Abstract
Introduction
To investigate the 24-month efficacy and safety of iStent inject trabecular microbypass system implantation combined with phacoemulsification in subjects with primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) and concomitant cataract.
Methods
This prospective, uncontrolled, interventional case series included 36 eyes (29 subjects) with POAG of mild to moderate severity and coexisting cataract that underwent combined phacoemulsification and implantation of a second-generation trabecular microbypass stent (iStent inject®). Main outcome measures involved mean intraocular pressure (IOP), number of antiglaucoma medications, and proportional analysis of eyes with IOP ≤ 18 mmHg or ≤ 15 mmHg, or with 0 or ≥ 2 glaucoma medications. Secondary outcome measures involved the cup-to-disc ratio, corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA), and adverse issues.
Results
In 36 eyes, the mean IOP at baseline was 18.28 ± 2.87 mmHg, which decreased to 14.24 ± 1.36 (22.1%) and 14.46 ± 1.56 mmHg (20.9%) at 18 and 24 months, respectively (p < 0.001). At the last follow-up, 100% of eyes had an IOP ≤ 18 mmHg (vs. 50% preoperatively), and 75.7% of eyes had an IOP ≤ 15 mmHg (vs. 16.7% preoperatively); 58.3% of eyes achieved ≥ 20% IOP reduction from preoperative status. At baseline, eyes were treated with a mean of 2.35 ± 1.18 medications, which was reduced to 0.80 ± 1.04 (66% reduction) and 0.69 ± 0.95 medications (70.6% reduction) at 18 and 24 months, respectively (p < 0.001). At the last follow-up, 54.1% of eyes were medication-free (vs. 0% preoperatively) and 24.3% of eyes were treated with ≥ 2 medications (vs. 64.9% preoperatively). This combined procedure demonstrated an excellent safety profile with no reported intraoperative complications or adverse events; CDVA was maintained throughout the entire follow-up period.
Conclusions
This real-world series demonstrated that iStent inject device implantation at the time of phacoemulsification is a safe and effective method to decrease IOP and the necessity for antiglaucoma medications in patients with mild-to-moderate POAG and cataract; no associated vision-threatening complications were noted.
Keywords: Cataract, iStent inject, Minimally Invasive Glaucoma surgery, POAG, Primary open angle glaucoma
Key Summary Points
| A real-world series demonstrated that iStent inject device implantation at the time of phacoemulsification is a safe and effective method to decrease intraocular pressure (IOP) and the necessity for antiglaucoma medications in patients with mild-to-moderate primary open-angle glaucoma and cataract. |
| At the last follow-up, 100% of eyes had an IOP ≤ 18 mmHg (vs. 50% preoperatively) and 75.7% of eyes had an IOP ≤ 15 mmHg (vs. 16.7% preoperatively); 58.3% of eyes achieved ≥20% IOP reduction from preoperative status. |
| At the last follow-up, 54.1 % of eyes were medication-free (vs. 0% preoperatively) and 24.3 % of eyes were treated with ≥2 medications (vs. 64.9% preoperatively). |
| Future research could include a greater number of participants, a longer follow-up period, and/or an analysis of the retinal nerve fiber layer and visual field over time. |
Introduction
Glaucoma is the most common cause of permanent vision loss, and intraocular pressure (IOP) remains the sole modifiable risk factor to halt the progression of vision loss [1, 2]. Primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) is recognized as the most prevalent glaucoma subtype [3]. The mainstay of treatment for open-angle glaucoma (OAG) is primarily aimed at reducing the IOP [4].
Conservative management typically involves topical antiglaucoma therapy and/or laser trabeculoplasty [4]. Topical antiglaucoma medications are the first-line treatment; however, they are associated with adverse effects including ocular surface disease, poor compliance, cost, decreased quality of life, and conjunctival inflammation affecting future surgical outcomes [5–7]. Laser trabeculoplasty procedures also are considered an effective method for early treatment [8]. However, their IOP-reducing effect may be temporary, such as in the recent LIGHT trial wherein approximately one-third of patients needed additional therapy (medication or repeat laser) during the 3-year follow-up period; this presents a challenge as glaucoma is a lifelong disease [8–10]. Incisional glaucoma surgeries—i.e., a trabeculectomy or tube shunt procedure—more effectively reduce IOP; however, these types of surgeries are associated with vision-threatening complications such as bleb-related complications, endophthalmitis, and chronic hypotony [11, 12].
Over the past decade, management for OAG has undergone significant progress following the development of minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) which has a better safety profile and incorporates several novel surgical techniques [13]. MIGS has expanded over the last decade to fill the gap between topical glaucoma therapy and incisional glaucoma surgery. Although MIGS procedures typically do not result in the dramatic IOP reduction obtained by traditional incisional glaucoma surgery, they can provide clinically meaningful IOP and medication reductions while retaining an excellent safety profile. They also spare the conjunctiva in case further incisional glaucoma surgery is needed later on. Thus the benefits of MIGS surgeries can extend to both clinical (e.g., IOP, medications, and avoidance of filtering surgery) and non-clinical effects (e.g., improved ocular surface, quality of life, and compliance) [6, 7, 14, 15].
The first-generation trabecular microbypass stent, iStent (Glaukos Corporation, San Clemente, CA, USA), is the first US Food and Drug Administration-approved MIGS device. The stent is implanted into Schlemm’s canal to bypass aqueous outflow resistance in the trabecular meshwork, enhancing the physiological outflow and reducing the IOP [16]. A second-generation microbypass trabecular stent system (iStent® Inject, Glaukos Corp.) has recently been introduced and involves the insertion of two micro-scale stents to enhance up to 5–6 clock hours of aqueous outflow. Both models (iStent and iStent inject) are biocompatible, nonferromagnetic, micro-sized, heparin-coated titanium stents which are implanted ab internally into Schlemm’s canal with a single-use stainless-steel inserter or injector [17]. The iStent inject was developed to achieve a greater reduction in IOP than the first-generation iStent, based on studies that showed that additional IOP reduction could be attained with insertion of multiple first-generation iStents [18, 19]. Cataract extraction itself also can reduce IOP and medication in glaucomatous eyes, although the effect is typically temporary [20, 21].
At present, minimal data exist on the combination of iStent inject and phacoemulsification in Middle Eastern patients. As such, the objective of this study was to investigate the safety and efficacy of iStent inject implantation with cataract extraction in terms of IOP, medication dependence, and visual acuity in eyes with POAG and cataract in the Saudi population.
Methods
Study Design
This prospective, uncontrolled, non-randomized interventional series included patients with POAG of mild to moderate severity and concomitant cataract who underwent combined phacoemulsification and implantation of iStent inject second-generation trabecular microbypass stents. All procedures were performed by one surgeon (A.H.) at a single center (King Fahad Hospital of the University in Khobar, Saudi Arabia (KFHU) over a 2-year period (March 2019–April 2021). The study protocol adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki 1964 and was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of KFHU. Preoperative written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Participants were Saudi adults (18 years of age or older) with visually significant cataracts who were medically managed for mild to moderate POAG (mean deviation between 0 and − 12 dB at presentation), who underwent cataract extraction without intraoperative complications. Participants with a corneal scar, active uveitis, concomitant retinopathy, active neovascularization, significant ocular comorbidities, or forms of glaucoma other than POAG were excluded. IOP was measured according to the standard practice for clinical glaucoma studies using Goldmann applanation tonometry. All participants had cataracts (corrected distance visual acuity [CDVA] less than 20/40) and needed further glaucoma intervention due to insufficient IOP control, non-compliance with topical medications, and/or medication burden. The following preoperative details were obtained: age, IOP, cup/disc ratio, number of antiglaucoma therapies, and CDVA. Postoperative details included IOP, CDVA, the number of antiglaucoma medications, postoperative complications, and the need for further glaucoma intervention. Consistent with evidence from the Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study, topical antiglaucoma medication was resumed if the IOP was higher than 18 mmHg at any point during the follow-up period, to decrease the long-term progression of visual field defects [22].
Trabecular Microbypass iStent Inject System and Surgical Procedure
The iStent inject device consists of two preloaded biocompatible titanium stents on a single injector. Each stent has four outlet lumens to enable multidirectional aqueous humor outflow from the anterior chamber downstream to collector channels. The combined surgery started with phacoemulsification through a temporal clear corneal incision with the insertion of an intraocular lens in the bag, which was followed by administering an intracameral miotic agent (acetylcholine 1%); then, an ophthalmic viscoelastic device was injected into the anterior chamber. After rotation of both the patient’s head and the microscope, the non-dominant hand gently placed a goniolens on the corneal surface to visualize the angle. Next, the injector was advanced through the corneal incision under gonioscopic visualization to reach the nasal aspect of trabecular meshwork, into which the first stent was implanted, followed by repositioning the stent injector tip laterally 2–3 hours from the first stent to insert the second stent. After that, the injector was withdrawn from the eye, and the stents were confirmed to be placed properly. At the end of the procedure, the ophthalmic viscoelastic substance was removed, and the self-sealing of the corneal incision was confirmed. Lastly, a subconjunctival injection of a mixture of dexamethasone and gentamicin was given.
Postoperative Medication and Follow-up
Postoperatively, prednisolone acetate 1% (Pred Forte; Allergan, Inc., Irvine, CA) was prescribed with a tapering dose over a 6-week period along with topical moxifloxacin 0.05% (Vigamox; Alcon Laboratories, Inc., Fort Worth, TX) for 2 weeks. All preoperative topical antiglaucoma medications were discontinued. Postoperative data were obtained on day 1, at 2 weeks, and during months 1, 3, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 24.
Effectiveness and Safety Evaluations
Effectiveness measures included mean IOP and the mean number of glaucoma medications. Pre- and postoperative topical antiglaucoma single formulations containing two combined medications were counted as two medications for analysis purposes. Safety parameters included postoperative complications, CDVA data using a Snellen chart, optic disc cupping progression, and further surgical interventions. A postoperative gonioscopic examination was performed at each follow-up visit to ensure proper stent positioning.
Statistical Analysis
For analysis purposes, the CDVA was converted to the logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution. Descriptive analyses (mean and standard deviation) were used to summarize the IOP, number of antiglaucoma medications, CDVA, and cup-to-disc (CD) ratio. Proportional analyses were completed for the percentage of eyes with an IOP ≤ 18 mmHg or an IOP ≤ 15 mmHg; and for the proportion of eyes on 0 or ≥ 2 medications. IBM SPSS for Windows (version 22; IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for all analyses. The normality of the data was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. The IOP, CDVA, and cup-to-disc ratio were compared with an independent sample t test. The number of glaucoma medications was compared with the Mann–Whitney U test. p values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. All figures were created with Microsoft Excel (2019, Microsoft Corp., USA). Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
Results
Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
Thirty-six eyes from 29 subjects with a mean age of 61.6 ± 10.0 years (range 32.0–81.0 years) were involved in this study. All eyes were diagnosed with cataract and POAG without history of previous glaucoma surgery or laser procedures. All eyes underwent iStent inject implantation combined with phacoemulsification and IOL implantation between March 2019 and April 2021. The baseline demographics and clinical characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of participants
| Parameter (n = 36) | Valuea |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 61.6 ± 10.0 (32.0–81.0) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 48.3% (14) |
| Female | 51.7% (15) |
| IOP (mmHg) | 18.28 ± 2.87 (12.00–25.00) |
| CDVA (logMAR) | 0.72 ± 0.61 (0.10–3.00) |
| Number of medications | 2.35 ± 1.18 (1.0–4.0) |
| Medication burden | |
| 0 medications | 0% (0) |
| ≥ 2 medications | 64.9% (24) |
| CD ratio | 0.59 ± 0.13 (0.40–0.80) |
SD standard deviation, CDVA corrected distance visual acuity, IOP intraocular pressure, CD ratio cup-to-disc ratio
aData are presented as mean ± SD (range) or % (n)
Intraocular Pressure
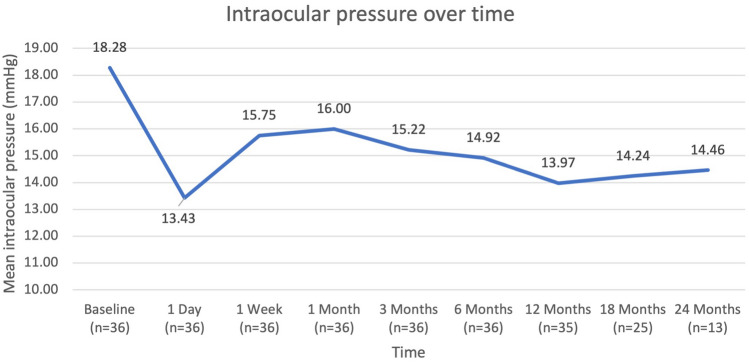
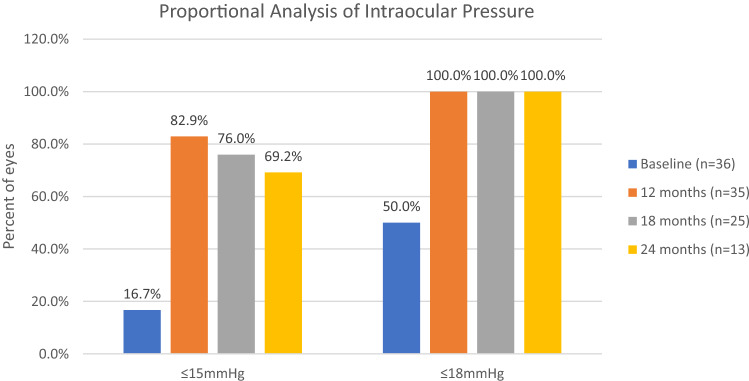
At baseline, the mean IOP was 18.28 ± 2.87 mmHg, with 50% of eyes having an IOP ≤ 18 mmHg and 16.7% of eyes having an IOP ≤ 15 mmHg. At 12 months postoperatively, the mean IOP decreased by 23.6% to 13.97 ± 1.44 mmHg (p < 0.001); 100% of eyes had an IOP ≤ 18 mmHg, and 82.9% had an IOP ≤ 15 mmHg; 58.8% of eyes had ≥ 20% reduction in IOP. At 18 months postoperatively, the mean IOP decreased by 22.1% to 14.24 ± 1.36 mmHg (p < 0.001); 100% of eyes had an IOP ≤ 18 mmHg, and 76% had an IOP ≤ 15 mmHg; 56% of eyes had ≥ 20% reduction in IOP. At 24 months postoperatively, the mean IOP had decreased by 20.9% to 14.46 ± 1.56 mmHg (p < 0.001); 100% of eyes had an IOP ≤ 18 mmHg, and 69.2% had an IOP ≤ 15 mmHg; 69.2% of eyes had ≥ 20% reduction in IOP. At the last follow-up, the mean IOP had decreased by 23.1% to 14.05 ± 1.72 mmHg (p < 0.001); 100% of eyes had an IOP ≤ 18 mmHg, and 75.7% of eyes had an IOP ≤ 15 mmHg; 58.3% of eyes had ≥ 20% reduction in IOP. Figure 1 shows the mean IOP throughout the 24-month postoperative period, and Fig. 2 shows the proportional analysis for IOP at baseline and at the 12-, 18-, and 24-month postoperative visits.
Fig. 1.
Trend of mean intraocular pressure over 24 months
Fig. 2.
Proportional analysis of intraocular pressure over 24 months
Medication Burden
There was a meaningful decline in medication burden postoperatively. At baseline, eyes were treated with a mean of 2.35 ± 1.18 medications, no eyes were medication-free, and 64.9% of eyes were treated with ≥ 2 medications. At 12 months postoperatively, there was a 63.4% decrease in medications to 0.86 ± 1.00 medications (p < 0.001); 48.6% of eyes were medication-free and 28.6% of eyes were being treated with ≥ 2 medications. At 18 months postoperatively, there was a 66% reduction in medications to 0.80 ± 1.04 medications (p < 0.001); 52% of eyes were medication-free and 24% of eyes were being treated with ≥ 2 medications. At 24 months postoperatively, there was a 70.6% reduction in the number of medications to 0.69 ± 0.95 medications (p < 0.001); 61.5% of eyes were medication-free and 30.8% of eyes were being treated with ≥ 2 medications. At the last follow-up visit, there was a 60% reduction in medications to 0.94 ± 1.12 medications (p < 0.001); 54.1% of eyes were medication-free and 24.3% of eyes were being treated with ≥ 2 medications. Figure 3 shows the mean number of medications from the preoperative visit to 24 months postoperatively, and Fig. 4 shows the proportional analysis of the medication burden preoperatively as well as at the 12- and 24-month visits.
Fig. 3.
Mean number of antiglaucoma medications over 24 months
Fig. 4.
Burden of glaucoma medications over 24 months
Visual Acuity and Cup-to-Disc Ratio
All subjects were implanted with iStent inject following phacoemulsification and IOL implantation. The mean CDVA improved from 0.72 ± 0.61 logMAR (Snellen 20/105) preoperatively to 0.31 ± 0.32 logMAR (Snellen 20/41, a gain of 4.1 lines) at the 12-month visit (p = 0.001) and 0.24 ± 0.21 logMAR (Snellen 20/35, a gain of 4.8 lines) at the 24-month visit (p < 0.001); this was consistent with the expected post-phacoemulsification improvement in CDVA.
The CD ratio remained stable postoperatively. The mean CD ratio was 0.59 ± 0.13 preoperatively, 0.59 ± 0.13 at the 12-month visit (p = 0.941), and 0.59 ± 0.12 at the 24-month visit (p = 0.973).
Safety Outcomes
In this cohort, 36 eyes underwent uneventful implantation of two iStent inject stents and cataract surgery. Transient mild corneal edema and ocular discomfort were noted at the initial postoperative follow-up, which were expected following cataract surgery alone and resolved spontaneously with no sequelae. There were no reported adverse events of hyphema, hypopyon, intraocular inflammation, choroidal effusion, or hemorrhage through the entire follow-up period. Also, there were no stent-related adverse issues such as stent occlusion or peripheral anterior synechiae; and further glaucoma surgery was not needed in any eye through to the last visit.
Postoperatively, a transient steroid response occurred in one eye at the 1-month visit which was managed with tapering the steroid drops and careful observation. In this eye, the IOP was 18 mmHg preoperatively and 16 mmHg, 17 mmHg, 22 mmHg, 17 mmHg, 14 mmHg, and 16 mmHg at the 1-day, 1-week, and 1-, 3-, 6-, and 12-month visits. The eye was medication-free through to the 12-month visit. In this eye, the CDVA was 1.0 logMAR (Snellen 20/200) preoperatively and 0.10 logMAR (Snellen 20/25) at the 12-month visit.
Discussion
With the growing use of the iStent inject procedure and the minimal data that exist on surgical outcomes in Middle East populations, the present study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of second-generation iStent inject implantation at the time of cataract extraction in the Saudi population. The dataset thus contributes much-needed evidence on surgical outcomes in distinct populations and clinical settings.
The present study was conducted at a single center in a real-world setting, and a single surgeon operated on 36 eyes with concomitant POAG and cataract that underwent combined iStent inject implantation with cataract surgery. This prospective series demonstrated a safe and substantial reduction in IOP and glaucoma medications. In addition, the micro-scale, ab interno nature of the implantation procedure preserves the conjunctiva in case additional surgery is needed in the future.
The mean IOP was significantly reduced from 18.28 mmHg at baseline to 14.24 (22.1%) and 14.46 mmHg (20.9%) at the 18- and 24-month follow-up visit, respectively. In addition, the target IOP of ≤ 15 mmHg was reached in 75.5% of eyes at the final follow-up visit (75.5% vs. 16.7% preoperatively). This is a particularly impactful outcome considering that a 1-mmHg IOP reduction decreases glaucoma progression by 10%, as established by the Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial [23]. Thus, the 4-mmHg IOP reduction in the present study is considered clinically important.
Regarding medication burden, the current study demonstrated a notable decrease in the mean number of medications by 67.65% from baseline. Furthermore, 54.1% of eyes in this study were medication-free at the final follow-up visit (compared to 0% preoperatively), while 40.6% of eyes were able to eliminate at least two medications from their original regimen. The reduction in medication burden is meaningful considering the known side effects of medications such as poor compliance, ocular surface disturbance, costs, and quality of life [5–7].
The IOP and medication reductions observed in the present study are consistent with previously reported outcomes [24–27]. For example, a multicenter analysis of 1-year outcomes of iStent inject at the time of cataract extraction in distinct glaucoma subtypes reported that IOP and medication reduction from baseline were 23.2% and 71.5%, respectively [24]. Similarly, a prospective cohort study evaluated the 36-month outcome of the iStent inject with phacoemulsification in various glaucoma subtypes and demonstrated that the mean IOP and medication reductions from baseline were 37% and 68%, respectively [27]. In this same cohort, 100% of eyes achieved IOP ≤ 18 mmHg and 71% achieved ≤ 15 mmHg, also 78% of eyes had ≥ 20% reduction in IOP while 54% of eyes were medication-free at the last follow-up. This was consistent with our study outcome in which 100% of eyes achieved IOP ≤ 18 mmHg and 75.7% achieved ≤ 15 mmHg, also 58.3% of eyes had ≥ 20% reduction in IOP and 54.1% of eyes were medication-free. The slight variability in the mean IOP reduction is likely due to the lower mean baseline IOPs in our study (18.28 ± 2.87 mmHg) compared to the aforementioned study (22.6 ± 6.2 mmHg) [27].
The safety profile of this procedure was highly favorable, consistent with previously published studies [15, 24, 27]. The post-phacoemulsification CDVA improvement was preserved throughout follow-up, confirming that this device did not interfere with the visual expectation after cataract surgery. Furthermore, there were no significant postoperative adverse events such as those observed in incisional glaucoma surgeries (e.g., bleb-related infections, endophthalmitis, hypotony, or choroidal detachment) [11, 12]. In addition, there were no stent-related adverse events such as occlusion, and no eyes needed secondary glaucoma surgery through to the last visit.
Trabecular microbypass iStent devices have favorable safety and efficacy profiles and provide many advantages over topical antiglaucoma medications alone [28]. Poor compliance can be a significant barrier to achieve glaucoma control and appears to worsen glaucoma progression [29]. Even with perfect compliance, diurnal changes in drug activity can result in IOP fluctuations and subsequent optic nerve head damage [30]. In contrast, surgical interventions have been shown to result in less IOP variability than topical antiglaucoma medications, allowing for more consistent IOP reduction [31]. The favorable safety profile makes this procedure helpful in managing patients with POAG and cataracts. Additionally, patients are usually able to decrease their use of topical antiglaucoma medications and hence improve their quality of life by adding stent implantation at the time of cataract extraction [6].
Certain limitations exist in the current cohort. Considering that this was a real-world series, a medication washout period was not attempted for safety and ethical purposes. As all iStent injects were implanted at the time of cataract extraction, the outcome of stent implantation could not be parsed apart from that of cataract extraction. However, studies have shown that combining the iStent inject with phacoemulsification achieved consistent and sustained IOP reduction compared to phacoemulsification alone, whose effect fades over time [15, 24, 32]. Future research could include a greater number of participants, a longer follow-up period, and/or an analysis of the retinal nerve fiber layer and visual field over time.
Conclusions
The present real-world study offers some of the first data yet available on iStent inject implantation with cataract surgery in a Middle Eastern population. The results indicate that this combined procedure is an effective method to significantly decrease the IOP and the need for antiglaucoma medications in patients with POAG and cataract, while also preserving excellent safety and avoiding vision-threatening complications or additional glaucoma surgery.
Acknowledgements
We thank the participants of the study.
Funding
No financial sponsorship was received for the work in this study; the patients were seen as part of Dr. Ahmed Habash’s normal clinical practice. The Rapid Service Fees were funded by Glaukos Corporation. Dr. Habash had full access to all of the data in this study and takes complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Authorship Contributions
Wael Otaif wrote the initial draft of the manuscript. Ahmed Al-Habash contributed to interpretation of data and assisted in the preparation and reviewing of the manuscript. Both authors approved the final version of the manuscript and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Prior Presentation
The preliminary results were published on a preprint server as a poster presentation at European Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery (ESCRS) (https://www.escrs.org/amsterdam2020/programme/posters-details.asp?id=36023) [1].
Disclosures
Ahmed Al-Habash and Wael Otaif confirm they have nothing to disclose.Ahmed Al-Habash and Wael Otaif confirm they have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Data Availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
- 1.Quigley H, Broman AT. The number of people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006;90(3):262–267. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2005.081224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bourne RRA, Stevens GA, White RA, et al. Causes of vision loss worldwide, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2013 doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70113-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kapetanakis VV, Chan MPY, Foster PJ, Cook DG, Owen CG, Rudnicka AR. Global variations and time trends in the prevalence of primary open angle glaucoma (POAG): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Ophthalmol. 2016;100(1):86–93. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-307223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ting NS, Li Yim JFT, Ng JY. Different strategies and cost-effectiveness in the treatment of primary open angle glaucoma. Clin Outcomes Res. 2014;6:523–530. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S30697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Inoue K. Managing adverse effects of glaucoma medications. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014;8:903–913. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S44708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Habash AA, Nagshbandi AA. Quality of life after combined cataract and minimally invasive glaucoma surgery in glaucoma patients. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020;14:3049–3056. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S276124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Samuelson TW, Singh IP, Williamson BK, et al. Quality of life in primary open-angle glaucoma and cataract: an analysis of VFQ-25 and OSDI from the iStent inject® pivotal trial. Am J Ophthalmol. 2021 doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2021.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Realini T. Selective laser trabeculoplasty. J Glaucoma. 2008;17(6):497–502. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e31817d2386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ayala M. Long-term outcomes of selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT) treatment. Open Ophthalmol J. 2011;5(1):32–34. doi: 10.2174/1874364101105010032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gazzard G, Konstantakopoulou E, Garway-Heath D, et al. Selective laser trabeculoplasty versus eye drops for first-line treatment of ocular hypertension and glaucoma (LiGHT): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10180):1505–1516. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32213-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Conlon R, Saheb H, Ahmed IIK. Glaucoma treatment trends: a review. Can J Ophthalmol. 2017;52(1):114–124. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjo.2016.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.DeBry PW, Perkins TW, Heatley G, Kaufman P, Brumback LC. Incidence of late-onset bleb-related complications following trabeculectomy with mitomycin. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120(3):297–300. doi: 10.1001/archopht.120.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Richter GM, Coleman AL. Minimally invasive glaucoma surgery: current status and future prospects. Clin Ophthalmol. 2016;10:189–206. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S80490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen DZ, Sng CCA. Safety and efficacy of microinvasive glaucoma surgery. J Ophthalmol. 2017 doi: 10.1155/2017/3182935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Samuelson TW, Sarkisian SR, Lubeck DM, et al. Prospective, randomized, controlled pivotal trial of an ab interno implanted trabecular micro-bypass in primary open-angle glaucoma and cataract: two-year results. Ophthalmology. 2019;126(6):811–821. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bahler CK, Smedley GT, Zhou J, Johnson DH. Trabecular bypass stents decrease intraocular pressure in cultured human anterior segments. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004;138(6):988–994. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2004.07.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bahler CK, Hann CR, Fjield T, Haffner D, Heitzmann H, Fautsch MP. Second-generation trabecular meshwork bypass stent (iStent inject) increases outflow facility in cultured human anterior segments. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012;153(6):1206–1213. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2011.12.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Saheb H, Donnenfeld ED, Solomon KD, et al. Five-year outcomes prospective study of two first-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents (iStent®) in open-angle glaucoma. Curr Eye Res. 2021;46(2):224–231. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1795881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Katz LJ, Erb C, CarcellerGuillamet A, et al. Long-term titrated IOP control with one, two, or three trabecular micro-bypass stents in open-angle glaucoma subjects on topical hypotensive medication: 42-month outcomes. Clin Ophthalmol. 2018;12:255–262. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S152268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Azuara-Blanco A, Burr J, Ramsay C, et al. Effectiveness of early lens extraction for the treatment of primary angle-closure glaucoma (EAGLE): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10052):1389–1397. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30956-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Effect of cataract surgery on intraocular pressure control in glaucoma patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001;27(11):1779–1786. doi: 10.1016/S0886-3350(01)01036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gaasterland DE, Ederer F, Beck A, et al. The Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study (AGIS): 7. The relationship between control of intraocular pressure and visual field deterioration. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000;130(4):429–440. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9394(00)00538-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Leske MC, Heijl A, Hussein M, Bengtsson B, Hyman L, Komaroff E. Factors for glaucoma progression and the effect of treatment: the early manifest glaucoma trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121(1):48–56. doi: 10.1001/archopht.121.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Clement CI, Howes F, Ioannidis AS, Shiu M, Manning D. One-year outcomes following implantation of second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents in conjunction with cataract surgery for various types of glaucoma or ocular hypertension: multicenter, multi-surgeon study. Clin Ophthalmol. 2019;13:491–499. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S187272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Manning D. Real-world case series of iStent or iStent inject trabecular micro-bypass stents combined with cataract surgery. Ophthalmol Ther. 2019;8(4):549–561. doi: 10.1007/s40123-019-00208-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Arriola-Villalobos P, Martinez-De-La-Casa JM, Diaz-Valle D, Morales-Fernandez L, Fernandez-Perez C, Garcia-Feijoo J. Glaukos iStent inject® trabecular micro-bypass implantation associated with cataract surgery in patients with coexisting cataract and open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension: a long-term study. J Ophthalmol. 2016 doi: 10.1155/2016/1056573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hengerer FH, Auffarth GU, Riffel C, Conrad-Hengerer I. Prospective, non-randomized, 36-month study of second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents with phacoemulsification in eyes with various types of glaucoma. Ophthalmol Ther. 2018;7(2):405–415. doi: 10.1007/s40123-018-0152-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fechtner RD, Voskanyan L, Vold SD, et al. Five-year, prospective, randomized, multi-surgeon trial of two trabecular bypass stents versus prostaglandin for newly diagnosed open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmol Glaucoma. 2019;2(3):156–166. doi: 10.1016/j.ogla.2019.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sleath B, Blalock S, Covert D, et al. The relationship between glaucoma medication adherence, eye drop technique, and visual field defect severity. Ophthalmology. 2011;118(12):2398–2402. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.05.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nouri-Mahdavi K, Medeiros FA, Weinreb RN. Fluctuation of intraocular pressure as a predictor of visual field progression. Arch Ophthalmol. 2008;126(8):1168–1169. doi: 10.1001/archopht.126.8.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Muniesa MJ, Ezpeleta J, Benítez I. Fluctuations of the intraocular pressure in medically versus surgically treated glaucoma patients by a contact lens sensor. Am J Ophthalmol. 2019;203:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2019.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fea AM, Consolandi G, Zola M, et al. Micro-bypass implantation for primary open-angle glaucoma combined with phacoemulsification: 4-year follow-up. J Ophthalmol. 2015 doi: 10.1155/2015/795357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.