Abstract
目的
探讨miR-671-5p影响骨肉瘤的迁移侵袭的相关机制。
方法
通过NCBI在线数据库筛选骨肉瘤中差异表达的微小RNA(miRNA)、预测miRNA的靶蛋白并进行功能分析;实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)用于检测转染过表达miR-671-5p质粒后con组和miR-671-5p组骨肉瘤细胞中miR-671-5p的表达情况;通过Transwell实验检测转染质粒后骨肉瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭能力;Western blot实验检测相关蛋白在骨肉瘤细胞中的表达情况;荧光素酶报告基因检测重组人SMAD家族成员3(SMAD3)的3’UTR中是否含有miR-671-5p的结合位点。
结果
MiR-671-5p在骨肉瘤组织和细胞中表达下调(P < 0.05)。qRT-PCR证明转染过表达miR-671-5p质粒后,细胞转染成功(P < 0.05)。过表达骨肉瘤细胞中的miR-671-5p后细胞的迁移和侵袭能力明显降低(P < 0.05),并且miR-671-5p能够抑制骨肉瘤细胞的上皮间质转化(EMT)(P < 0.05);Western blot结果显示SMAD3在骨肉瘤细胞中表达上调(P < 0.05);荧光素酶报告基因检测证实miR-671-5p与SMAD3的3’UTR之间存在结合位点(P < 0.05);Western blot结果显示转染过表达SMAD3质粒后,SMAD3表达明显升高(P < 0.05),而miR-671-5p能明显抑制SMAD3的表达(P < 0.05);Transwell实验证明SMAD3能够促进骨肉瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭能力(P < 0.05),而miR-671-5p则能够逆转这种促进作用(P < 0.05)。
结论
MiR-671-5p能够通过负向调控SMAD3抑制骨肉瘤细胞迁移和侵袭能力。
Keywords: miR-671-5p, SMAD3, 迁移, 侵袭, 上皮间质转化, 骨肉瘤
Abstract
Objective
To explore the role of miR-671-5p in regulating the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma and the underlying mechanisms.
Methods
The differentially expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) in osteosarcoma were screened in the NCBI online database, and the target proteins of these miRNAs were predicted and their functions were analyzed. Osteosarcoma cells were transfected with a plasmid overexpressing miR-671-5p, and the transfection efficiency was assessed using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). The changes in the migration and invasion of the transfected cells were examined with Transwell assay, and the expressions of proteins related with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) were detected using Western blotting. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed to determine whether the 3'UTR of SMAD3 contained a targeted binding site of miR-671-5p.
Results
MiR-671-5p was significantly down-regulated in both osteosarcoma tissues and osteosarcoma cells (P < 0.05). The osteosarcoma cells overexpressing miR-671-5p showed significantly reduced migration and invasion abilities (P < 0.05) with obviously lowered expressions of EMT-related proteins (P < 0.05). SMAD3 was highly expressed in osteosarcoma cells (P < 0.05), and dual-luciferase reporter assay confirmed the presence of a targeted binding site between miR-671-5p and the 3'UTR of SMAD3 (P < 0.05). In osteosarcoma cells transfected with a SMAD3-overexpressing plasmid (P < 0.05), the high expression of SMAD3 significantly inhibited by miR-671-5p overexpression (P < 0.05). Transwell assay demonstrated that SMAD3 overexpression significantly promoted the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells (P < 0.05), and while miR-671-5p overexpression obviously reversed this effect (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
MiR-671-5p can inhibit the invasion and migration of osteosarcoma cells by negatively regulating SMAD3.
Keywords: miR-671-5p, SMAD3, migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, osteosarcoma
骨肉瘤是最常见于儿童和青少年患者的骨肿瘤,其特征是治疗后转移进展和复发的高风险[1]。由于患者的生存率较低,这种疾病有效的治疗管理仍然是难以捉摸的[2]。为了实现更有效的治疗管理方案,从而提高患者的生存率,在临床环境中为骨肉瘤的治疗确定更有针对性的治疗方法至关重要[3]。
miRNA是小的内源RNA,可在转录后调控基因表达,在各种细胞和生理过程(例如细胞增殖和分化)中发挥重要作用[4-6]。据报道它们的异常表达与各种人类肿瘤的进展和转移密切相关,有关的功能研究已被证实[7, 8],miRNA充当肿瘤抑制物或癌基因,并且针对miRNA的miRNA模拟物和分子已在临床前开发中显示出希望[9]。前期已有研究证明miR-671-5p能够结合相关靶蛋白从而影响肿瘤的发生发展,能够通过抑制成纤维生长因子受体2阻断人食道鳞状细胞癌的进展[10]。MiR-671-5p的过表达能够影响结肠癌的预后,并会加速结肠癌细胞的增殖,迁移和侵袭[11]。另外,MiR-671-5p也能够通过结合釉丛蛋白1在抑制骨肉瘤细胞生长、迁移和侵袭中发挥关键作用[12]。但是,miR-671-5p影响骨肉瘤发展进程的其他分子机制尚不明确。
在本研究中,我们研究了miR-671-5p在骨肉瘤中的作用,并探讨了miR-671-5p与其下游靶基因SMAD3在体外的相互作用,结果表明,miR-671-5p通过结合其下游靶基因SMAD3影响骨肉瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭能力。
1. 材料和方法
1.1. 主要仪器和试剂
Lipofectamine 2000(Invitrogen),miR-671-5p上下游引物(上海生工生物工程有限公司),β-actin(ab8226)、SMAD3(ab40854)、Vimentin(ab92547)、N- cadherin(ab76001)抗体(Abcam)。
1.2. 网上在线数据库
NCBI在线数据库(<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/" target="_blank">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/</a>)中GSE28423数据集筛选骨肉瘤细胞中差异表达的miRNAs,GSE70414数据集对骨肉瘤细胞中log<sub>2</sub>FC > 1,<italic>P</italic> < 0.05的mRNA进行筛选;starbase数据库(<a href="http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/" target="_blank">http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/</a>)、miRDB数据库(<a href="http://mirdb.org/" target="_blank">http://mirdb.org/</a>)、TargetScan数据库(<a href="http://www.targetscan.org/vert_72/" target="_blank">http://www.targetscan.org/vert_72/</a>)预测可能与miR-671-5p结合的hub基因。
1.3. 细胞培养和转染
人成骨细胞hFOB1.19,骨肉瘤细胞MG63、U2OS、Saos-2,人胚胎肾细胞HEK293T均购自美国模式培养物保藏所(ATCC),并按照其培养条件进行培养。培养24h,并在细胞达到0.70时通过Lipofectamine 2000将质粒转入细胞中。细胞分组为:con(转染过表达miR-671-5p对照质粒的骨肉瘤细胞);miR-671-5p(转染过表达miR-671-5p质粒的骨肉瘤细胞);NC(转染过表达SMAD3对照质粒的骨肉瘤细胞);SMAD3(转染过表达SMAD3质粒的骨肉瘤细胞);SMAD3+miR-671-5p(共转染过表达SMAD3和过表达miR-671-5p质粒的骨肉瘤细胞)。
1.4. qRT-PCR
TRIzol提取各组细胞的总RNA,ReverTra AceR Qpcr RT Kit试剂盒逆转录获得cDNA,以cDNA为模板,U6为内参,运行条件为95 ℃ 30 s、95 ℃ 5 s、65 ℃ 30 s、72 ℃ 30 s、循环数为35,PCR检测细胞中miR-671-5p的表达情况。2-△△CT计算结果。miR-671-5p上游引物为:GCGCGCATAAAGTAGAAAGC;下游引物为:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT;茎环结构:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACAGTAGT
1.5. Transwell实验
将4×104具有不同miR-671-5p或SMAD3表达水平的骨肉瘤细胞分别接种在无FBS的MEM培养基中,并置于小室或铺有Matrigel小室的上腔室中。然后,下腔注入10% FBS的MEM培养基。24 h后甲醇固定15 min,轻拭上室的细胞,Giemsa染色1 h,PBS清洗,吸弃PBS晾干后进行拍照。镜下随机选择5个视野拍照,取其平均值作为最终结果。
1.6. Western blot
提取各组细胞的总蛋白,测量蛋白质浓度,在10% SDS-PAGE凝胶上分离并转移到PVDF膜上,封闭,一抗4 ℃过夜,洗膜,二抗常温孵育1 h,洗膜,显影,曝光,分析灰度值,计算结果。抗体配制如下:SMAD3(1∶ 500),Vimentin(1∶1000),N-cadherin(1∶500),β-actin(1∶ 1000)作为内参。
1.7. 荧光素酶报告基因检测
HEK293T细胞接种到24孔板中,并在细胞数量达到0.70时利用Lipofectamine 2000将miR-671-5p过表达质粒及对照质粒、SMAD3野生型SMAD3-3’UTR-Wt及突变型SMAD3-3’UTR-Mut质粒共转染。培养24 h后,检测各组细胞的荧光素酶活性,分析相对荧光强度,计算结果。
1.8. 统计学分析
实验重复3次,实验数据表示为均数±标准差,使用SPSS 17.0软件进行统计分析,两组之间差异分析采用独立样本t检验,多样本均数之间的比较采用方差分析,P < 0.05被认为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1. MiR-671-5p在骨肉瘤组织和细胞中表达下调
通过NCBI在线数据库获得数据集GSE28423,筛选出|log2FC| > 4的miRNAs并制作热图(图 1A),GSE28423数据集发现miR-671-5p的log2FC=-4.80、P < 0.05,在骨肉瘤细胞中可能发挥抑癌基因的作用。通过qRT-PCR发现在10例骨肉瘤组织中,与癌旁正常骨组织相比,骨肉瘤组织中miR-671-5p的表达明显降低(图 1B)。因此,我们选择miR-671-5p作为研究对象。qRT-PCR结果显示与人成骨细胞hFOB1.19相比,在骨肉瘤细胞中miR-671-5p的表达明显下调(图 1C)。MiR-671-5p主要参与的前10位KEGG通路,包括Wnt信号通路、癌症通路、细胞周期等,这些通路在癌症中都发挥着至关重要的作用,因此我们可以推测miR-671-5p也许参与相关通路的调控从而影响骨肉瘤的发展进程(图 1D)。
1.
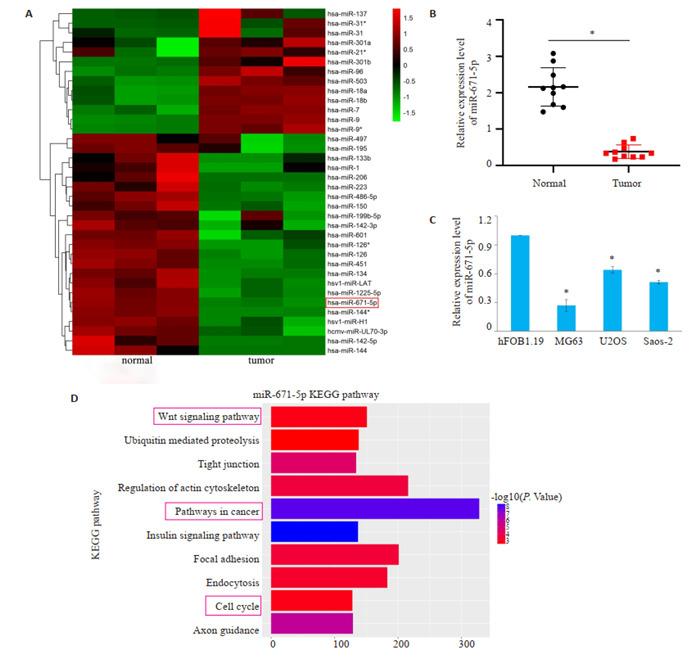
MiR-671-5p在骨肉瘤组织和细胞中表达下调
MiR-671-5p expression is down-regulated in osteosarcoma tissues and cells. A: Heatmap of the differentially expressed miRNAs with |log2FC| >4 in the GSE28423; B: Expression of miR-671-5p in 10 patients with osteosarcoma (*P < 0.05). C: Expression of miR-671-5p in osteosarcoma cells (*P < 0.05 vs hFOB1.19 group). D: KEGG analyses of miR-671-5p.
2.2. MiR-671-5p抑制骨肉瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭
将miR-671-5p过表达质粒和对照质粒转染入骨肉瘤细胞,qRT-PCR结果显示与对照组相比,过表达miR-671-5p组中miR-671-5p表达(MG63:P < 0.0001;Saos-2:P=0.0002)明显上调(图 2A)。Transwell迁移实验发现,与对照组相比,过表达miR-671-5p组穿膜细胞数(MG63:P=0.0017;Saos- 2:P=0.0014)明显减少(图 2B)。而Transwell侵袭实验结果显示,与对照组相比,过表达miR-671-5p组穿膜细胞数(MG63:P=0.0124;Saos-2:P < 0.0001)明显降低(图 2C)。
2.
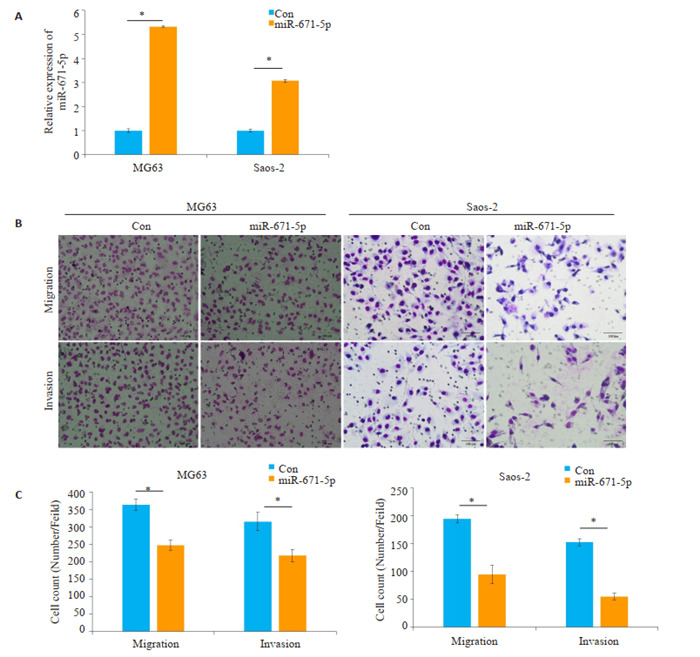
MiR-671-5p对骨肉瘤细胞迁移和侵袭能力的影响
Effect of miR-671-5p overexpression on migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells. A: Expression of miR-671-5p in different groups after transfection. B, C: Transwell assay for examining cell invasion and migration abilities in each group (scale bar=100 μm). *P < 0.05.
2.3. MiR-671-5p抑制骨肉瘤细胞的EMT的发生
Western blot结果显示,与对照组相比,过表达miR-671-5p组中Vimentin(MG63:P=0.0054;Saos-2:P=0.003)和N- cadherin(MG63:P=0.0138;Saos- 2:P= 0.0244)的表达明显降低(图 3)。
3.
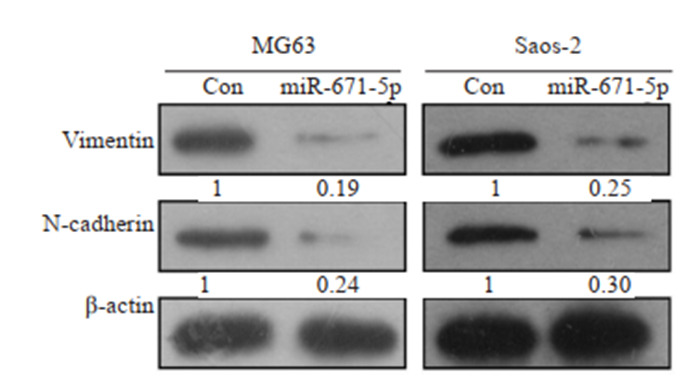
Western blot检测miR-671-5p对骨肉瘤细胞EMT的影响
Western blotting for detecting expressions of EMT-related proteins in osteosarcoma cells overexpressing miR-671-5p.
2.4. SMAD3为miR-671-5p的关键基因
网上数据库starbase、miRDB、TargetScan预测可能与miR-671-5p结合的靶蛋白取其交集并获取hub基因,构建degree得分前10位的蛋白互作网络关系图(图 4A),将网上数据库预测的hub基因与骨肉瘤数据集GSE70414中log2FC > 1,P < 0.05的mRNA取交集(图 4B),发现SMAD3既在骨肉瘤中表达上调,又与miR-671- 5p结合。Western blot检测在骨肉瘤细胞中SMAD3的表达情况,发现与人成骨细胞hFOB1.19相比,SMAD3在骨肉瘤细胞中表达明显上调(图 4C)。荧光素酶报告基因检测结果显示,与con/Wt-SMAD3-3’ UTR组相比,miR-671-5p/Wt-SMAD3-3’UTR组的相对荧光活性明显降低,而con/Mut-SMAD3-3’UTR组与miR- 671- 5p/Mut- SMAD3- 3’UTR组则无明显差异(图 4D)。
4.
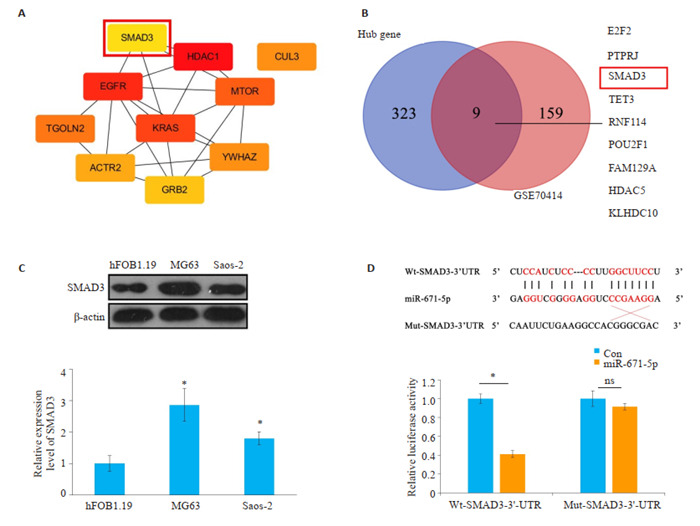
SMAD3为miR-671-5p的关键基因
SMAD3 is a key gene for miR-671-5p. A: Protein interaction network of the top10 target genes associated with miR-671-5p; B: Venn diagram of the hub genes and GSE70414. C: Expression of SMAD3 in osteosarcoma cells (*P < 0.05 vs hFOB1.19 group). D: Relative luciferase activity in different groups measured by luciferase report experiment. *P < 0.05.
2.5. MiR-671-5p调控SMAD3抑制骨肉瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭
通过Western blot发现,与NC组相比,SMAD3组SMAD3的表达(MG63:P=0.0006;Saos- 2:P=0.0009)明显升高,而SMAD3+miR-671-5p组SMAD3的表达(MG63:P=0.0008;Saos- 2:P=0.0018)则少于SMAD3组(图 5A)。Transwell迁移实验发现,与NC组相比,SMAD3组穿膜细胞数(MG63:P=0.0006;Saos- 2:P= 0.0003)明显升高,而SMAD3+miR-671-5p组的穿膜细胞数(MG63:P=0.0018;Saos- 2:P=0.0014)则少于SMAD3组(图 5B)。Transwell侵袭实验发现,与NC组相比,SMAD3组穿膜细胞数(MG63:P=0.0003;Saos-2:P=0.0003)明显升高,而SMAD3+miR-671-5p组的穿膜细胞数(MG63:P=0.0003;Saos- 2:P=0.0034)则少于SMAD3组。
5.
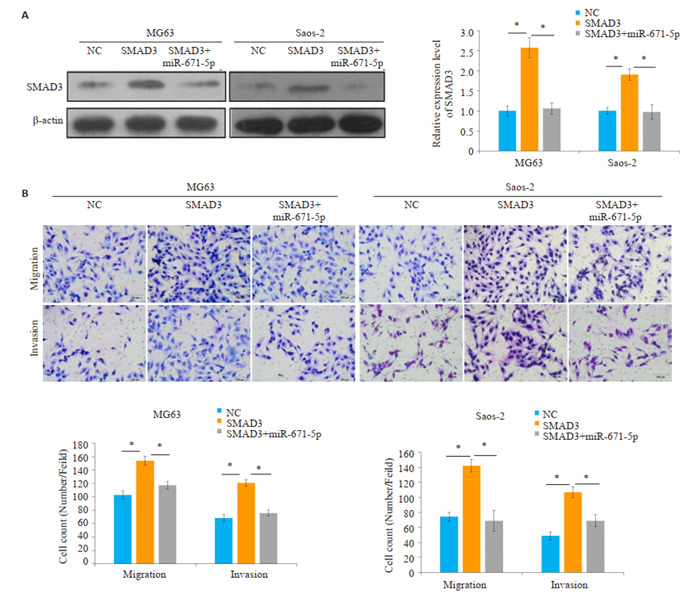
MiR-671-5p调控SMAD3抑制骨肉瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭
MiR-671-5p targets SMAD3 to inhibit the invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells. A: Expression of SMAD3 in osteosarcoma cells in different groups. B: Transwell assay for examining migration and invasion abilities of cells transfected with the plasmids for overexpression of SMAD3, miR-671-5p, or both. scale bar=100 μm, *P < 0.05.
3. 讨论
骨肉瘤的诊疗现在大多基于标准的选择诊疗法,包括积极的手术切除、全身化疗和靶向放疗[13]。本文致力于找到新的肿瘤标志物和靶点治疗,从而降低骨肉瘤的发展。目前有报道阐明,miRNA与骨肉瘤的化疗敏感性和耐药性有着密切相关性[14, 15]。也有报道称miRNA可能参与骨肉瘤的抗辐射并能够降低放疗的敏感性从而对其今后的治疗起着非常重要的作用[16]。因此,探索miRNA的分子机制,找到新的肿瘤标志物和靶点治疗对降低骨肉瘤的耐化学性,提高其对化疗和放疗的敏感性尤为重要。本文正是以此为切入点,通过NCBI在线数据库筛选出在骨肉瘤中相对表达下调的miR-671-5p作为研究对象。我们通过质粒转染,过表达miR-671-5p后,发现骨肉瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭能力降低,证实miR-671-5p可以作为一种抑癌基因在骨肉瘤的发展进程中发挥相应的作用。前期研究表明多种miRNA的异常表达对骨肉瘤今后的发展起着至关重要的作用[17-19]。MiR-627-3p可以通过靶向PTN降低骨肉瘤细胞的增殖和转移能力[20]。这为我们探索miR- 671-5p在骨肉瘤的发展进程中如何发挥作用提供了思路。
EMT是一种可逆的细胞生物学程序,参与侵袭、血管生成和转移相关的化疗耐药[21]。本文通过Western blot实验检测在骨肉瘤中miR-671-5p对EMT的影响。在生理EMT过程中,上皮细胞通过特定程序转化为具有间质表型细胞的生物学过程并且失去了与基底膜的连接等上皮表型使细胞获得了较高的迁移与侵袭能力。在肿瘤细胞中,EMT受到来自肿瘤及其微环境的刺激,如生长因子和细胞因子的异常调节,导致迁移和侵袭表型[22-24]。本文已经证明过表达miR-671-5p能够抑制EMT的发生,而通过transwell迁移和侵袭实验也证明miR-671-5p能够抑制骨肉瘤的迁移和侵袭能力,这正与我们的预期结果相符合。在EMT期间,细胞间以及细胞与细胞外基质间的相互黏连作用被重塑,从而导致上皮细胞彼此之间以及下层基底膜之间的分离,并激活了一个新的转录程序来促进间充质的命运[25, 26]。 本研究通过western blot实验发现过表达miR-671-5p质粒后,骨肉瘤细胞中EMT的相关标志物Vimentin、N-cadherin的表达明显降低,过表达miR-671-5p能抑制EMT的发生。
有文献报道称miR-139可以通过负向调控ROCK1的表达影响骨肉瘤细胞的增殖和侵袭能力[27]。本研究通过相应的生物信息学和实验证明miR-671-5p对骨肉瘤的迁移运动和侵袭能力具有一定的抑制作用,也进一步为miRNA对骨肉瘤今后的发展提供有力依据。在本研究中,我们通过生物信息学发现SMAD3是miR-671-5p的关键基因,在骨肉瘤中表达上调。因此,我们把SMAD3作为后期研究对象。SMAD蛋白能够介导细胞内转化生长因子-β(TGF-β)信号传导,通过多种机制对TGF-β超家族信号通路产生抑制作用,并在肿瘤的生长,侵袭和转移中扮演着至关重要的角色[28-31]。在本研究中,荧光素酶报告基因检测证实miR- 671- 5p与SMAD3之间存在结合位点。通过Transwell实验进一步探究miR-671-5p与SMAD3相互作用对骨肉瘤发展进程的影响,发现SMAD3可以促进骨肉瘤细胞的迁移运动和侵袭能力,而miR-671-5p则能够抑制这种作用。
综上所述,我们研究发现在骨肉瘤中miR-671-5p表达下调,抑制骨肉瘤EMT的发生,并且能够通过负向调控SMAD3抑制骨肉瘤的迁移和侵袭能力,了解miR-671-5p在骨肉瘤发展进程中的作用,将为后期miR-671-5p作为骨肉瘤潜在的治疗靶点提供基础,为未来骨肉瘤的治疗提供新的理论依据。
Biography
胡雅琼,硕士,E-mail: hyqhyq66@163.com
Funding Statement
潍坊市科技局医学类项目(2019YX061);山东省自然科学基金(ZR2019MH033)
References
- 1.Biazzo A, De Paolis M. Multidisciplinary approach to osteosarcoma. Acta Orthop Belg. 2016;82(4):690–8. [Biazzo A, De Paolis M. Multidisciplinary approach to osteosarcoma [J]. Acta Orthop Belg, 2016, 82(4): 690-8.] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brown HK, Tellez-Gabriel M, Heymann D. Cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett. 2017;386:189–95. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.11.019. [Brown HK, Tellez-Gabriel M, Heymann D. Cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 386: 189-95.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhou HY, Chen LH, Qin M, et al. An miRNA signature associated with tumor mutation burden in endometrial cancer. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(11):BSR20203398. doi: 10.1042/BSR20203398. [Zhou HY, Chen LH, Qin M, et al. An miRNA signature associated with tumor mutation burden in endometrial cancer[J]. Biosci Rep, 2020, 40(11): BSR20203398.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lu TX, Rothenberg ME. MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141(4):1202–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034. [Lu TX, Rothenberg ME. MicroRNA[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2018, 141(4): 1202-7.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhang LP, Liu QH, Mu QJ, et al. MiR-429 suppresses proliferation and invasion of breast cancer via inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Thorac Cancer. 2020;11(11):3126–38. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13620. [Zhang LP, Liu QH, Mu QJ, et al. MiR-429 suppresses proliferation and invasion of breast cancer via inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2020, 11(11): 3126-38.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.张 丽萍, 白 俊, 胡 雅琼, et al. MiR-204通过靶向调控HNRNPA2B1抑制乳腺癌的侵袭和转移. http://www.j-smu.com/CN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.06.15. 南方医科大学学报. 2020;40(6):869–75. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.06.15. [张丽萍, 白俊, 胡雅琼, 等. MiR-204通过靶向调控HNRNPA2B1抑制乳腺癌的侵袭和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(6): 869-75.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li H, Mu Q, Zhang G, et al. Linc00426 accelerates lung adenocarcinoma progression by regulating miR-455-5p as a molecular sponge. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(12):1051. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03259-2. [Li H, Mu Q, Zhang G, et al. Linc00426 accelerates lung adenocarcinoma progression by regulating miR-455-5p as a molecular sponge[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(12): 1051.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhou DD, Li HL, Liu W, et al. miR-193a-3p promotes the invasion, migration, and mesenchymal transition in glioma through regulating BTRC. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/349192046_miR-193a-3p_Promotes_the_Invasion_Migration_and_Mesenchymal_Transition_in_Glioma_through_Regulating_BTRC/download. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8928509. doi: 10.1155/2021/8928509. [Zhou DD, Li HL, Liu W, et al. miR-193a-3p promotes the invasion, migration, and mesenchymal transition in glioma through regulating BTRC[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 8928509.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(3):203–22. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.246. [Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2017, 16(3): 203-22.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Li XY, Nie CJ, Tian BQ, et al. miR-671-5p blocks the progression of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing FGFR2. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(9):1892–904. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.32429. [Li XY, Nie CJ, Tian BQ, et al. miR-671-5p blocks the progression of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing FGFR2[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2019, 15(9): 1892-904.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jin W, Shi J, Liu M. Overexpression of miR-671-5p indicates a poor prognosis in colon cancer and accelerates proliferation, migration, and invasion of colon cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:6865–73. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S219421. [Jin W, Shi J, Liu M. Overexpression of miR-671-5p indicates a poor prognosis in colon cancer and accelerates proliferation, migration, and invasion of colon cancer cells[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 6865-73.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ma C, Nie ZK, Guo HM, et al. MiR-671-5p plays a promising role in restraining osteosarcoma cell characteristics through targeting TUFT1. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/jbt.22490. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020;34(7):e22490. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22490. [Ma C, Nie ZK, Guo HM, et al. MiR-671-5p plays a promising role in restraining osteosarcoma cell characteristics through targeting TUFT1[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2020, 34(7): e22490.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jafari F, Javdansirat S, Sanaie S, et al. Osteosarcoma: a comprehensive review of management and treatment strategies. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2020;49:151654. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2020.151654. [Jafari F, Javdansirat S, Sanaie S, et al. Osteosarcoma: a comprehensive review of management and treatment strategies[J]. Ann Diagn Pathol, 2020, 49: 151654.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.ElKordy MA, ElBaradie TS, ElSebai HI, et al. Osteosarcoma of the jaw: Challenges in the diagnosis and treatment. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2018;30(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jnci.2018.02.001. [ElKordy MA, ElBaradie TS, ElSebai HI, et al. Osteosarcoma of the jaw: Challenges in the diagnosis and treatment[J]. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst, 2018, 30(1): 7-11.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.He Y, Zhou H, Wang W, et al. Construction of a circRNA-miRNAmRNA regulatory network reveals potential mechanism and treatment options for osteosarcoma. Front Genet. 2021;12:632359. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.632359. [He Y, Zhou H, Wang W, et al. Construction of a circRNA-miRNAmRNA regulatory network reveals potential mechanism and treatment options for osteosarcoma[J]. Front Genet, 2021, 12: 632359.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lei J, He MY, Li J, et al. miRNA identification by nuclease digestion in ELISA for diagnosis of osteosarcoma[J]. Biotechnol Appl Biochem, 2021. Online ahead of print.
- 17.Zhang H, Wang J, Ren T, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-206 inhibits osteosarcoma progression by targeting TRA2B. Cancer Lett. 2020;490:54–65. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.07.008. [Zhang H, Wang J, Ren T, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-206 inhibits osteosarcoma progression by targeting TRA2B[J]. Cancer Lett, 2020, 490: 54-65.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li J, Zhang F, Li H, et al. Circ_0010220-mediated miR-503-5p/ CDCA4 axis contributes to osteosarcoma progression tumorigenesis. Gene. 2020;763:145068. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145068. [Li J, Zhang F, Li H, et al. Circ_0010220-mediated miR-503-5p/ CDCA4 axis contributes to osteosarcoma progression tumorigenesis [J]. Gene, 2020, 763: 145068.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang X, Peng L, Gong X, et al. miR-423-5p inhibits osteosarcoma proliferation and invasion through directly targeting STMN1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(6):2249–59. doi: 10.1159/000495085. [Wang X, Peng L, Gong X, et al. miR-423-5p inhibits osteosarcoma proliferation and invasion through directly targeting STMN1[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 50(6): 2249-59.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.He M, Shen P, Qiu C, et al. miR-627-3p inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting PTN. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31413208. Aging: Albany NY. 2019;11(15):5744–56. doi: 10.18632/aging.102157. [He M, Shen P, Qiu C, et al. miR-627-3p inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting PTN[J]. Aging: Albany NY, 2019, 11(15): 5744-56.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 21.Chong ZX, Yeap SK, Ho WY. Unraveling the roles of miRNAs in regulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in osteosarcoma. Pharmacol Res. 2021;172:105818. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105818. [Chong ZX, Yeap SK, Ho WY. Unraveling the roles of miRNAs in regulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in osteosarcoma[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2021, 172: 105818.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dongre A, Weinberg RA. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. http://www.nature.com/articles/s41580-018-0080-4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(2):69–84. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0080-4. [Dongre A, Weinberg RA. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 20(2): 69-84.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mittal V. Epithelial mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2018;13:395–412. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-020117-043854. [Mittal V. Epithelial mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2018, 13: 395-412.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang Y, Weinberg RA. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer: complexity and opportunities. Front Med. 2018;12(4):361–73. doi: 10.1007/s11684-018-0656-6. [Zhang Y, Weinberg RA. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer: complexity and opportunities[J]. Front Med, 2018, 12(4): 361-73.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang X, Li C, Yao W, et al. MicroRNA-761 suppresses tumor progression in osteosarcoma via negatively regulating ALDH1B1. Life Sci. 2020;262:118544. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118544. [Wang X, Li C, Yao W, et al. MicroRNA-761 suppresses tumor progression in osteosarcoma via negatively regulating ALDH1B1 [J]. Life Sci, 2020, 262: 118544.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mishra R, Nathani S, Varshney R, et al. Berberine reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and modulates histone methylation in osteosarcoma cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(11):8499–511. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05892-8. [Mishra R, Nathani S, Varshney R, et al. Berberine reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and modulates histone methylation in osteosarcoma cells[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2020, 47(11): 8499-511.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fan GT, He ZW, Cao LL, et al. miR-139 inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting ROCK1. Front Biosci Landmark Ed. 2019;24:1167–77. doi: 10.2741/4773. [Fan GT, He ZW, Cao LL, et al. miR-139 inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting ROCK1[J]. Front Biosci Landmark Ed, 2019, 24: 1167-77.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ansar M, Wang CJ, Wang YH, et al. SMAD3 Hypomethylation as a Biomarker for Early Prediction of Colorectal Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19):7395. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197395. [Ansar M, Wang CJ, Wang YH, et al. SMAD3 Hypomethylation as a Biomarker for Early Prediction of Colorectal Cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(19): 7395.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tang PM, Zhou S, Meng XM, et al. Smad3 promotes cancer progression by inhibiting E4BP4-mediated NK cell development. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14677. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14677. [Tang PM, Zhou S, Meng XM, et al. Smad3 promotes cancer progression by inhibiting E4BP4-mediated NK cell development [J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8: 14677.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang Y, He H, Liyanarachchi S, et al. The role of SMAD3 in the genetic predisposition to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Genet Med. 2018;20(9):927–35. doi: 10.1038/gim.2017.224. [Wang Y, He H, Liyanarachchi S, et al. The role of SMAD3 in the genetic predisposition to papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Genet Med, 2018, 20(9): 927-35.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zabini D, Granton E, Hu Y, et al. Loss of SMAD3 promotes vascular remodeling in pulmonary arterial hypertension via MRTF disinhibition. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;197(2):244–60. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201702-0386OC. [Zabini D, Granton E, Hu Y, et al. Loss of SMAD3 promotes vascular remodeling in pulmonary arterial hypertension via MRTF disinhibition[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2018, 197(2): 244-60.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


