. aeruginosa bacteremia
In multivariable analysis, urinary tract infection and previous exposure to fluoroquinolones and glycopeptides were independent risk factors for CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA (Table 3). Risk factors for CRPA were the presence of an underlying cerebrovascular accident and previous exposure to carbapenems. Risk factors for MDRPA were the presence of an underlying cerebrovascular accident, a device with a ventilator and an indwelling urinary catheter, and hepatobiliary tract infection. Age greater than or equal to 70 years was an independent risk factor for XDRPA. Solid cancer was associated with a significantly lower risk of MDRPA and XDRPA.
Table 3. Risk factors associated with antimicrobial resistance in P. aeruginosa bacteremia.
| Risk factors | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRPA bacteremia | ||||
| Underlying cerebrovascular accident | 4.2 (1.8–9.6) | 0.001 | ||
| Previous exposure to | ||||
| Carbapenems | 4.7 (1.6–13.5) | 0.005 | ||
| Fluoroquinolones | 2.7 (1.3–5.7) | 0.009 | ||
| Glycopeptides | 3.1 (1.1–8.8) | 0.034 | ||
| Urinary tract infection | 4.1 (1.9–8.8) | < 0.001 | ||
| MDRPA bacteremia | ||||
| Underlying cerebrovascular accident | 2.5 (1.1–5.5) | 0.029 | ||
| Underlying solid cancer | 0.5 (0.3–0.9) | 0.017 | ||
| Device with ventilator | 3.6 (1.2–10.7) | 0.021 | ||
| With indwelling urinary catheter | 2.3 (1.1–4.6) | 0.021 | ||
| Previous exposure to | ||||
| Fluoroquinolones | 2.4 (1.2–4.8) | 0.015 | ||
| Glycopeptides | 4.7 (1.9–11.2) | 0.001 | ||
| Urinary tract infection | 4.8 (2.1–10.8) | < 0.001 | ||
| Hepatobiliary tract infection | 13.2 (6.0–28.9) | < 0.001 | ||
| XDRPA bacteremia | ||||
| Age ≥ 70 | 2.3 (1.1–4.8) | 0.022 | ||
| Underlying solid cancer | 0.5 (0.2–1.0) | 0.042 | ||
| Previous exposure to | ||||
| Fluoroquinolones | 3.5 (1.7–7.5) | 0.001 | ||
| Glycopeptides | 2.9 (1.2–7.1) | 0.016 | ||
| Urinary tract infection | 3.6 (1.6–7.9) | 0.001 | ||
OR = odds ratio, CI = confidence interval, CRPA = carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa, MDRPA = multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa, XDRPA = extensively drug-resistant P. aeruginosa.
Clinical outcomes and risk factors for 30-day mortality
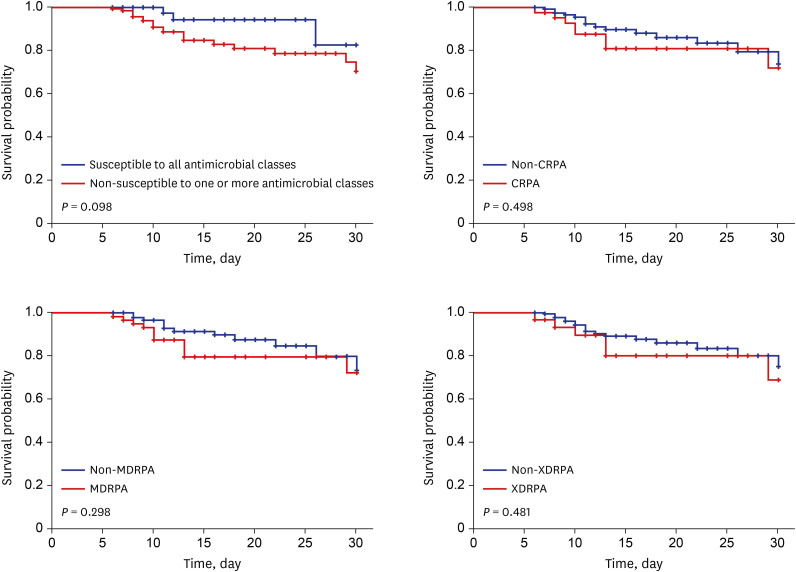
The 30-day mortality rate was 27.1% (80/295; Table 2). Of those, 56 (70.0%) had septic shock and 49 (61.3%) died within 5-day after bacteremia. Independent risk factors for 30-day mortality were the presence of underlying hematologic malignancy, ICU stay, polymicrobial bacteremia, septic shock, and respiratory tract as the primary site of infection (Table 4). The 30-day mortality did not differ between multidrug-resistant strains and non-multidrug-resistant strains (Table 2). In subgroup analysis for patients (169/295, 57.3%) without polymicrobial bacteremia, those receiving active antimicrobial therapy, and hospitalization for more than 5 days after the onset of bacteremia, antibiotic resistant strains and multidrug-resistant strains resulted in a higher 30-day mortality rate than strains susceptible to all antibiotics and non-multidrug-resistant strains, but this was not statistically significant (Fig. 4).
Table 4. Risk factors for 30-day mortality in patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia.
| Characteristics | Non-survivor (n = 80) | Survivor (n = 215) | Univariable HR (95% CI) | P | Multivariable HR (95% CI) | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age ≥ 65 | 49 (61.3) | 128 (59.5) | 1.2 (0.8–1.9) | 0.418 | ||||
| Male sex | 59 (73.8) | 138 (64.2) | 0.7 (0.4–1.1) | 0.146 | ||||
| Underlying conditions | ||||||||
| Cardiovascular disease | 9 (11.3) | 21 (9.8) | 1.0 (0.5–1.9) | 0.892 | ||||
| Cerebrovascular accident | 5 (6.3) | 35 (16.3) | 0.3 (0.1–0.9) | 0.021 | ||||
| Chronic kidney disease | 10 (12.5) | 14 (6.5) | 1.5 (0.8–3.0) | 0.206 | ||||
| COPD or chronic lung disease | 2 (2.5) | 5 (2.3) | 1.0 (0.3–4.2) | 0.967 | ||||
| Dementia | 1 (1.3) | 13 (6.0) | 0.3 (0.1–2.5) | 0.294 | ||||
| Diabetes | 26 (32.5) | 58 (27.0) | 1.2 (0.8–2.0) | 0.384 | ||||
| Heart failure | 5 (6.3) | 9 (4.2) | 1.9 (0.7–4.6) | 0.183 | ||||
| Hypertension | 27 (33.8) | 85 (39.5) | 0.8 (0.5–1.2) | 0.270 | ||||
| Liver disease | 3 (3.8) | 9 (4.2) | 0.9 (0.3–2.9) | 0.882 | ||||
| Solid cancer | 44 (55.0) | 111 (51.6) | 1.1 (0.7–1.8) | 0.512 | ||||
| Hematologic malignancy | 16 (20.0) | 10 (4.7) | 2.8 (1.6–4.9) | < 0.001 | 2.3 (1.3–4.0) | 0.005 | ||
| Immunosuppressive therapy | 35 (43.8) | 67 (31.2) | 1.5 (0.9–2.3) | 0.071 | ||||
| Neutropenia | 28 (35.0) | 26 (12.1) | 2.7 (1.7–4.3) | < 0.001 | ||||
| Transplantation | 2 (2.5) | 5 (2.3) | 1.1 (0.3–4.3) | 0.931 | ||||
| CCI score ≥ 5 | 49 (61.3) | 121 (56.3) | 1.2 (0.8–1.9) | 0.439 | ||||
| Healthcare-associated infection | 65 (81.3) | 180 (83.7) | 0.8 (0.5–1.4) | 0.400 | ||||
| Previous surgery within 90 days | 20 (25.0) | 46 (21.4) | 1.1 (0.7–1.9) | 0.587 | ||||
| Any antibiotic exposure within 90 days | 65 (81.3) | 156 (72.6) | 1.3 (0.7–2.2) | 0.397 | ||||
| Colonization with MDROs | ||||||||
| CRE | 1 (1.3) | 3 (1.4) | 1.6 (0.2–11.6) | 0.638 | ||||
| ESBL | 4 (5.0) | 23 (10.7) | 0.5 (0.2–1.2) | 0.126 | ||||
| MRAB | 9 (11.3) | 7 (3.3) | 2.0 (1.0–4.1) | 0.049 | ||||
| MRSA | 2 (2.5) | 3 (1.4) | 1.2 (0.3–5.2) | 0.738 | ||||
| VRE | 9 (11.3) | 10 (4.7) | 1.8 (0.9–3.6) | 0.095 | ||||
| ICU stay | 25 (31.3) | 23 (10.7) | 2.3 (1.5–3.8) | < 0.001 | 1.7 (1.1–2.8) | 0.025 | ||
| Devices during time at risk | ||||||||
| Central venous catheter | 35 (43.8) | 72 (33.5) | 1.2 (0.8–1.9) | 0.342 | ||||
| Ventilator | 17 (21.3) | 12 (5.6) | 2.6 (1.5–4.5) | < 0.001 | ||||
| Indwelling urinary catheter | 34 (42.5) | 66 (30.7) | 1.4 (0.9–2.2) | 0.132 | ||||
| Antimicrobial resistance | ||||||||
| CRPA | 22 (27.5) | 51 (23.7) | 1.1 (0.7–1.8) | 0.774 | ||||
| MDRPA | 28 (35.0) | 78 (36.3) | 0.9 (0.6–1.4) | 0.669 | ||||
| XDRPA | 14 (17.5) | 33 (15.3) | 1.0 (0.6–1.8) | 0.904 | ||||
| Polymicrobial infection | 21 (26.3) | 29 (13.5) | 1.8 (1.1–3.0) | 0.017 | 1.8 (1.1–3.1) | 0.032 | ||
| Shock on the first day of bacteremia | 56 (70.0) | 28 (13.0) | 8.5 (5.3–13.8) | < 0.001 | 6.4 (3.8–10.7) | < 0.001 | ||
| Primary site of infection | ||||||||
| Hepato-biliary tract | 15 (18.8) | 64 (29.8) | 0.6 (0.4–1.1) | 0.096 | ||||
| Gastrointestinal tract | 7 (8.8) | 12 (5.6) | 1.2 (0.7–3.3) | 0.283 | ||||
| Respiratory tract | 35 (43.8) | 34 (15.8) | 3.4 (2.2–5.2) | < 0.001 | 1.7 (1.0–2.8) | 0.034 | ||
| Urinary tract | 7 (8.8) | 43 (20.0) | 0.4 (0.2–0.9) | 0.023 | ||||
| Central venous catheter | 7 (8.8) | 32 (14.9) | 0.5 (0.2–1.1) | 0.088 | ||||
| Skin and soft tissue | 2 (2.5) | 10 (4.7) | 0.5 (0.1–2.1) | 0.372 | ||||
| Surgical site | 1 (1.3) | 1 (0.5) | 3.3 (0.5–23.7) | 0.239 | ||||
| Primary bloodstream | 6 (7.5) | 19 (8.8) | 0.9 (0.4–2.1) | 0.824 | ||||
| Invasive drainage procedures | 9 (11.3) | 53 (24.7) | 0.5 (0.2–0.9) | 0.024 | ||||
| Active antimicrobial therapy | 67 (83.8) | 177 (82.3) | 0.7 (0.4–1.3) | 0.292 | ||||
| Concordant empirical antimicrobial therapy | 56 (70.0) | 125 (58.1) | 1.4 (0.9–2.3) | 0.141 | ||||
| Single antibiotics | 42 (52.5) | 109 (50.7) | ||||||
| Aminoglycoside | 0 (0) | 6 (2.8) | ||||||
| Anti-pseudomonal cephalosporine | 12 (15.0) | 23 (10.7) | ||||||
| Anti-pseudomonal penicillin | 5 (6.3) | 39 (18.1) | ||||||
| Carbapenem | 17 (21.3) | 31 (14.4) | ||||||
| Fluoroquinolone | 1 (1.3) | 8 (3.7) | ||||||
| Colistin | 7 (8.8) | 2 (0.9) | ||||||
| Combination antibiotics | 14 (17.5) | 16 (7.4) | ||||||
| Anti-pseudomonal cephalosporine + aminoglycoside | 1 (1.3) | 2 (0.9) | ||||||
| Anti-pseudomonal cephalosporine + fluoroquinolone | 1 (1.3) | 1 (0.5) | ||||||
| Anti-pseudomonal penicillin + fluoroquinolone | 9 (11.3) | 12 (5.6) | ||||||
| Carbapenem + aminoglycoside | 2 (2.5) | 0 (0) | ||||||
| Carbapenem + fluoroquinolone | 1 (1.3) | 1 (0.5) | ||||||
Values are presented as number (%).
HR = hazard ratio, CI = confidence interval, COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, CCI = Charlson comorbidity index, MDRO = multidrug-resistant organism, CRE = carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, ESBL = extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing bacteria, MRAB = multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, MRSA = methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, VRE = vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, ICU = intensive care unit, CRPA = carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa, MDRPA = multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa, XDRPA = extensively drug-resistant P. aeruginosa.
Fig. 4. Survival curve according to antibiotic resistance in patientsa with P. aeruginosa bacteremia.
CRPA = carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa, MDRPA = multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa, XDRPA = extensively drug-resistant P. aeruginosa.
aPatients who did not show polymicrobial bacteremia, received active antimicrobial therapy during their hospital stay, and were hospitalized for more than 5 days after the onset of bacteremia.
DISCUSSION
Our study provides antimicrobial susceptibility trends in P. aeruginosa bacteremia and risk factors for their antimicrobial resistance in a tertiary hospital for 12 years. XDRPA showed an increasing trend, and CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA were also gradually increasing in the non-ICU setting. Previous exposure to fluoroquinolones and glycopeptides and urinary tract infection were independent risk factors associated with CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA. CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA were associated with discordant empirical antimicrobial therapy.
The report of Kor-GLASS, a surveillance system for antimicrobial resistance in general hospitals and nursing hospitals, on blood samples from general hospitals in 2017 showed that the rates of P. aeruginosa susceptibility to amikacin, meropenem, ceftazidime, piperacillin-tazobactam, and ciprofloxacin were 92.6%, 77.9%, 84.6%, 81.2%, and 83.9%.13 MDRPA and XDRPA increased slightly, from 15% and 11% in 2016 to 19.2% and 15.4%, respectively in 2019.29 However, in blood samples from nursing hospitals in 2019, the rates of CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA were 56.3%, 71.9%, and 62.5%, respectively, which were higher than those of general hospitals.29 The results of our study showed higher resistance to ceftazidime, piperacillin-tazobactam, and fluoroquinolones and higher rates of MDRPA and XDRPA than the results of general hospitals identified by Kor-GLASS. Korean National Healthcare-associated Infections Surveillance System (KONIS) reports revealed that the rate of imipenem-resistant P. aeruginosa increased since 2017 (45% from July 2013 to June 2017 vs. 51.1% from July 2017 to June 2020).30 Although comparisons with KONIS reports are limited because blood and other specimens are not separated, our study showed a slight decrease in CRPA and MDRPA during 2017–2020 compared with that during 2013–2016. In 2016, in the ICU of our hospital, the CRE increased sharply. Subsequently, to prevent the spread of multidrug-resistant bacteria, multifaceted strategies were applied, such as active surveillance culture of CRE; separating the ICU into a clean zone, waiting zone, and MDRO zone; donning protective equipment for all patients; access control; enhancing environmental cleaning; strengthening infection control monitoring; and antimicrobial stewardship. Our multifaceted efforts might have reduced the spread of resistant bacteria. However, further studies are needed to assess whether these strategies were effective in reducing antibiotic-resistant P. aeruginosa infection in the ICU. Additionally, it is necessary to provide antimicrobial susceptibility results classified by region and hospital for infection control and early active antimicrobial therapy.
Previous studies have reported prior exposure to fluoroquinolones and carbapenems and prior hospital stay as risk factors for MDRPA and XDRPA.14,15 Moreover, MDRPA was significantly associated with a prior ICU stay, highly invasive device scores, bedridden state, and prior exposure to aminoglycosides and cephalosporins, and XDRPA was associated with receiving total parenteral nutrition and hematologic malignancy.15,16 Risk factors for CRPA were prior exposure to fluoroquinolones, carbapenem, piperacillin-tazobactam, and vancomycin and an indwelling catheter.14,18,19,31 Similar to the results of previous studies, our study showed that prior exposure to fluoroquinolone was a risk factor for CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA and devices with ventilator and indwelling urinary catheters were risk factors for MDRPA. In addition, urinary tract infection and prior exposure to glycopeptides were independent risk factors of CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA. In our study, patients with solid cancers showed a significantly lower risk of MDRPA and XDRPA. Approximately half of these patients did not receive chemotherapy and 20% of these patients were identified with P. aeruginosa bacteremia during hospitalization for the evaluation of recently confirmed cancer. They had short hospital stays before bacteremia and infrequently required devices such as an indwelling urinary catheter and ventilators. Although these findings seemed reasonable based on our results, further follow-up studies are necessary.
Several studies have shown that infections due to antibiotic-resistant P. aeruginosa are associated with high mortality rates.15,18,19,32,33 Bug-drug mismatches are common in multidrug-resistant strains, and delayed active antibiotics are associated with poor prognosis.6 Contrary to previous research results, in our study, we did not identify the adverse effects of discordant empirical antimicrobial therapy and antibiotic resistance on mortality in P. aeruginosa bacteremia. This could be due to the effect of disease severity, primary site of infection, and virulence of pathogens rather than antibiotic resistance or appropriate antimicrobial therapy.17,34,35,36,37 In our study, the mortality rate was high in seriously ill patients with septic shock on the first day of bacteremia, and 61.3% of deaths occurred within 5 days. Urinary tract infection and hepatobiliary tract infection were more common than respiratory tract infection as the causative site of CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA. Moreover, most of the patients with hepatobiliary tract infection received appropriate drainage procedures. We did not conduct a case-control study that adjusted for disease severity and underlying disease. Further, it was difficult to determine the effects of concordant empirical antimicrobial therapy because the frequency of antibiotic use, such as that of colistin, was low in patients with XDRPA bacteremia. However, CRPA, MDRPA, and XDRPA were significantly associated with discordant empirical antimicrobial therapy. Although disease severity, bacterial virulence, and primary site of infection are uncontrollable risk factors for mortality, the adverse effects of delayed active antimicrobial therapy, which has been identified in several studies, might be improved by identifying risk factors.3,5,6 Most new antibiotics recommended in the treatment guidelines for multidrug-resistant gram negative pathogens, such as ceftazidime-avibactam and imipenem-relebactam, are not available, and ceftolozane/tazobactam is not covered by insurance in Korea.11 Thus, empirical antibiotic therapy including colistin might be considered for patients with urinary tract infection with a history of prior exposure to fluoroquinolones and glycopeptides, especially in elderly patients or patients with a history of cerebrovascular accident. In particular, XDR infection should be considered for patients who have been transferred from nursing hospitals, considering the antimicrobial susceptibility trends of the region and hospital.29 Further studies are needed on effects of colistin-containing empirical antibiotics based on risk factors for antibiotic-resistant P. aeruginosa on microbiological and clinical treatment failure and mortality.
Our study had several limitations. First, this study was a single-center study conducted at a tertiary university hospital in the southeastern region of Korea, and the number of P. aeruginosa samples was relatively small; therefore, our results might not be extrapolated to other hospitals and regions of the country. Second, because it was a retrospective study, we cannot rule out unmeasured uncertainty, such as hopeless discharge or hospice care in patients with cancer. Moreover, the severity score on the first day of bacteremia, excluding shock, could not be measured and the type of antibiotic used before transport to the hospital might not be accurate. Third, recent studies reported a problem with the antimicrobial susceptibility testing of colistin, and the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and CLSI both recommend broth microdilution for colistin susceptibility tests.38 In our study, this method was not applied in colistin sensitivity tests; therefore, the colistin sensitivity results might not be accurate.
In conclusion, P. aeruginosa infections with multidrug-resistance strains are gradually increasing in Korea. The identification of antimicrobial susceptibility trends and risk factors for antibiotic resistance could be important for providing concordant empirical antimicrobial therapy to patients with P. aeruginosa infection. Further studies on the outcomes of empirical antimicrobial treatment based on risk factors for antibiotic-resistant P. aeruginosa are warranted.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The results of this study were presented at ID Week 2019 in Washington, D.C., USA on 2–6 October 2019 (Abstract No. 181).
Footnotes
Funding: This work was supported by the 2019 Inje University research grant.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
- Conceptualization: Kang JS, Moon C.
- Data curation: Kang JS, Mun SJ.
- Formal analysis: Kang JS.
- Funding acquisition: Kang JS.
- Investigation: Kang JS.
- Methodology: Kang JS.
- Supervision: Moon C, Lee S, Lee SH, Lee JE, Lee SO.
- Validation: Kang JS.
- Writing - original draft: Kang JS.
- Writing - review & editing: Kang JS, Moon C, Mun SJ, Lee S, Lee SH, Lee JE, Lee SO.
References
- 1.Parkins MD, Gregson DB, Pitout JD, Ross T, Laupland KB. Population-based study of the epidemiology and the risk factors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa bloodstream infection. Infection. 2010;38(1):25–32. doi: 10.1007/s15010-009-9145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Callejas-Díaz A, Fernández-Pérez C, Ramos-Martínez A, Múñez-Rubio E, Sánchez-Romero I, Vargas Núñez JA. Impact of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteraemia in a tertiary hospital: mortality and prognostic factors. Med Clin (Barc) 2019;152(3):83–89. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2018.04.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kang CI, Kim SH, Kim HB, Park SW, Choe YJ, Oh MD, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia: risk factors for mortality and influence of delayed receipt of effective antimicrobial therapy on clinical outcome. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37(6):745–751. doi: 10.1086/377200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Suárez C, Peña C, Tubau F, Gavaldà L, Manzur A, Dominguez MA, et al. Clinical impact of imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa bloodstream infections. J Infect. 2009;58(4):285–290. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2009.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Buehrle DJ, Shields RK, Clarke LG, Potoski BA, Clancy CJ, Nguyen MH. Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia: risk factors for mortality and microbiologic treatment failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;61(1):e01243-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01243-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kadri SS, Adjemian J, Lai YL, Spaulding AB, Ricotta E, Prevots DR, et al. Difficult-to-treat resistance in gram-negative bacteremia at 173 US hospitals: retrospective cohort analysis of prevalence, predictors, and outcome of resistance to all first-line agents. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;67(12):1803–1814. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Merchant S, Proudfoot EM, Quadri HN, McElroy HJ, Wright WR, Gupta A, et al. Risk factors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in Asia-Pacific and consequences of inappropriate initial antimicrobial therapy: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2018;14:33–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2018.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2013. [Updated 2013]. [Accessed July 15, 2021]. https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/pdf/ar-threats-2013-508.pdf .
- 9.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2019. [Updated 2019]. [Accessed July 15, 2021]. https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/threats-report/2019-ar-threats-report-508.pdf .
- 10.Horcajada JP, Montero M, Oliver A, Sorlí L, Luque S, Gómez-Zorrilla S, et al. Epidemiology and treatment of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019;32(4):e00031-19. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00031-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tamma PD, Aitken SL, Bonomo RA, Mathers AJ, van Duin D, Clancy CJ. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidance on the treatment of extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Enterobacterales (ESBL-E), carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa with difficult-to-treat resistance (DTR-P. aeruginosa) Clin Infect Dis. 2021;72(7):e169–e183. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC) Korean Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System: KARMS 2016 Annual Report. Cheongju, Korea: KCDC; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liu C, Yoon EJ, Kim D, Shin JH, Shin JH, Shin KS, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in South Korea: a report from the Korean Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (Kor-GLASS) for 2017. J Infect Chemother. 2019;25(11):845–859. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2019.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Raman G, Avendano EE, Chan J, Merchant S, Puzniak L. Risk factors for hospitalized patients with resistant or multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018;7:79. doi: 10.1186/s13756-018-0370-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Aloush V, Navon-Venezia S, Seigman-Igra Y, Cabili S, Carmeli Y. Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: risk factors and clinical impact. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50(1):43–48. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.1.43-48.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Palavutitotai N, Jitmuang A, Tongsai S, Kiratisin P, Angkasekwinai N. Epidemiology and risk factors of extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e0193431. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Samonis G, Vardakas KZ, Kofteridis DP, Dimopoulou D, Andrianaki AM, Chatzinikolaou I, et al. Characteristics, risk factors and outcomes of adult cancer patients with extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Infection. 2014;42(4):721–728. doi: 10.1007/s15010-014-0635-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lee CH, Su TY, Ye JJ, Hsu PC, Kuo AJ, Chia JH, et al. Risk factors and clinical significance of bacteremia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant only to carbapenems. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017;50(5):677–683. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2015.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Joo EJ, Kang CI, Ha YE, Kang SJ, Park SY, Chung DR, et al. Risk factors for mortality in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia: clinical impact of antimicrobial resistance on outcome. Microb Drug Resist. 2011;17(2):305–312. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2010.0170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 29th ed. Wayne, PA, USA: CLSI; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yo CH, Hsein YC, Wu YL, Hsu WT, Ma MH, Tsai CH, et al. Clinical predictors and outcome impact of community-onset polymicrobial bloodstream infection. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2019;54(6):716–722. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Haque M, Sartelli M, McKimm J, Abu Bakar M. Health care-associated infections - an overview. Infect Drug Resist. 2018;11:2321–2333. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S177247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Revelas A. Healthcare - associated infections: a public health problem. Niger Med J. 2012;53(2):59–64. doi: 10.4103/0300-1652.103543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) CDC/NHSN surveillance definitions for specific types of infections. [Updated 2021]. [Accessed July 15, 2021]. https://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/17pscnosinfdef_current.pdf .
- 25.Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315(8):801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18(3):268–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Aryee A, Rockenschaub P, Gill MJ, Hayward A, Shallcross L. The relationship between clinical outcomes and empirical antibiotic therapy in patients with community-onset gram-negative bloodstream infections: a cohort study from a large teaching hospital. Epidemiol Infect. 2020;148:e225. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820002083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kadri SS, Lai YL, Warner S, Strich JR, Babiker A, Ricotta EE, et al. Inappropriate empirical antibiotic therapy for bloodstream infections based on discordant in-vitro susceptibilities: a retrospective cohort analysis of prevalence, predictors, and mortality risk in US hospitals. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30477-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Korean Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA) National Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Korea 2019 Annual Report. Cheongju, Korea: KDCA; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Korean National Healthcare-associated Infections Surveillance System (KONIS) ICU reports. [Updated 2021]. [Accessed May 1, 2021]. http://konis.cafe24.com/xe/reports_icu_y .
- 31.Tuon FF, Gortz LW, Rocha JL. Risk factors for pan-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia and the adequacy of antibiotic therapy. Braz J Infect Dis. 2012;16(4):351–356. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2012.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nathwani D, Raman G, Sulham K, Gavaghan M, Menon V. Clinical and economic consequences of hospital-acquired resistant and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2014;3(1):32. doi: 10.1186/2047-2994-3-32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bassetti M, Vena A, Croxatto A, Righi E, Guery B. How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Drugs Context. 2018;7:212527. doi: 10.7573/dic.212527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Montero MM, López Montesinos I, Knobel H, Molas E, Sorlí L, Siverio-Parés A, et al. Risk factors for mortality among patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa bloodstream infections: What is the influence of XDR phenotype on outcomes? J Clin Med. 2020;9(2):514. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kim YJ, Jun YH, Kim YR, Park KG, Park YJ, Kang JY, et al. Risk factors for mortality in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia; retrospective study of impact of combination antimicrobial therapy. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:161. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Peña C, Cabot G, Gómez-Zorrilla S, Zamorano L, Ocampo-Sosa A, Murillas J, et al. Influence of virulence genotype and resistance profile in the mortality of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bloodstream infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;60(4):539–548. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jeong SJ, Yoon SS, Bae IK, Jeong SH, Kim JM, Lee K. Risk factors for mortality in patients with bloodstream infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: clinical impact of bacterial virulence and strains on outcome. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;80(2):130–135. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2014.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Matuschek E, Åhman J, Webster C, Kahlmeter G. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of colistin - evaluation of seven commercial MIC products against standard broth microdilution for Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter spp. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018;24(8):865–870. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]