Abstract
Simple Summary
Microbial dysbiosis has been credited as one of the contributing factors to the development and progression of gastrointestinal tract cancer. The altered microbiota influences carcinogenesis through the induction of instability and damage to genetic material, modulation of host metabolic and inflammatory pathways, production of carcinogenic metabolites, and suppression of host antitumor response. These microbes secrete extracellular vesicles that are possibly carrying carcinogenic bioactive metabolites within their cargo. Studies have illustrated the ability of bacterial extracellular vesicles to cross the intestinal epithelial barrier and selectively accumulate near intestinal tumor cells. The purpose of this systemic review was to highlight the possible role of gut bacterial vesicles in the development, progression, and pathogenesis of gastrointestinal tract cancer and their possible involvement in the modulation of the tumor microenvironment. An infinitesimal amount of research has been carried out on the impact of bacterial extracellular vesicles on oncogenesis and tumor progression. This review aimed to encourage more investigations on this subject.
Abstract
Bacterial extracellular vesicles are membrane-enclosed, lipid bi-layer nanostructures that carry different classes of biomolecules, such as nucleic acids, lipids, proteins, and diverse types of small molecular metabolites, as their cargo. Almost all of the bacteria in the gut secrete extracellular vesicles to assist them in competition, survival, material exchange, host immune modulation, infection, and invasion. The role of gut microbiota in the development, progression, and pathogenesis of gastrointestinal tract (GIT) cancer has been well documented. However, the possible involvement of bacterial extracellular vesicles (bEVs) in GIT cancer pathophysiology has not been given due attention. Studies have illustrated the ability of bEVs to cross physiological barriers, selectively accumulate near tumor cells, and possibly alter the tumor microenvironment (TME). A systematic search of original published works related to bacterial extracellular vesicles on gastrointestinal cancer was performed for this review. The current systemic review outlines the possible impact of gut microbiota derived bEVs in GIT cancer in light of present-day understanding. The necessity of using advanced sequencing technologies, such as genetic, proteomic, and metabolomic investigation methodologies, to facilitate an understanding of the interrelationship between cancer-associated bacterial vesicles and gastrointestinal cancer is also emphasized. We further discuss the clinical and pharmaceutical potential of bEVs, along with future efforts needed to understand the mechanism of interaction of bEVs in GIT cancer pathogenesis.
Keywords: gastrointestinal tract, microbiota, extracellular vesicles, cancer
1. Introduction
The human gastrointestinal system is one of the most complex known microbial systems; it is colonized by trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses [1,2], with bacteria being the largest group [3]. Studies have indicated that microbiota influence the development and progression of cancer by modulating the tumor microenvironment (TME) [4,5,6,7]. The alteration in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) microbiota, with an increase in pathogenic bacteria concomitant with a decrease in beneficial bacteria, is observed during the development of gastrointestinal cancers [2,8]. Gut microorganisms maintain host homeostasis and immunity, referred to as eubiosis [9], by utilizing different metabolic and immunomodulatory properties to sustain a balanced host health status. Alterations in microbial community in GIT may lead to a loss of ability to maintain homeostatic conditions, which contributes to cancer pathogenesis and progression [9,10]. Studies suggest that dysbiosis of the gut microbiome also alters its metabolic products, influencing host metabolic and inflammatory pathways, thereby disturbing homeostasis and paving the way to carcinogenesis [11]. Microbial dysbiosis has also been attributed to reduced responses to anticancer therapies due to the ability of certain microbes to metabolize drugs and influence immune responses within the TME [12]. Substantial evidence indicates that the carcinogenic effects of microbiota can be transferred to healthy mice by fecal microbiota transfer (FMT) from mice or human patients suffering from GIT cancer [13].
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have been known to be produced by almost all forms of life including eukaryotes and prokaryotes [14,15]. EVs have also been found in different biofluids such as saliva [16], serum [17], plasma [17], amniotic fluid [16], breast milk [18], and urine [19]. Bacterial extracellular vesicles (bEVs) are membrane-enclosed lipid bi-layer structures secreted by almost all known bacteria. Bacteria secrete EVs that range from 20 to 400 nm in size [20,21] and contain different classes of biomolecules such as nucleic acids [22,23,24], lipids [25,26], proteins [27,28,29], and diverse types of small molecular metabolites [30,31]. bEVs display multiple bacterial cell surface components, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [32,33], peptidoglycan (PG) [34,35], outer membrane proteins [36], enzymes [37,38], and toxins [39,40], many of which belong to the microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) or pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) [37,41]. Thus, many bEVs have the ability to stimulate different pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as Toll-like receptors [42,43] and to activate different signaling pathways related to cytokines [41,44], chemokine [45], and inflammatory responses [41,42] in the host cell. These inflammatory substances have been observed to play an active role in tumor pathogenesis [46,47,48]. In addition, certain bEVs have been shown to selectively bind to the host cell surfaces [49,50]. bEVs are believed to facilitate cell-to-cell communication among microbes and also between host and microbe. They regulate recipient cells, for instance, via horizontal transfer of genetic material [51,52,53,54], delivery of toxins and virulence factors [38,55], and antimicrobial substances [56,57]. bEVs serve as efficient delivery vehicles for different microbial bioactive substances and genetic materials, since within the vesicles, they are protected from degradation by RNases, DNases, and other host enzymatic and immune activities by the lipid envelope [22,23,58].
The possibility of changes in the gene expression of cancer cells due to the horizontal transfer of exogenous genetic material from the gut microbiome has previously been speculated [59,60]. Bacterial genetic material has been found to be integrated in the DNA of human cancer samples much more frequently than in DNA samples from healthy individuals [60], raising the possibility of bacterial regulation of host cells, either by direct integration of bacterial genetic material or by epigenetic alteration, through the production of pro-carcinogenic proteins and enzymes [61]. It can be speculated that the migration of genetic material or pro-carcinogenic bacterial material to the cancer site is feasible if we consider the possibility of the involvement of bacterial vesicles in their transport, as these bacterial foreign materials would be safe as they would easily evade the host immune mechanism, being enclosed inside the membrane envelope. Studies have indicated that the packaging of cargo into bEVs is not random but rather a well-organized selective process, whereby bacteria transfer their nucleic acid [62], proteins [36,55], virulence factors, toxins, and other metabolites [36,43,63] into secreted vesicles. Thus, we can presume that this selective packaging gives bacterial vesicles an evolutionary advantage whereby the individual bacterial species can influence other bacteria and host cells according to their needs, e.g., for a symbiotic relationship [57,64] or for the destruction of competing bacteria [65]. Similarly, bacteria may also influence the host cells by modulating the host genetic or physiological environment, leading to the initiation of a diseased condition.
EVs secreted by tumor cells have been known to be involved in the development and progression of tumors by facilitating interaction between tumor and stroma [66,67], protecting a tumor from the host immune system [68], initiation of angiogenesis [69,70], invasion of tumor extracellular matrix [71,72], and even the metastasis [73,74] of tumor cells to new locations. A large number of studies related to the effects of tumor cell-derived vesicles on tumor pathogenesis, development, progression, and metastasis have been carried out by many research groups [75,76], but the role of bacterial vesicle counterparts has been largely undermined. Limited studies performed in that direction indicate the possible involvement of bEVs in TME. These investigations indicate that bEVs showed increased affinity to cancer cells by being accumulated in the surrounding space as well as being easily transported inside the cancer cells [20,49,77]. Further studies are required to reveal the reasons for the targeted affinity of these vesicles to tumor cells, mechanisms of entry, and their roles in the modulation of a cell’s genetic and cytosolic environment in relation to cancer pathogenesis.
Similarly, there seems to be a mutual exchange of metabolites between cancer cells and microorganisms aided by their respective vesicles [78]. Contrary to the involvement of bEVs in cancer pathogenesis, different kinds of integrins, proteins, and keratins that are specific to EVs derived from colorectal cancer (CRC) have been detected in altered microbial populations of GIT, which offers evidence of the modulation of gut microorganisms by cancer cells. In their review, Barteneva et al. (2017) [15] tabulated the matching protein sequences in GIT microorganisms with data from proteomic analysis of CRC-derived EVs.
Despite an enormous interest in the role of EVs and a plethora of separation methods available for the isolation and separation of EVs, there is no consensus on reliable isolation and analysis protocols [79,80]. Most of the available EV isolation and analysis protocols are focused on human EVs [79,81,82,83]. Few articles on bEV isolation mention the methodological challenges in separating bEVs from host-derived EVs as one of the main reasons for bEVs being less thoroughly investigated in relation to human health [80,84]. High-throughput methods of “omics” have become a standard research tool for the study of microorganisms in recent years [85]. The -omics technology has made it possible to identify the viable but unculturable microorganisms in the gut [86]. The advances in -omics technologies have revolutionized the understanding of the microbial community, its composition, and its activity as a whole [87]. The use of these advancements has been very limited in the study of bEVs in relation to GIT cancer. Implementation of proper purification techniques is essential in order to obtain reliable -omics data and also to identify EV-specific functions and biomarkers [79]. Conversely, the knowledge gained by different -omics studies may be implemented to devise reliable guideline for the isolation, purification, and further study of bEVs.
This review discusses the probable role of bacterial secreted vesicles in the development, progression, and pathogenies of cancers affecting the GIT in the light of our current understanding. The effects of cancer-associated gut microorganisms on the pathology of intestinal cancers are well documented, but their interrelationships with bEVs are only starting to be investigated. A large number of studies regarding host tumor tissue secreted membrane vesicles have also been carried out, but those of bEVs are largely missing. The emphasis of this review is to highlight the necessity of using the latest gene sequencing methods along with proteomics and metabolomics in order to increase the scope of knowledge regarding the inter-relationship between bEVs and GIT cancer.
2. Method
A Scopus and PubMed search were conducted. The query combined four separate search items: (i) “bacteria”, including bacteria, microbiome; (ii) extracellular vesicle, including outer membrane vesicle, bEV, exosome, microvesicle; (iii) gastrointestinal tract, including oral, esophagus, gastric, stomach, gut, pancreas, liver, small intestine, large intestine, jejunum, duodenum, ileum, caecum, colon, colorectal, and rectum; (iv) cancer, including tumor, adenoma, carcinoma, malignant, neoplasm. No time interval was introduced. Only original studies written in English were considered. The retrieved records were collected into Covidence. All abstracts were critically assessed to select only those providing meaningful information related to the topic. Only studies related to bEVs on GIT cancers were included. A flow diagram with a summary of the methodology is provided in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Flow diagram representing a summary of the methodology for this review.
3. GIT Cancer Statistics
Gastrointestinal cancer has high incidence, mortality, and morbidity rates according to the latest estimates of the Global Cancer Statistics 2020 (Table 1).
Table 1.
| Cancer | Incidence in 2020 | Number of Deaths in 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| Lip, oral cancer | 377,713 | 177,757 |
| Esophageal cancer | 604,100 | 544,076 |
| Stomach cancer | 1,089,103 | 768,793 |
| Colorectal cancer | 1,931,590 | 935,173 |
| Hepatic cancer | 905,677 | 830,108 |
| Pancreatic cancer | 495,773 | 466,003 |
4. GIT Cancer-Associated Microbiota
A human host harbors about around 1013–1014 bacteria in his/her body, with the colon accommodating the highest number as reviewed in [7,13,90]. This large number of microbes contributes to a significant amount of genetic diversity in the human host, with the estimated number of genes contributed by intestinal microbiota being at least 100 times that of human genes as reviewed in [13,90]. Although these microorganisms are generally credited with the maintenance of homeostasis in the gastrointestinal environment, studies suggest that altered diversity and dysbiosis of gut bacteria lead to numerous gut-related diseases including GIT cancer [91,92,93]. Our microbiome plays a vital role in the maintenance of health, metabolism, and the immune system, and these components are also affected by a shift in the population of gut bacteria [64,94]. The association between gut bacteria and intestinal carcinogenesis was first suggested in 1974, when a carcinogenic substance injected into germ-free rats showed a lower incidence of GIT cancer than the colonized counterpart [13,95]. Since then, a large number of studies have broadened our understanding regarding the role of gut microorganisms in cancer pathogenesis [96,97,98].
A normal oral microbiome is composed of more than 600 different bacterial species. Alteration of the oral microbiome has been associated with oral precancerous lesions and oral carcinomas [99]. The microorganisms that have been strongly correlated with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) include Porphyromonas gingivalis [100] and Capnocytophaga gingivalis [101], and members of the genera Streptococcus [102], Peptostreptococcus [102], and Prevotella [101]. Other bacteria found in higher numbers in OSCC patients as compared with healthy individuals include Fusobacterium nucleatum, Prevotella melaninogenica, Streptococcus mitis, and members of the genera Rothia, Gemella, and Lactobacillus [103,104]. The most common bacteria associated with esophageal cancer are Escherichia coli [105], Porphyromonas gingivalis [106], Fusobacterium nucleatum [107], and members of Lactobacillus [108] and Enterobacteriaceae [109].
Helicobacter pylori has been listed as a major causative agent for gastric cancer [110]. Other bacteria common in gastric cancer are Lactobacillus coleohominis [111], Klebsiella pneumoniae [112], Acinetobacter baumannii [112], and members of the genera Streptococcus [92], Veillonella, Prevotella [92], Fusobacterium [113], Lachnospiraceae [114], Leptotrichia [115], and Clostridium [116].
Similarly, an increased prevalence of Fusobacterium nucleatum [117], Escherichia coli [118], Streptococcus bovis [119], Streptococcus gallolyticus [119], Bacteroides fragilis [6], species of Dorea [120] and Porphyromonas [120], and a diminished number of Pseudomonas, Prevotella, Acinetobacter, and Catenibacterium [121] are associated with CRC.
The majority of hepatic cancer cases are associated with the hepatitis B and C virus and an increased abundance of Clostridium [12], Bacteroides [122], and Ruminococcaceae [122].
Helicobacter pylori [123], Pseudomonas aeruginosa [124], and Fusobacterium [125] are associated with pancreatic cancer.
Table 2 illustrates dysbiosis in GIT cancers.
Table 2.
Dysbiosis in GIT cancers.
| Cancerous Condition | Normal Microflora in That Part of GIT | Increased in Cancer | Decreased in Cancer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral squamous cell carcinoma |
Streptococcus gordonii, Streptococcus mitis, Streptococcus sangius, Gemella sangius, and Granulicatella adiacens [126] Capnocytophaga, Fusobacterium, Lactobacterium, Porphyromonas, Peptostreptococcus, Staphylococcus, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria [127] |
Streptococcus mitis, and Capnocytophaga [101] Fusobacterium, Dialister, Peptostreptococcus, Filifactor, Peptococcus, Catonella, and Parvimonas [128] |
Firmicutes and Actinobacteria [99] Streptococcaceae, Micrococcaceae Actinomycetaceae and Carnobacteriaceae, Streptococcus, Veillonella, and Rothia [103] |
| Esophageal adenocarcinoma |
Streptococcus viridians [129] Firmicutes, Bacteroides, Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, Fusobacteria, Streptococcus spp., Haemophilus, Neisseria, Prevotella, and Veillonella, [130,131] |
Enterobacteriaceae, Lactobacillus, Akkermansia, and Lactobacillus [109,132] |
Firmicutes Veillonella, and Granulicatella [109,132] |
| Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes and Spirochaetes [130,133] Streptococcus, Prevotella, Porphyromona, and Treponema [134,135,136] |
Lautropia, Bulleidia, Catonella, Corynebacterium, Moryella, Peptococcus, and Cardiobacterium [135] | |
| Gastric cancer | Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Fusobacteria, Proteobacteria, Streptococcus, and Prevotella [137,138,139,140] | Lachnospiraceae [111], Achromobacter, Lactobacillus, Citrobacter, Clostridium, and Rhodococcus [141], Prevotella, Veillonella [139] Lactobacillus coleohominis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Acinetobacter baumannii [111,112,140] |
Porphyromonas, Neisseria, and Streptococcus sinensis [111,142] |
| Colorectal cancer | Bacteroides, Firmicutes [143], Prevotella, Clostridium, Eubacterium [144], Lactobacillus, Streptococcus [145], and Acinobacter [146] |
Fusobacterium, Porphyromonas, Peptostreptococcus, and Mogibacterium Bacteroids [6,121,147] Streptocpccus bovis, Helicobacter pylori, Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis, Clostridium septicum, and Fusobacterium nucleatum [117,118,148] |
Clostridium and Bacteroides, Pseudomonas, Prevotella, Acinetobacter, and Catenibacterium, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, Rosebura, and Eupacteria [121,147,148] |
FMT experiments, from tumor-bearing hosts to germ-free mice, have been reported to induce carcinogenesis in the recipient mice [149,150]. These studies illustrate the influence of cancer-associated bacteria in the initiation and progression of carcinogenesis [151,152]. Wong et al. (2017) [149] observed the promotion of tumorigenesis by the upregulation of proinflammatory genes and oncogenic factors as well as increased immune cell infiltration, when germ-free C57BL/6 mice were inoculated with feces from patients with CRC [149]. Li et al. (2019) [150] showed enhanced progression of intestinal adenoma in Apcmin/+ mice via activation of the Wnt signaling pathway in the mice fed with gavage from CRC patients [150]. Similar results were obtained by Sobhania et al. (2019) [153] when fecal microbiota from CRC patients were transferred to germ-free mice, resulting in the induction of tumorigenesis via gene methylation [153]. Similarly, FMT experiments have also indicated that fecal microbiota transfers from drug-sensitive patients or healthy donors enhances the antitumor immune responses [154,155].
A large number of studies conducted over the past few decades have attributed the interaction between host cells and microorganisms as one of the major factors for the development and progression of cancer by modulating various host physiological processes [156,157,158]. The ability of cancer-associated intestinal bacteria to stimulate pro-tumor inflammation [46,159], the production of carcinogenic metabolites [159], the activation of carcinogenic signaling pathways [46], the induction of instability and damage to genetic material [160], the inhibition of apoptosis [12,161], the alteration of an antitumor immune response [162], among many other mechanisms, have been associated with intestinal cancer pathogenesis. Many gut microbiota produce metabolites that cause genetic instability and damage to DNA [160,163]; thus, the presence of such bacteria or their membrane vesicles can be directly linked to mutagenesis, resulting in cancer. The ability of microorganisms to influence cancer development and progression suggests a possible interaction between TME and gut microbiota.
5. Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles
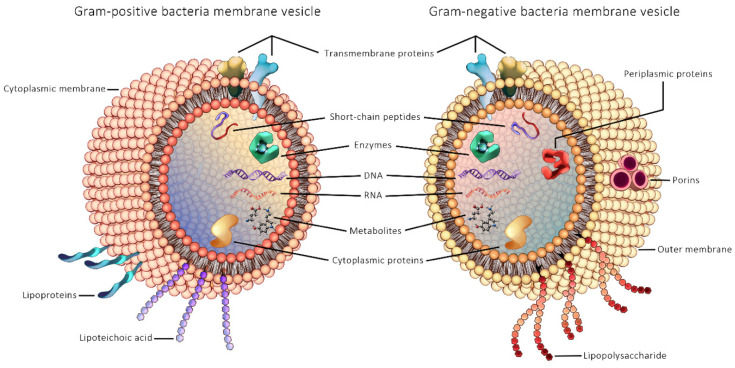
Microbe-derived EVs have emerged as an important novel research topic in the context of understanding the role of gut microbial communities in human health and disease. The first study of bEVs reported secreted bEVs produced by the Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli in cultures in 1966 [164], while EVs from Gram-positive bacteria was first published only in 2009, from Staphylococcus aureus [165]. The reason for the delayed discovery of vesicles from Gram-positive bacteria has been attributed to the thick PG cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria that was assumed to act as a barrier to their release [165]. General structure of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bEVs are illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2.
General structure of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial extracellular vesicles.
The EVs of Gram-negative bacteria are produced by controlled blebbing of the outer membrane and then released into the external environment; thus, they are called outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) as reviewed in [166]. The actual mechanism of OMV biogenesis is poorly understood, but several mechanistic models of their discharge have been proposed. Hoekstra et al. (1976) [167] suggested that the cleavage of the bond between the peptidoglycan layer and outer membrane leads to a bulging of OMVs followed by their detachment from the bacterial surface [167]. Another model suggests the accumulation of misfolded proteins or LPS or PG fragments leads to a depletion of crosslinks between PG and LPS and an increase in turgor pressure, and the release of OMVs finally occurs by the bulging of these vesicles through the bacterial surface [168,169,170]. Roier et al. (2016) [171] proposed the formation of OMVs due to the accumulation of phospholipids as a result of the deletion or decreased expression of vacj and yrb genes [171]. Recent studies suggested a new pathway leading to the formation of vesicles named as the outer-inner membrane vesicles (OIMVs) and explosive outer-membrane vesicles (EOMVs) based on explosive cell lysis triggered by the enzymatic action of endolysins [172,173,174,175]. Very little is known about the process of the creation of a membrane vesicle in Gram-positive bacteria. Membrane vesicle genesis in the Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus were shown to be induced by the hydrolytic action of endolysins and autolysins, respectively, whereby cytoplasmic membrane materials protrude through the hole in the PG layer of the cell wall, resulting in the release of the vesicles [176,177].
Initially, membrane vesicle production was thought to be related to a stress response or an adaptive response to an adverse environment as a result of membrane instability [168,178]; later, findings suggested that the production of membrane vesicles is a well-regulated process with selective packaging of the components [178,179,180,181,182]. Proteomic analysis carried out on OMVs derived from Escherichia coli resulted in highly enriched outer membrane proteins, while inner membrane proteins were deficient, suggesting that the formation of a vesicle is not a random process [29]. Studies have demonstrated the selective incorporation of specific virulent protein gingipain in EVs produced by the human oral pathogen Prophyromonas gingivalis [36,183]. Similarly, proteomic analysis of Helicobacter pylori-derived vesicles conducted at different stages of growth revealed varying protein cargo, also reinforcing the notion of selective packaging [179].
bEVs carry a diversity of cargo compounds within them, including nucleic acids, proteins, and toxins, which help them in competition [165], survival [165], material exchange [165], host immune modulation [184,185], and infection [58]. Emerging evidence suggests that there exists a host–microbe interspecies communication between human and microorganisms, possibly aided by microbial EVs, which modulates certain human host functions [186,187]. The long-standing evolutionary connection between microorganisms and host may have enabled microorganisms to coexist in a close relationship with humans. Different studies have established that bEVs have evolved as a novel secretory mechanism employed by bacteria to deliver various cargo into the host cells without the need for the bacteria to have contact with the host cells [165,188,189,190]. Escherichia coli OMV have been found to fuse with lipid rafts in the host colonic epithelial cell [190]. Studies have demonstrated that bEVs fuse with lipid rafts in the plasma membrane to deliver multiple virulence factors directly to the host cytoplasm in a coordinated manner [189,190,191]. Koeppen and Hampton (2016) [24] demonstrated a pathogen–host interaction that reduces the innate immune response in the airway epithelial cells of mice and humans by a regulatory sRNA contained inside EVs secreted by Pseudomonas aeruginosa residing in infected cells [24]. bEVs were found to deliver LPS into the target cell cytosol, triggering caspase-11-dependent effector responses leading to innate immune responses during infection with Gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli [192,193]. During infection, bEVs of bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumonia, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Helicobacter pylori, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa [194,195], have been found to effectively alter the host cell environment, making it favorable for the bacteria to survive within the host cell [196]. As bEVs may contribute as vehicles that carry necessary cargo for this purpose, these EVs can be speculated to be a very efficient communication vehicle that carry information in forms of active signaling molecules between same and different species [189,197,198].
The isolation and purification of bEVs is a difficult process and often requires expensive equipment and complex purification protocols. Commonly used techniques for EV isolation are precipitation [169,199] and ultrafiltration [84,200]; the techniques used for EV purification are ultracentrifugation [80,201], density gradient fractionation [202,203], and immunoaffinity [81,84]. Work on bEV isolation protocols is still in its infancy. Patel et al. (2019) [204] demonstrated that the choice of isolation protocol can lead to a change in the yield, protein quantification, size distribution, and surface charge of EVs [204]; thus, isolation methods should be chosen carefully [205]. However, a detailed discussion of the isolation, purification, and characterization techniques of EVs is outside the scope of this review but has been extensively reported elsewhere as reviewed in [80,81,82,83,202,205,206,207,208].
The emerging role of bEVs in cancer and other physiological and pathological conditions has created a pressing need for an efficient labeling and tracking procedure to visualize and detect bEVs in target organs [209,210]. Non-invasive imaging modalities can provide an accurate understanding of the distribution and kinetics of bEVs in in vivo conditions [210]. Different labeling agents have been used for the study of EVs such as lipophilic tracer dyes [211,212], magnetic particles [213], radionuclides [214], and fluorescence [215,216]. The in vivo distribution, kinetics, dynamics, and fate of bEVs are largely unexplored. Most studies have focused on the study of EVs derived from different non-bacterial cells, and only a handful of studies have been conducted on bEVs. Fluorescent dyes, such as Rhodamine-R18, have been utilized to label OMVs from Pseudomonas aeruginosa [189] and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans [191] to study the fusion of OMVs with the host cell. Rhodamine-R18 only fluoresces upon fusion of OMVs to the host cell membrane and, thus, an increase in fluorescence can be interpreted as an increase in OMV fusion; this allows for visual confirmation and quantitation of OMV fusion with host cells [189,191]. Similarly, different dyes, such as 3,3′-dioctadecyloxacarbocyanine perchlorate (DiO), 1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindodicarbocyanine perchlorate (DiD) [217,218], fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) [190], have been used to investigate bEV–host cell interactions. The use of these labeling and tracking methods may also help to understand the interaction of these bEVs with host cells by injecting them into germ-free mice. This might eliminate the microbiota component from the equation and help us understand the impact of bEVs in cancer initiation and development in the absence of causative microorganisms.
6. Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles in the Tumor Microenvironment
The TME is composed of a complex ecosystem containing diverse types of cells, including cancer cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts, endothelial cells, adipocytes, mesenchymal stem cells, immune cells such as macrophages, T cells, B cells, and infiltrated cytokines, as well as non-cellular components, such as micro vesicles, and the extracellular matrix as reviewed in [219,220,221,222]. Studies have indicated that the interaction between tumor cells, the neighboring cells, and immune cells moderates tumor growth, progression, and metastasis as reviewed in [223,224]. Studies carried out on tumor cell-derived EVs have shown that they play a significant role in regulating key signaling pathways to modulate the TME and, thus, tumor progression. These studies even indicate that EVs derived from tumor stromal cells are capable of affecting the various properties of cancer cells, such as drug resistance, proliferation, and their ability to evade the immune mechanism, and may even take part in forming a new niche for metastatic cells in distant organs [225]. Though EVs derived from host cancer cells and cancer stroma cells have been extensively studied with respect to their role in tumor progression, drug resistance, angiogenesis, tumor proliferation, and metastasis as reviewed in [223,224], similar studies on bEVs have been largely overlooked.
Intestinal bEVs have been reported to enter the host circulatory system and have been found in the nearby organs [226,227]. Though the entry of bEVs into the host blood stream is generally attributed to conditions compromising the barrier integrity of intestinal epithelial cells, recent investigations reveal this phenomenon to be common in healthy individuals as well [80,228]. A mouse model study showed that bEVs isolated from the blood of mice contained bacterial genomic DNA fragments that matched the genetic material in microbiota residing in the GIT [229]. An in vivo whole-body imaging study was performed to evaluate the absorption of bacteria and their EVs across the intestinal barrier and their movement into the host organs. Pseudomonas panacis cells and their EVs were orally administered to mice and the EVs were found to be present in the heart and lungs 5 min after their administration. Imaging data 12 h after the inoculation showed the systemic distribution of bEVs including organs, such as the liver, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle [188]. These studies show that bEVs have the ability to cross the intestinal barrier and travel to distant organs and possibly release their cargo there.
Helicobacter pylori, a Gram-negative intestinal pathogen that colonizes the epithelial lining of the human stomach, has been listed as a Group 1 carcinogenic agent in humans by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) [110]. Though extensive studies have been carried out focusing on the role of Helicobacter pylori in the initiation and progression of gastric cancer, the role of Helicobacter pylori-derived bEVs in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer has largely remained unexplored. Helicobacter pylori-derived bEVs have been found to be upregulated in the gastric juice of gastric cancer patients when compared with normal controls [230]. Choi et al. (2017) [230] demonstrated that Helicobacter pylori-derived bEVs infiltrate into gastric mucosa as well as gastric epithelial cells. When Helicobacter pylori-derived bEVs labeled with Dil stain were applied to gastric epithelial cells and observed 12 h post administration, it was found that large numbers of vesicles were present inside the gastric epithelial cells [230]. CagA- and VacA-positive strains of Helicobacter pylori have already been associated with the induction of apoptosis in the adenocarcinoma gastric cell line (AGS) and the severity of the precancerous condition of gastric cancer [125]. The presence of CagA and VacA proteins has been demonstrated in EVs isolated from Helicobacter pylori. Turkina et al. (2015) [231] demonstrated that Helicobacter Pylori EVs containing CagA increase ATP affinity to H1 histone proteins in chromosomes, which may lead to the initiation of cancer [231,232]. A study conducted by Tyler et al. (2014) [217] showed the potential of bEVs isolated from Escherichia coli to induce carcinogenesis in intestinal epithelial cells. The internalization of Escherichia coli-derived bEVs into the Caco-2 cell line was determined by fluorescent dye labeling, and further investigations were carried out that showed an alteration of cell growth, damage to DNA, and aneuploidy in the presence of these bEVs [217]. These findings suggest that bEVs might infiltrate into gastric mucosa and gastric epithelial cells and possibly play an important role in GIT cancer.
Different studies have also indicated that bEVs could accumulate at the site of TME. Oh Youn Kim et al. (2017) [49] showed that intravenously injected Escherichia coli OMVs accumulated specifically near the tumor tissues in BALB/c mice bearing CT26 tumors. These bEVs attracted T cells and natural killer (NK) cells and induced the production of antitumor cytokines and interferons at the tumor site [49]. To avoid the possible adverse effects due to the bacterial endotoxin, bEVs were isolated from A acyltransferase (msbB) inactivated Escherichia coli. The bEVs were labeled with Cyanine7 (Cy7) fluorescence, and the fluorescence intensity of Cy7 in the whole body and different organs was measured with in vivo imaging system after 12 h of injection. Strong fluorescence signals were observed in tumor tissue. When the radiation efficiency of Cy7 was measured against each organ weight, the tumor tissue was found to have the highest intensity, suggesting accumulation of labeled bEVs in the tumor tissue site [49]. Likewise, Kudelaidi Kuerbana et al. (2000) [233] observed a massive accumulation of OMVs derived from attenuated Klebsiella pneumonia in the tumor area of BALB/c nude mice induced with a non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) A549 cell line. When free doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) and an equivalent dose of DOX-loaded bEVs were introduced to A549 cell lines in vitro, a massive number of DOX-containing vesicles were observed in the tumor cells in 12 h post-infection in contrast to free DOX, which accumulated only after 24 h, indicating improved transport of the drug when it was encapsulated in the bEVs. It was also observed that DOX-OMVs could induce macrophages to release TNF-α and IL-6 [233]. When fluorescent-labeled bacterial vesicles of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron were orally administered to C57BL/6 mice, high intensity signals were observed in the small intestine, stomach, caecum, and colon, while low intensity was observed in the liver, lungs, and heart after 8 h, indicating the bacterial vesicles could pass through the intestinal epithelial barrier and enter into the intestinal cells and even migrate to distant organs [228]. The same study indicated an uptake of bacterial vesicles within 48 h by the human colonic epithelial cell line Caco-2 when bacterial vesicles from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron were incubated with the cell line [228]. When bEVs isolated from Vibrio cholera, Escherichia coli (BL21), and Shigella flexneri were intramurally injected into mice bearing a CT26 colon tumor, it was observed that all the membrane vesicles inhibited tumor growth significantly but in varying amounts, with the most pronounced inhibition caused by Escherichia coli (BL21) bEVs [77]. The naked bacterial vesicles resulted in inflammatory reactions due to the release of cytokines, such as interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α, that resulted in the death of the mice. Further studies were carried out only with vesicles isolated from Escherichia coli (BL21). The vesicles were labeled with Cy7 fluorescence and when injected into mice, showed accumulation of vesicles at the tumor site. But accumulation of vesicles decreased in subsequent injections. The membrane vesicles were encapsulated in biocompatible calcium phosphate by a biomineralization process to avoid adverse reactions and the experiment was repeated. Strong fluorescence signals were observed at tumor sites even after 24 h of final injection indicating efficient accumulation of the vesicles in the tumor site [77]. When global transcriptome profiling analysis was performed for tumors treated with membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli, the following were observed: significant gene suppression of immune suppressive genes such as Tcaim and Socs6, increased expression of immune activation-related genes such as Tlrs and Gzmc, and the upregulation of apoptosis genes Nod1 and Tnfrsf1a [77].
A large number of studies have indicated the role of inflammation as a major risk factor in the promotion and progression of tumorigenesis including various GIT cancers such as CRC, gastric cancer, pancreatic cancers, and esophageal cancers [234,235]. The presence of inflammatory carcinogenic metabolites in cancer cells have been generally attributed to the interaction between the TME and resident microbiota [236,237]. bEVs have also been found to induce a significant influence on the expression of inflammatory mediators such as interleukins and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) [238]. Since many compounds associated with inflammation are also found in bacterial membrane vesicles [239,240] and these bEVs are found near the TME, the possible role of bEVs in these processes cannot be ruled out.
Studies provide evidence that Enterococcus faecalis and Escherichia coli produce extracellular toxins causing chromosomal instability as well as free radicals targeting DNA, which can contribute to CRC development [225,241]. It is easy to speculate that the vesicles produced by these bacteria may also carry these toxins and free radicals and possibly cause the modulation of genetic material in host intestinal cells that could lead to oncogenesis. The microbial dysbiosis between healthy and cancerous conditions, along with the accumulation of bacterial vesicles in the TME, gives clues suggesting these vesicles released by the altered microbial community could act as tumor-promoting agents by invoking the immunogenic mechanism of the TME, via the suppression of immune cells, the production of carcinogenic metabolites, and the modification of the TME [49,77,242].
Although the direct involvement of bacterial pathogen in carcinogenesis has been reported [243,244], the involvement of tumor-influencing metabolic substances in a free state or packaged inside the bacterial membrane vesicle is a huge possibility [245,246]. Bacterial nucleic acid fragments have been detected in the host circulatory system [229], but it remains unclear whether these nucleic acids appeared due to the diffusion through the intestinal epithelium or were carried as cargo of the bacterial vesicles. The transfer of carcinogenic property might not be possible by free circulation of pathogenic bacteria or a bacterial component in host circulation, since these would elicit the host’s immune responses [247,248], leading to different host physiological changes. One possible explanation for this phenomenon may be the transfer of free metabolites or the cancer-inducing substances enclosed inside the bEVs, which can evade these host immune responses [20], and when presented with a favorable environment, induce carcinogenesis. Further investigation in this direction, to determine whether these vesicles carrying microbial nucleic materials are driving cancer pathogenesis or just coincidences, is essential.
Microbial dysbiosis in a cancerous condition, along with the accumulation of bacterial vesicles in the TME, gives indications that these vesicles released by the altered microbial community could act as tumor-promoting agents by invoking immunogenic mechanisms in the TME, via suppression of immune cells, production of carcinogenic metabolites, and modification of the TME [49,77,242]. Therefore, it is tempting to speculate that these vesicles might be one of the factors explaining the link between disturbances in the gut microbial community and oncogenesis.
All this evidence suggests that bEVs may not only have the capacity to enter the TME efficiently but might also influence the tumor environment by releasing various oncogenic metabolites or inducing the components of the TME to release them.
7. Interactions between bEVs and GIT Cancers
The last few decades have seen huge advancements in metagenomic, metabolomic, metaproteomic, and bioinformatics technologies in the field of biology [249,250,251,252]. These advancements in sequencing technologies and computational methods have enhanced the accurate and comprehensive analysis of microbial communities directly from the available source, without the complication of cultivation as reviewed in [249]. However, the use of these advanced technologies has been very limited in the analysis of bEVs related to GIT cancers. Along with the study of the process of biogenesis and the structure of the bacterial membrane vesicles, the content of the vesicles has also been a fascinating field of interest among scientists lately. Different biochemical, proteomic, and genetic analyses have shown that bEVs carry a large diversity of bioactive cargo compounds and an abundant number of metabolites as reviewed in [166,253,254,255].
7.1. Contents of bEVs That Potentially Affect GIT Cancers
7.1.1. DNA
DNA fragments were found in Pseudomonas aeruginosa membrane vesicles when the bacteria lysed spontaneously, releasing membrane vesicles which contained cytosolic contents [174]. Many studies in the past have also reported DNA in the membrane vesicles of different bacteria such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Streptococcus mutant, and Escherichia coli [29,256]. The presence of DNA fragments in bacterial membrane vesicles has been attributed to the exchange of genetic material in the same and/or different species, facilitated by the membrane vesicles for the transfer of virulence factors and the antibiotic gene transfer between them [191,257]. Recent studies have shown that DNA cargo is carried into host cells inside membrane vesicles [62]. Studies have also indicated that bacterial DNA material integrated into the human genome more readily in tumor cells than in normal cells [60]. It remains undetermined whether the DNA carried within the vesicles may be the source of the integrated DNA [62]. The implications of vesicle-associated DNA fragments in host–pathogen interactions remains understudied.
7.1.2. RNA
Recent studies have identified msRNAs and sRNAs in bEVs with sizes comparable to that of mRNA. The sRNA and msRNA have been thought to have regulatory functions in eukaryotes. Therefore, it has been speculated that these RNAs contained within bEVs participate in the modulation of the cancer microenvironment [258,259,260]. A high amount of mRNA encoding for DNA-binding proteins and membrane proteins along with DNA, tmRNA, and RNase P were also observed in the membrane vesicles of Vibrio cholerae O395 by Langlete et al. (2019) [261]. tRNA and rRNA fragments have been found in the membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli [254]. RNA profiling analysis of Salmonella spp.-derived membrane vesicles revealed higher RNA concentrations in EVs than in the cytosol [262].
7.1.3. Protein
Liu et al. (2019) [263] recently performed proteomic analyses of Fusobacterium nucleatum EVs and found that 6 out of 98 proteins were autotransporter proteins [263]. One of these autotransporter proteins in Fusobacterium nucleatum, Fap2 protein, is known to provide protection to CRC cells by restraining the immune response, such as NK cell cytotoxicity, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, and a T-cell attack [264], by interacting with the T-cell immunoglobulin and ITIM (TIGIT) receptor domain [264,265] thus promoting tumor progression. An abundance of autotransporter proteins in Fusobacterium nucleatum EVs indicates the role of bEVs in cancer progression and opens up a whole new dimension for the study of microbial EV proteomics in cancer research.
7.1.4. Metabolomes
In a metagenomic profiling study based on 16 S rDNA amplicon sequencing carried out on bEVs isolated from healthy volunteers and CRC patients demonstrated an alteration of gut microbiota with a significant increase in the abundance of Firmicutes and Proteobacteria in CRC subjects. In addition, Proteus spp. could only be detected in CRC patients. Similarly, metabolomic analysis carried out in the same study indicated phenol, ethanolamine, oxalic acid, succinic acid, furoic acid, palmitic acid, hexanoic acid, and oleic acid increased while butanoic acid was reduced in CRC patients. The authors summarized their findings by suggesting the combined use of metagenomic and metabolomic biomarkers for the diagnosis of CRC [241].
7.2. Potential Effects of bEVs on GIT Cancers
A study conducted by Vdovikova et al. (2018) [245] illustrated that bEVs from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae were involved in the increase in gene expression associated with cellular differentiation in colon cancer cells. In their study, HCT8 cells from human ileocecal colorectal adenocarcinoma were co-cultured with membrane vesicles isolated from Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli for 5 h. RNA from membrane vesicle-treated cells were isolated and RNA sequencing performed. A total of 1434 and 685 genes were found to be differentially regulated by Escherichia coli membrane vesicles and Vibrio cholerae membrane vesicles, respectively. Approximately 51% (738 out of 1434) of the genes treated by Escherichia coli membrane vesicles and approximately 68% (465 out of 685) of the genes treated by Vibrio cholerae vesicles were significantly upregulated compared to control cells. The results suggest that Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli vesicles induce differential gene expression in HCT8 cells [245]. Similarly, to study the impact of membrane vesicles on the activation of gene transcripts in HCT8 cells, Vdovikova et al. (2018) [245] analyzed the distribution of reads from RNA sequencing experiments from transcription start sites (TSS) and the termination end sites (TES) at genes that were upregulated after vesicle treatment. They observed an increase in the H3K4me3 signal around the TSS of genes upregulated by both Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae membrane vesicles individually. The result showed membrane vesicles derived from both Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae impacted the activation of the gene transcription. The authors suggested that the study further enhances the current knowledge of the role of Vibrio cholerae-derived membrane vesicles on the differentiation of intestinal cancer via selective gene transcription [245]. This study helps to form a basis for further research on how bacterial vesicles influence gene expression of cells that might be influencing the cancer microenvironment.
An increased abundance of Fusobacterium spp. has been reported in the intestines of patients with CRC [77,266,267]. Fusobacterium nucleatum has been associated with the development, progression, and metastasis of CRC [266] by the stimulation of inflammatory pathways, such as the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathways [267], increased production of CXCL1 and IL-8 [268] and drug resistance [269]. Fusobacterium nucleatum has also been found to activate Toll-like receptor 4 (TRL4) signaling to NF-κB, which resulted in an increased proliferation of CRC cells. A study conducted by Engevik et al. (2021) [50] indicated that OMVs secreted by Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. polymorphum can activate TRL4 and influence the NF-κB pathway, thereby promoting proinflammatory cytokine production. When purified, OMVs from Fusobacterium nucleatum were applied to the human colon cell line HT-29, an approximately eight-fold increase in IL-8 production and an approximately six-fold increase in TNF production were observed [50].
All these studies indicate that there are a large number of genetic, proteomic, and metabolomic investigations that still need to be performed in order to expand our understanding of the interrelationship between cancer-associated bacterial vesicles and gastrointestinal cancer. Without a targeted study, one can only speculate about the possibility of interaction between tumor-associated bacteria with the host cells in the TME through bEV cargo content.
8. Clinical and Pharmaceutical Potential of bEVs
Oh Youn Kim et al. (2017) [49] demonstrated that when OMVs derived from A acyltransferase (msbB) inactivated Escherichia coli were intravenously injected into BALB/c mice bearing a CT26 colon tumor, these ∆msbB OMVs specifically targeted and accumulated in tumor tissue and fully eradicated established tumors by inducing the production of anti-cancerous cytokines CXCL10 and interferon-γ from NK and T cells. The team found a dose-dependent reduction in tumor volume with complete elimination of tumor tissue with 5 μg of ∆msbB OMVs. The mice were further challenged with CT26 colon tumor cells after 4 weeks and again after 3 weeks to study immunological memory; both of the challenges were rejected. Similar results were obtained when different strains of mice were subjected to MC38 colon cancer cells under similar conditions [49]. Similarly, Shuang et al. (2020) [77] reported that when OMVs prepared from Escherichia coli BL21 cells injected into mice bearing a CT26 tumor, they inhibited tumor growth to a significant level. Here, the OMVs were encapsulated with calcium phosphate (CaP) to prevent the inflammation that resulted when only OMVs were used. The encapsulation also enabled an efficient accumulation of OMVs at the tumor site even after repeated injections. At the tumor site, due to the acidic environment, the calcium phosphate shells dissolved, which helped to neutralize the acidic environment and thereby facilitated the immune cells to infiltrate, resulting in the promotion of antitumor responses [77]. The outer membrane of bEVs can be integrated with different biocompatible compounds [77,233] to prevent the adverse effects of naked vesicles and also increase the targeting potential of the vesicle. The integration of anti-tumor and chemotherapeutic drugs inside the protective layer of the vesicle along with enhanced tumor targeting and accumulation possess a enormous possibility for a future cancer treatment strategy. Similar studies using cell lines other than the CRC cell line have also been conducted and yield analogous results [233]. The outer membrane of bEVs may be integrated with different biocompatible compounds to make the vesicles more stable in the circulatory system. This experiment provides an insight into a novel method for the treatment of cancer.
Vesicles expressing pathogen-derived factors and changes in bEV abundance in host factors can serve as diagnostic biomarkers [270,271], indicators of disease progression, and capture of these pathogen-derived EVs may be used for further analysis. Changes in bEV composition during disease progression makes them excellent biomarker candidates [272]. The first blood-based EV diagnostic test for cancer became commercially available in January of 2016 in the United States [272,273]. If the disease-specific bEV biomarker becomes available, more chip-based diagnostic tools may be developed. Similarly, novel microbiome markers may be developed for the early diagnosis of GIT cancers by analyzing bEVs from blood samples.
It has been established that bEVs have the intrinsic targeting potential to selectively target other microorganisms as well as host cells [49,77]. In addition, different bioengineering techniques have been put forward to enhance the targeting properties of EVs [77]. If this cell-specific targeting potential could be augmented with the advanced imaging techniques for the labeling of the EVs in real-time imaging, a powerful diagnostic tool could be developed. The knowledge gained so far for tracking EVs may be used to develop novel, non-invasive imaging techniques, which can provide a better prospective of the in vivo therapeutic effects of bEVs by providing a precise glimpse of the in vivo distribution and dynamics of the EVs [210]. Efficient preclinical and clinical in vivo tracking techniques are key instruments for the development and optimization of vesicle-based diagnosis and treatment [274].
Since the bacterial vesicles are derived from different bacterial species with diverse membrane compositions and genetic makeups, these vesicles also have heterologous sizes, surface components, and diverse molecular cargo composition and, thus, have the capability for a variety of biological functioning as reviewed in [175]. The ability of these vesicles to cross the biological barrier, without causing adverse effects, remaining stable in the circulatory system and transporting its cargo specifically and selectively to the targeted TME may be utilized for various pharmaceutical purposes. Although it carries huge potential and possibility, the use of bEVs for treatment and as drug delivery vehicles in GIT cancer has been less studied.
Another advantage of bacterial vesicles is that the bacteria can be modified genetically to produce desired agents useful in imaging, therapy, and targeted delivery to be localized specifically in membrane-derived vesicles [275,276,277], and it may be mass-produced in large quantities [278,279]. With the ability to bioengineer vesicles to make them target-specific, ease of surface molecule modulation, imaging capabilities, mass production, and the ability to carry the desired payload, bEVs may emerge into a powerful theranostic tool [276,280,281].
Systemic administration of cancer drug-carrying bEVs may be a better alternative to oral administration due to the fact of their stability in the circulatory system, their ability to target and accumulate specifically at the tumor site, and their easy absorption into the cancer cells, thus reducing the higher dose and chemotoxicity of the cancer drugs. The outer membrane proteins can be modified to reduce endotoxicity by modifying the lipopolysaccharide pathways [282]. These vesicles can be loaded with the desired chemotherapeutic agents and anti-tumor agents, and outer proteins can be bioengineered to carry specific surface proteins to aid targeted therapy [49,283]. The nanosized and non-replicative status of EVs together with their resistance to enzymes and low pH, along with their ability to selectively interact with different types of mucosal and systemic host cells, makes them ideal candidates for drug delivery [284], targeted therapy, and imaging.
Adaptation of the studies carried out in cell lines and orthotopic modes into clinical translation presents another major hurdle. Further studies on this front are necessary, using different experimental designs so that the results of these findings could be translated to suit human patients.
Huge potential lies ahead in the utilization of bEVs for diagnosis, imaging, and targeted therapy for different kinds of cancers including cancers of the GIT.
9. Conclusions
There have only been a handful of studies dedicated to investigating the role of bEVs with respect to their impact on oncogenesis and tumor progression. In their review, Antonios Chronopoulos and Raghu Kalluri (2020) [20] suggested that bEVs might prove to be the important missing link between cancer and associated gut microorganisms [20]. An increased number of investigations using the latest technologies, such as metagenomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and bioinformatics, need to be carried out to understand the interaction between bEVs and GIT cancers. A bEV-based antitumor strategy could bring new insights for the development of novel cancer therapy in the future. These investigations will help to establish possible prevention, diagnosis, and treatment protocols for gastrointestinal cancer.
Acknowledgments
J.R. thanks the Academy of Finland for grants 328768 and 299749.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.B.A. and J.R.; Methodology, S.B.A. and J.R.; literature review, S.B.A.; writing—original draft preparation, S.B.A.; writing—review and editing, S.B.A., V.K., P.K. and J.R.; visualization, S.S.; supervision, J.R.; project administration, J.R.; funding acquisition, P.K. and J.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors received no specific funding for this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Gill S.R., Pop M., DeBoy R.T., Eckburg P.B., Turnbaugh P.J., Samuel B.S., Gordon J.I., Relman D.A., Fraser-Liggett C.M., Nelson K.E. Metagenomic Analysis of the Human Distal Gut Microbiome. Science. 2006;312:1355. doi: 10.1126/science.1124234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Meng C., Bai C., Brown T.D., Hood L.E., Tian Q. Human Gut Microbiota and Gastrointestinal Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018;16:33–49. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2017.06.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen D., Wu J., Jin D., Wang B., Cao H. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Cancer Management: Current Status and Perspectives. Int. J. Cancer. 2019;145:2021–2031. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kostic A.D., Chun E., Robertson L., Glickman J.N., Gallini C.A., Michaud M., Clancy T.E., Chung D.C., Lockhead P., Hold G.L., et al. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Potentiates Intestinal Tumorigenesis and Modulates the Tumor-Immune Microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe. 2013;14:207–215. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Goodwin A.C., Shields C.E.D., Wu S., Huso D.L., Wu X., Murray-Stewart T.R., Prietz-Hacker A., Rabizadeh S., Woster P.M., Sears C.L., et al. Polyamine Catabolism Contributes to Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides Fragilis-Induced Colon Tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:15354–15359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010203108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Boleij A., Hechenbleikner E.M., Goodwin A.C., Badani R., Stein E.M., Lazarev M.G., Ellis B., Carroll K.C., Albesiano E., Wick E.C., et al. The Bacteroides Fragilis Toxin Gene Is Prevalent in the Colon Mucosa of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2015;60:208. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fulbright L.E., Ellermann M., Arthur J.C. The Microbiome and the Hallmarks of Cancer. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006480. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schroeder B.O., Bäckhed F. Signals from the Gut Microbiota to Distant Organs in Physiology and Disease. Nat. Med. 2016;22:1079–1089. doi: 10.1038/nm.4185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Panebianco C., Potenza A., Andriulli A., Pazienza V. Exploring the Microbiota to Better Understand Gastrointestinal Cancers Physiology. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018;56:1400–1412. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2017-1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lyte M. The Microbial Organ in the Gut as a Driver of Homeostasis and Disease. Med. Hypotheses. 2010;74:634–638. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2009.10.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Poutahidis T., Erdman S.E. Commensal Bacteria Modulate the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2016;380:356–358. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.12.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Elsalem L., Jum’ah A.A., Alfaqih M.A., Aloudat O. The Bacterial Microbiota of Gastrointestinal Cancers: Role in Cancer Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Perspectives. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2020;13:151–185. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S243337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yu L.C.H., Wei S.C., Ni Y.H. Impact of Microbiota in Colorectal Carcinogenesis: Lessons from Experimental Models. Intest. Res. 2018;16:346–357. doi: 10.5217/ir.2018.16.3.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Macia L., Nanan R., Hosseini-Beheshti E., Grau G.E. Host-and Microbiota-Derived Extracellular Vesicles, Immune Function, and Disease Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:107. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Barteneva N.S., Baiken Y., Fasler-Kan E., Alibek K., Wang S., Maltsev N., Ponomarev E.D., Sautbayeva Z., Kauanova S., Moore A., et al. Extracellular Vesicles in Gastrointestinal Cancer in Conjunction with Microbiota: On the Border of Kingdoms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer. 2017;1868:372–393. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Keller S., Ridinger J., Rupp A.K., Janssen J.W., Altevogt P. Body Fluid Derived Exosomes as a Novel Template for Clinical Diagnostics. J. Transl. Med. 2011;9:86. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Palviainen M., Saraswat M., Varga Z., Kitka D., Neuvonen M., Puhka M., Joenväärä S., Renkonen R., Nieuwland R., Takatalo M., et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Plasma and Serum Are Carriers of Extravesicular Cargo—Implications for Biomarker Discovery. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0236439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zonneveld M.I., Brisson A.R., van Herwijnen M.J.C., Tan S., van de Lest C.H.A., Redegeld F.A., Garssen J., Wauben M.H.M., Nolte-‘t Hoen E.N. Recovery of Extracellular Vesicles from Human Breast Milk Is Influenced by Sample Collection and Vesicle Isolation Procedures. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2014;3:24215. doi: 10.3402/jev.v3.24215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yuana Y., Böing A.N., Grootemaat A.E., van der Pol E., Hau C.M., Cizmar P., Buhr E., Sturk A., Nieuwland R. Handling and Storage of Human Body Fluids for Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2015;4:29260. doi: 10.3402/jev.v4.29260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chronopoulos A., Kalluri R. Emerging Role of Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer. Oncogene. 2020;39:6951–6960. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01509-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chang X., Wang S.L., Zhao S.B., Shi Y.H., Pan P., Gu L., Yao J., Li Z.S., Bai Y. Extracellular Vesicles with Possible Roles in Gut Intestinal Tract Homeostasis and IBD. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020;2020:1945832. doi: 10.1155/2020/1945832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Renelli M., Matias V., Lo Y.R., Beveridge J.T. DNA-Containing Membrane Vesicles of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa PAO1 and Their Genetic Transformation Potential. Microbiology. 2004;150:2161–2169. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26841-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dorward D.W., Garon C.F., Judd R.C. Export and Intercellular Transfer of DNA via Membrane Blebs of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. J. Bacteriol. 1989;171:2499–2505. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2499-2505.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Koeppen K., Hampton T.H., Jarek M., Scharfe M., Gerber S.A., Mielcarz D.W., Demers E.G., Dolben E.L., Hammond J.H., Hogan D.A., et al. A Novel Mechanism of Host-Pathogen Interaction through SRNA in Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:e1005672. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.McBroom A.J., Kuehn M.J. Outer Membrane Vesicles. EcoSal Plus. 2005;1 doi: 10.1128/ecosal.2.2.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wensink J., Witholt B. Outer-Membrane Vesicles Released by Normally Growing Escherichia coli Contain Very Little Lipoprotein. Eur. J. Biochem. 1981;116:331–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Scorza F.B., Doro F., Rodriguez-Ortega M.J., Stella M., Liberatori S., Taddei A.R., Serino L., Moriel D.G., Nesta B., Fontana M.R., et al. Proteomics Characterization of Outer Membrane Vesicles from the Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli DeltatolR IHE3034 Mutant. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP. 2008;7:473–485. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M700295-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kwon S.O., Gho Y.S., Lee J.C., Kim S.I. Proteome Analysis of Outer Membrane Vesicles from a Clinical Acinetobacter Baumannii Isolate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009;297:150–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lee E.Y., Joo Y.B., Gun W.P., Choi D.S., Ji S.K., Kim H.J., Park K.S., Lee J.O., Kim Y.K., Kwon K.H., et al. Global Proteomic Profiling of Native Outer Membrane Vesicles Derived from Escherichia coli. Proteomics. 2007;7:3143–3153. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200700196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fateh A., Vaziri F., Rahimi Janani F., Ahmadi Badi S., Ghazanfari M., Davari M., Arsang A., Siadat S. New Insight into the Application of Outer Membrane Vesicles of Gram-Negative Bacteria. Vaccine Res. 2015;2:93–96. doi: 10.18869/acadpub.vacres.2.5.93. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Badi S.A., Moshiri A., Fateh A., Jamnani F.R., Sarshar M., Vaziri F., Siadat S.D. Microbiota-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as New Systemic Regulators. Front. Microbiol. 2017;8:1610. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Work E., Knox K.W., Vesk M. The Chemistry and Electron Microscopy of an Extracellular Lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1966;133:438–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kesty N.C., Kuehn M.J. Incorporation of Heterologous Outer Membrane and Periplasmic Proteins into Escherichia coli Outer Membrane Vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:2069–2076. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307628200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Furuyama N., Sircili M.P. Outer Membrane Vesicles (OMVs) Produced by Gram-Negative Bacteria: Structure, Functions, Biogenesis, and Vaccine Application. BioMed Res. Int. 2021:1490732. doi: 10.1155/2021/1490732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kaparakis M., Turnbull L., Carneiro L., Firth S., Coleman H.A., Parkington H.C., Le Bourhis L., Karrar A., Viala J., Mak J., et al. Bacterial Membrane Vesicles Deliver Peptidoglycan to NOD1 in Epithelial Cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2010;12:372–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Veith P.D., Chen Y.-Y., Gorasia D.G., Chen D., Glew M.D., O’Brien-Simpson N.M., Cecil J.D., Holden J.A., Reynolds E.C. Porphyromonas Gingivalis Outer Membrane Vesicles Exclusively Contain Outer Membrane and Periplasmic Proteins and Carry a Cargo Enriched with Virulence Factors. J. Proteome Res. 2014;13:2420–2432. doi: 10.1021/pr401227e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ellis T.N., Kuehn M.J. Virulence and Immunomodulatory Roles of Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010;74:81–94. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00031-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kadurugamuwa J.L., Beveridge T.J. Virulence Factors Are Released from Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in Association with Membrane Vesicles during Normal Growth and Exposure to Gentamicin: A Novel Mechanism of Enzyme Secretion. J. Bacteriol. 1995;177:3998. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.14.3998-4008.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kunsmann L., Rüter C., Bauwens A., Greune L., Glüder M., Kemper B., Fruth A., Wai S.N., He X., Lloubes R., et al. Virulence from Vesicles: Novel Mechanisms of Host Cell Injury by Escherichia coli O104:H4 Outbreak Strain. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:13252. doi: 10.1038/srep13252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kolling G.L., Matthews K.R. Export of Virulence Genes and Shiga Toxin by Membrane Vesicles of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999;65:1843–1848. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.5.1843-1848.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ellis T.N., Leiman S.A., Kuehn M.J. Naturally Produced Outer Membrane Vesicles from Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Elicit a Potent Innate Immune Response via Combined Sensing of Both Lipopolysaccharide and Protein Components. Infect. Immun. 2010;78:3822–3831. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00433-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schaar V., de Vries S.P.W., Vidakovics M.L.A.P., Bootsma H.J., Larsson L., Hermans P.W.M., Bjartell A., Mörgelin M., Riesbeck K. Multicomponent Moraxella Catarrhalis Outer Membrane Vesicles Induce an Inflammatory Response and Are Internalized by Human Epithelial Cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2011;13:432–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shen Y., Torchia M.L.G., Lawson G.W., Karp C.L., Ashwell J.D., Mazmanian S.K. Outer Membrane Vesicles of a Human Commensal Mediate Immune Regulation and Disease Protection. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;12:509–520. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mehanny M., Koch M., Lehr C.-M., Fuhrmann G. Streptococcal Extracellular Membrane Vesicles Are Rapidly Internalized by Immune Cells and Alter Their Cytokine Release. Front. Immunol. 2020;11:80. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Fábrega M.J., Aguilera L., Giménez R., Varela E., Alexandra Cañas M., Antolín M., Badía J., Baldomà L. Activation of Immune and Defense Responses in the Intestinal Mucosa by Outer Membrane Vesicles of Commensal and Probiotic Escherichia coli Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2016;7:705. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Francescone R., Hou V., Grivennikov S.I. Microbiome, Inflammation and Cancer. Cancer J. 2014;20:181. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Grivennikov S.I., Wang K., Mucida D., Stewart C.A., Schanbl B., Jauch D., Taniguchi K., Yu G.Y., Österreicher C.H., Hung K.E., et al. Adenoma-Linked Barrier Defects and Microbial Products Drive IL-23/IL-17-Mediated Tumour Growth. Nature. 2012;491:254–258. doi: 10.1038/nature11465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bongers G., Pacer M.E., Geraldino T.H., Chen L., He Z., Hashimoto D., Furtado G.C., Ochando J., Kelley K.A., Clemente J.C., et al. Interplay of Host Microbiota, Genetic Perturbations, and Inflammation Promotes Local Development of Intestinal Neoplasms in Mice. J. Exp. Med. 2014;211:457–472. doi: 10.1084/jem.20131587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kim O.Y., Park H.T., Dinh N.T.H., Choi S.J., Lee J., Kim J.H., Lee S.W., Gho Y.S. Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles Suppress Tumor by Interferon-γ-Mediated Antitumor Response. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:626. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00729-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Engevik M.A., Danhof H.A., Ruan W., Engevik A.C., Chang-Graham A.L., Engevik K.A., Shi Z., Zhao Y., Brand C.K., Krystofiak E.S., et al. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Secretes Outer Membrane Vesicles and Promotes Intestinal Inflammation. mBio. 2021;12:e02706-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02706-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Klieve A.V., Yokoyama M.T., Forster R.J., Ouwerkerk D., Bain P.A., Mawhinney E.L. Naturally Occurring DNA Transfer System Associated with Membrane Vesicles in Cellulolytic Ruminococcus spp. of Ruminal Origin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005;71:4248–4253. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.8.4248-4253.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Domingues S., Nielsen K.M. Membrane Vesicles and Horizontal Gene Transfer in Prokaryotes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017;38:16–21. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2017.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rumbo C., Fernández-Moreira E., Merino M., Poza M., Mendez J.A., Soares N.C., Mosquera A., Chaves F., Bou G. Horizontal Transfer of the OXA-24 Carbapenemase Gene via Outer Membrane Vesicles: A New Mechanism of Dissemination of Carbapenem Resistance Genes in Acinetobacter Baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011;55:3084–3090. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00929-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Deng Y., Xu H., Su Y., Liu S., Xu L., Guo Z., Jinjun W., Cheng C., Feng J. Horizontal Gene Transfer Contributes to Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance of Vibrio Harveyi 345 Based on Complete Genome Sequence Analysis. BMC Genom. 2019;20:761. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5379-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Roier S., Blume T., Klug L., Wagner G.E., Elhenawy W., Zangger K., Prassl R., Reidl J., Daum G., Feldman M.F., et al. A Basis for Vaccine Development: Comparative Characterization of Haemophilus Influenzae Outer Membrane Vesicles. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015;305:298–309. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2014.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Stentz R., Horn N., Cross K., Salt L., Brearley C., Livermore D.M., Carding S.R. Cephalosporinases Associated with Outer Membrane Vesicles Released by Bacteroides spp. Protect Gut Pathogens and Commensals against β-Lactam Antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015;70:701–709. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lee J., Lee E.Y., Kim S.H., Kim D.K., Park K.S., Kim K.P., Kim Y.K., Roh T.Y., Gho Y.S. Staphylococcus Aureus Extracellular Vesicles Carry Biologically Active β-Lactamase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013;57:2589–2595. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00522-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Jiang Y., Kong Q., Roland K.L., Curtiss R., III Membrane Vesicles of Clostridium Perfringens Type A Strains Induce Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014;304:431–443. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2014.02.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sieber K.B., Gajer P., Hotopp J.C.D. Modeling the Integration of Bacterial RRNA Fragments into the Human Cancer Genome. BMC Bioinform. 2016;17:134. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-0982-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Riley D.R., Sieber K.B., Robinson K.M., White J.R., Ganesan A., Nourbakhsh S., Dunning Hotopp J.C. Bacteria-Human Somatic Cell Lateral Gene Transfer Is Enriched in Cancer Samples. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013;9:1003107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Abril A.G., Lanzi P.G., Notario V. Horizontal Gene Transfer. Springer International Publishing; New York, NY, USA: 2019. Implications of Lateral or Horizontal Gene Transfer from Bacteria to the Human Gastrointestinal System for Cancer Development and Treatment; pp. 377–397. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bitto N.J., Chapman R., Pidot S., Costin A., Lo C., Choi J., D’Cruze T., Reynolds E.C., Dashper S.G., Turnbull L., et al. Bacterial Membrane Vesicles Transport Their DNA Cargo into Host Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:7072. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07288-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Horstman A.L., Kuehn M.J. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Secretes Active Heat-Labile Enterotoxin via Outer Membrane Vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:12489–12496. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.17.12489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Bryant W.A., Stentz R., le Gall G., Sternberg M.J.E., Carding S.R., Wilhelm T. In Silico Analysis of the Small Molecule Content of Outer Membrane Vesicles Produced by Bacteroides Thetaiotaomicron Indicates an Extensive Metabolic Link between Microbe and Host. Front. Microbiol. 2017;8:2440. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Vasilyeva N.V., Tsfasman I.M., Suzina N.E., Stepnaya O.A., Kulaev I.S. Secretion of Bacteriolytic Endopeptidase L5 of Lysobacter sp. XL1 into the Medium by Means of Outer Membrane Vesicles. FEBS J. 2008;275:3827–3835. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Dolo V., D’Ascenzo S., Violini S., Pompucci L., Festuccia C., Ginestra A., Vittorelli M.L., Canevari S., Pavan A. Matrix-Degrading Proteinases Are Shed in Membrane Vesicles by Ovarian Cancer Cells in Vivo and in Vitro. Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 1999;17:131–140. doi: 10.1023/A:1006500406240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sidhu S.S., Mengistab A.T., Taucher A.N., LaVail J., Basbaum C. The Microvesicle as a Vehicle for EMMPRIN in Tumor-Stromal Interactions. Oncogene. 2004;23:956–963. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Valenti R., Huber V., Iero M., Filipazzi P., Parmiani G., Rivoltini L. Tumor-Released Microvesicles as Vehicles of Immunosuppression. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2912–2917. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kucharzewska P., Christianson H.C., Welch J.E., Svensson K.J., Fredlund E., Ringér M., Mörgelin M., Bourseau-Guilmain E., Bengzon J., Belting M. Exosomes Reflect the Hypoxic Status of Glioma Cells and Mediate Hypoxia-Dependent Activation of Vascular Cells during Tumor Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:7312–7317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1220998110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Taraboletti G., D’Ascenzo S., Borsotti P., Giavazzi R., Pavan A., Dolo V. Shedding of the Matrix Metalloproteinases MMP-2, MMP-9, and MT1-MMP as Membrane Vesicle-Associated Components by Endothelial Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2002;160:673–680. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64887-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Ginestra A., La Placa MD., Saladino F., Cassara D., Nagase H., Vittorelli M.L. The Amount and Proteolytic Content of Vesicles Shed by Human Cancer Cell Lines Correlates with Their in Vitro Invasiveness. Anticancer Res. 1998;18:3433–3437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Angelucci A., D’Ascenzo S., Festuccia C., Gravina G.L., Bologna M., Dolo V., Pavan A. Vesicle-Associated Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Promotes Invasion in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 2000;18:163–170. doi: 10.1023/A:1006778000173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kim H.K., Song K.S., Park Y.S., Kang Y.H., Lee Y.J., Lee K.R., Kim H.K., Ryu K.W., Bae J.M., Kim S. Elevated Levels of Circulating Platelet Microparticles, VEGF, IL-6 and RANTES in Patients with Gastric Cancer: Possible Role of a Metastasis Predictor. Eur. J. Cancer. 2003;39:184–191. doi: 10.1016/S0959-8049(02)00596-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Hao S., Ye Z., Li F., Meng Q., Qureshi M., Yang J., Xiang J. Epigenetic Transfer of Metastatic Activity by Uptake of Highly Metastatic B16 Melanoma Cell-Released Exosomes. Exp. Oncol. 2006;28:126–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hu W., Liu C., Bi Z.-Y., Zhou Q., Zhang H., Li L.-L., Zhang J., Zhu W., Song Y.-Y.-Y., Zhang F., et al. Comprehensive Landscape of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived RNAs in Cancer Initiation, Progression, Metastasis and Cancer Immunology. Mol. Cancer. 2020;19:102. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01199-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Han L., Lam E.W.F., Sun Y. Extracellular Vesicles in the Tumor Microenvironment: Old Stories, but New Tales. Mol. Cancer. 2019;18:59. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-0980-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Qing S., Lyu C., Zhu L., Pan C., Wang S., Li F., Wang J., Yue H., Gao X., Jia R., et al. Biomineralized Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles Potentiate Safe and Efficient Tumor Microenvironment Reprogramming for Anticancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2020;32:2002085. doi: 10.1002/adma.202002085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Chen Y., Xu Y., Zhong H., Yuan H., Liang F., Liu J., Tang W. Extracellular Vesicles in Inter-Kingdom Communication in Gastrointestinal Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021;11:1087–1103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Van Deun J., Mestdagh P., Sormunen R., Cocquyt V., Vermaelen K., Vandesompele J., Bracke M., de Wever O., Hendrix A. The Impact of Disparate Isolation Methods for Extracellular Vesicles on Downstream RNA Profiling. J. Extracell. Vesciles. 2014;3:24858. doi: 10.3402/jev.v3.24858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Tulkens J., de Wever O., Hendrix A. Analyzing Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles in Human Body Fluids by Orthogonal Biophysical Separation and Biochemical Characterization. Nat. Protoc. 2020;15:40–67. doi: 10.1038/s41596-019-0236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Momen-Heravi F., Balaj L., Alian S., Mantel P.-Y., Halleck A.E., Trachtenberg A.J., Soria C.E., Oquin S., Bonebreak C.M., Saracoglu E., et al. Current Methods for the Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles. Biol. Chem. 2013;394:1253–1262. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Taylor D.D., Zacharias W., Gercel-Taylor C. Exosome Isolation for Proteomic Analyses and RNA Profiling. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011;728:235–246. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-068-3_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Coumans F.A.W., Brisson A.R., Buzas E.I., Dignat-George F., Drees E.E.E., El-Andaloussi S., Emanueli C., Gasecka A., Hendrix A., Hill A.F., et al. Methodological Guidelines to Study Extracellular Vesicles. Circ. Res. 2017;120:1632–1648. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.309417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Klimentová J., Stulík J. Methods of Isolation and Purification of Outer Membrane Vesicles from Gram-Negative Bacteria. Microbiol. Res. 2015;170:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2014.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Fonseka P., Pathan M., Chitti S.V., Kang T., Mathivanan S. FunRich Enables Enrichment Analysis of OMICs Datasets. J. Mol. Biol. 2021;433:166747. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.166747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Daliri E.B.-M., Ofosu F.K., Chelliah R., Lee B.H., Oh D.-H. Challenges and Perspective in Integrated Multi-Omics in Gut Microbiota Studies. Biomolecules. 2021;11:300. doi: 10.3390/biom11020300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Shokeen B., Dinis M.D.B., Haghighi F., Tran N.C., Lux R. Omics and Interspecies Interaction. Periodontology. 2021;85:101–111. doi: 10.1111/prd.12354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., Laversanne M., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A., Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:209–249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.IARC The Global Cancer Observatory (Globocan) 2020. [(accessed on 26 July 2021)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/
- 90.Mukherji R., Weinberg B.A. The Gut Microbiome and Potential Implications for Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Colorectal Cancer. 2020;9:CRC25. doi: 10.2217/crc-2020-0007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Sobhani I., Tap J., Roudot-Thoraval F., Roperch J.P., Letulle S., Langella P., Corthier G., van Nhieu J.T., Furet J.P. Microbial Dysbiosis in Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Patients. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:16393. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Shen X.J., Rawls J.F., Randall T., Burcal L., Mpande C.N., Jenkins N., Jovov B., Abdo Z., Sandler R.S., Keku T.O. Molecular Characterization of Mucosal Adherent Bacteria and Associations with Colorectal Adenomas. Gut Microbes. 2010;1:138. doi: 10.4161/gmic.1.3.12360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Kasai C., Sugimoto K., Moritani I., Tanaka J., Oya Y., Inoue H., Tameda M., Shiraki K., Ito M., Takei Y., et al. Comparison of Human Gut Microbiota in Control Subjects and Patients with Colorectal Carcinoma in Adenoma: Terminal Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism and next-Generation Sequencing Analyses. Oncol. Rep. 2016;35:325–333. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.De Vos W.M., de Vos E.A. Role of the Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease: From Correlation to Causation. Nutr. Rev. 2012;70:S45–S56. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Reddy B.S., Narisawa T., Weisburger J.H. Colon Carcinogenesis in Germ-Free Rats with Intrarectal 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine and Subcutaneous Azoxymethane. Cancer Res. 1976;36:2874–2876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Dapito D.H., Mencin A., Gwak G.-Y., Pradere J.-P., Jang M.-K., Mederacke I., Caviglia J.M., Khiabanian H., Adeyemi A., Bataller R., et al. Promotion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by the Intestinal Microbiota and TLR4. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:504. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Yu A.I., Zhao L., Eaton K.A., Ho S., Chen J., Poe S., Becker J., Gonzalez A., McKinstry D., Hasso M., et al. Gut Microbiota Modulate CD8 T Cell Responses to Influence Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis. Cell Rep. 2020;31:107471. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.03.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Ge Y., Wang X., Guo Y., Yan J., Abuduwaili A., Aximujiang K., Yan J., Wu M. Gut Microbiota Influence Tumor Development and Alter Interactions with the Human Immune System. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021;40:42. doi: 10.1186/S13046-021-01845-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Schmidt B.L., Kuczynski J., Bhattacharya A., Huey B., Corby P.M., Queiroz E.L.S., Nightingale K., Kerr A.R., DeLacure M.D., Veeramachaneni R., et al. Changes in Abundance of Oral Microbiota Associated with Oral Cancer. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:98741. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Katz J., Onate M.D., Pauley K.M., Bhattacharyya I., Cha S. Presence of Porphyromonas Gingivalis in Gingival Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2011;3:209. doi: 10.4248/IJOS11075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Mager D., Haffajee A., Devlin P., Norris C., Posner M., Goodson J. The Salivary Microbiota as a Diagnostic Indicator of Oral Cancer: A Descriptive, Non-Randomized Study of Cancer-Free and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Subjects. J. Transl. Med. 2005;3:27. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-3-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Pushalkar S., Ji X., Li Y., Estilo C., Yegnanarayana R., Singh B., Li X., Saxena D. Comparison of Oral Microbiota in Tumor and Non-Tumor Tissues of Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. BMC Microbiol. 2012;12:144. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Zhang L., Liu Y., Zheng H.J., Zhang C.P. The Oral Microbiota May Have Influence on Oral Cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020;9:476. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Pushalkar S., Mane S.P., Ji X., Li Y., Evans C., Crasta O.R., Morse D., Meagher R., Singh A., Saxena D. Microbial Diversity in Saliva of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011;61:269–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2010.00773.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Zaidi A.H., Kelly L.A., Kreft R.E., Barlek M., Omstead A.N., Matsui D., Boyd N.H., Gazarik K.E., Heit M.I., Nistico L., et al. Associations of Microbiota and Toll-like Receptor Signaling Pathway in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:52. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2093-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Gao S., Li S., Ma Z., Liang S., Shan T., Zhang M., Zhu X., Zhang P., Liu G., Zhou F., et al. Presence of Porphyromonas Gingivalis in Esophagus and Its Association with the Clinicopathological Characteristics and Survival in Patients with Esophageal Cancer. Infect. Agents Cancer. 2016;11:3. doi: 10.1186/s13027-016-0049-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Yamamura K., Baba Y., Nakagawa S., Mima K., Miyake K., Nakamura K., Sawayama H., Kinoshita K., Ishimoto T., Iwatsuki M., et al. Human Microbiome Fusobacterium Nucleatum in Esophageal Cancer Tissue Is Associated with Prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;22:5574–5581. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Li D., He R., Hou G., Ming W., Fan T., Chen L., Zhang L., Jiang W., Wang W., Lu Z., et al. Characterization of the Esophageal Microbiota and Prediction of the Metabolic Pathways Involved in Esophageal Cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020;10:268. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Snider E.J., Compres G., Freedberg D.E., Khiabanian H., Nobel Y.R., Stump S., Uhlemann AC., Lightdale C.J., Abrams J.A. Alterations to the Esophageal Microbiome Associated with Progression from Barrett’s Esophagus to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2019;28:1687–1693. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-19-0008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Asaka M., Sepulveda A.R., Sugiyama T., Graham D.Y. Gastric Cancer. Helicobacter Pylori Physiol. Genet. 1128.
- 111.Aviles-Jimenez F., Vazquez-Jimenez F., Medrano-Guzman R., Mantilla A., Torres J. Stomach Microbiota Composition Varies between Patients with Non-Atrophic Gastritis and Patients with Intestinal Type of Gastric Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2014;4:4202. doi: 10.1038/srep04202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Khosravi Y., Dieye Y., Poh B.H., Ng C.G., Loke M.F., Goh K.L., Vadivelu J. Culturable Bacterial Microbiota of the Stomach of Helicobacter Pylori Positive and Negative Gastric Disease Patients. Sci. World J. 2014;2014 doi: 10.1155/2014/610421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Coker O.O., Dai Z., Nie Y., Zhao G., Cao L., Nakatsu G., Wu W.K., Wong S.H., Chen Z., Sung J.J.Y., et al. Mucosal Microbiome Dysbiosis in Gastric Carcinogenesis. Gut. 2018;67:1024–1032. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Wang L., Zhou J., Xin Y., Geng C., Tian Z., Yu X., Dong Q. Bacterial Overgrowth and Diversification of Microbiota in Gastric Cancer. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016;28:261–266. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Schulz C., Schütte K., Mayerle J., Malfertheiner P. The Role of the Gastric Bacterial Microbiome in Gastric Cancer: Helicobacter Pylori and Beyond. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019;12:1756284819894062. doi: 10.1177/1756284819894062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Hsieh Y.-Y., Tung S.-Y., Pan H.-Y., Yen C.-W., Xu H.-W., Lin Y.-J., Deng Y.-F., Hsu W.-T., Wu C.-S., Li C. Increased Abundance of Clostridium and Fusobacterium in Gastric Microbiota of Patients with Gastric Cancer in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:158. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18596-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Ray K. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Found in Colon Cancer Tissue—Could an Infection Cause Colorectal Cancer? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011;8:662. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2011.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Martin H.M., Campbell B.J., Hart C.A., Mpofu C., Nayar M., Singh R., Englyst H., Williams H.F., Rhodes J.M. Enhanced Escherichia coli Adherence and Invasion in Crohn’s Disease and Colon Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:80–93. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.03.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Abdulamir A.S., Hafidh R.R., Bakar F.A. The Association of Streptococcus Bovis/Gallolyticus with Colorectal Tumors: The Nature and the Underlying Mechanisms of Its Etiological Role. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011;30:11. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Wang X., Jia Y., Wen L., Mu W., Wu X., Liu T., Liu X., Fang J., Luan Y., Chen P., et al. Porphyromonas Gingivalis Promotes Colorectal Carcinoma by Activating the Hematopoietic NLRP3 Inflammasome. Cancer Res. 2021;81:2745–2759. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Yang J., McDowell A., Kim E.K., Seo H., Lee W.H., Moon C.M., Kym S.M., Lee D.H., Park Y.S., Jee Y.K., et al. Development of a Colorectal Cancer Diagnostic Model and Dietary Risk Assessment through Gut Microbiome Analysis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019;51:1–15. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0313-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Ponziani F.R., Bhoori S., Castelli C., Putignani L., Rivoltini L., del Chierico F., Sanguinetti M., Morelli D., Paroni Sterbini F., Petito V., et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Associated with Gut Microbiota Profile and Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology. 2019;69:107–120. doi: 10.1002/hep.30036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Bulajic M., Panic N., Löhr J.M. Helicobacter Pylori and Pancreatic Diseases. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2014;5:380. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Gaida M.M., Mayer C., Dapunt U., Stegmaier S., Schirmacher P., Wabnitz G.H., Hänsch G.M. Expression of the Bitter Receptor T2R38 in Pancreatic Cancer: Localization in Lipid Droplets and Activation by a Bacteria-Derived Quorum-Sensing Molecule. Oncotarget. 2016;7:12623. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Mitsuhashi K., Nosho K., Sukawa Y., Matsunaga Y., Ito M., Kurihara H., Kanno S., Igarashi H., Naito T., Adachi Y., et al. Association of Fusobacterium Species in Pancreatic Cancer Tissues with Molecular Features and Prognosis. Oncotarget. 2015;6:7209–7220. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Aas J.A., Paster B.J., Stokes L.N., Olsen I., Dewhirst F.E. Defining the Normal Bacterial Flora of the Oral Cavity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005;43:5721. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.11.5721-5732.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Zaura E., Keijser B.J., Huse S.M., Crielaard W. Defining the Healthy “Core Microbiome” of Oral Microbial Communities. BMC Microbiol. 2009;9:259. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Zhao H., Chu M., Huang Z., Yang X., Ran S., Hu B., Zhang C., Liang J. Variations in Oral Microbiota Associated with Oral Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:11773. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11779-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Gagliardi D., Makihara S., Corsi P.R., de Toledo Viana A., Wiczer M.V.F.S., Nakakubo S., Mimica L.M.J. Microbial Flora of the Normal Esophagus. Dis. Esophagus. 1998;11:248–250. doi: 10.1093/dote/11.4.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Lv J., Guo L., Liu J.-J., Zhao H.-P., Zhang J., Wang J.-H. Alteration of the Esophageal Microbiota in Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019;25:2149. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i18.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Fillon S.A., Harris J.K., Wagner B.D., Kelly C.J., Stevens M.J., Moore W., Fang R., Schroeder S., Masterson J.C., Robertson C.E., et al. Novel Device to Sample the Esophageal Microbiome—The Esophageal String Test. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e42938. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Hibberd A.A., Lyra A., Ouwehand A.C., Rolny P., Lindegren H., Cedgård L., Wettergren Y. Intestinal Microbiota Is Altered in Patients with Colon Cancer and Modified by Probiotic Intervention. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2017;4:e000145. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2017-000145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Park C.H., Lee S.K. Exploring Esophageal Microbiomes in Esophageal Diseases: A Systematic Review. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020;26:171–179. doi: 10.5056/jnm19240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Peters B.A., Wu J., Pei Z., Yang L., Purdue M.P., Freedman N.D., Jacobs E.J., Gapstur S.M., Hayes R.B., Ahn J. Oral Microbiome Composition Reflects Prospective Risk for Esophageal Cancers. Cancer Res. 2017;77:6777–6787. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Chen X., Winckler B., Lu M., Cheng H., Yuan Z., Yang Y., Jin L., Ye W. Oral Microbiota and Risk for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a High-Risk Area of China. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:143603. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Liu Y., Lin Z., Lin Y., Chen Y., Peng X.E., He F., Liu S., Yan S., Huang L., Lu W., et al. Streptococcus and Prevotella Are Associated with the Prognosis of Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018;67:1058–1068. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Bik E.M., Eckburg P.B., Gill S.R., Nelson K.E., Purdom E.A., Francois F., Perez-Perez G., Blaser M.J., Relman D.A. Molecular Analysis of the Bacterial Microbiota in the Human Stomach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:732–737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506655103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Rajilic-Stojanovic M., Figueiredo C., Smet A., Hansen R., Kupcinskas J., Rokkas T., Andersen L., Machado J.C., Ianiro G., Gasbarrini A., et al. Systematic Review: Gastric Microbiota in Health and Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020;51:582–602. doi: 10.1111/apt.15650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Jo H.J., Kim J., Kim N., Park J.H., Nam R.H., Seok Y.-J., Kim Y.-R., Kim J.S., Kim J.M., Kim J.M., et al. Analysis of Gastric Microbiota by Pyrosequencing: Minor Role of Bacteria Other Than Helicobacter Pylori in the Gastric Carcinogenesis. Helicobacter. 2016;21:364–374. doi: 10.1111/hel.12293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Conti L., Annibale B., Lahner E. Autoimmune Gastritis and Gastric Microbiota. Microorganisms. 2020;8:1827. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8111827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Ferreira R.M., Pereira-Marques J., Pinto-Ribeiro I., Costa J.L., Carneiro F., Machado J.C., Figueiredo C. Gastric Microbial Community Profiling Reveals a Dysbiotic Cancer-Associated Microbiota. Gut. 2018;67:226–236. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Andersson A.F., Lindberg M., Jakobsson H., Bäckhed F., Nyrén P., Engstrand L. Comparative Analysis of Human Gut Microbiota by Barcoded Pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:2836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Eckburg P.B., Bik E.M., Bernstein C.N., Purdom E., Dethlefsen L., Sargent M., Gill S.R., Nelson K.E., Relman D.A. Diversity of the Human Intestinal Microbial Flora. Science. 2005;308:1635. doi: 10.1126/science.1110591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Gerritsen J., Smidt H., Rijkers G.T., de Vos W.M. Intestinal Microbiota in Human Health and Disease: The Impact of Probiotics. Genes Nutr. 2011;6:209. doi: 10.1007/s12263-011-0229-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Booijink C.C.G.M., El-Aidy S., Rajilić-Stojanović M., Heilig H.G.H.J., Troost F.J., Smidt H., Kleerebezem M., de Vos W.M., Zoetendal E.G. High Temporal and Inter-Individual Variation Detected in the Human Ileal Microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2010;12:3213–3227. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Van den Bogert B., de Vos W.M., Zoetendal E.G., Kleerebezem M. Microarray Analysis and Barcoded Pyrosequencing Provide Consistent Microbial Profiles Depending on the Source of Human Intestinal Samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011;77:2071. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02477-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Liu X., Cheng Y., Shao L., Ling Z., Huang Y. Alterations of the Predominant Fecal Microbiota and Disruption of the Gut Mucosal Barrier in Patients with Early-Stage Colorectal Cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2020;2020 doi: 10.1155/2020/2948282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Jahani-Sherafat S., Alebouyeh M., Moghim S., Amoli H.A., Ghasemian-Safaei H. Role of Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis of Colorectal Cancer; A Review Article. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench. 2018;11:101–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Wong S.H., Zhao L., Zhang X., Nakatsu G., Han J., Xu W., Xiao X., Kwong T.N.Y., Tsoi H., Wu W.K.K., et al. Gavage of Fecal Samples From Patients With Colorectal Cancer Promotes Intestinal Carcinogenesis in Germ-Free and Conventional Mice. Gastroenterology. 2017;153:1621–1633. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Li L., Li X., Zhong W., Yang M., Xu M., Sun Y., Ma J., Liu T., Song X., Dong W., et al. Gut Microbiota from Colorectal Cancer Patients Enhances the Progression of Intestinal Adenoma in Apcmin/+ Mice. EBioMedicine. 2019;48:301–315. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.09.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Hu B., Elinav E., Huber S., Strowig T., Hao L., Hafemann A., Jin C., Wunderlich C., Wunderlich T., Eisenbarth S.C., et al. Microbiota-Induced Activation of Epithelial IL-6 Signaling Links Inflammasome-Driven Inflammation with Transmissible Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:9862–9867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307575110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Couturier-Maillard A., Secher T., Rehman A., Normand S., Arcangelis A.D., Haesler R., Huot L., Grandjean T., Bressenot A., Delanoye-Crespin A., et al. NOD2-Mediated Dysbiosis Predisposes Mice to Transmissible Colitis and Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2013;123:700–711. doi: 10.1172/JCI62236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Sobhani I., Bergsten E., Couffin S., Amiot A., Nebbad B., Barau C., de’Angelis N., Rabot S., Canoui-Poitrine F., Mestivier D., et al. Colorectal Cancer-Associated Microbiota Contributes to Oncogenic Epigenetic Signatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2019;116:24285–24295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1912129116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Vétizou M., Pitt J.M., Daillère R., Lepage P., Waldschmitt N., Flament C., Rusakiewicz S., Routy B., Roberti M.P., Duong C.P.M., et al. Anticancer Immunotherapy by CTLA-4 Blockade Relies on the Gut Microbiota. Science. 2015;350:1079–1084. doi: 10.1126/science.aad1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Park R., Umar S., Kasi A. Immunotherapy in Colorectal Cancer: Potential of Fecal Transplant and Microbiota-Augmented Clinical Trials. Curr. Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2020;16:81–88. doi: 10.1007/s11888-020-00456-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Huang Y., Fan X.-G., Wang Z.-M., Zhou J.-H., Tian X.-F., Li N. Identification of Helicobacter Species in Human Liver Samples from Patients with Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004;57:1273–1277. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2004.018556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Shanahan F., O’Toole P.W. Host–Microbe Interactions and Spatial Variation of Cancer in the Gut. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2014;14:511–512. doi: 10.1038/nrc3765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Yuan C., Burns M.B., Subramanian S., Blekhman R. Interaction between Host MicroRNAs and the Gut Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer. mSystems. 2018;3:e00205–e00217. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00205-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Louis P., Hold G.L., Flint H.J. The Gut Microbiota, Bacterial Metabolites and Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014;12:661–672. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Nougayrede JP., Homburg S., Taieb F., Boury M., Brzuszkiewicz E., Gottschalk G., Buchrieser C., Jacker J., Dobrindt U., Oswald E. Escherichia coli Induces DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Eukaryotic Cells. Science. 2006;313:848–851. doi: 10.1126/science.1127059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Nasr R., Shamseddine A., Mukherji D., Nassar F., Temraz S. The Crosstalk between Microbiome and Immune Response in Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:6586. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Sethi V., Kurtom S., Tarique M., Lavania S., Malchiodi Z., Hellmund L., Zhang L., Sharma U., Giri B., Garg B., et al. Gut Microbiota Promotes Tumor Growth in Mice by Modulating Immune Response. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:33–37. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Guerra L., Guidi R., Frisan T. Do Bacterial Genotoxins Contribute to Chronic Inflammation, Genomic Instability and Tumor Progression? FEBS J. 2011;278:4577–4588. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Silva Rosa da Luz B., Azevedo V., Le-loir Y., Guedon E. Staphylococcus Aureus [Working Title] IntechOpen; London, UK: 2021. Extracellular Vesicles and Their Role in Staphylococcus Aureus Resistance and Virulence. [Google Scholar]
- 165.Lee E.Y., Choi D.Y., Kim D.K., Kim J.W., Park J.O., Kim S., Kim S.H., Desiderio D.M., Kim Y.K., Kim K.P., et al. Gram-Positive Bacteria Produce Membrane Vesicles: Proteomics-Based Characterization of Staphylococcus Aureus-Derived Membrane Vesicles. Proteomics. 2009;9:5425–5436. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200900338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Nagakubo T., Nomura N., Toyofuku M. Cracking Open Bacterial Membrane Vesicles. Front. Microbiol. 2020;10:3026. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Hoekstra D., van der Laan J.W., de Leij L., Witholt B. Release of Outer Membrane Fragments from Normally Growing Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1976;455:889–899. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.McBroom A.J., Kuehn M.J. Release of Outer Membrane Vesicles by Gram-Negative Bacteria Is a Novel Envelope Stress Response. Mol. Microbiol. 2007;63:545–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Zhou L., Srisatjaluk R., Justus D.E., Doyle R.J. On the Origin of Membrane Vesicles in Gram-Negative Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998;163:223–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1998.tb13049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Tashiro Y., Sakai R., Toyofuku M., Sawada I., Nakajima-Kambe T., Uchiyama H., Nomura N. Outer Membrane Machinery and Alginate Synthesis Regulators Control Membrane Vesicle Production in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2009;191:7509. doi: 10.1128/JB.00722-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Roier S., Zingl F.G., Cakar F., Durakovic S., Kohl P., Eichmann T.O., Klug L., Gadermaier B., Weinzerl K., Prassl R., et al. A Novel Mechanism for the Biogenesis of Outer Membrane Vesicles in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:10515. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Devos S., Putte W.V., Vitse J., Driessche G.V., Stremersch S., Broek W.V.D., Raemdonck K., Braeckmans K., Stahlberg H., Kudryashev M., et al. Membrane Vesicle Secretion and Prophage Induction in Multidrug-Resistant Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia in Response to Ciprofloxacin Stress. Environ. Microbiol. 2017;19:3930–3937. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Koning R.I., de Breij A., Oostergetel G.T., Nibbeing P.H., Koster A.J., Dijkshoorn L. Cryo-Electron Tomography Analysis of Membrane Vesicles from Acinetobacter Baumannii ATCC19606 T. Res. Microbiol. 2013;164:397–405. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2013.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Turnbull L., Toyofuku M., Hynen A.L., Kurosawa M., Pessi G., Petty N.K., Osvath S.R., Cárcamo-Oyarce G., Gloag E.S., Shimoni R., et al. Explosive Cell Lysis as a Mechanism for the Biogenesis of Bacterial Membrane Vesicles and Biofilms. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:11220. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Toyofuku M., Nomura N., Eberl L. Types and Origins of Bacterial Membrane Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019;17:13–24. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0112-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Toyofuku M., Cárcamo-Oyarce G., Yamamoto T., Eisenstein F., Hsiao C.C., Kurosawa M., Gademann K., Pilhofer M., Nomura N., Eberl L. Prophage-Triggered Membrane Vesicle Formation through Peptidoglycan Damage in Bacillus Subtilis. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:481. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00492-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Wang X., Thompson C.D., Weidenmaier C., Lee J.C. Release of Staphylococcus Aureus Extracellular Vesicles and Their Application as a Vaccine Platform. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:1379. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03847-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.McBroom A.J., Johnson A.P., Vemulapalli S., Kuehn M.J. Outer Membrane Vesicle Production by Escherichia coli Is Independent of Membrane Instability. J. Bacteriol. 2006;188:5385–5392. doi: 10.1128/JB.00498-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Zavan L., Bitto N.J., Johnston E.L., Greening D.W., Kaparakis-Liaskos M. Helicobacter Pylori Growth Stage Determines the Size, Protein Composition, and Preferential Cargo Packaging of Outer Membrane Vesicles. Proteomics. 2019;19:1800209. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201970004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Schwechheimer C., Kuehn M.J. Outer-Membrane Vesicles from Gram-Negative Bacteria: Biogenesis and Functions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015;13:605–619. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Deatherage B.L., Lara J.C., Bergsbaken T., Barrett S.L.R., Lara S., Cookson B.T. Biogenesis of Bacterial Membrane Vesicles. Mol. Microbiol. 2009;72:1395–1407. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Schwechheimer C., Sullivan C.J., Kuehn M.J. Envelope Control of Outer Membrane Vesicle Production in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Biochemistry. 2013;52:3031–3040. doi: 10.1021/bi400164t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Haurat M.F., Aduse-Opoku J., Rangarajan M., Dorobantu L., Gray M.R., Curtis M.A., Feldman M.F. Selective Sorting of Cargo Proteins into Bacterial Membrane Vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;286:1269–1276. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.185744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Olaya-Abril A., Prados-Rosales R., McConnell M.J., Martín-Peña R., González-Reyes J.A., Jiménez-Munguía I., Gómez-Gascón L., Fernández J., Luque-García J.L., García-Lidón C., et al. Characterization of Protective Extracellular Membrane-Derived Vesicles Produced by Streptococcus Pneumoniae. J. Proteom. 2014;106:46–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.04.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Rivera J., Cordero R.J.B., Nakouzi A.S., Frases S., Nicola A., Casadevall A. Bacillus Anthracis Produces Membrane-Derived Vesicles Containing Biologically Active Toxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:19002–19007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008843107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Gurung M., Moon D.C., Choi C.W., Lee J.H., Bae Y.C., Kim J., Lee Y.C., Seol S.Y., Cho D.T., Kim S.I., et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Produces Membrane-Derived Vesicles That Induce Host Cell Death. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e27958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Prados-Rosales R., Baena A., Martinez L.R., Luque-Garcia J., Kalscheuer R., Veeraraghavan U., Camara C., Nosanchuk J.D., Besra G.S., Chen B., et al. Mycobacteria Release Active Membrane Vesicles That Modulate Immune Responses in a TLR2-Dependent Manner in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011;121:1471–1483. doi: 10.1172/JCI44261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Choi Y., Kwon Y., Kim D.K., Jeon J., Jang S.C., Wang T., Ban M., Kim M.H., Jeon S.G., Kim M.S., et al. Gut Microbe-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Induce Insulin Resistance, Thereby Impairing Glucose Metabolism in Skeletal Muscle. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:15878. doi: 10.1038/srep15878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Bomberger J.M., MacEachran D.P., Coutermarsh B.A., Ye S., O’Toole G.A., Stanton B.A. Long-Distance Delivery of Bacterial Virulence Factors by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Outer Membrane Vesicles. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000382. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Kesty N.C., Manson K.M., Reedy M., Miller S.E., Kuehn M.J. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vesicles Target Toxin Delivery into Mammalian Cells. EMBO J. 2004;23:4538–4549. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Rompikuntal P.K., Thay B., Khan M.K., Alanko J., Penttinen A.-M., Asikainen S., Wai S.N., Oscarsson J. Perinuclear Localization of Internalized Outer Membrane Vesicles Carrying Active Cytolethal Distending Toxin from Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 2012;80:31. doi: 10.1128/IAI.06069-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Vanaja S.K., Russo A.J., Behl B., Banerjee I., Yankova M., Deshmukh S.D., Rathinam V.A.K. Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles Mediate Cytosolic Localization of LPS and Caspase-11 Activation. Cell. 2016;165:1106–1119. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Santos J.C., Dick M.S., Lagrange B., Degrandi D., Pfeffer K., Yamamoto M., Meunier E., Pelczar P., Henry T., Broz P. LPS Targets Host Guanylate-binding Proteins to the Bacterial Outer Membrane for Non-canonical Inflammasome Activation. EMBO J. 2018;37:e98089. doi: 10.15252/embj.201798089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Kaparakis-Liaskos M., Ferrero R.L. Immune Modulation by Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015;15:375–387. doi: 10.1038/nri3837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Dagnelie M.A., Corvec S., Khammari A., Dréno B. Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles: A New Way to Decipher Host-Microbiota Communications in Inflammatory Dermatoses. Exp. Dermatol. 2020;29:22–28. doi: 10.1111/exd.14050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Bielaszewska M., Rüter C., Bauwens A., Greune L., Jarosch K.A., Steil D., Zhang W., He X., Lloubes R., Fruth A., et al. Host Cell Interactions of Outer Membrane Vesicle-Associated Virulence Factors of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157: Intracellular Delivery, Trafficking and Mechanisms of Cell Injury. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006159. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Chatterjee S., Mondal A., Mitra S., Basu S. Acinetobacter Baumannii Transfers the BlaNDM-1 Gene via Outer Membrane Vesicles. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017;72:2201–2207. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Toyofuku M., Morinaga K., Hashimoto Y., Uhl J., Shimamura H., Inaba H., Schmitt-Kopplin P., Eberl L., Nomura N. Membrane Vesicle-Mediated Bacterial Communication. ISME J. 2017;11:1504–1509. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2017.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Oishi S., Miyashita M., Kiso A., Kikuchi Y., Ueda O., Hirai K., Shibata Y., Fujimura S. Cellular Locations of Proteinases and Association with Vesicles in Porphyromonas Gingivalis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2010;15:397–402. doi: 10.1186/2047-783X-15-9-397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Vergauwen G., Dhondt B., van Deun J., de Smedt E., Berx G., Timmerman E., Gevaert K., Miinalainen I., Cocquyt V., Braems G., et al. Confounding Factors of Ultrafiltration and Protein Analysis in Extracellular Vesicle Research. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:2704. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02599-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Habier J., May P., Heintz-Buschart A., Ghosal A., Wienecke-Baldacchino A.K., Nolte Hoen E.N.M., Wilmes P., Fritz J.V. Extraction and Analysis of RNA Isolated from Pure Bacteria-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018;1737:213–230. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7634-8_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Chutkan H., MacDonald I., Manning A., Kuehn M.J. Quantitative and Qualitative Preparations of Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013;966:259–272. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-245-2_16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Sjöström A.E., Sandblad L., Uhlin B.E., Wai S.N. Membrane Vesicle-Mediated Release of Bacterial RNA. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:15329. doi: 10.1038/srep15329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Patel G.K., Khan M.A., Zubair H., Srivastava S.K., Khushman M., Singh S., Singh A.P. Comparative Analysis of Exosome Isolation Methods Using Culture Supernatant for Optimum Yield, Purity and Downstream Applications. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:5335. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41800-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Malhotra S., Amin Z.M., Dobhal G., Cottam S., Nann T., Goreham R.V. Novel Devices for Isolation and Detection of Bacterial and Mammalian Extracellular Vesicles. Microchim. Acta. 2021;188:139. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04790-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Melo J., Pinto V., Fernandes T., Malheiro A.R., Osório H., Figueiredo C., Leite M. Isolation Method and Characterization of Outer Membranes Vesicles of Helicobacter Pylori Grown in a Chemically Defined Medium. Front. Microbiol. 2021;12:1253. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.654193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Royo F., Théry C., Falcón-Pérez J.M., Nieuwland R., Witwer K.W. Methods for Separation and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles: Results of a Worldwide Survey Performed by the ISEV Rigor and Standardization Subcommittee. Cells. 2020;9:1955. doi: 10.3390/cells9091955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Hartjes T.A., Mytnyk S., Jenster G.W., van Steijn V., van Royen M.E. Extracellular Vesicle Quantification and Characterization: Common Methods and Emerging Approaches. Bioengineering. 2019;6:7. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering6010007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Morales-Kastresana A., Telford B., Musich T.A., McKinnon K., Clayborne C., Braig Z., Rosner A., Demberg T., Watson D.C., Karpova T.S., et al. Labeling Extracellular Vesicles for Nanoscale Flow Cytometry. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:1878. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01731-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Gangadaran P., Hong C.M., Ahn B.C. An Update on in Vivo Imaging of Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery Vehicles. Front. Pharmacol. 2018;9:169. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Ohno S.I., Takanashi M., Sudo K., Ueda S., Ishikawa A., Matsuyama N., Fujita K., Mizutani T., Ohgi T., Ochiya T., et al. Systemically Injected Exosomes Targeted to EGFR Deliver Antitumor MicroRNA to Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Ther. 2013;21:185–191. doi: 10.1038/mt.2012.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Grange C., Tapparo M., Bruno S., Chatterjee D., Quesenberry P.J., Tetta C., Camussi G. Biodistribution of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in a Model of Acute Kidney Injury Monitored by Optical Imaging. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014;33:1055–1063. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Piffoux M., Gazeau F., Wilhelm C., Silva A.K.A. Imaging and Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles. Des. Appl. Nanopart. Biomed. Imaging. 2017:43–68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-42169-8_3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Hwang D.W., Choi H., Jang S.C., Yoo M.Y., Park J.Y., Choi N.E., Oh H.J., Ha S., Lee Y.-S., Jeong J.M., et al. Noninvasive Imaging of Radiolabeled Exosome-Mimetic Nanovesicle Using 99mTc-HMPAO. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:15636. doi: 10.1038/srep15636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Gangadaran P., Rajendran R.L., Lee H.W., Kalimuthu S., Hong C.M., Jeong S.Y., Lee S.W., Lee J., Ahn B.C. Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Activates VEGF Receptors and Accelerates Recovery of Hindlimb Ischemia. J. Control. Release. 2017;264:112–126. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Hoshino A., Costa-Silva B., Shen T.-L., Rodrigues G., Hashimoto A., Tesic Mark M., Molina H., Kohsaka S., di Giannatale A., Ceder S., et al. Tumour Exosome Integrins Determine Organotropic Metastasis. Nature. 2015;527:329–335. doi: 10.1038/nature15756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Tyrer P.C., Frizelle F.A., Keenan J.I. Escherichia coli-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles Are Genotoxic to Human Enterocyte-like Cells. Infect. Agents Cancer. 2014;9:2. doi: 10.1186/1750-9378-9-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Parker H., Chitcholtan K., Hampton M.B., Keenan J.I. Uptake of Helicobacter Pylori Outer Membrane Vesicles by Gastric Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2010;78:5054–5061. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00299-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Tan S., Xia L., Yi P., Han Y., Tang L., Pan Q., Tian Y., Rao S., Oyang L., Liang J., et al. Exosomal MiRNAs in Tumor Microenvironment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020;39:67. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01570-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Hanahan D., Coussens L.M. Accessories to the Crime: Functions of Cells Recruited to the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:309–322. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Rossi G.R., Trindade E.S., Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes F. Tumor Microenvironment-Associated Extracellular Matrix Components Regulate NK Cell Function. Front. Immunol. 2020;11:73. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Wei R., Liu S., Zhang S., Min L., Zhu S. Cellular and Extracellular Components in Tumor Microenvironment and Their Application in Early Diagnosis of Cancers. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2020;2020:6283796. doi: 10.1155/2020/6283796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Sullivan R., Maresh G., Zhang X., Salomon C., Hooper J., Margolin D., Li L. The Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles as Communication Vehicles within the Tumor Microenvironment and Beyond. Front. Endocrinol. 2017;8:194. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Tao S.C., Guo S.C. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Tumour Microenvironment. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020;18:163. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00643-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Huycke M.M., Abrams V., Moore D.R. Enterococcus Faecalis Produces Extracellular Superoxide and Hydrogen Peroxide That Damages Colonic Epithelial Cell DNA. Carcinogenesis. 2002;23:529–536. doi: 10.1093/carcin/23.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Behzadi E., Mahmoodzadeh Hosseini H., Imani Fooladi A.A. The Inhibitory Impacts of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on the Growth of Hepatic Cancer Cells. Microb. Pathog. 2017;110:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Jang S.C., Kim S.R., Yoon Y.J., Park K.S., Kim J.H., Lee J., Kim O.Y., Chio E.J., Kim D.K., Choi D.S., et al. In Vivo Kinetic Biodistribution of Nano-Sized Outer Membrane Vesicles Derived from Bacteria. Small. 2015;11:456–461. doi: 10.1002/smll.201401803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Jones E.J., Booth C., Fonseca S., Parker A., Cross K., Miquel-Clopés A., Hautefort I., Mayer U., Wileman T., Stentz R., et al. The Uptake, Trafficking, and Biodistribution of Bacteroides Thetaiotaomicron Generated Outer Membrane Vesicles. Front. Microbiol. 2020;11:57. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Park J.Y., Choi J., Lee Y., Lee J.E., Lee E.H., Kwon H.J., Yang J., Jeong B.R., Kim Y.K., Han P.L. Metagenome Analysis of Bodily Microbiota in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease Using Bacteria-Derived Membrane Vesicles in Blood. Exp. Neurobiol. 2017;26:369–379. doi: 10.5607/en.2017.26.6.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Choi H., Choi J.P., Seo J., Kim B.J., Rho M., Han J.K., Kim J.G. Helicobacter Pylori-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Increased in the Gastric Juices of Gastric Adenocarcinoma Patients and Induced Inflammation Mainly via Specific Targeting of Gastric Epithelial Cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017;49:330. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Turkina M.V., Olofsson A., Magnusson K.E., Arnqvist A., Vikström E. Helicobacter Pylori Vesicles Carrying CagA Localize in the Vicinity of Cell-Cell Contacts and Induce Histone H1 Binding to ATP in Epithelial Cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015;362 doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnv076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Bostanshirin N., Bereimipour A., Aghasafi M., Mehtararaghinia R., Ebrahimisadrabadi A., Jalili A. The Regulatory Role of Exosomal CagA and MicroRNAs Derived from H. Pylori-Related Gastric Cancer Cells on Signaling Pathways Related to Cancer Development: A Bioinformatics Aspect. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2020;29:1295–1312. doi: 10.1007/s00580-020-03167-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Kuerban K., Gao X., Zhang H., Liu J., Dong M., Wu L., Ye R., Feng M., Ye L. Doxorubicin-Loaded Bacterial Outer-Membrane Vesicles Exert Enhanced Anti-Tumor Efficacy in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2020;10:1534–1548. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Borrello M.G., Alberti L., Fischer A., Degl’Innocenti D., Ferrario C., Gariboldi M., Marchesi F., Allavena P., Greco A., Collini P., et al. Induction of a Proinflammatory Program in Normal Human Thyrocytes by the RET/PTC1 Oncogene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:14825–14830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503039102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Huang H.W., Chang C.C., Wang C.S., Lin K.H. Association between Inflammation and Function of Cell Adhesion Molecules Influence on Gastrointestinal Cancer Development. Cells. 2021;10:67. doi: 10.3390/cells10010067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Johnson C.H., Dejea C.M., Elder D., Hoang L.T., Santidrian A.F., Feilding B.H., Ivanisevic J., Cho K., Wick E.C., Hechenbleikner E.M., et al. Metabolism Links Bacterial Biofilms and Colon Carcinogenesis. Cell Metab. 2015;21:891–897. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.04.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Weir T.L., Manter D.K., Sheflin A.M., Barnett B.A., Heuberger A.L., Ryan E.P. Stool Microbiome and Metabolome Differences between Colorectal Cancer Patients and Healthy Adults. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e70803. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Choi M.S., Ze E.Y., Park J.Y., Shin T.-S., Kim J.G. Helicobacter Pylori-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles Stimulate Interleukin 8 Secretion through Nuclear Factor Kappa B Activation. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021;36:857. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2019.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Pfalzgraff A., Correa W., Heinbockel L., Schromm A.B., Lübow C., Gisch N., Martinez-de-Tejada G., Brandenburg K., Weindl G. LPS-Neutralizing Peptides Reduce Outer Membrane Vesicle-Induced Inflammatory Responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids. 2019;1864:1503–1513. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.05.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Galka F., wai S.N., Kusch H., Engelmann S., Hecker M., Schmeck B., Hippenstiel S., Uhlin B.E., Steinert M. Proteomic Characterization of the Whole Secretome of Legionella Pneumophila and Functional Analysis of Outer Membrane Vesicles. Infect. Immun. 2008;76:1825–1836. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01396-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Kim D.J., Yang J., Seo H., Lee W.H., Ho Lee D., Kym S., Park Y.S., Kim J.G., Jang I.J., Kim Y.K., et al. Colorectal Cancer Diagnostic Model Utilizing Metagenomic and Metabolomic Data of Stool Microbial Extracellular Vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:2860. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59529-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Johnson C.H., Spilker M.E., Goetz L., Peterson S.N., Siuzdak G. Metabolite and Microbiome Interplay in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2016;76:6146–6152. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Chu F.-F., Esworthy R.S., Chu P.G., Longmate J.A., Huycke M.M., Wilczynski S., Doroshow J.H. Bacteria-Induced Intestinal Cancer in Mice with Disrupted Gpx1 and Gpx2 Genes. Cancer Res. 2004;64:962–968. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Mughini-Gras L., Schaapveld M., Kramers J., Mooij S., Neefjes-Borst E.A., van Pelt W., Neefjes J. Increased Colon Cancer Risk after Severe Salmonella Infection. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0189721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Vdovikova S., Gilfillan S., Wang S., Dongre M., Wai S.N., Hurtado A. Modulation of Gene Transcription and Epigenetics of Colon Carcinoma Cells by Bacterial Membrane Vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:7434. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25308-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Chitcholtan K., Hampton M.B., Keenan J.I. Outer Membrane Vesicles Enhance the Carcinogenic Potential of Helicobacter Pylori. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:2400–2405. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Hemmi H., Takeuchi O., Kawai T., Kaisho T., Sato S., Sanjo H., Matsumoto M., Hoshino K., Wagner H., Takeda K., et al. A Toll-like Receptor Recognizes Bacterial DNA. Nature. 2000;408:740–745. doi: 10.1038/35047123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Janeway C.A., Medzhitov R. Innate Immunity: Lipoproteins Take Their Toll on the Host. Curr. Biol. 1999;9:R879–R882. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(00)80073-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Valenzuela L., Chi A., Beard S., Orell A., Guiliani N., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D.F., Jerez C.A. Genomics, Metagenomics and Proteomics in Biomining Microorganisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006;24:197–211. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2005.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Wang N., Zhu F., Chen L., Chen K. Proteomics, Metabolomics and Metagenomics for Type 2 Diabetes and Its Complications. Life Sci. 2018;212:194–202. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.09.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Keller C., Wei P., Wancewicz B., Cross T.W.L., Rey F.E., Li L. Extraction Optimization for Combined Metabolomics, Peptidomics, and Proteomics Analysis of Gut Microbiota Samples. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020;56:e4625. doi: 10.1002/jms.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Tebani A., Afonso C., Marret S., Bekri S. Omics-Based Strategies in Precision Medicine: Toward a Paradigm Shift in Inborn Errors of Metabolism Investigations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016;17:1555. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Bandu R., Oh J.W., Kim K.P. Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteome Profiling of Extracellular Vesicles and Their Roles in Cancer Biology. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019;51:1–10. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0218-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Ghosal A., Upadhyaya B.B., Fritz J.V., Heintz-Buschart A., Desai M.S., Yusuf D., Huang D., Baumuratov A., Wang K., Galas D., et al. The Extracellular RNA Complement of Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Open. 2015;4:252–266. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Campos J.H., Soares R.P., Ribeiro K., Cronemberger Andrade A., Batista W.L., Torrecilhas A.C. Extracellular Vesicles: Role in Inflammatory Responses and Potential Uses in Vaccination in Cancer and Infectious Diseases. J. Immunol. Res. 2015;2015:832057. doi: 10.1155/2015/832057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Liao S., Klein M.I., Heim K.P., Fan Y., Bitoun J.P., Ahn S.J., Burne R.A., Koo H., Brady L.J., Wen Z.T. Streptococcus Mutans Extracellular DNA Is Upregulated during Growth in Biofilms, Actively Released via Membrane Vesicles, and Influenced by Components of the Protein Secretion Machinery. J. Bacteriol. 2014;196:2355–2366. doi: 10.1128/JB.01493-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Cai J., Han Y., Ren H., Chen C., He D., Zhou L., Eisner G.M., Asico L.D., Jose P.A., Zeng C. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of Donor Genomic DNA to Recipient Cells Is a Novel Mechanism for Genetic Influence between Cells. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013;5:227–238. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjt011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Choi J.W., Um J.H., Cho J.H., Lee H.J. Tiny RNAs and Their Voyage via Extracellular Vesicles: Secretion of Bacterial Small RNA and Eukaryotic MicroRNA. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017;242:1475–1481. doi: 10.1177/1535370217723166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Choi J.W., Kim S.C., Hong S.H., Lee H.J. Secretable Small RNAs via Outer Membrane Vesicles in Periodontal Pathogens. J. Dent. Res. 2017;96:458–466. doi: 10.1177/0022034516685071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Anfossi S., Calin G.A. Gut Microbiota: A New Player in Regulating Immune- and Chemo-Therapy Efficacy. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020;3:356. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2020.04. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Langlete P., Krabberød A.K., Winther-Larsen H.C. Vesicles From Vibrio Cholerae Contain AT-Rich DNA and Shorter MRNAs That Do Not Correlate With Their Protein Products. Front. Microbiol. 2019;10:2708. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Malabirade A., Habier J., Heintz-Buschart A., May P., Godet J., Halder R., Etheridge A., Galas D., Wilmes P., Fritz J.V. The RNA Complement of Outer Membrane Vesicles from Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium under Distinct Culture Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2018;9:2015. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 263.Liu J., Hsieh C.L., Gelincik O., Devolder B., Sei S., Zhang S., Lipkin S.M., Chang Y.F. Proteomic Characterization of Outer Membrane Vesicles from Gut Mucosa-Derived Fusobacterium Nucleatum. J. Proteom. 2019;195:125–137. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2018.12.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Sun C.-H., Li B.-B., Wang B., Zhao J., Zhang X.-Y., Li T.-T., Li W.-B., Tang D., Qiu M.-J., Wang X.-C., et al. The Role of Fusobacterium Nucleatum in Colorectal Cancer: From Carcinogenesis to Clinical Management. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2019;5:178–187. doi: 10.1016/j.cdtm.2019.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Gur C., Ibrahim Y., Isaacson B., Yamin R., Abed J., Gamliel M., Enk J., Bar-On Y., Stanietsky-Kaynan N., Coppenhagen-Glazer S., et al. Binding of the Fap2 Protein of Fusobacterium Nucleatum to Human Inhibitory Receptor TIGIT Protects Tumors from Immune Cell Attack. Immunity. 2015;42:344–355. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.01.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Abed J., Maalouf N., Manson A.L., Earl A.M., Parhi L., Emgård J.E.M., Klutstein M., Tayeb S., Almogy G., Atlan K.A., et al. Colon Cancer-Associated Fusobacterium Nucleatum May Originate From the Oral Cavity and Reach Colon Tumors via the Circulatory System. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020;10:400. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Chen S., Su T., Zhang Y., Lee A., He J., Ge Q., Wang L., Si J., Zhuo W., Wang L. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Promotes Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Modulating KRT7-AS/KRT7. Gut Microbes. 2020;11:511–525. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2019.1695494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Casasanta M.A., Yoo C.C., Udayasuryan B., Sanders B.E., Umanã A., Zhang Y., Peng H., Duncan A.J., Wang Y., Li L., et al. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Host-Cell Binding and Invasion Induces IL-8 and CXCL1 Secretion That Drives Colorectal Cancer Cell Migration. Sci. Signal. 2020;13 doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aba9157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Yu T.C., Guo F., Yu Y., Sun T., Ma D., Han J., Qian Y., Kryczek I., Sun D., Nagarsheth N., et al. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Promotes Chemoresistance to Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Autophagy. Cell. 2017;170:548–563. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Kim J.R., Han K., Han Y., Kang N., Shin T.-S., Park H.J., Kim H., Kwon W., Lee S., Kim Y.-K., et al. Microbiome Markers of Pancreatic Cancer Based on Bacteria-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Acquired from Blood Samples: A Retrospective Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Biology. 2021;10:219. doi: 10.3390/biology10030219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 271.Kim S.I., Kang N., Leem S., Yang J., Jo H., Lee M., Kim H.S., Dhanasekaran D.N., Kim Y.K., Park T., et al. Metagenomic Analysis of Serum Microbe-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Diagnostic Models to Differentiate Ovarian Cancer and Benign Ovarian Tumor. Cancers. 2020;12:1309. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Rodrigues M., Fan J., Lyon C., Wan M., Hu Y. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Viral and Bacterial Infections: Pathogenesis, Diagnostics, and Therapeutics. Theranostics. 2018;8:2709–2721. doi: 10.7150/thno.20576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Sheridan C. Exosome Cancer Diagnostic Reaches Market. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016;34:359–360. doi: 10.1038/nbt0416-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Gangadaran P., Hong C.M., Ahn B.C. Current Perspectives on in Vivo Noninvasive Tracking of Extracellular Vesicles with Molecular Imaging. BioMed Res. Int. 2017;2017:9158319. doi: 10.1155/2017/9158319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.Richter M., Vader P., Fuhrmann G. Approaches to Surface Engineering of Extracellular Vesicles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021;173:416–426. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.03.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.Gujrati V., Prakash J., Malekzadeh-Najafabadi J., Stiel A., Klemm U., Mettenleiter G., Aichler M., Walch A., Ntziachristos V. Bioengineered Bacterial Vesicles as Biological Nano-Heaters for Optoacoustic Imaging. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:1114. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09034-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Huang Y., Beringhs A.O., Chen Q., Song D., Chen W., Lu X., Fan T.-H., Nieh M.-P., Lei Y. Genetically Engineered Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles with Expressed Nanoluciferase Reporter for in Vivo Bioluminescence Kinetic Modeling through Noninvasive Imaging. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019;2:5608–5615. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.9b00690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Gerritzen M.J.H., Martens D.E., Wijffels R.H., van der Pol L., Stork M. Bioengineering Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles as Vaccine Platform. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017;35:565–574. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 279.Balhuizen M.D., Veldhuizen E.J.A., Haagsman H.P. Outer Membrane Vesicle Induction and Isolation for Vaccine Development. Front. Microbiol. 2021;12:79. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.629090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Gujrati V., Kim S., Kim S.-H., Min J.J., Choy H.E., Kim S.C., Jon S. Bioengineered Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles as Cell-Specific Drug-Delivery Vehicles for Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano. 2014;8:1525–1537. doi: 10.1021/nn405724x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 281.Chen D.J., Osterrieder N., Metzger S.M., Buckles E., Doody A.M., DeLisa M.P., Putnam D. Delivery of Foreign Antigens by Engineered Outer Membrane Vesicle Vaccines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:3099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805532107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 282.Kroniger T., Otto A., Becher D. Proteomic Analysis of Bacterial (Outer) Membrane Vesicles: Progress and Clinical Potential. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2018;15:623–626. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2018.1505509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 283.Kim O.Y., Dinh N.T.H., Park H.T., Choi S.J., Hong K., Gho Y.S. Bacterial Protoplast-Derived Nanovesicles for Tumor Targeted Delivery of Chemotherapeutics. Biomaterials. 2017;113:68–79. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.10.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 284.Stentz R., Carvalho A.L., Jones E.J., Carding S.R. Fantastic Voyage: The Journey of Intestinal Microbiota-Derived Microvesicles through the Body. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018;46:1021–1027. doi: 10.1042/BST20180114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]