The structures of the six hydrogen-bonded 1:1 compounds of 4-methylquinoline with 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid, 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid, 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoic acid, 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid, 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid and 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid have been determined at 185–190 K. In each crystal, the acid and base molecules are linked by a short hydrogen bond between a carboxy/carboxylate O atom and an N atom of the base.
Keywords: crystal structure, 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid, 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid, 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoic acid, 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid, 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid, 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid, 4-methylquinoline, hydrogen bond, disorder, Hirshfeld surface
Abstract
The structures of the six hydrogen-bonded 1:1 compounds of 4-methylquinoline (C10H9N) with chloro- and nitro-substituted benzoic acids (C7H4ClNO4), namely, 4-methylquinolinium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate, C10H10N+·C7H3ClNO4 −, (I), 4-methylquinoline–2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid (1/1), C10H9N·C7H4ClNO4, (II), 4-methylquinolinium 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoate, C10H9.63N0.63+·C7H3.37ClNO4 0.63−, (III), 4-methylquinolinium 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate, C10H9.54N0.54+·C7H3.46ClNO4 0.54−, (IV), 4-methylquinolinium 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate, C10H10N+·C7H3ClNO4 −, (V), and 4-methylquinolinium 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate, C10H10N+·C7H3ClNO4 −, have been determined at 185–190 K. In each compound, the acid and base molecules are linked by a short hydrogen bond between a carboxy (or carboxylate) O atom and an N atom of the base. The O⋯N distances are 2.5652 (14), 2.556 (3), 2.5485 (13), 2.5364 (13), 2.5568 (13) and 2.5252 (11) Å, respectively, for compounds (I)–(VI). In the hydrogen-bonded acid–base units of (III) and (IV), the H atoms are each disordered over two positions with O site:N site occupancies of 0.37 (3):0.63 (3) and 0.46 (3):0.54 (4), respectively, for (III) and (IV). The H atoms in the hydrogen-bonded units of (I), (V) and (VI) are located at the N-atom site, while the H atom in (II) is located at the O-atom site. In all the crystals of (I)–(VI), π–π stacking interactions between the quinoline ring systems and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are observed. Similar layer structures are constructed in (IV)–(VI) through these interactions together with π–π interactions between the benzene rings of the adjacent acid molecules. A short Cl⋯Cl contact and an N—O⋯π interaction are present in (I), while a C—H⋯Cl hydrogen bond and a π–π interaction between the benzene ring of the acid molecule and the quinoline ring system in (II), and a C—H⋯π interaction in (III) are observed. Hirshfeld surfaces for the title compounds mapped over d norm and shape index were generated to visualize the weak intermolecular interactions.
Chemical context
The properties of hydrogen bonds formed between organic acids and organic bases depend on the pK
a values of the acids and bases as well as the intermolecular interactions in the crystals. In our ongoing studies of crystal structures for the system of quinoline derivatives–chloro- and nitro-substituted benzoic acids, we have shown that three compounds of quinoline with 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid, 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid and 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid (Gotoh & Ishida, 2009 ▸), and three compounds of 6-methylquinoline with 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid, 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid and 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid (Gotoh & Ishida, 2020 ▸) have a short double-well O—H⋯N/O⋯H—N hydrogen bond between the carboxy O atom and the aromatic N atom. The ΔpK
a [pK
a(base) – pK
a(acid)] values of these compounds are in the range 2.93–3.38. Although the pK
a value of 4-methylquinoline is 5.66, which is slight larger than quinoline (pK
a = 4.90) and 6-methylquinoline (pK
a = 5.20), the system of 4-methylquinoline–chloro- and nitro-substituted benzoic acids is an attractive candidate for studying short hydrogen bonds and also weak intermolecular interactions. We report here crystal structures of six hydrogen-bonded compounds, namely, 4-methylquinolinium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate, (I), 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid–4-methylquinoline, (II), 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoic acid–4-methylquinoline, (III), 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid–4-methylquinoline, (IV), 4-methylquinolinium 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate, (V), and 4-methylquinolinium 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate, (VI). The ΔpK
a values are 3.62, 3.44, 4.04, 3.84, 3.69 and 3.80, respectively, for (I)–(VI) (Table 1 ▸).
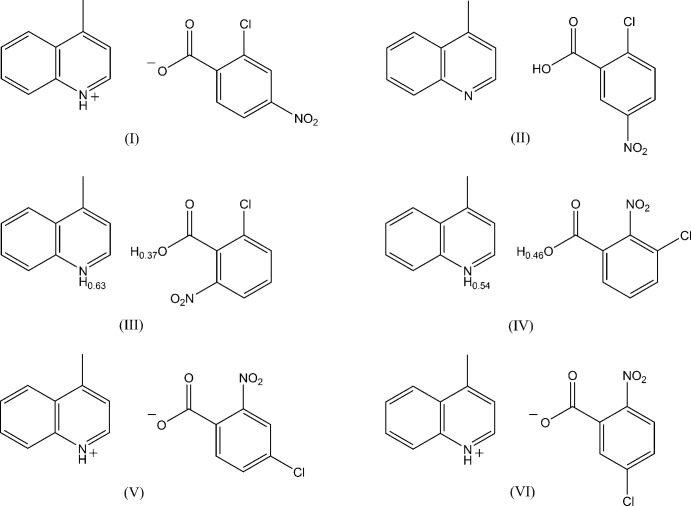
Table 1. Dihedral angles in the acid-base unit (°), hydrogen position and ΔpK a .
A, B, C, D and E are the dihedral angles between the C1–C6 ring and the N2/C8–C16 ring system, between the O1/C7/O2 plane and the N2/C8–C16 ring system, between the C1–C6 ring and the O1/C7/O2 plane, between the C1–C6 ring and the O3/N1/O4 plane, and between the N2/C8–C16 ring system and the nitro group attached to it, respectively.
| A | B | C | D | E | H-atom site | ΔpK a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid | |||||||
| (I) | 69.15 (5) | 26.60 (16) | 51.29 (17) | 17.77 (14) | N | 3.62 | |
| a | 3.15 (7) | 43.0 (2) | 39.9 (2) | 12.2 (2) | O | 2.86 | |
| b | 1.11 (4) | 28.59 (12) | 29.36 (12) | 8.24 (11) | O/N | 3.16 | |
| c | 3.94 (17) | 7.5 (5) | 4.3 (5) | 2.5 (5) | 36.2 (5) | O | 0.76 |
| 2-Chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid | |||||||
| (II) | 13.81 (10) | 14.1 (3) | 24.6 (3) | 9.7 (3) | O | 3.44 | |
| a | 1.92 (4) | 22.48 (14) | 21.02 (14) | 0.50 (13) | O | 2.68 | |
| b | 2.15 (4) | 24.51 (15) | 22.63 (15) | 0.77 (14) | O | 2.98 | |
| 2-Chloro-6-nitrobenzoic acid | |||||||
| (III) | 61.05 (5) | 35.42 (16) | 84.53 (16) | 21.7 (8), 14.7 (14) | O/N | 4.04 | |
| 3-Chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid | |||||||
| (IV) | 59.45 (4) | 37.30 (13) | 22.39 (13) | 75.20 (13) | O/N | 3.84 | |
| a | 4.71 (5) | 6.18 (16) | 9.22 (16) | 84.97 (13) | O/N | 3.08 | |
| b | 14.50 (5) | 12.55 (18) | 3.14 (18) | 85.04 (11) | O/N | 3.38 | |
| c | 2.59 (4) | 9.95 (12) | 9.45 (12) | 86.14 (13) | 31.67 (11) | O | 0.98 |
| d | 10.99 (4) | 12.08 (13) | 2.40 (13) | 88.54 (13) | 5.58 (12) | O | 1.42 |
| 4-Chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid | |||||||
| (V) | 61.21 (5) | 67.42 (14) | 10.22 (14) | 80.76 (15) | N | 3.69 | |
| a | 31.65 (4) | 18.77 (13) | 13.71 (13) | 76.44 (17) | O/N | 2.93 | |
| b | 30.39 (9) | 21.7 (3) | 16.4 (3) | 74.4 (3) | O/N | 3.23 | |
| 5-Chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid | |||||||
| (VI) | 58.90 (4) | 23.54 (13) | 35.43 (13) | 57.13 (11) | N | 3.80 | |
| a | 54.43 (5) | 5.41 (15) | 49.95 (15) | 33.31 (13) | O/N | 3.04 | |
| c | 37.37 (6) | 2.9 (2) | 40.3 (2) | 47.12 (19) | 11.3 (2) | O | 0.94 |
Structural commentary
The molecular structures of compounds (I)–(VI) are shown in Fig. 1 ▸. In each compound, the acid and base molecules are linked by a short hydrogen bond between the O atom of the carboxy (or carboxylate) group and the N atom of the base with O⋯N distances of 2.5652 (14), 2.556 (3), 2.5485 (13), 2.5364 (13), 2.5568 (13) and 2.5252 (11) Å, respectively, for compounds (1)–(VI) (Tables 2 ▸–7 ▸ ▸ ▸ ▸ ▸). In (III) and (IV), the H atoms in these hydrogen bonds are each disordered over two sites with O site:N site occupancies of 0.37 (3):0.63 (3) and 0.46 (3):0.54 (3), respectively, for (III) and (IV). In (I), (V) and (VI), the H atoms in the hydrogen bonds are located at the N site, while in (II) they are located at the O-atom site. In addition, a weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bond is observed in each of the acid–base units of (I) and (VI) (C15—H15⋯O2; Tables 2 ▸ and 7 ▸). The nitro group in (III) is disordered over two orientations around the N1—C6 bond with occupancies of 0.46 (3) and 0.54 (3).
Figure 1.
Molecular structures of the title compounds (I)–(VI), showing the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level and H atoms are shown as small spheres of arbitrary radii. In the hydrogen bonds between the carboxy O atom and the base N atom of compounds (III) and (IV), the H atoms are each disordered over two positions. The nitro group in (III) is disordered around the N1—C6 bond. Dashed lines in (I), (II), (V) and (VI) indicate the N—H⋯O, O—H⋯N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
Cg3 is the centroid of the C11–C16 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯O1 | 0.900 (19) | 1.678 (19) | 2.5652 (14) | 167.7 (18) |
| C6—H6⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.39 | 3.3066 (16) | 163 |
| C8—H8⋯O3ii | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.4199 (16) | 151 |
| C9—H9⋯O2iii | 0.95 | 2.44 | 3.3360 (16) | 158 |
| C15—H15⋯O2 | 0.95 | 2.36 | 3.2835 (17) | 163 |
| N1—O3⋯Cg3iv | 1.22 (1) | 3.26 (1) | 4.3171 (13) | 145 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (i) -x, -y+1, -z+1; (ii) -x, -y+1, -z+2; (iii) x, y+1, z; (iv) x, y-1, z+1.
Table 3. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯N2 | 0.91 (7) | 1.68 (7) | 2.556 (3) | 162 (7) |
| C3—H3⋯O4i | 0.95 | 2.40 | 3.280 (4) | 154 |
| C4—H4⋯O3ii | 0.95 | 2.54 | 3.188 (3) | 126 |
| C17—H17A⋯O2iii | 0.98 | 2.57 | 3.479 (4) | 155 |
| C17—H17C⋯Cl1iv | 0.98 | 2.81 | 3.535 (4) | 131 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x-1, y, z; (ii) -x+1, -y+3, -z+1; (iii) x, y-1, z; (iv) -x, -y+1, -z.
Table 4. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (III) .
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯N2 | 0.84 (4) | 1.71 (4) | 2.5485 (13) | 177 (6) |
| N2—H2⋯O1 | 0.89 (2) | 1.66 (2) | 2.5485 (13) | 176 (2) |
| C5—H5⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.49 | 3.1489 (15) | 126 |
| C13—H13⋯O2ii | 0.95 | 2.36 | 3.2889 (17) | 165 |
| C14—H14⋯Cg1ii | 0.95 | 2.89 | 3.6596 (15) | 138 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, -y+{\script{1\over 2}}, z+{\script{1\over 2}}; (ii) x, y, z-1.
Table 5. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (IV) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯N2 | 0.84 (3) | 1.70 (3) | 2.5364 (13) | 175 (3) |
| N2—H2⋯O1 | 0.89 (2) | 1.65 (2) | 2.5364 (13) | 175 (3) |
| C6—H6⋯O3i | 0.95 | 2.59 | 3.4705 (14) | 155 |
| C9—H9⋯O2ii | 0.95 | 2.41 | 3.1739 (15) | 137 |
| C17—H17C⋯O2iii | 0.98 | 2.47 | 3.4155 (17) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x-1, y, z; (ii) -x+1, -y+1, -z+1; (iii) -x+1, -y, -z+1.
Table 6. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (V) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯O1 | 1.06 (2) | 1.50 (2) | 2.5568 (13) | 179 (4) |
| C8—H8⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.2779 (16) | 132 |
| C12—H12⋯O2ii | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.3391 (18) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) -x+1, -y, -z+1; (ii) -x, -y+1, -z+1.
Table 7. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (VI) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯O1 | 1.03 (2) | 1.52 (2) | 2.5252 (11) | 165 (2) |
| C9—H9⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.34 | 3.2856 (13) | 171 |
| C12—H12⋯O3ii | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.5065 (14) | 166 |
| C15—H15⋯O2 | 0.95 | 2.57 | 3.4583 (13) | 155 |
| C17—H17A⋯O2ii | 0.98 | 2.41 | 3.3524 (16) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+{\script{1\over 2}}, y-{\script{1\over 2}}, z; (ii) -x+{\script{3\over 2}}, -y+{\script{3\over 2}}, -z+1.
The dihedral angles made by the benzene C1–C6 ring, the carboxy/carboxylate O1/C7/O2 plane and the nitro O3/N1/O4 plane of the acid, and the quinoline N2/C8–C16 ring system of the base in each hydrogen-bonded acid-base unit of (I)–(VI) are summarized in Table 1 ▸, together with those in compounds of other quinoline derivatives with chloro- and nitro-substituted benzoic acids, which contain similar hydrogen-bonded acid-base units (Gotoh & Ishida, 2009 ▸, 2011 ▸, 2019a ▸,b ▸, 2020 ▸). The H-atom position in the short hydrogen bond and the ΔpK a value of each compound are also given in Table 1 ▸. In each acid–base unit of compounds of (I) and (III)–(VI), the acid C1–C6 ring and the quinoline N2/C8–C16 ring system are considerably twisted with respect to each other with dihedral angles of 58.90 (4)–69.15 (5)°, which are much larger than those of other compounds. In the acid–base unit of (II), the acid ring and the quinoline ring system are slightly twisted by 13.18 (10)°, which is still larger compared with those of quinoline–2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid [1.92 (4)°] and 6-methylquinoline–2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid [2.15 (4)°]. These results suggest that the methyl group substituted to the quinoline ring system at the 4-position has an effect on the molecular packing, which prevents the aromatic rings of the acid and base lying in the same plane in the crystal.
In all the compounds of 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid and 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid, the nitro O3/N1/O4 group is approximately perpendicular to the benzene C1–C6 ring with dihedral angles of 74.4 (3)–88.54 (13)°, while in the 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoic acid molecule of compound (III), where the nitro group and the Cl atom are adjacent to the carboxy group, the carboxy O1/C7/O2 group is almost perpendicular to the benzene ring with a dihedral angle of 84.53 (16)°. In the compounds of 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid, the nitro and carboxy/carboxylate groups are both twisted by 33.31 (13)–57.13 (11)° out of the benzene ring plane. These large twists are mainly ascribable to intramolecular steric repulsion between the nitro group and the carboxy/carboxylate group.
The correlation between the H-atom position in the short hydrogen bond and the ΔpK a value is observed for each system of quinoline and 6-methylquinoline compounds, while for the title compounds (I)–(VI) this correlation is somewhat low.
Supramolecular features
In all the crystals of (I)–(VI), π–π interactions between the quinoline ring systems, related by an inversion centre to each other, are observed. The centroid–centroid distances between the quinoline ring systems, namely, Cg2⋯Cg2, Cg2⋯Cg3 and Cg3⋯Cg3, are 3.4323 (7)–3.7751 (8), 3.5878 (7)–3.9304 (9) and 3.7719 (8)–3.9227 (9) Å, respectively, where Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the N2/C8–C11/C16 and C11–C16 rings of the quinoline ring system, respectively. The base molecules in the crystals of (I) and (II) form dimeric units via these π–π interactions, while in (III)–(VI) inversion-related base molecules are alternately stacked in column-like structures. On the other hand, π–π interactions between the inversion-related acid molecules are only observed in crystals (IV)–(VI); the centroid-centroid distances, Cg1⋯Cg1, are 3.5702 (7)–3.8602 (6) Å, where Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring. Detailed supramolecular features in the crystals formed through these π–π interactions combined with other weak intermolecular interactions are described below.
In the crystal of (I), the hydrogen-bonded acid–base units, which are related by an inversion centre to each other, are linked into a centrosymmetric dimeric unit via π–π interactions between the quinoline ring systems [Cg2⋯Cg2vi = 3.7318 (7) Å and Cg2⋯Cg3vi = 3.5955 (7) Å; symmetry code: (vi) −x + 1, −y + 2, −z + 1]. The dimeric units are further linked via a C—H⋯O hydrogen bond (C9—H9⋯O2iii; symmetry code as given in Table 2 ▸), forming a ribbon structure propagating along the b-axis direction (Fig. 2 ▸). The ribbons are connected into a layer lying parallel to the (101) plane (Fig. 3 ▸) via another C—H⋯O hydrogen bond (C8—H8⋯O3ii; Table 2 ▸). In the layer, the acid molecules are arranged in an antiparallel manner with Cg1⋯Cg1ii = 4.0685 (7) Å. Between the layers, an N—O⋯π interaction (N1—O3⋯Cg3iv; Table 2 ▸), a short Cl⋯Cl contact [Cl1⋯Cl1v = 3.3391 (5) Å; symmetry code: (v) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 2] and a C—H⋯O hydrogen bond (C6—H6⋯O2i; Table 2 ▸) are observed.
Figure 2.
A packing diagram of (I), showing the ribbon structure running along the b-axis direction formed via the N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (green dashed lines) and π–π interactions (magenta dashed lines). H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonds are omitted for clarity. Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the N2/C8–C11/C16 and C11–C16 rings, respectively. [Symmetry codes: (vi) −x + 1, −y + 2, −z + 1; (vii) x, y − 1, z.]
Figure 3.
A packing diagram of (I), showing a layer structure parallel to (101) formed via the N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (green dashed lines) and π–π interactions (magenta dashed lines). H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonds are omitted for clarity. Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring. [Symmetry codes: (ii) −x, −y + 1, −z + 2; (iii) x, y + 1, z.]
In the crystal of (II), the acid–base units are linked via C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (C3—H3⋯O4i and C4—H4⋯O3ii; symmetry codes as given in Table 3 ▸), forming a tape structure propagating along the a-axis direction (Fig. 4 ▸). The tapes are further linked into a three-dimensional network through C—H⋯O and C—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds (C17—H17A⋯O2iii and C17—H17C⋯Cl1iv; Table 3 ▸). In addition, π–π interactions are observed between the acid and base aromatic rings and between the base ring systems; the centroid–centroid distances are 3.8339 (16), 3.5056 (15) and 3.8381 (15) Å, respectively, for Cg1⋯Cg3v, Cg2⋯Cg2vi and Cg2⋯Cg3vi [symmetry codes: (v) x, y + 1, z; (vi) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z]. The acid–base units are linked via these π–π interactions, forming a ribbon structure along the b-axis direction (Fig. 5 ▸).
Figure 4.
A packing diagram of (II) viewed along the c axis, showing the tape structure formed via the C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (green dashed lines). [Symmetry codes: (i) x − 1, y, z; (ii) −x + 1, −y + 3, −z + 1.]
Figure 5.
A packing diagram of (II), showing the ribbon structure running along the b-axis direction formed via the O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds (green dashed lines) and π–π interactions (magenta dashed lines). H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonds are omitted for clarity. Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C1–C6, N2/C8–C11/C16 and C11–C16 rings, respectively. [Symmetry codes: (v) x, y + 1, z; (vi) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z; (vii) x, y − 1, z.]
In the crystal of (III), the acid–base units are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and a C—H⋯π interaction (C5—H5⋯O1i, C13—H13⋯O2ii and C14—H14⋯Cg1ii; symmetry codes as in Table 4 ▸), forming a ribbon structure along the c-axis direction (Fig. 6 ▸). The base molecules are further stacked in a column along the a axis via π–π interactions between the quinoline ring systems (Fig. 7 ▸), and thus the hydrogen-bonded acid–base units form a three-dimensional network. The centroid–centroid distances are 3.4323 (7), 3.4850 (7), 3.6810 (7) and 3.5878 (7) Å, respectively, for Cg2⋯Cg2iv, Cg2⋯Cg2v, Cg2⋯Cg3iv and Cg2⋯Cg3v [symmetry codes: (iv) −x, −y, −z + 1; (v) −x + 1, −y, −z + 1].
Figure 6.
A partial packing diagram of (III) viewed along the a axis, showing the ribbon structure formed by the O—H⋯N/O⋯H—N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (green dashed lines), and C—H⋯π interactions (magenta dashed lines). H atoms not involved in the intermolecular interactions and the disordered O atoms of the minor component of the nitro group are omitted for clarity. [Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y +
 , z +
, z +
 ; (ii) x, y, z − 1; (iii) x, −y +
; (ii) x, y, z − 1; (iii) x, −y +
 , z −
, z −
 .]
.]
Figure 7.
A packing diagram of (III), showing the column structure of the base molecules formed via the π–π interactions (magenta dashed lines). H atoms not involved in the O—H⋯N/O⋯H—N hydrogen bonds (green dashed lines) and the disordered O atoms of the minor component of the nitro group are omitted for clarity. Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the N2/C8–C11/C16 and C11–C16 rings, respectively. [Symmetry codes: (iv) −x, −y, −z + 1; (v) −x + 1, −y, −z + 1.]
In the crystal of (IV), the hydrogen-bonded acid–base units are linked into a ribbon structure along the a-axis direction (Fig. 8 ▸) via C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (C6—H3⋯O3i and C17—H17C⋯O2iii; symmetry codes as in Table 5 ▸) and π–π interactions between the quinoline ring systems. The centroid–centroid distances are 3.5037 (8), 3.6022 (8) and 3.9227 (9) Å, respectively, for Cg2⋯Cg2iii, Cg2⋯Cg3iv and Cg3⋯Cg3iv [symmetry codes: (iii) −x + 1, −y, z + 1; (iv) −x, −y, −z + 1]. The ribbons are further linked into a layer parallel to the (011) plane (Fig. 9 ▸) via a π–π interaction between the acid rings with a centroid–centroid distance (Cg1⋯Cg1v) of 3.6685 (8) Å [symmetry code: (v) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z]. The layers are linked by a C—H⋯O hydrogen bond (C9—H9⋯O2ii; Table 5 ▸).
Figure 8.
A packing diagram of (IV), showing the ribbon structure formed via the π–π interactions (magenta dashed lines), and the O—H⋯N/O⋯H—N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (green dashed lines). Except for the methyl group, H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonds are omitted for clarity. Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the N2/C8–C11/C16 and C11–C16 rings, respectively. [Symmetry codes: (i) x − 1, y, z; (iii) −x + 1, −y, −z + 1; (iv) −x, −y, −z + 1.]
Figure 9.
A packing diagram of (IV), showing the layer structure formed via the π–π interactions (magenta dashed lines), and the O—H⋯N/O⋯H—N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (green dashed lines). Except for the methyl group, H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonds are omitted for clarity. Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring. [Symmetry codes: (iii) −x + 1, −y, −z + 1; (v) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1.]
In the crystal of (V), the acid and base molecules are arranged in a similar manner to those in (IV) as shown in Figs. 8 ▸ and 9 ▸. The hydrogen-bonded acid–base units in (V) are linked into a ribbon structure along the a-axis direction (Fig. 10 ▸) via a C—H⋯O hydrogen bond (C12—H12⋯O2ii; symmetry code as in Table 6 ▸) and π–π interactions between the quinoline ring systems. The ribbons are further linked into a layer parallel to the (011) plane via a π–π interaction between the acid rings. The centroid–centroid distances of the π–π interactions are 3.5702 (7), 3.7751 (8), 3.7870 (8), 3.9304 (9) and 3.7719 (8) Å, respectively, for Cg1⋯Cg1vi, Cg2⋯Cg2iii, Cg2⋯Cg3ii, Cg2⋯Cg3iii and Cg3⋯Cg3ii [symmetry codes: (ii) −x, −y + 1, −z + 1; (iii) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1; (iv) −x + 1, −y, −z + 2]. Between the layers, a C—H⋯O hydrogen bond is observed (C8—H8⋯O2i; Table 6 ▸).
Figure 10.
A packing diagram of (V), showing the ribbon structure formed via the π–π interactions (magenta dashed lines), and the N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (green dashed lines). H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonds are omitted for clarity. Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the N2/C8–C11/C16 and C11–C16 rings, respectively. [Symmetry codes: (ii) −x, −y + 1, −z + 1; (iii) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1.]
Although the crystal system of (VI) (monoclinic, C2/c) is different from those of (IV) and (V) (triclinic, P
 ), the molecules in the crystal of (VI) are arranged in a similar manner to those in (IV) and (V). The acid–base units, which are related by an inversion centre to each other, are linked together via π–π interactions between the quinoline ring systems and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds [Cg2⋯Cg3ii = 3.8048 (7) Å; C12—H12⋯O3ii and C17—H17A⋯O2ii; symmetry code as given in Table 7 ▸], forming a centrosymmetric dimeric unit. The dimeric units are further linked into a ribbon structure along the b-axis direction (Fig. 11 ▸) via other π–π interactions between the quinoline ring systems with Cg2⋯Cg2iii = 3.4710 (6) Å and Cg2⋯Cg3iii = 3.8841 (7) Å [symmetry code: (iii) −x +
), the molecules in the crystal of (VI) are arranged in a similar manner to those in (IV) and (V). The acid–base units, which are related by an inversion centre to each other, are linked together via π–π interactions between the quinoline ring systems and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds [Cg2⋯Cg3ii = 3.8048 (7) Å; C12—H12⋯O3ii and C17—H17A⋯O2ii; symmetry code as given in Table 7 ▸], forming a centrosymmetric dimeric unit. The dimeric units are further linked into a ribbon structure along the b-axis direction (Fig. 11 ▸) via other π–π interactions between the quinoline ring systems with Cg2⋯Cg2iii = 3.4710 (6) Å and Cg2⋯Cg3iii = 3.8841 (7) Å [symmetry code: (iii) −x +
 , −y +
, −y +
 , −z + 1]. The ribbons are connected into a layer parallel to (10
, −z + 1]. The ribbons are connected into a layer parallel to (10
 ) via a weak π–π interaction between adjacent acid rings with Cg1⋯Cg1iv = 3.8602 (6) Å [symmetry code: (iv) −x + 1, y, −z +
) via a weak π–π interaction between adjacent acid rings with Cg1⋯Cg1iv = 3.8602 (6) Å [symmetry code: (iv) −x + 1, y, −z +
 ]. Between the layers, a C—H⋯O hydrogen bond (C9—H9⋯O2i; Table 7 ▸) is observed.
]. Between the layers, a C—H⋯O hydrogen bond (C9—H9⋯O2i; Table 7 ▸) is observed.
Figure 11.
A packing diagram of (VI), showing the ribbon structure formed via the π–π interactions (magenta dashed lines), and the N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (green dashed lines). H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonds are omitted for clarity. Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the N2/C8–C11/C16 and C11–C16 rings, respectively. [Symmetry codes: (ii) −x +
 , −y +
, −y +
 , −z + 1; (iii) −x +
, −z + 1; (iii) −x +
 , −y +
, −y +
 , −z + 1.]
, −z + 1.]
Hirshfeld surfaces for compounds (I)–(VI) mapped over d norm and shape index (Turner et al., 2017 ▸; McKinnon et al., 2004 ▸, 2007 ▸) are shown in Fig. 12 ▸. The π–π interactions are indicated by blue and red triangles on the shape-index surfaces (white circles in Fig. 12 ▸). On all the surfaces of the quinoline ring systems except one of the back view of (II), the π–π interactions between the quinoline ring systems are observed. On the surfaces of both acid and base molecules of the back view of (II), the π–π interactions between the acid ring and the quinoline ring system are shown, while the interactions between the acid rings are observed on the acid ring surfaces of (IV)–(VI). The C—H⋯O interactions in (I)–(VI) are indicated by faint-red spots on the d norm surfaces (black arrows). In addition, the short Cl⋯Cl contact and the N—O⋯π interaction in (I), and the C—H⋯Cl interaction in (II) are shown as faint-red spots on the d norm surfaces (green, magenta and cyan arrows, respectively). On the shape-index surfaces of (I) and (III), large red areas corresponding to the N—O⋯π and C—H⋯π interactions (magenta and violet arrows, respectively) are observed.
Figure 12.
Hirshfeld surfaces [front (top) and back (bottom) views] for compounds (I)–(VI) mapped over d norm and shape index. Each surface is viewed approximately perpendicular to the molecular plane. The π–π interactions are shown by white circles, and the Cl⋯Cl contacts, the C—H⋯O, C—H⋯Cl, N—O⋯π and C—H⋯π interactions are indicated by green, black, green cyan, magenta and violet arrows, respectively.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD Version 5.42, last update September 2021; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for organic co-crystals/salts of 4-methylquinoline with carboxylic acid derivatives showed one structure, namely, 4-methylquinoline hydrogensquarate (CSD refcode GUKWAN; Kotov et al., 2018 ▸). A search for organic co-crystals/salts of 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid, 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid, 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoic acid, 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid, 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid and 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid gave 76, 19, 0, 11, 15 and 11 structures, respectively. Limiting the search for quinoline derivatives of these compounds gave 4, 3, 0, 5, 3 and 2 compounds, namely, for 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid: 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid–6-methylquinoline (BUZNIW; Gotoh & Ishida, 2020 ▸), 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid–5-nitroquinoline (NUBHEA; Gotoh & Ishida, 2019b ▸), 8-hydroxyquinolinium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate (WOPDEM; Babu & Chandrasekaran, 2014 ▸), 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid–quinoline (YAGFAP; Gotoh & Ishida, 2011 ▸), for 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid: 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid–6-methylquinoline (BUZNOC; Gotoh & Ishida, 2020 ▸), 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid–quinoline (AJIWIA; Gotoh & Ishida, 2009 ▸), 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolinium 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoate dihydrate (HIHPIY; Tan, 2007 ▸), for 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid: 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid–6-methylquinoline (BUZNUI; Gotoh & Ishida, 2020 ▸), 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid–5-nitroquinoline (XOWVUD; Gotoh & Ishida, 2019a ▸), 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid–6-nitroquinoline (XOWWAK, Gotoh & Ishida, 2019a ▸), 8-hydroxyquinolin-1-ium 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (XOWWEO; Gotoh & Ishida, 2019a ▸), 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid–quinoline (AJIWOG, Gotoh & Ishida, 2009 ▸), for 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid: 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid–6-methylquinoline (BUZPAQ; Gotoh & Ishida, 2020 ▸), 4-hydroxyquinolin-1-ium 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (WOVZOZ; Gotoh & Ishida, 2019c ▸), 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid–quinoline (AJIWUM; Gotoh & Ishida, 2009 ▸), and for 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid: 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzic acid–quinoline (AJIXAT, Gotoh & Ishida, 2009 ▸) and 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoic acid–5-nitroquinoline (NUBHIE; Gotoh & Ishida, 2019b ▸).
Of these compounds, AJIWOG, AJIWUM, AJIXAT, BUZNIW, BUZNUI and BUZPAQ show disordered O—H⋯N/O⋯H—N hydrogen bonds, while WOVZOZ shows a disorder structure in the O—H⋯O hydrogen bond accompanied by a keto-enol tautomerization in the base molecule.
Synthesis and crystallization
Single crystals of the title compounds (I)–(VI) were obtained by slow evaporation from acetonitrile solutions of 4-methylquinoline with the appropriate chloro-nitrobenzoic acid in a 1:1 molar ratio at room temperature [120 ml of an acetonitrile solution of 4-methylquinoline (0.20 g) and chloro-nitrobenzoic acid (0.28 g for each acid)].
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 8 ▸. All H atoms in compounds (I)–(VI) were found in difference-Fourier maps. The O-bound H atom in (II) and the N-bound H atoms in (I), (V) and (VI) were refined freely; the refined O—H and N—H distances are given in Tables 2 ▸, 3 ▸, 6 ▸ and 7 ▸. For (III) and (IV), H atoms in the N⋯H⋯O hydrogen bonds were found to be disordered over two positions in difference-Fourier maps. The positional parameters and occupancy factors were refined, with bond-length restraints of N—H = 0.88 (1) Å and O—H = 0.84 (1) Å, and with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(N or O); the refined distances are given in Tables 4 ▸ and 5 ▸. Other H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.95 or 0.98 Å) and treated as riding, with U iso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5U eq(C).
Table 8. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | (III) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | |||
| Chemical formula | C10H10N+·C7H3ClNO4 − | C10H9N·C7H4ClNO4 | C10H9.63N0.63+·C7H3.37ClNO4 0.63− |
| M r | 344.75 | 344.75 | 344.75 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P\overline{1} | Triclinic, P\overline{1} | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 185 | 185 | 185 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.6975 (4), 9.2527 (4), 10.1865 (5) | 7.6353 (4), 9.3827 (6), 11.3756 (7) | 6.6401 (3), 23.2126 (5), 10.3386 (3) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 72.7483 (15), 86.4281 (16), 74.5728 (15) | 91.453 (3), 95.204 (3), 107.773 (3) | 90, 99.3926 (15), 90 |
| V (Å3) | 754.55 (6) | 771.65 (8) | 1572.16 (9) |
| Z | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.27 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.55 × 0.50 × 0.32 | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.05 | 0.35 × 0.28 × 0.25 |
| Data collection | |||
| Diffractometer | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII |
| Absorption correction | Numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999 ▸) | Numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999 ▸) | Numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.868, 0.915 | 0.938, 0.986 | 0.909, 0.935 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 22243, 4404, 3822 | 14544, 4486, 2563 | 32362, 4588, 3854 |
| R int | 0.043 | 0.038 | 0.022 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.704 | 0.703 | 0.704 |
| Refinement | |||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.042, 0.122, 1.13 | 0.068, 0.257, 1.19 | 0.044, 0.125, 1.07 |
| No. of reflections | 4404 | 4486 | 4588 |
| No. of parameters | 222 | 222 | 244 |
| No. of restraints | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.44, −0.28 | 0.91, −0.58 | 0.52, −0.40 |
| (IV) | (V) | (VI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | |||
| Chemical formula | C10H9.54N0.54+·C7H3.46ClNO4 0.54− | C10H10N+·C7H3ClNO4 − | C10H10N+.C7H3ClNO4 − |
| M r | 344.75 | 344.75 | 344.75 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P\overline{1} | Triclinic, P\overline{1} | Monoclinic, C2/c |
| Temperature (K) | 185 | 185 | 190 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 7.5234 (10), 7.8017 (11), 13.6341 (17) | 7.6858 (3), 8.3615 (3), 13.5746 (5) | 16.2625 (10), 7.5099 (4), 25.3105 (15) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 80.934 (4), 80.227 (3), 89.150 (4) | 82.5485 (13), 80.8927 (12), 65.0929 (11) | 90, 99.4086 (19), 90 |
| V (Å3) | 778.73 (18) | 779.33 (5) | 3049.6 (3) |
| Z | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.28 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.35 × 0.29 × 0.22 | 0.51 × 0.45 × 0.15 | 0.30 × 0.21 × 0.12 |
| Data collection | |||
| Diffractometer | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII |
| Absorption correction | Numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999 ▸) | Numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999 ▸) | Numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.914, 0.942 | 0.868, 0.960 | 0.916, 0.968 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 16767, 4544, 4017 | 18635, 3566, 3290 | 29037, 4457, 3913 |
| R int | 0.028 | 0.027 | 0.022 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.704 | 0.649 | 0.703 |
| Refinement | |||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.036, 0.103, 1.07 | 0.036, 0.102, 1.04 | 0.036, 0.099, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 4544 | 3566 | 4457 |
| No. of parameters | 225 | 222 | 222 |
| No. of restraints | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.44, −0.38 | 0.38, −0.18 | 0.47, −0.16 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II, III, IV, V, VI. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991Isup8.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IIsup9.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IIIsup10.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IIIsup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IVsup11.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IVsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991Vsup12.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) V. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991Vsup6.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991VIsup13.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) VI. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991VIsup7.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate (I). Crystal data
| C10H10N+·C7H3ClNO4− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 344.75 | F(000) = 356.00 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.517 Mg m−3 |
| a = 8.6975 (4) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| b = 9.2527 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 20962 reflections |
| c = 10.1865 (5) Å | θ = 3.2–30.2° |
| α = 72.7483 (15)° | µ = 0.28 mm−1 |
| β = 86.4281 (16)° | T = 185 K |
| γ = 74.5728 (15)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 754.55 (6) Å3 | 0.55 × 0.50 × 0.32 mm |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate (I). Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII diffractometer | 3822 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.043 |
| ω scans | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 3.2° |
| Absorption correction: numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.868, Tmax = 0.915 | k = −13→13 |
| 22243 measured reflections | l = −14→14 |
| 4404 independent reflections |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate (I). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.122 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.13 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0733P)2 + 0.0819P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4404 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 222 parameters | Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate (I). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate (I). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.32990 (4) | 0.49410 (3) | 0.93689 (3) | 0.03079 (11) | |
| O1 | 0.14650 (13) | 0.72397 (10) | 0.67810 (9) | 0.0348 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.17832 (14) | 0.56790 (11) | 0.54222 (9) | 0.0379 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.06312 (12) | 0.05267 (11) | 1.18988 (10) | 0.0363 (2) | |
| O4 | −0.15473 (12) | 0.09130 (11) | 1.07952 (11) | 0.0371 (2) | |
| N1 | −0.02872 (13) | 0.12105 (11) | 1.09235 (11) | 0.0273 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.22641 (12) | 0.95808 (11) | 0.50904 (10) | 0.0252 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.193 (2) | 0.874 (2) | 0.558 (2) | 0.058 (6)* | |
| C1 | 0.10772 (13) | 0.47157 (12) | 0.77222 (11) | 0.0220 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.17864 (13) | 0.42010 (12) | 0.90230 (11) | 0.0222 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.13592 (13) | 0.30429 (12) | 1.00803 (11) | 0.0239 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.187120 | 0.267833 | 1.095810 | 0.029* | |
| C4 | 0.01662 (13) | 0.24410 (12) | 0.98114 (12) | 0.0239 (2) | |
| C5 | −0.05810 (14) | 0.29108 (13) | 0.85435 (12) | 0.0259 (2) | |
| H5 | −0.140805 | 0.247959 | 0.839335 | 0.031* | |
| C6 | −0.00900 (14) | 0.40299 (13) | 0.74954 (12) | 0.0251 (2) | |
| H6 | −0.055755 | 0.433693 | 0.660379 | 0.030* | |
| C7 | 0.14979 (14) | 0.59753 (13) | 0.65289 (12) | 0.0241 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.18122 (15) | 1.08320 (14) | 0.55384 (12) | 0.0274 (2) | |
| H8 | 0.108530 | 1.083030 | 0.627431 | 0.033* | |
| C9 | 0.23804 (14) | 1.21539 (13) | 0.49531 (12) | 0.0268 (2) | |
| H9 | 0.203126 | 1.304456 | 0.528283 | 0.032* | |
| C10 | 0.34486 (14) | 1.21633 (13) | 0.38964 (11) | 0.0240 (2) | |
| C11 | 0.39172 (13) | 1.08266 (13) | 0.33915 (11) | 0.0239 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.49945 (15) | 1.07123 (15) | 0.22966 (13) | 0.0300 (2) | |
| H12 | 0.544342 | 1.156119 | 0.185742 | 0.036* | |
| C13 | 0.53934 (17) | 0.93898 (17) | 0.18668 (14) | 0.0360 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.611735 | 0.933167 | 0.113483 | 0.043* | |
| C14 | 0.47410 (17) | 0.81181 (17) | 0.24992 (15) | 0.0361 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.501707 | 0.721573 | 0.218226 | 0.043* | |
| C15 | 0.37123 (16) | 0.81710 (14) | 0.35670 (13) | 0.0300 (2) | |
| H15 | 0.328586 | 0.730472 | 0.399948 | 0.036* | |
| C16 | 0.32896 (13) | 0.95269 (13) | 0.40207 (11) | 0.0240 (2) | |
| C17 | 0.41066 (16) | 1.35602 (14) | 0.32995 (13) | 0.0297 (2) | |
| H17A | 0.527472 | 1.321940 | 0.331657 | 0.045* | |
| H17B | 0.375456 | 1.429869 | 0.384385 | 0.045* | |
| H17C | 0.372032 | 1.407486 | 0.234819 | 0.045* |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate (I). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.03215 (17) | 0.03700 (18) | 0.02937 (16) | −0.01980 (13) | 0.00018 (11) | −0.00912 (12) |
| O1 | 0.0553 (6) | 0.0235 (4) | 0.0299 (4) | −0.0195 (4) | 0.0110 (4) | −0.0083 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0618 (7) | 0.0351 (5) | 0.0256 (4) | −0.0271 (5) | 0.0103 (4) | −0.0110 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0435 (5) | 0.0304 (5) | 0.0294 (5) | −0.0118 (4) | 0.0015 (4) | 0.0013 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0384 (5) | 0.0358 (5) | 0.0410 (5) | −0.0222 (4) | 0.0093 (4) | −0.0076 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0320 (5) | 0.0225 (4) | 0.0283 (5) | −0.0115 (4) | 0.0071 (4) | −0.0059 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0284 (5) | 0.0233 (4) | 0.0237 (4) | −0.0109 (4) | 0.0018 (4) | −0.0031 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0248 (5) | 0.0192 (4) | 0.0228 (5) | −0.0082 (4) | 0.0023 (4) | −0.0055 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0233 (5) | 0.0219 (5) | 0.0243 (5) | −0.0094 (4) | 0.0020 (4) | −0.0078 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0262 (5) | 0.0228 (5) | 0.0224 (5) | −0.0074 (4) | 0.0012 (4) | −0.0053 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0266 (5) | 0.0186 (5) | 0.0260 (5) | −0.0087 (4) | 0.0048 (4) | −0.0040 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0264 (5) | 0.0230 (5) | 0.0304 (6) | −0.0117 (4) | 0.0003 (4) | −0.0062 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0283 (5) | 0.0229 (5) | 0.0248 (5) | −0.0102 (4) | −0.0024 (4) | −0.0044 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0273 (5) | 0.0223 (5) | 0.0240 (5) | −0.0111 (4) | 0.0012 (4) | −0.0049 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0307 (6) | 0.0265 (5) | 0.0246 (5) | −0.0113 (4) | 0.0052 (4) | −0.0044 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0313 (6) | 0.0221 (5) | 0.0269 (5) | −0.0092 (4) | 0.0032 (4) | −0.0056 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0246 (5) | 0.0220 (5) | 0.0235 (5) | −0.0080 (4) | −0.0016 (4) | −0.0016 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0240 (5) | 0.0245 (5) | 0.0217 (5) | −0.0085 (4) | −0.0012 (4) | −0.0024 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0294 (6) | 0.0327 (6) | 0.0265 (5) | −0.0109 (5) | 0.0032 (4) | −0.0049 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0355 (7) | 0.0431 (7) | 0.0315 (6) | −0.0110 (6) | 0.0085 (5) | −0.0148 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0392 (7) | 0.0349 (6) | 0.0389 (7) | −0.0094 (5) | 0.0037 (5) | −0.0184 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0336 (6) | 0.0262 (5) | 0.0324 (6) | −0.0105 (5) | 0.0001 (5) | −0.0093 (5) |
| C16 | 0.0254 (5) | 0.0238 (5) | 0.0228 (5) | −0.0083 (4) | −0.0014 (4) | −0.0046 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0326 (6) | 0.0240 (5) | 0.0314 (6) | −0.0128 (5) | 0.0027 (5) | −0.0020 (4) |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate (I). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C2 | 1.7331 (11) | C8—C9 | 1.3957 (15) |
| O1—C7 | 1.2628 (13) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C7 | 1.2329 (14) | C9—C10 | 1.3770 (16) |
| O3—N1 | 1.2176 (14) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| O4—N1 | 1.2221 (14) | C10—C11 | 1.4294 (16) |
| N1—C4 | 1.4674 (14) | C10—C17 | 1.5007 (15) |
| N2—C8 | 1.3236 (16) | C11—C16 | 1.4155 (15) |
| N2—C16 | 1.3686 (15) | C11—C12 | 1.4213 (17) |
| N2—H2 | 0.90 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.3721 (19) |
| C1—C2 | 1.3908 (15) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3948 (15) | C13—C14 | 1.408 (2) |
| C1—C7 | 1.5169 (14) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3869 (15) | C14—C15 | 1.3686 (19) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3766 (16) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C15—C16 | 1.4142 (16) |
| C4—C5 | 1.3787 (17) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3846 (15) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| O3—N1—O4 | 124.18 (10) | C10—C9—C8 | 119.81 (11) |
| O3—N1—C4 | 118.01 (10) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.1 |
| O4—N1—C4 | 117.78 (10) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.1 |
| C8—N2—C16 | 121.80 (10) | C9—C10—C11 | 118.97 (10) |
| C8—N2—H2 | 115.9 (13) | C9—C10—C17 | 119.91 (11) |
| C16—N2—H2 | 122.1 (13) | C11—C10—C17 | 121.12 (10) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 118.15 (10) | C16—C11—C12 | 117.55 (11) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 124.07 (10) | C16—C11—C10 | 118.54 (10) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 117.78 (10) | C12—C11—C10 | 123.91 (10) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.81 (10) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.75 (12) |
| C3—C2—Cl1 | 117.20 (9) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C1—C2—Cl1 | 120.94 (8) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 117.58 (10) | C12—C13—C14 | 120.68 (12) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 121.2 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 121.2 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 123.04 (10) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.54 (12) |
| C3—C4—N1 | 117.88 (10) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| C5—C4—N1 | 119.05 (10) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 118.01 (10) | C14—C15—C16 | 119.41 (12) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 121.0 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.3 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 121.0 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.3 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 121.33 (11) | N2—C16—C15 | 119.51 (10) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 | N2—C16—C11 | 119.42 (10) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.3 | C15—C16—C11 | 121.08 (11) |
| O2—C7—O1 | 127.32 (10) | C10—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—C1 | 117.26 (9) | C10—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 115.38 (10) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 121.44 (11) | C10—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—H8 | 119.3 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.3 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.18 (17) | C16—N2—C8—C9 | −0.99 (18) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −179.94 (10) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | −0.74 (19) |
| C6—C1—C2—Cl1 | 177.53 (8) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.89 (18) |
| C7—C1—C2—Cl1 | −2.23 (16) | C8—C9—C10—C17 | −177.80 (11) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.77 (17) | C9—C10—C11—C16 | −1.39 (16) |
| Cl1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.56 (8) | C17—C10—C11—C16 | 178.29 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.57 (17) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 179.23 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4—N1 | 179.74 (9) | C17—C10—C11—C12 | −1.09 (18) |
| O3—N1—C4—C3 | −17.00 (15) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.49 (18) |
| O4—N1—C4—C3 | 164.68 (11) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 179.88 (12) |
| O3—N1—C4—C5 | 161.25 (11) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.1 (2) |
| O4—N1—C4—C5 | −17.08 (16) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.9 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.61 (18) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.9 (2) |
| N1—C4—C5—C6 | −177.54 (10) | C8—N2—C16—C15 | −178.90 (11) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −2.68 (18) | C8—N2—C16—C11 | 1.46 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 2.47 (17) | C14—C15—C16—N2 | −179.84 (12) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | −177.75 (10) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.21 (19) |
| C2—C1—C7—O2 | 130.38 (13) | C12—C11—C16—N2 | 179.17 (10) |
| C6—C1—C7—O2 | −49.38 (16) | C10—C11—C16—N2 | −0.25 (16) |
| C2—C1—C7—O1 | −51.76 (16) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.47 (17) |
| C6—C1—C7—O1 | 128.48 (12) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | −179.89 (10) |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate (I). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg3 is the centroid of the C11–C16 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O1 | 0.900 (19) | 1.678 (19) | 2.5652 (14) | 167.7 (18) |
| C6—H6···O2i | 0.95 | 2.39 | 3.3066 (16) | 163 |
| C8—H8···O3ii | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.4199 (16) | 151 |
| C9—H9···O2iii | 0.95 | 2.44 | 3.3360 (16) | 158 |
| C15—H15···O2 | 0.95 | 2.36 | 3.2835 (17) | 163 |
| N1—O3···Cg3iv | 1.22 (1) | 3.26 (1) | 4.3171 (13) | 145 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x, −y+1, −z+2; (iii) x, y+1, z; (iv) x, y−1, z+1.
4-Methylquinoline–2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid (1/1) (II). Crystal data
| C10H9N·C7H4ClNO4 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 344.75 | F(000) = 356.00 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.484 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.6353 (4) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| b = 9.3827 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 9512 reflections |
| c = 11.3756 (7) Å | θ = 3.0–30.1° |
| α = 91.453 (3)° | µ = 0.27 mm−1 |
| β = 95.204 (3)° | T = 185 K |
| γ = 107.773 (3)° | Platelet, colorless |
| V = 771.65 (8) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.05 mm |
4-Methylquinoline–2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid (1/1) (II). Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII diffractometer | 2563 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.038 |
| ω scans | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 3.0° |
| Absorption correction: numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999) | h = −9→10 |
| Tmin = 0.938, Tmax = 0.986 | k = −13→13 |
| 14544 measured reflections | l = −15→15 |
| 4486 independent reflections |
4-Methylquinoline–2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid (1/1) (II). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.068 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.257 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.19 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1416P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4486 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 222 parameters | Δρmax = 0.91 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.58 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
4-Methylquinoline–2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid (1/1) (II). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
4-Methylquinoline–2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid (1/1) (II). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | −0.03754 (10) | 0.97793 (9) | 0.28787 (8) | 0.0688 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.4426 (3) | 0.8113 (2) | 0.27937 (18) | 0.0550 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.401 (10) | 0.721 (8) | 0.238 (6) | 0.17 (3)* | |
| O2 | 0.1900 (4) | 0.8238 (2) | 0.1691 (2) | 0.0705 (7) | |
| O3 | 0.7457 (3) | 1.4293 (2) | 0.54603 (18) | 0.0510 (5) | |
| O4 | 0.8405 (2) | 1.2413 (2) | 0.50002 (19) | 0.0515 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.7203 (3) | 1.3046 (2) | 0.49943 (18) | 0.0386 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.3941 (3) | 0.5596 (2) | 0.1685 (2) | 0.0465 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.3346 (4) | 1.0135 (3) | 0.3225 (2) | 0.0384 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.1888 (3) | 1.0712 (3) | 0.3399 (2) | 0.0420 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.2183 (4) | 1.2039 (3) | 0.4056 (2) | 0.0445 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.117494 | 1.240795 | 0.416034 | 0.053* | |
| C4 | 0.3935 (3) | 1.2831 (3) | 0.4562 (2) | 0.0384 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.415578 | 1.375700 | 0.499746 | 0.046* | |
| C5 | 0.5360 (3) | 1.2245 (2) | 0.4418 (2) | 0.0346 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.5106 (3) | 1.0921 (2) | 0.3766 (2) | 0.0366 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.611816 | 1.054882 | 0.368761 | 0.044* | |
| C7 | 0.3130 (4) | 0.8720 (3) | 0.2488 (2) | 0.0462 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.2387 (4) | 0.4902 (3) | 0.1035 (2) | 0.0493 (6) | |
| H8 | 0.146250 | 0.538936 | 0.096541 | 0.059* | |
| C9 | 0.1990 (4) | 0.3519 (3) | 0.0444 (2) | 0.0467 (6) | |
| H9 | 0.083758 | 0.308531 | −0.001836 | 0.056* | |
| C10 | 0.3317 (4) | 0.2774 (3) | 0.0539 (2) | 0.0460 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.5048 (3) | 0.3480 (2) | 0.12444 (19) | 0.0352 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.6504 (4) | 0.2871 (4) | 0.1402 (3) | 0.0545 (7) | |
| H12 | 0.636763 | 0.192542 | 0.102077 | 0.065* | |
| C13 | 0.8077 (5) | 0.3570 (4) | 0.2068 (3) | 0.0643 (9) | |
| H13 | 0.903299 | 0.311688 | 0.216432 | 0.077* | |
| C14 | 0.8312 (4) | 0.4947 (4) | 0.2615 (3) | 0.0581 (8) | |
| H14 | 0.944487 | 0.542707 | 0.308477 | 0.070* | |
| C15 | 0.6987 (4) | 0.5661 (3) | 0.2515 (2) | 0.0494 (6) | |
| H15 | 0.719222 | 0.661767 | 0.289891 | 0.059* | |
| C16 | 0.5265 (4) | 0.4906 (3) | 0.1804 (2) | 0.0407 (5) | |
| C17 | 0.2954 (6) | 0.1291 (3) | −0.0083 (3) | 0.0663 (9) | |
| H17A | 0.308435 | 0.055894 | 0.049069 | 0.099* | |
| H17B | 0.384247 | 0.136518 | −0.066635 | 0.099* | |
| H17C | 0.169533 | 0.096781 | −0.048532 | 0.099* |
4-Methylquinoline–2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid (1/1) (II). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0441 (4) | 0.0620 (5) | 0.0871 (6) | 0.0058 (3) | −0.0173 (4) | −0.0221 (4) |
| O1 | 0.0728 (14) | 0.0406 (10) | 0.0539 (11) | 0.0230 (9) | 0.0045 (9) | −0.0123 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0988 (18) | 0.0491 (12) | 0.0566 (12) | 0.0232 (12) | −0.0230 (12) | −0.0203 (10) |
| O3 | 0.0466 (10) | 0.0364 (9) | 0.0627 (12) | 0.0073 (7) | −0.0089 (8) | −0.0114 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0359 (9) | 0.0534 (11) | 0.0668 (12) | 0.0176 (8) | 0.0023 (8) | −0.0033 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0352 (10) | 0.0369 (10) | 0.0432 (11) | 0.0113 (8) | 0.0030 (8) | −0.0016 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0537 (13) | 0.0396 (11) | 0.0455 (12) | 0.0131 (9) | 0.0075 (9) | −0.0053 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0492 (13) | 0.0284 (10) | 0.0344 (11) | 0.0085 (9) | 0.0017 (9) | −0.0028 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0384 (12) | 0.0390 (12) | 0.0450 (13) | 0.0101 (9) | −0.0065 (10) | −0.0047 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0371 (12) | 0.0416 (12) | 0.0542 (14) | 0.0138 (10) | −0.0017 (10) | −0.0087 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0356 (11) | 0.0323 (11) | 0.0463 (13) | 0.0109 (9) | 0.0009 (9) | −0.0079 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0390 (12) | 0.0291 (10) | 0.0338 (10) | 0.0084 (8) | 0.0017 (8) | −0.0009 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0429 (13) | 0.0319 (11) | 0.0358 (11) | 0.0124 (9) | 0.0061 (9) | −0.0006 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0654 (17) | 0.0331 (11) | 0.0380 (12) | 0.0129 (11) | 0.0035 (11) | −0.0028 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0437 (14) | 0.0566 (16) | 0.0452 (13) | 0.0122 (12) | 0.0048 (11) | 0.0001 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0461 (14) | 0.0491 (14) | 0.0397 (12) | 0.0094 (11) | −0.0028 (10) | −0.0008 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0552 (15) | 0.0412 (13) | 0.0337 (11) | 0.0039 (11) | 0.0039 (10) | −0.0050 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0413 (12) | 0.0340 (11) | 0.0300 (10) | 0.0109 (9) | 0.0050 (9) | −0.0012 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0601 (17) | 0.0626 (18) | 0.0518 (15) | 0.0310 (14) | 0.0171 (13) | 0.0137 (14) |
| C13 | 0.0526 (17) | 0.084 (2) | 0.0628 (19) | 0.0265 (16) | 0.0152 (15) | 0.0222 (18) |
| C14 | 0.0385 (14) | 0.078 (2) | 0.0502 (15) | 0.0075 (13) | −0.0007 (11) | 0.0121 (15) |
| C15 | 0.0504 (15) | 0.0489 (14) | 0.0374 (12) | −0.0006 (11) | 0.0022 (10) | −0.0039 (11) |
| C16 | 0.0452 (13) | 0.0404 (12) | 0.0355 (11) | 0.0112 (10) | 0.0071 (9) | −0.0006 (10) |
| C17 | 0.092 (2) | 0.0448 (15) | 0.0506 (16) | 0.0073 (15) | 0.0014 (15) | −0.0109 (13) |
4-Methylquinoline–2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid (1/1) (II). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C2 | 1.723 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.380 (4) |
| O1—C7 | 1.310 (4) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O1—H1 | 0.91 (7) | C9—C10 | 1.395 (4) |
| O2—C7 | 1.214 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| O3—N1 | 1.224 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.440 (3) |
| O4—N1 | 1.235 (3) | C10—C17 | 1.481 (4) |
| N1—C5 | 1.462 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.397 (4) |
| N2—C8 | 1.313 (4) | C11—C16 | 1.423 (3) |
| N2—C16 | 1.356 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.333 (5) |
| C1—C6 | 1.397 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.405 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.373 (5) |
| C1—C7 | 1.509 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.383 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.372 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.380 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C15—C16 | 1.446 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.380 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.383 (3) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C7—O1—H1 | 102 (4) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.7 |
| O3—N1—O4 | 123.8 (2) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.7 |
| O3—N1—C5 | 118.12 (19) | C9—C10—C11 | 118.8 (2) |
| O4—N1—C5 | 118.0 (2) | C9—C10—C17 | 120.4 (3) |
| C8—N2—C16 | 118.2 (2) | C11—C10—C17 | 120.8 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 118.0 (2) | C12—C11—C16 | 118.7 (2) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 117.9 (2) | C12—C11—C10 | 124.7 (2) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 124.1 (2) | C16—C11—C10 | 116.6 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.4 (2) | C13—C12—C11 | 122.4 (3) |
| C3—C2—Cl1 | 115.90 (19) | C13—C12—H12 | 118.8 |
| C1—C2—Cl1 | 122.63 (19) | C11—C12—H12 | 118.8 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.3 (2) | C12—C13—C14 | 119.8 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.4 (2) | C15—C14—C13 | 123.1 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.8 | C15—C14—H14 | 118.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.8 | C13—C14—H14 | 118.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.6 (2) | C14—C15—C16 | 117.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—N1 | 118.62 (19) | C14—C15—H15 | 121.2 |
| C6—C5—N1 | 118.8 (2) | C16—C15—H15 | 121.2 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.3 (2) | N2—C16—C11 | 122.8 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.4 | N2—C16—C15 | 118.7 (2) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.4 | C11—C16—C15 | 118.5 (2) |
| O2—C7—O1 | 125.0 (2) | C10—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—C1 | 122.6 (3) | C10—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 112.4 (2) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 125.2 (3) | C10—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—H8 | 117.4 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 117.4 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 118.5 (2) | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.9 (4) | C16—N2—C8—C9 | −0.8 (4) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −178.0 (2) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | 0.6 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—Cl1 | −174.82 (18) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.3 (4) |
| C7—C1—C2—Cl1 | 5.2 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C17 | −179.8 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −179.0 (2) |
| Cl1—C2—C3—C4 | 176.8 (2) | C17—C10—C11—C12 | 0.4 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.6 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C16 | 0.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.6 (4) | C17—C10—C11—C16 | 179.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −177.4 (2) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.8 (4) |
| O3—N1—C5—C4 | −8.7 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −179.8 (3) |
| O4—N1—C5—C4 | 170.1 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.8 (4) |
| O3—N1—C5—C6 | 172.3 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.1 (5) |
| O4—N1—C5—C6 | −9.0 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.5 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.1 (4) | C8—N2—C16—C11 | 0.8 (4) |
| N1—C5—C6—C1 | 179.15 (19) | C8—N2—C16—C15 | 179.8 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.9 (3) | C12—C11—C16—N2 | 178.8 (2) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | 178.1 (2) | C10—C11—C16—N2 | −0.6 (3) |
| C6—C1—C7—O2 | −154.9 (3) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—C7—O2 | 25.1 (4) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | −179.6 (2) |
| C6—C1—C7—O1 | 23.9 (3) | C14—C15—C16—N2 | −179.5 (2) |
| C2—C1—C7—O1 | −156.2 (2) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.5 (4) |
4-Methylquinoline–2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid (1/1) (II). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···N2 | 0.91 (7) | 1.68 (7) | 2.556 (3) | 162 (7) |
| C3—H3···O4i | 0.95 | 2.40 | 3.280 (4) | 154 |
| C4—H4···O3ii | 0.95 | 2.54 | 3.188 (3) | 126 |
| C17—H17A···O2iii | 0.98 | 2.57 | 3.479 (4) | 155 |
| C17—H17C···Cl1iv | 0.98 | 2.81 | 3.535 (4) | 131 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z; (ii) −x+1, −y+3, −z+1; (iii) x, y−1, z; (iv) −x, −y+1, −z.
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoate (III). Crystal data
| C10H9.63N0.63+·C7H3.37ClNO40.63−− | F(000) = 712.00 |
| Mr = 344.75 | Dx = 1.456 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 6.6401 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 25957 reflections |
| b = 23.2126 (5) Å | θ = 3.1–30.1° |
| c = 10.3386 (3) Å | µ = 0.27 mm−1 |
| β = 99.3926 (15)° | T = 185 K |
| V = 1572.16 (9) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.35 × 0.28 × 0.25 mm |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoate (III). Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII diffractometer | 3854 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.022 |
| ω scans | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Absorption correction: numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.909, Tmax = 0.935 | k = −32→32 |
| 32362 measured reflections | l = −14→14 |
| 4588 independent reflections |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoate (III). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.125 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0685P)2 + 0.4164P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4588 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 244 parameters | Δρmax = 0.52 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoate (III). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement was performed using all reflections. The weighted R-factor (wR) and goodness of fit (S) are based on F2. R-factor (gt) are based on F. The threshold expression of F2 > 2.0 sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factor (gt). |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoate (III). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Cl1 | 0.71027 (7) | 0.10339 (2) | 1.02427 (4) | 0.05678 (15) | |
| O1 | 0.34983 (15) | 0.13094 (4) | 0.76226 (8) | 0.0326 (2) | |
| H1 | 0.328 (8) | 0.1007 (14) | 0.717 (5) | 0.049* | 0.37 (3) |
| O2 | 0.18762 (19) | 0.08197 (5) | 0.89869 (10) | 0.0468 (3) | |
| O3A | 0.0115 (12) | 0.2046 (4) | 0.8201 (5) | 0.0463 (13) | 0.54 (3) |
| O4A | −0.0751 (8) | 0.2537 (6) | 0.9776 (7) | 0.0623 (19) | 0.54 (3) |
| O3B | −0.0248 (19) | 0.1914 (7) | 0.8468 (19) | 0.078 (3) | 0.46 (3) |
| O4B | −0.021 (3) | 0.2723 (4) | 0.9405 (16) | 0.076 (4) | 0.46 (3) |
| N1 | 0.04842 (19) | 0.22525 (5) | 0.92742 (12) | 0.0376 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.28090 (14) | 0.04202 (4) | 0.61720 (9) | 0.02414 (19) | |
| H2 | 0.300 (4) | 0.0736 (7) | 0.666 (2) | 0.036* | 0.63 (3) |
| C1 | 0.36395 (19) | 0.16626 (5) | 0.97746 (10) | 0.0258 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.5557 (2) | 0.15998 (6) | 1.05519 (12) | 0.0324 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.6290 (2) | 0.19756 (7) | 1.15678 (14) | 0.0401 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.761107 | 0.192060 | 1.206500 | 0.048* | |
| C4 | 0.5092 (2) | 0.24273 (6) | 1.18481 (14) | 0.0412 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.557720 | 0.268328 | 1.254673 | 0.049* | |
| C5 | 0.3182 (2) | 0.25079 (5) | 1.11112 (13) | 0.0365 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.234047 | 0.281705 | 1.130255 | 0.044* | |
| C6 | 0.25041 (19) | 0.21305 (5) | 1.00842 (11) | 0.0283 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.28934 (19) | 0.12224 (5) | 0.87118 (11) | 0.0266 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.28861 (17) | −0.00796 (5) | 0.67783 (11) | 0.0266 (2) | |
| H8 | 0.308842 | −0.008856 | 0.770917 | 0.032* | |
| C9 | 0.26769 (18) | −0.05958 (5) | 0.60825 (12) | 0.0283 (2) | |
| H9 | 0.273935 | −0.095108 | 0.654330 | 0.034* | |
| C10 | 0.23797 (17) | −0.05958 (5) | 0.47294 (12) | 0.0272 (2) | |
| C11 | 0.22837 (16) | −0.00558 (5) | 0.40662 (11) | 0.0244 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.19706 (19) | 0.00027 (6) | 0.26760 (12) | 0.0335 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.180685 | −0.033200 | 0.214019 | 0.040* | |
| C13 | 0.1903 (2) | 0.05339 (7) | 0.21055 (13) | 0.0395 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.169884 | 0.056667 | 0.117731 | 0.047* | |
| C14 | 0.2134 (2) | 0.10307 (6) | 0.28825 (14) | 0.0373 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.208084 | 0.139770 | 0.247145 | 0.045* | |
| C15 | 0.24365 (18) | 0.09990 (5) | 0.42260 (13) | 0.0301 (2) | |
| H15 | 0.258987 | 0.133966 | 0.474193 | 0.036* | |
| C16 | 0.25156 (16) | 0.04526 (5) | 0.48282 (11) | 0.0233 (2) | |
| C17 | 0.2150 (2) | −0.11468 (6) | 0.39687 (16) | 0.0402 (3) | |
| H17A | 0.081819 | −0.115295 | 0.339800 | 0.060* | |
| H17B | 0.224727 | −0.147324 | 0.457681 | 0.060* | |
| H17C | 0.323533 | −0.117515 | 0.343293 | 0.060* |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoate (III). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0537 (2) | 0.0714 (3) | 0.0417 (2) | 0.0315 (2) | −0.00294 (16) | −0.00849 (18) |
| O1 | 0.0511 (5) | 0.0267 (4) | 0.0208 (4) | −0.0049 (4) | 0.0088 (4) | −0.0020 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0706 (7) | 0.0442 (5) | 0.0286 (5) | −0.0253 (5) | 0.0173 (5) | −0.0089 (4) |
| O3A | 0.041 (2) | 0.064 (3) | 0.0298 (17) | 0.0180 (18) | −0.0048 (11) | −0.0085 (14) |
| O4A | 0.0501 (18) | 0.068 (4) | 0.069 (2) | 0.0233 (19) | 0.0096 (17) | −0.023 (2) |
| O3B | 0.047 (3) | 0.086 (6) | 0.092 (6) | 0.014 (3) | −0.020 (4) | −0.050 (5) |
| O4B | 0.076 (5) | 0.048 (3) | 0.088 (5) | 0.032 (3) | −0.031 (4) | −0.021 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0447 (6) | 0.0327 (5) | 0.0347 (6) | 0.0086 (5) | 0.0043 (5) | −0.0038 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0241 (4) | 0.0274 (4) | 0.0211 (4) | 0.0004 (3) | 0.0041 (3) | −0.0024 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0332 (6) | 0.0250 (5) | 0.0191 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0040 (4) | −0.0011 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0344 (6) | 0.0360 (6) | 0.0259 (5) | 0.0040 (5) | 0.0020 (4) | −0.0015 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0396 (7) | 0.0467 (7) | 0.0306 (6) | −0.0056 (6) | −0.0040 (5) | −0.0030 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0567 (9) | 0.0334 (6) | 0.0308 (6) | −0.0102 (6) | −0.0011 (6) | −0.0079 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0545 (8) | 0.0237 (5) | 0.0308 (6) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0052 (5) | −0.0048 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0365 (6) | 0.0240 (5) | 0.0236 (5) | 0.0005 (4) | 0.0030 (4) | −0.0012 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0343 (6) | 0.0249 (5) | 0.0202 (5) | 0.0015 (4) | 0.0033 (4) | −0.0026 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0253 (5) | 0.0323 (6) | 0.0225 (5) | 0.0015 (4) | 0.0050 (4) | 0.0023 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0253 (5) | 0.0272 (5) | 0.0330 (6) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0068 (4) | 0.0035 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0214 (5) | 0.0273 (5) | 0.0340 (6) | −0.0012 (4) | 0.0073 (4) | −0.0056 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0191 (4) | 0.0316 (5) | 0.0229 (5) | −0.0006 (4) | 0.0042 (4) | −0.0040 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0277 (6) | 0.0504 (7) | 0.0227 (5) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.0044 (4) | −0.0072 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0325 (6) | 0.0636 (9) | 0.0226 (5) | 0.0020 (6) | 0.0047 (5) | 0.0072 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0334 (6) | 0.0450 (7) | 0.0343 (6) | 0.0041 (5) | 0.0076 (5) | 0.0147 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0288 (5) | 0.0300 (6) | 0.0321 (6) | 0.0010 (4) | 0.0063 (4) | 0.0043 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0200 (5) | 0.0281 (5) | 0.0222 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0044 (4) | −0.0009 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0390 (7) | 0.0321 (6) | 0.0505 (8) | −0.0048 (5) | 0.0106 (6) | −0.0155 (6) |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoate (III). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C2 | 1.7288 (13) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C7 | 1.2720 (14) | C8—C9 | 1.3928 (17) |
| O1—H1 | 0.841 (10) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C7 | 1.2140 (16) | C9—C10 | 1.3805 (17) |
| O3A—N1 | 1.196 (7) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| O4A—N1 | 1.232 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.4251 (16) |
| O3B—N1 | 1.190 (9) | C10—C17 | 1.4961 (17) |
| O4B—N1 | 1.201 (5) | C11—C16 | 1.4134 (15) |
| N1—C6 | 1.4879 (17) | C11—C12 | 1.4248 (16) |
| N2—C8 | 1.3157 (15) | C12—C13 | 1.365 (2) |
| N2—C16 | 1.3731 (14) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| N2—H2 | 0.887 (10) | C13—C14 | 1.399 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.3888 (16) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.3978 (17) | C14—C15 | 1.3726 (18) |
| C1—C7 | 1.5229 (15) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3908 (19) | C15—C16 | 1.4100 (16) |
| C3—C4 | 1.375 (2) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.382 (2) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3934 (17) | ||
| C7—O1—H1 | 108 (4) | N2—C8—H8 | 119.3 |
| O3B—N1—O4B | 124.0 (7) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.3 |
| O3A—N1—O4A | 123.7 (4) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.61 (11) |
| O3B—N1—C6 | 119.8 (5) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.7 |
| O3A—N1—C6 | 118.4 (3) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.7 |
| O4B—N1—C6 | 115.8 (4) | C9—C10—C11 | 118.37 (10) |
| O4A—N1—C6 | 117.8 (3) | C9—C10—C17 | 121.21 (12) |
| C8—N2—C16 | 121.22 (10) | C11—C10—C17 | 120.42 (12) |
| C8—N2—H2 | 117.8 (18) | C16—C11—C12 | 117.86 (11) |
| C16—N2—H2 | 120.9 (18) | C16—C11—C10 | 118.30 (10) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 115.27 (10) | C12—C11—C10 | 123.84 (11) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 124.47 (11) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.75 (12) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 120.22 (10) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 122.86 (12) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C3—C2—Cl1 | 118.09 (11) | C12—C13—C14 | 120.25 (12) |
| C1—C2—Cl1 | 119.05 (9) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.60 (13) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.2 | C15—C14—C13 | 121.39 (12) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.2 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.3 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.84 (12) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.3 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C14—C15—C16 | 118.94 (12) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.24 (13) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.4 | N2—C16—C15 | 119.01 (10) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.4 | N2—C16—C11 | 120.18 (10) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 123.18 (12) | C15—C16—C11 | 120.81 (10) |
| C1—C6—N1 | 119.51 (10) | C10—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—N1 | 117.30 (11) | C10—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—O1 | 126.71 (11) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—C1 | 118.40 (10) | C10—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 114.82 (10) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 121.31 (10) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.13 (19) | C6—C1—C7—O1 | 98.00 (14) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −177.61 (12) | C2—C1—C7—O1 | −84.49 (14) |
| C6—C1—C2—Cl1 | −179.59 (9) | C16—N2—C8—C9 | 0.11 (17) |
| C7—C1—C2—Cl1 | 2.68 (16) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | −0.05 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.9 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.28 (17) |
| Cl1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.40 (12) | C8—C9—C10—C17 | −179.94 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.7 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C16 | 0.54 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.5 (2) | C17—C10—C11—C16 | −179.80 (11) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.36 (18) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −179.58 (11) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | 176.26 (12) | C17—C10—C11—C12 | 0.08 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6—N1 | 177.02 (11) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.15 (17) |
| C7—C1—C6—N1 | −5.35 (18) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −179.73 (11) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.6 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.2 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | −176.84 (12) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.1 (2) |
| O3B—N1—C6—C1 | 8.6 (14) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.05 (19) |
| O3A—N1—C6—C1 | −19.0 (5) | C8—N2—C16—C15 | 179.75 (10) |
| O4B—N1—C6—C1 | −164.4 (14) | C8—N2—C16—C11 | 0.17 (16) |
| O4A—N1—C6—C1 | 157.3 (8) | C14—C15—C16—N2 | −179.72 (11) |
| O3B—N1—C6—C5 | −172.9 (14) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.15 (18) |
| O3A—N1—C6—C5 | 159.4 (5) | C12—C11—C16—N2 | 179.62 (10) |
| O4B—N1—C6—C5 | 14.1 (14) | C10—C11—C16—N2 | −0.49 (16) |
| O4A—N1—C6—C5 | −24.2 (8) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.05 (16) |
| C6—C1—C7—O2 | −84.88 (16) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | 179.94 (10) |
| C2—C1—C7—O2 | 92.63 (16) |
4-Methylquinolinium 2-chloro-6-nitrobenzoate (III). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···N2 | 0.84 (4) | 1.71 (4) | 2.5485 (13) | 177 (6) |
| N2—H2···O1 | 0.89 (2) | 1.66 (2) | 2.5485 (13) | 176 (2) |
| C5—H5···O1i | 0.95 | 2.49 | 3.1489 (15) | 126 |
| C13—H13···O2ii | 0.95 | 2.36 | 3.2889 (17) | 165 |
| C14—H14···Cg1ii | 0.95 | 2.89 | 3.6596 (15) | 138 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) x, y, z−1.
4-Methylquinolinium 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (IV). Crystal data
| C10H9.54N0.54+·C7H3.46ClNO40.54−− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 344.75 | F(000) = 356.00 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.470 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.5234 (10) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| b = 7.8017 (11) Å | Cell parameters from 14620 reflections |
| c = 13.6341 (17) Å | θ = 3.1–30.2° |
| α = 80.934 (4)° | µ = 0.27 mm−1 |
| β = 80.227 (3)° | T = 185 K |
| γ = 89.150 (4)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 778.73 (18) Å3 | 0.35 × 0.29 × 0.22 mm |
4-Methylquinolinium 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (IV). Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII diffractometer | 4017 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.028 |
| ω scans | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Absorption correction: numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999) | h = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.914, Tmax = 0.942 | k = −10→10 |
| 16767 measured reflections | l = −19→19 |
| 4544 independent reflections |
4-Methylquinolinium 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (IV). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.103 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0589P)2 + 0.1388P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4544 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 225 parameters | Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
4-Methylquinolinium 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (IV). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
4-Methylquinolinium 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (IV). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Cl1 | 0.86435 (3) | 0.88078 (4) | −0.07310 (2) | 0.03700 (9) | |
| O1 | 0.32371 (11) | 0.40966 (11) | 0.26115 (7) | 0.0398 (2) | |
| H1 | 0.318 (6) | 0.339 (4) | 0.3152 (18) | 0.060* | 0.46 (3) |
| O2 | 0.56467 (12) | 0.53822 (11) | 0.29489 (6) | 0.03676 (18) | |
| O3 | 0.87768 (12) | 0.52646 (12) | 0.12927 (8) | 0.0450 (2) | |
| O4 | 0.86170 (12) | 0.78937 (12) | 0.16317 (6) | 0.0410 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.80578 (11) | 0.66730 (12) | 0.13027 (7) | 0.02921 (18) | |
| N2 | 0.30583 (11) | 0.21139 (11) | 0.42899 (7) | 0.02971 (18) | |
| H2 | 0.318 (4) | 0.278 (3) | 0.3693 (12) | 0.045* | 0.54 (3) |
| C1 | 0.47878 (12) | 0.61791 (12) | 0.13339 (7) | 0.02463 (18) | |
| C2 | 0.64206 (12) | 0.69496 (12) | 0.08391 (7) | 0.02335 (18) | |
| C3 | 0.65928 (13) | 0.79149 (12) | −0.01201 (7) | 0.02544 (18) | |
| C4 | 0.51016 (14) | 0.81598 (14) | −0.06009 (8) | 0.0305 (2) | |
| H4 | 0.520225 | 0.883772 | −0.125138 | 0.037* | |
| C5 | 0.34671 (14) | 0.74038 (14) | −0.01204 (9) | 0.0318 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.244061 | 0.756140 | −0.044445 | 0.038* | |
| C6 | 0.33155 (13) | 0.64142 (13) | 0.08340 (8) | 0.0288 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.218788 | 0.589069 | 0.114930 | 0.035* | |
| C7 | 0.45882 (13) | 0.51586 (13) | 0.23876 (8) | 0.02791 (19) | |
| C8 | 0.34235 (14) | 0.26031 (14) | 0.51192 (9) | 0.0334 (2) | |
| H8 | 0.382978 | 0.376070 | 0.508800 | 0.040* | |
| C9 | 0.32371 (15) | 0.14881 (15) | 0.60416 (9) | 0.0336 (2) | |
| H9 | 0.350523 | 0.189658 | 0.662139 | 0.040* | |
| C10 | 0.26665 (13) | −0.01971 (14) | 0.61092 (8) | 0.0293 (2) | |
| C11 | 0.23111 (12) | −0.07674 (12) | 0.52147 (7) | 0.02621 (19) | |
| C12 | 0.17762 (15) | −0.24889 (14) | 0.51777 (9) | 0.0347 (2) | |
| H12 | 0.163822 | −0.333039 | 0.577111 | 0.042* | |
| C13 | 0.14562 (17) | −0.29488 (16) | 0.42911 (10) | 0.0403 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.110950 | −0.410964 | 0.427749 | 0.048* | |
| C14 | 0.16351 (16) | −0.17203 (17) | 0.33985 (10) | 0.0395 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.139455 | −0.205611 | 0.279328 | 0.047* | |
| C15 | 0.21525 (14) | −0.00529 (15) | 0.34041 (8) | 0.0329 (2) | |
| H15 | 0.227352 | 0.077170 | 0.280383 | 0.039* | |
| C16 | 0.25086 (12) | 0.04439 (13) | 0.43088 (7) | 0.02605 (19) | |
| C17 | 0.24210 (18) | −0.14002 (17) | 0.70976 (9) | 0.0420 (3) | |
| H17A | 0.116898 | −0.182138 | 0.727282 | 0.063* | |
| H17B | 0.270185 | −0.077702 | 0.762387 | 0.063* | |
| H17C | 0.323199 | −0.238764 | 0.704128 | 0.063* |
4-Methylquinolinium 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (IV). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.02892 (13) | 0.04837 (17) | 0.02927 (14) | −0.01052 (10) | 0.00070 (10) | 0.00234 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0339 (4) | 0.0411 (4) | 0.0395 (4) | −0.0140 (3) | −0.0068 (3) | 0.0110 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0414 (4) | 0.0382 (4) | 0.0302 (4) | −0.0095 (3) | −0.0086 (3) | 0.0001 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0310 (4) | 0.0465 (5) | 0.0587 (6) | 0.0088 (3) | −0.0142 (4) | −0.0051 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0398 (4) | 0.0503 (5) | 0.0349 (4) | −0.0183 (4) | −0.0104 (3) | −0.0065 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0232 (4) | 0.0370 (4) | 0.0265 (4) | −0.0061 (3) | −0.0045 (3) | −0.0013 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0233 (4) | 0.0298 (4) | 0.0324 (4) | −0.0037 (3) | −0.0010 (3) | 0.0027 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0232 (4) | 0.0226 (4) | 0.0273 (4) | −0.0020 (3) | −0.0026 (3) | −0.0029 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0211 (4) | 0.0241 (4) | 0.0254 (4) | −0.0013 (3) | −0.0045 (3) | −0.0049 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0240 (4) | 0.0259 (4) | 0.0255 (4) | −0.0036 (3) | −0.0013 (3) | −0.0040 (3) |
| C4 | 0.0318 (5) | 0.0327 (5) | 0.0265 (4) | 0.0001 (4) | −0.0067 (4) | −0.0010 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0264 (5) | 0.0354 (5) | 0.0350 (5) | 0.0005 (4) | −0.0103 (4) | −0.0041 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0219 (4) | 0.0291 (5) | 0.0350 (5) | −0.0025 (3) | −0.0043 (4) | −0.0038 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0263 (4) | 0.0258 (4) | 0.0292 (5) | −0.0017 (3) | −0.0010 (4) | −0.0009 (3) |
| C8 | 0.0259 (5) | 0.0310 (5) | 0.0428 (6) | −0.0037 (4) | −0.0042 (4) | −0.0056 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0287 (5) | 0.0403 (6) | 0.0339 (5) | 0.0020 (4) | −0.0074 (4) | −0.0103 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0244 (4) | 0.0352 (5) | 0.0261 (4) | 0.0056 (4) | −0.0021 (4) | −0.0015 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0211 (4) | 0.0279 (4) | 0.0269 (4) | 0.0010 (3) | 0.0004 (3) | −0.0007 (3) |
| C12 | 0.0340 (5) | 0.0270 (5) | 0.0388 (6) | −0.0009 (4) | 0.0016 (4) | −0.0004 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0370 (6) | 0.0336 (5) | 0.0506 (7) | −0.0034 (4) | −0.0027 (5) | −0.0126 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0342 (5) | 0.0488 (7) | 0.0385 (6) | 0.0007 (5) | −0.0064 (5) | −0.0164 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0286 (5) | 0.0429 (6) | 0.0259 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | −0.0032 (4) | −0.0029 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0190 (4) | 0.0299 (5) | 0.0268 (4) | −0.0007 (3) | −0.0002 (3) | −0.0009 (3) |
| C17 | 0.0474 (7) | 0.0469 (7) | 0.0275 (5) | 0.0104 (5) | −0.0033 (5) | 0.0028 (4) |
4-Methylquinolinium 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (IV). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C3 | 1.7240 (10) | C8—C9 | 1.3990 (16) |
| O1—C7 | 1.2857 (12) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O1—H1 | 0.843 (10) | C9—C10 | 1.3735 (16) |
| O2—C7 | 1.2261 (13) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| O3—N1 | 1.2185 (13) | C10—C11 | 1.4289 (14) |
| O4—N1 | 1.2230 (12) | C10—C17 | 1.5010 (15) |
| N1—C2 | 1.4753 (12) | C11—C12 | 1.4186 (14) |
| N2—C8 | 1.3206 (15) | C11—C16 | 1.4194 (13) |
| N2—C16 | 1.3678 (13) | C12—C13 | 1.3733 (18) |
| N2—H2 | 0.885 (10) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3913 (14) | C13—C14 | 1.4137 (19) |
| C1—C2 | 1.3922 (13) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C7 | 1.5134 (14) | C14—C15 | 1.3649 (17) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3891 (13) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.3887 (14) | C15—C16 | 1.4176 (14) |
| C4—C5 | 1.3840 (15) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3921 (15) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | ||
| C7—O1—H1 | 116 (3) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.01 (10) |
| O3—N1—O4 | 125.42 (10) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.0 |
| O3—N1—C2 | 117.11 (9) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.0 |
| O4—N1—C2 | 117.42 (9) | C9—C10—C11 | 118.16 (9) |
| C8—N2—C16 | 119.82 (9) | C9—C10—C17 | 120.72 (10) |
| C8—N2—H2 | 125 (2) | C11—C10—C17 | 121.12 (10) |
| C16—N2—H2 | 115 (2) | C12—C11—C16 | 117.78 (9) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 117.57 (9) | C12—C11—C10 | 123.60 (9) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 120.60 (8) | C16—C11—C10 | 118.62 (9) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 121.81 (8) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.54 (10) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.74 (9) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C3—C2—N1 | 117.82 (8) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C1—C2—N1 | 120.35 (8) | C12—C13—C14 | 120.97 (11) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.89 (9) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.5 |
| C4—C3—Cl1 | 119.23 (8) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.5 |
| C2—C3—Cl1 | 120.88 (7) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.16 (11) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.16 (9) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.4 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.4 | C14—C15—C16 | 119.76 (10) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.51 (9) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.1 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.1 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 | N2—C16—C15 | 118.62 (9) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 121.11 (9) | N2—C16—C11 | 120.61 (9) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.4 | C15—C16—C11 | 120.78 (9) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.4 | C10—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—O1 | 125.49 (10) | C10—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—C1 | 120.78 (9) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 113.73 (9) | C10—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 122.75 (10) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—H8 | 118.6 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 118.6 | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.26 (14) | C16—N2—C8—C9 | −1.42 (16) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −178.70 (9) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | 0.53 (17) |
| C6—C1—C2—N1 | −176.66 (9) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.18 (15) |
| C7—C1—C2—N1 | 4.90 (14) | C8—C9—C10—C17 | −178.68 (10) |
| O3—N1—C2—C3 | −101.75 (11) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 177.75 (10) |
| O4—N1—C2—C3 | 75.67 (12) | C17—C10—C11—C12 | −2.39 (15) |
| O3—N1—C2—C1 | 74.79 (12) | C9—C10—C11—C16 | −1.95 (14) |
| O4—N1—C2—C1 | −107.78 (11) | C17—C10—C11—C16 | 177.91 (9) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.32 (15) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −0.30 (15) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 177.81 (9) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 180.00 (10) |
| C1—C2—C3—Cl1 | −178.25 (7) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.57 (18) |
| N1—C2—C3—Cl1 | −1.76 (12) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.76 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.27 (15) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.06 (17) |
| Cl1—C3—C4—C5 | 178.31 (8) | C8—N2—C16—C15 | −179.04 (9) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.19 (16) | C8—N2—C16—C11 | 0.56 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.84 (15) | C14—C15—C16—N2 | 178.77 (10) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | 177.62 (9) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.82 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.89 (16) | C12—C11—C16—N2 | −178.59 (9) |
| C6—C1—C7—O2 | −156.92 (10) | C10—C11—C16—N2 | 1.12 (14) |
| C2—C1—C7—O2 | 21.48 (15) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.99 (14) |
| C6—C1—C7—O1 | 22.59 (14) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | −179.29 (9) |
| C2—C1—C7—O1 | −159.02 (10) |
4-Methylquinolinium 3-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (IV). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···N2 | 0.84 (3) | 1.70 (3) | 2.5364 (13) | 175 (3) |
| N2—H2···O1 | 0.89 (2) | 1.65 (2) | 2.5364 (13) | 175 (3) |
| C6—H6···O3i | 0.95 | 2.59 | 3.4705 (14) | 155 |
| C9—H9···O2ii | 0.95 | 2.41 | 3.1739 (15) | 137 |
| C17—H17C···O2iii | 0.98 | 2.47 | 3.4155 (17) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x+1, −y, −z+1.
4-Methylquinolinium 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (V). Crystal data
| C10H10N+·C7H3ClNO4− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 344.75 | F(000) = 356.00 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.469 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.6858 (3) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| b = 8.3615 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 19686 reflections |
| c = 13.5746 (5) Å | θ = 3.0–30.1° |
| α = 82.5485 (13)° | µ = 0.27 mm−1 |
| β = 80.8927 (12)° | T = 185 K |
| γ = 65.0929 (11)° | Platelet, colorless |
| V = 779.33 (5) Å3 | 0.51 × 0.45 × 0.15 mm |
4-Methylquinolinium 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (V). Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII diffractometer | 3290 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.027 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Absorption correction: numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.868, Tmax = 0.960 | k = −10→10 |
| 18635 measured reflections | l = −17→17 |
| 3566 independent reflections |
4-Methylquinolinium 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (V). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.102 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0588P)2 + 0.2103P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3566 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 222 parameters | Δρmax = 0.38 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
4-Methylquinolinium 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (V). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
4-Methylquinolinium 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (V). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.68899 (5) | −0.41758 (5) | 1.09613 (2) | 0.04437 (12) | |
| O1 | 0.55730 (12) | 0.11536 (12) | 0.67899 (7) | 0.0343 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.27487 (13) | 0.08937 (13) | 0.70351 (7) | 0.0361 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.04742 (14) | 0.09528 (15) | 0.90266 (8) | 0.0491 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.12351 (16) | −0.15067 (16) | 0.83652 (9) | 0.0518 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.16299 (14) | −0.04644 (15) | 0.87379 (8) | 0.0336 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.42785 (14) | 0.30577 (13) | 0.52175 (7) | 0.0270 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.483 (3) | 0.226 (3) | 0.5866 (16) | 0.075 (6)* | |
| C1 | 0.49025 (15) | −0.04440 (14) | 0.82541 (8) | 0.0237 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.36650 (16) | −0.10303 (15) | 0.89062 (8) | 0.0255 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.42201 (17) | −0.21590 (16) | 0.97438 (9) | 0.0291 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.334084 | −0.253809 | 1.017135 | 0.035* | |
| C4 | 0.61139 (17) | −0.27175 (16) | 0.99359 (9) | 0.0289 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.73961 (17) | −0.21407 (16) | 0.93296 (9) | 0.0294 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.868057 | −0.251966 | 0.948261 | 0.035* | |
| C6 | 0.67764 (16) | −0.10049 (15) | 0.84981 (9) | 0.0271 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.764664 | −0.059768 | 0.808401 | 0.033* | |
| C7 | 0.43193 (16) | 0.06384 (15) | 0.72882 (8) | 0.0261 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.50883 (17) | 0.25320 (16) | 0.43209 (9) | 0.0304 (2) | |
| H8 | 0.615416 | 0.141673 | 0.426068 | 0.036* | |
| C9 | 0.44242 (18) | 0.35661 (17) | 0.34601 (9) | 0.0314 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.504996 | 0.315398 | 0.282367 | 0.038* | |
| C10 | 0.28780 (17) | 0.51732 (16) | 0.35173 (9) | 0.0291 (2) | |
| C11 | 0.19978 (16) | 0.57586 (15) | 0.44844 (9) | 0.0264 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.04213 (18) | 0.74036 (17) | 0.46435 (11) | 0.0350 (3) | |
| H12 | −0.011398 | 0.817344 | 0.408744 | 0.042* | |
| C13 | −0.03350 (19) | 0.78908 (18) | 0.55913 (12) | 0.0400 (3) | |
| H13 | −0.138711 | 0.900418 | 0.568996 | 0.048* | |
| C14 | 0.0424 (2) | 0.67651 (19) | 0.64235 (10) | 0.0393 (3) | |
| H14 | −0.012424 | 0.712464 | 0.707852 | 0.047* | |
| C15 | 0.19339 (18) | 0.51667 (17) | 0.63033 (9) | 0.0327 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.243434 | 0.440717 | 0.686908 | 0.039* | |
| C16 | 0.27446 (16) | 0.46528 (15) | 0.53306 (8) | 0.0253 (2) | |
| C17 | 0.2148 (2) | 0.6286 (2) | 0.25939 (10) | 0.0405 (3) | |
| H17A | 0.075011 | 0.665044 | 0.263552 | 0.061* | |
| H17B | 0.278616 | 0.560052 | 0.200744 | 0.061* | |
| H17C | 0.243044 | 0.733558 | 0.253298 | 0.061* |
4-Methylquinolinium 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (V). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0431 (2) | 0.0486 (2) | 0.03629 (19) | −0.01563 (16) | −0.01541 (14) | 0.01651 (14) |
| O1 | 0.0291 (4) | 0.0417 (5) | 0.0307 (4) | −0.0157 (4) | −0.0063 (3) | 0.0105 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0291 (4) | 0.0476 (5) | 0.0321 (4) | −0.0169 (4) | −0.0112 (3) | 0.0094 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0271 (5) | 0.0596 (7) | 0.0399 (5) | 0.0006 (5) | −0.0017 (4) | 0.0002 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0427 (6) | 0.0587 (7) | 0.0673 (7) | −0.0319 (5) | −0.0236 (5) | 0.0105 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0237 (5) | 0.0446 (6) | 0.0295 (5) | −0.0139 (5) | −0.0045 (4) | 0.0094 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0260 (5) | 0.0278 (5) | 0.0268 (5) | −0.0114 (4) | −0.0037 (4) | 0.0016 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0229 (5) | 0.0244 (5) | 0.0231 (5) | −0.0086 (4) | −0.0033 (4) | −0.0019 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0213 (5) | 0.0285 (5) | 0.0254 (5) | −0.0085 (4) | −0.0039 (4) | −0.0018 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0275 (6) | 0.0331 (6) | 0.0257 (5) | −0.0127 (5) | −0.0026 (4) | 0.0017 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0313 (6) | 0.0283 (5) | 0.0243 (5) | −0.0089 (5) | −0.0073 (4) | 0.0013 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0240 (5) | 0.0328 (6) | 0.0303 (6) | −0.0094 (4) | −0.0079 (4) | 0.0000 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0244 (5) | 0.0298 (5) | 0.0277 (5) | −0.0116 (4) | −0.0036 (4) | −0.0010 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0252 (5) | 0.0262 (5) | 0.0245 (5) | −0.0083 (4) | −0.0038 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0270 (6) | 0.0286 (5) | 0.0333 (6) | −0.0096 (4) | −0.0013 (4) | −0.0035 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0334 (6) | 0.0371 (6) | 0.0255 (5) | −0.0168 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | −0.0042 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0305 (6) | 0.0346 (6) | 0.0272 (5) | −0.0189 (5) | −0.0057 (4) | 0.0031 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0249 (5) | 0.0275 (5) | 0.0294 (5) | −0.0135 (4) | −0.0044 (4) | 0.0007 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0295 (6) | 0.0293 (6) | 0.0450 (7) | −0.0105 (5) | −0.0086 (5) | 0.0014 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0295 (6) | 0.0317 (6) | 0.0548 (8) | −0.0079 (5) | −0.0006 (5) | −0.0104 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0362 (7) | 0.0434 (7) | 0.0386 (7) | −0.0168 (6) | 0.0054 (5) | −0.0141 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0345 (6) | 0.0379 (6) | 0.0278 (6) | −0.0173 (5) | −0.0010 (5) | −0.0035 (5) |
| C16 | 0.0246 (5) | 0.0268 (5) | 0.0270 (5) | −0.0131 (4) | −0.0027 (4) | −0.0016 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0429 (7) | 0.0485 (8) | 0.0309 (6) | −0.0212 (6) | −0.0104 (5) | 0.0106 (6) |
4-Methylquinolinium 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (V). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C4 | 1.7291 (12) | C8—C9 | 1.3887 (17) |
| O1—C7 | 1.2804 (14) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C7 | 1.2313 (14) | C9—C10 | 1.3699 (18) |
| O3—N1 | 1.2127 (15) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| O4—N1 | 1.2220 (16) | C10—C11 | 1.4239 (16) |
| N1—C2 | 1.4780 (14) | C10—C17 | 1.4938 (17) |
| N2—C8 | 1.3156 (15) | C11—C16 | 1.4107 (16) |
| N2—C16 | 1.3652 (15) | C11—C12 | 1.4132 (17) |
| N2—H2 | 1.06 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.364 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.3936 (15) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3948 (15) | C13—C14 | 1.405 (2) |
| C1—C7 | 1.5085 (15) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3790 (16) | C14—C15 | 1.3601 (19) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3859 (17) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C15—C16 | 1.4062 (16) |
| C4—C5 | 1.3863 (17) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3834 (16) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| O3—N1—O4 | 125.32 (12) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.82 (11) |
| O3—N1—C2 | 117.47 (11) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.6 |
| O4—N1—C2 | 117.09 (11) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.6 |
| C8—N2—C16 | 120.67 (10) | C9—C10—C11 | 117.95 (11) |
| C8—N2—H2 | 120.5 (12) | C9—C10—C17 | 121.06 (11) |
| C16—N2—H2 | 118.8 (12) | C11—C10—C17 | 120.99 (11) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 116.89 (10) | C16—C11—C12 | 118.02 (11) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 122.38 (10) | C16—C11—C10 | 118.57 (10) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 120.58 (10) | C12—C11—C10 | 123.40 (11) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 123.52 (10) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.30 (12) |
| C3—C2—N1 | 115.15 (10) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C1—C2—N1 | 121.33 (10) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 117.23 (10) | C12—C13—C14 | 120.75 (12) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 121.4 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.6 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 121.4 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.6 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.84 (11) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.82 (12) |
| C3—C4—Cl1 | 118.83 (9) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C5—C4—Cl1 | 119.33 (9) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.97 (11) | C14—C15—C16 | 119.15 (12) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.5 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.4 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.5 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.4 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 121.49 (11) | N2—C16—C15 | 118.72 (11) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 | N2—C16—C11 | 120.32 (10) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.3 | C15—C16—C11 | 120.96 (11) |
| O2—C7—O1 | 126.25 (11) | C10—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—C1 | 118.37 (10) | C10—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 115.33 (10) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 121.66 (11) | C10—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—H8 | 119.2 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.2 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −2.12 (17) | C16—N2—C8—C9 | −0.01 (17) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | 173.58 (10) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | −0.70 (18) |
| C6—C1—C2—N1 | 177.81 (10) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.00 (17) |
| C7—C1—C2—N1 | −6.48 (16) | C8—C9—C10—C17 | −179.56 (11) |
| O3—N1—C2—C3 | 97.04 (13) | C9—C10—C11—C16 | −0.65 (16) |
| O4—N1—C2—C3 | −79.28 (14) | C17—C10—C11—C16 | 179.91 (10) |
| O3—N1—C2—C1 | −82.90 (14) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 178.67 (11) |
| O4—N1—C2—C1 | 100.78 (14) | C17—C10—C11—C12 | −0.77 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.31 (18) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.21 (17) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.63 (10) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −179.11 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.49 (18) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.6 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—Cl1 | −178.45 (9) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.2 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.37 (18) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.49 (19) |
| Cl1—C4—C5—C6 | 178.58 (9) | C8—N2—C16—C15 | −179.53 (11) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.58 (18) | C8—N2—C16—C11 | 0.35 (16) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 2.23 (16) | C14—C15—C16—N2 | 179.02 (11) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | −173.56 (10) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.86 (18) |
| C2—C1—C7—O2 | −5.64 (16) | C12—C11—C16—N2 | −179.37 (10) |
| C6—C1—C7—O2 | 169.91 (11) | C10—C11—C16—N2 | −0.01 (16) |
| C2—C1—C7—O1 | 176.77 (10) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.51 (16) |
| C6—C1—C7—O1 | −7.68 (15) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | 179.86 (10) |
4-Methylquinolinium 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (V). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O1 | 1.06 (2) | 1.50 (2) | 2.5568 (13) | 179 (4) |
| C8—H8···O2i | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.2779 (16) | 132 |
| C12—H12···O2ii | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.3391 (18) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
4-Methylquinolinium 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (VI). Crystal data
| C10H10N+.C7H3ClNO4− | F(000) = 1424.00 |
| Mr = 344.75 | Dx = 1.502 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 16.2625 (10) Å | Cell parameters from 24067 reflections |
| b = 7.5099 (4) Å | θ = 3.0–30.0° |
| c = 25.3105 (15) Å | µ = 0.28 mm−1 |
| β = 99.4086 (19)° | T = 190 K |
| V = 3049.6 (3) Å3 | Prism, colorless |
| Z = 8 | 0.30 × 0.21 × 0.12 mm |
4-Methylquinolinium 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (VI). Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPIDII diffractometer | 3913 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.022 |
| ω scans | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 3.0° |
| Absorption correction: numerical (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999) | h = −22→22 |
| Tmin = 0.916, Tmax = 0.968 | k = −10→10 |
| 29037 measured reflections | l = −35→35 |
| 4457 independent reflections |
4-Methylquinolinium 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (VI). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.099 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0586P)2 + 1.3567P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4457 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 222 parameters | Δρmax = 0.47 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
4-Methylquinolinium 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (VI). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
4-Methylquinolinium 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (VI). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.35497 (2) | 0.25440 (3) | 0.21927 (2) | 0.03174 (9) | |
| O1 | 0.58343 (5) | 0.52232 (13) | 0.37347 (3) | 0.0379 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.51224 (5) | 0.73265 (12) | 0.40930 (3) | 0.03410 (19) | |
| O3 | 0.50836 (5) | 1.00336 (12) | 0.32498 (4) | 0.0393 (2) | |
| O4 | 0.38124 (6) | 1.04110 (12) | 0.33823 (3) | 0.03630 (19) | |
| N1 | 0.43689 (6) | 0.95186 (12) | 0.32389 (3) | 0.02602 (17) | |
| N2 | 0.70950 (5) | 0.49554 (12) | 0.44591 (3) | 0.02496 (17) | |
| C1 | 0.45930 (6) | 0.62497 (13) | 0.32235 (4) | 0.02159 (18) | |
| C2 | 0.41499 (6) | 0.77444 (13) | 0.30138 (4) | 0.02245 (18) | |
| C3 | 0.35187 (7) | 0.76754 (14) | 0.25743 (4) | 0.0276 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.322449 | 0.872401 | 0.244702 | 0.033* | |
| C4 | 0.33229 (6) | 0.60562 (15) | 0.23234 (4) | 0.0279 (2) | |
| H4 | 0.289265 | 0.597431 | 0.202146 | 0.033* | |
| C5 | 0.37668 (6) | 0.45573 (13) | 0.25212 (4) | 0.02356 (18) | |
| C6 | 0.43909 (6) | 0.46287 (13) | 0.29667 (4) | 0.02320 (18) | |
| H6 | 0.467928 | 0.357532 | 0.309587 | 0.028* | |
| C7 | 0.52359 (6) | 0.63089 (13) | 0.37316 (4) | 0.02337 (18) | |
| C8 | 0.77132 (6) | 0.42632 (14) | 0.42468 (4) | 0.0276 (2) | |
| H8 | 0.763497 | 0.406693 | 0.387111 | 0.033* | |
| C9 | 0.84757 (6) | 0.38107 (14) | 0.45538 (4) | 0.0267 (2) | |
| H9 | 0.890820 | 0.332639 | 0.438694 | 0.032* | |
| C10 | 0.86007 (6) | 0.40684 (13) | 0.51013 (4) | 0.02478 (19) | |
| C11 | 0.79365 (6) | 0.48165 (13) | 0.53362 (4) | 0.02323 (18) | |
| C12 | 0.79902 (7) | 0.51180 (16) | 0.58948 (4) | 0.0313 (2) | |
| H12 | 0.849207 | 0.485426 | 0.613072 | 0.038* | |
| C13 | 0.73200 (8) | 0.57880 (18) | 0.60938 (5) | 0.0362 (2) | |
| H13 | 0.735942 | 0.596465 | 0.646879 | 0.043* | |
| C14 | 0.65709 (7) | 0.62213 (17) | 0.57515 (5) | 0.0335 (2) | |
| H14 | 0.611455 | 0.669217 | 0.589773 | 0.040* | |
| C15 | 0.64983 (6) | 0.59662 (15) | 0.52088 (4) | 0.0283 (2) | |
| H15 | 0.599673 | 0.626737 | 0.497774 | 0.034* | |
| C16 | 0.71795 (6) | 0.52500 (13) | 0.49994 (4) | 0.02273 (18) | |
| C17 | 0.94142 (7) | 0.35605 (17) | 0.54355 (5) | 0.0340 (2) | |
| H17A | 0.967677 | 0.462034 | 0.561585 | 0.051* | |
| H17B | 0.978265 | 0.304870 | 0.520528 | 0.051* | |
| H17C | 0.931537 | 0.268016 | 0.570401 | 0.051* | |
| H2 | 0.6559 (13) | 0.524 (3) | 0.4196 (9) | 0.074 (6)* |
4-Methylquinolinium 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (VI). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.03751 (15) | 0.02625 (13) | 0.03075 (14) | −0.00503 (9) | 0.00350 (11) | −0.00484 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0330 (4) | 0.0476 (5) | 0.0287 (4) | 0.0189 (4) | −0.0077 (3) | −0.0084 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0337 (4) | 0.0406 (5) | 0.0259 (4) | 0.0105 (3) | −0.0015 (3) | −0.0072 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0335 (4) | 0.0350 (4) | 0.0470 (5) | −0.0106 (3) | −0.0008 (4) | −0.0006 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0455 (5) | 0.0292 (4) | 0.0349 (4) | 0.0063 (3) | 0.0084 (4) | −0.0037 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0308 (4) | 0.0231 (4) | 0.0224 (4) | −0.0004 (3) | −0.0007 (3) | 0.0023 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0237 (4) | 0.0265 (4) | 0.0234 (4) | 0.0025 (3) | 0.0004 (3) | 0.0026 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0187 (4) | 0.0252 (4) | 0.0205 (4) | 0.0016 (3) | 0.0021 (3) | 0.0008 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0220 (4) | 0.0225 (4) | 0.0222 (4) | 0.0001 (3) | 0.0018 (3) | 0.0002 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0257 (5) | 0.0259 (5) | 0.0282 (5) | 0.0033 (3) | −0.0041 (4) | 0.0019 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0249 (4) | 0.0299 (5) | 0.0261 (4) | 0.0000 (4) | −0.0044 (4) | −0.0005 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0233 (4) | 0.0238 (4) | 0.0237 (4) | −0.0025 (3) | 0.0043 (3) | −0.0021 (3) |
| C6 | 0.0218 (4) | 0.0238 (4) | 0.0240 (4) | 0.0022 (3) | 0.0038 (3) | 0.0015 (3) |
| C7 | 0.0220 (4) | 0.0262 (4) | 0.0208 (4) | 0.0016 (3) | 0.0001 (3) | 0.0020 (3) |
| C8 | 0.0283 (5) | 0.0294 (5) | 0.0248 (4) | 0.0018 (4) | 0.0038 (4) | 0.0015 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0234 (4) | 0.0270 (5) | 0.0300 (5) | 0.0023 (3) | 0.0049 (4) | 0.0009 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0213 (4) | 0.0212 (4) | 0.0303 (5) | −0.0004 (3) | −0.0004 (3) | 0.0018 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0220 (4) | 0.0216 (4) | 0.0247 (4) | −0.0012 (3) | −0.0005 (3) | 0.0020 (3) |
| C12 | 0.0300 (5) | 0.0361 (6) | 0.0252 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | −0.0028 (4) | −0.0005 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0389 (6) | 0.0431 (6) | 0.0258 (5) | 0.0008 (5) | 0.0026 (4) | −0.0053 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0321 (5) | 0.0360 (6) | 0.0333 (5) | 0.0040 (4) | 0.0084 (4) | −0.0044 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0247 (4) | 0.0290 (5) | 0.0307 (5) | 0.0040 (4) | 0.0029 (4) | 0.0001 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0226 (4) | 0.0208 (4) | 0.0238 (4) | 0.0002 (3) | 0.0008 (3) | 0.0021 (3) |
| C17 | 0.0226 (5) | 0.0376 (6) | 0.0387 (6) | 0.0040 (4) | −0.0042 (4) | 0.0001 (5) |
4-Methylquinolinium 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (VI). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C5 | 1.7338 (10) | C8—C9 | 1.3935 (14) |
| O1—C7 | 1.2686 (12) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C7 | 1.2288 (13) | C9—C10 | 1.3811 (15) |
| O3—N1 | 1.2211 (12) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| O4—N1 | 1.2277 (12) | C10—C11 | 1.4303 (14) |
| N1—C2 | 1.4698 (13) | C10—C17 | 1.4985 (14) |
| N2—C8 | 1.3215 (13) | C11—C16 | 1.4159 (13) |
| N2—C16 | 1.3700 (13) | C11—C12 | 1.4204 (14) |
| N2—H2 | 1.03 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.3691 (17) |
| C1—C2 | 1.3913 (13) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3938 (14) | C13—C14 | 1.4128 (17) |
| C1—C7 | 1.5197 (13) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3858 (14) | C14—C15 | 1.3726 (16) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3847 (15) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C15—C16 | 1.4105 (14) |
| C4—C5 | 1.3859 (14) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3893 (14) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| O3—N1—O4 | 124.43 (10) | C10—C9—C8 | 119.80 (9) |
| O3—N1—C2 | 117.73 (9) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.1 |
| O4—N1—C2 | 117.77 (9) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.1 |
| C8—N2—C16 | 120.70 (9) | C9—C10—C11 | 118.34 (9) |
| C8—N2—H2 | 116.0 (12) | C9—C10—C17 | 120.16 (9) |
| C16—N2—H2 | 123.3 (12) | C11—C10—C17 | 121.50 (9) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 117.31 (8) | C16—C11—C12 | 117.94 (9) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 122.75 (9) | C16—C11—C10 | 118.79 (9) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 119.82 (8) | C12—C11—C10 | 123.27 (9) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 123.05 (9) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.11 (10) |
| C3—C2—N1 | 116.47 (9) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C1—C2—N1 | 120.40 (8) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.06 (9) | C12—C13—C14 | 121.17 (10) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.5 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.4 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.5 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.4 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.71 (9) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.40 (10) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.6 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.8 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.6 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.8 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.02 (9) | C14—C15—C16 | 119.00 (10) |
| C4—C5—Cl1 | 118.81 (8) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.5 |
| C6—C5—Cl1 | 119.16 (8) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.83 (9) | N2—C16—C15 | 118.68 (9) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 | N2—C16—C11 | 119.95 (9) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.1 | C15—C16—C11 | 121.37 (9) |
| O2—C7—O1 | 127.13 (9) | C10—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O2—C7—C1 | 118.80 (9) | C10—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 114.03 (8) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 122.41 (10) | C10—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—H8 | 118.8 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 118.8 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.16 (15) | C16—N2—C8—C9 | −0.41 (16) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −174.95 (9) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | 0.62 (17) |
| C6—C1—C2—N1 | −175.55 (8) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.59 (15) |
| C7—C1—C2—N1 | 8.33 (14) | C8—C9—C10—C17 | 179.10 (10) |
| O3—N1—C2—C3 | −120.32 (11) | C9—C10—C11—C16 | 0.39 (14) |
| O4—N1—C2—C3 | 56.69 (13) | C17—C10—C11—C16 | −179.29 (10) |
| O3—N1—C2—C1 | 56.60 (13) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 179.10 (10) |
| O4—N1—C2—C1 | −126.39 (10) | C17—C10—C11—C12 | −0.58 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.07 (16) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.76 (16) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 175.77 (9) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −177.96 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.02 (16) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.11 (19) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.97 (16) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.4 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—Cl1 | −177.60 (8) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.59 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.86 (15) | C8—N2—C16—C15 | −179.05 (10) |
| Cl1—C5—C6—C1 | 177.70 (7) | C8—N2—C16—C11 | 0.20 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.20 (14) | C14—C15—C16—N2 | 178.31 (10) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | 176.04 (9) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.93 (16) |
| C2—C1—C7—O2 | 34.14 (15) | C12—C11—C16—N2 | −178.97 (9) |
| C6—C1—C7—O2 | −141.88 (10) | C10—C11—C16—N2 | −0.19 (14) |
| C2—C1—C7—O1 | −147.73 (10) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.25 (15) |
| C6—C1—C7—O1 | 36.25 (13) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | 179.04 (9) |
4-Methylquinolinium 5-chloro-2-nitrobenzoate (VI). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O1 | 1.03 (2) | 1.52 (2) | 2.5252 (11) | 165 (2) |
| C9—H9···O2i | 0.95 | 2.34 | 3.2856 (13) | 171 |
| C12—H12···O3ii | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.5065 (14) | 166 |
| C15—H15···O2 | 0.95 | 2.57 | 3.4583 (13) | 155 |
| C17—H17A···O2ii | 0.98 | 2.41 | 3.3524 (16) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1/2, y−1/2, z; (ii) −x+3/2, −y+3/2, −z+1.
References
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Babu, B. & Chandrasekaran, J. (2014). Private Communication (refcode WOPDEM). CCDC, Cambridge, England.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Gotoh, K. & Ishida, H. (2009). Acta Cryst. C65, o534–o538. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, K. & Ishida, H. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, K. & Ishida, H. (2019a). Acta Cryst. E75, 1552–1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, K. & Ishida, H. (2019b). Acta Cryst. E75, 1694–1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, K. & Ishida, H. (2019c). Acta Cryst. E75, 1853–1856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gotoh, K. & Ishida, H. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 1701–1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T. (1999). NUMABS. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Kotov, S., Mayer-Figge, H. & Zareva, S. (2018). Bulg. Chem. Commun. (Izvestiya po Khimiya), 50, 260.
- Macrae, C. F., Sovago, I., Cottrell, S. J., Galek, P. T. A., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Platings, M., Shields, G. P., Stevens, J. S., Towler, M. & Wood, P. A. (2020). J. Appl. Cryst. 53, 226–235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, J. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2007). Chem. Commun. pp. 3814–3816. [DOI] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, J. J., Spackman, M. A. & Mitchell, A. S. (2004). Acta Cryst. B60, 627–668. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (2006). PROCESS-AUTO. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku (2018). CrystalStructure. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 1–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tan, T. (2007). J. Mol. Struct. 840, 6–13.
- Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). CrystalExplorer17. University of Western Australia. http://hirshfeldsurface.net.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II, III, IV, V, VI. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991Isup8.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IIsup9.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IIIsup10.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IIIsup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IVsup11.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991IVsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991Vsup12.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) V. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991Vsup6.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991VIsup13.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) VI. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989021010896/hb7991VIsup7.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report














