Abstract
Background
Xinjiang is one of the regions with a high incidence of cervical cancer, and the genetic variation of human papillomavirus may increase its ability to infect the human body and enhance virus-mediated immune escape ability.
Methods
Sanger sequencing of the HPV16 genome from 165 samples positive for HPV16 infection and phylogenetic analysis of the E1 and E2 genes revealed the gene polymorphism of HPV16 in Xinjiang.
Results
The results showed that there were 109 samples with variations in HPV16 E1, 48 sites with nucleotide variations (19 missense variations and 29 synonymous variations), and 91 samples with variations in HPV16 E2, 25 sites with nucleotide variations (20 missense variations and five synonymous variations).
Conclusions
From the phylogenetic tree results, 149 samples were of the European variant and 16 samples were of the Asian variant. No African or North American/Asian variant types were found.
Keywords: Cervical exfoliated cells, Human papillomavirus, E1 and E2 genes, Genetic polymorphism, Sanger sequencing
Background
Cervical cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in women worldwide. According to the 2018 global cancer burden reported in the global cancer epidemiology database, the incidence and mortality of cervical cancer rank fourth among women [1]. The occurrence and development of cervical cancer are closely related to the development of the country and the economic and health conditions. As China is the most populous of developing countries, the number of patients with cervical cancer is still growing [2]. The incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in China vary from region to region, and the central and western regions are still the key areas of cervical cancer prevention and control in China [3]. The mortality rate in the western region is slightly higher than that in the central and eastern regions, which is related to the low rate of cervical cancer screening and high HPV (Human Papillomavirus) infection rate in the less developed regions. The positive rate for HPV in Xinjiang was 14.02%, and most cases involved HPV16, 18, 52 and 53 [4].
HPV infection is a recognized leading cause of cervical cancer worldwide [5]. According to the advance phylogenetic classification of HPV, the natural genetic variation of the virus is generally divided into four major variation lineages, the A lineage: European prototype EUR(A1-A3), Asian As(A4); B lineage: African type I (AF-1); C lineage: African type II (AF-2); D lineage: Asian-American type (AA) and North American type (NA) [6]. The epidemiology of infection with HPV strains in different countries and regions varies; the rate of infection with HPV16 in women in Xinjiang is high, and most of them are European strains [7, 8]. The HPV16 genome consists of six early genes (E1, E2, E4, E5, E6, E7), two late genes (L1, L2), and an upstream regulatory region (URR). E1 and E2 are highly conserved gene sequences that regulate viral genomic replication [9]. HPV E1, one of the most conservative proteins, plays a central role in initiating HPV DNA replication. The E2 protein is a key protein in the viral life cycle, and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, initiation of DNA replication, and viral genome segmentation [10, 11]. The structure of the HPV16 E2 protein is similar to that of a typical transcription factor, with a trans-activation domain and a carboxy-terminal DNA-binding domain separated by a variable hinge region. At the origin of DNA replication, E2 interacts with the HPV E1 replication helicase to promote cellular DNA replication [12]. HPV E2, through interaction with chromatin adapter proteins, binds the viral free genome to the host mitotic staining system during the division of infected cells, playing an important role in the segmentation of the viral genome [13]. The deletion of the E2 structure of the HPV16 virus gives rise to worse clinical consequences in patients with HPV16-positive tumors [14]. The integration of viral DNA, the destruction of E1 or E2 gene, and the loss of the inhibitory activity of the E2 protein on the early promoter are important steps in the process of malignant transformation [15–17]. The E1 and E2 proteins of HPV16 play an important role in the process of HPV infection in host cells. Therefore, studying the impact of amino acids on HPV infection is of great significance for the occurrence and development of cervical cancer.
Variations at the nucleotide sites of HPV16 E1 and E2 are associated with the development of cervical cancer [18, 19]. Therefore, analyzing the gene polymorphism of female cervical cancer in Xinjiang helps us to better understand the relationship between HPV gene variation and cervical cancer (Table 1).
Table 1.
Information on primer sequences
| Primer name | Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| E-1F | 5′-AAGCACACACGTAGACATTCG-3′ |
| E-1R | 5′-ACTGCAACCACCCCCACT-3′ |
| E-2F | 5′-GAGCTGCAAAAAGGAGATTATTTGA-3′ |
| E-2R | 5′-ATCCATTCTGGCGTGTCTCC-3′ |
| E-3F | 5′-TCATGGGGAATGGTTGTGTT-3′ |
| E-3R | 5′-CAAAACATATTACAGACCCTTGCAG-3′ |
| E-4F | 5′-GGTGATTGGAAGCAAATTGTTATG-3′ |
| E-4R | 5′-TCTAGGCGCATGTGTTTCCA-3′ |
| E-5F | 5′-GCACGAGGACGAGGACAAG-3′ |
| E-5R | 5′-CCCGCATGAACTTCCCATAC-3′ |
| E-6F | 5′-GAAGCATCAGTAACTGTGGTAGAGG-3′ |
| E-6R | 5′-TGTAACAATTGCACTTTTATGTTTT-3′ |
F: forward primer, R: reverse primer
Results
Variation analysis of HPV16 E1 and E2 genes
HPV16 E1 and E2 gene variation analysis: A total of 165 DNA samples positive for HPV16 infection were sequenced, and finally 115 samples mutated in E1 and E2 were obtained. The HPV16 prototype (European prototype, GenBank accession number: NC_001526.2) was used as the standard strain for comparison. The polymorphic sites are shown in Tables 2 and 3 (End of article).
Table 2.
HPV16 E1 gene variations and amino acid substitutions
| HPV16 E1 nucleotide variation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant site | AA | As | Af | Number of variation samples | Variation frequency | Amino acid change |
| (n = 109) | (%) | |||||
| T98C | T | T | T | 3 | 2.75 | I33T |
| T105C | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | D35D |
| A117C | A | A | A | 3 | 2.75 | E39D |
| A189C | A | A | A | 18 | 16.51 | E63D |
| G195A | G | G | G | 3 | 2.75 | E65E |
| G252A | G | G | G | 1 | 0.92 | Q84Q |
| C256T | C | C | C | 1 | 0.92 | L86L |
| T288C | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | S96S |
| G299A | A | G | G | 5 | 4.59 | G100E |
| A351C | A | A | A | 1 | 0.92 | K117N |
| T377C | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | L126S |
| T379C | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | F127L |
| T519C | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | S173S |
| A531T | A | A | A | 1 | 0.92 | G177G |
| T557C | T | T | T | 31 | 28.44 | I186T |
| C568T | C | C | C | 1 | 0.92 | P190S |
| T583C | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | L195L |
| T600C | T | T | T | 2 | 1.83 | T200T |
| G651A | G | A | G | 62 | 56.88 | V217V |
| T658A | A | T | T | 4 | 3.67 | S220T |
| T723C | C | T | T | 3 | 2.75 | F241F |
| T779C | T | T | T | 2 | 1.83 | L260S |
| T784A | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | L262T |
| A844T | A | A | A | 1 | 0.92 | K282* |
| T939C | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | R313R |
| A945G | A | A | A | 1 | 0.92 | T315T |
| A969G | A | A | A | 1 | 0.92 | K323K |
| A978G | G | G | G | 35 | 32.11 | I326M |
| A1068C | A | A | A | 8 | 7.34 | E356D |
| C1177T | T | C | T | 1 | 0.92 | L393L |
| A1294C | A | A | A | 5 | 4.59 | R432R |
| T1369C | T | T | T | 5 | 4.59 | L457L |
| T1374G | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | T458T |
| A1380G | A | A | A | 1 | 0.92 | L460L |
| T1390C | C | T | T | 15 | 13.76 | L464L |
| T1437C | T | T | T | 2 | 1.83 | A479A |
| G1473A | G | A | G | 30 | 27.52 | M491I |
| T1479C | C | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | F493F |
| C1480T | T | C | T | 28 | 25.69 | L494L |
| T1512G | T | T | T | 2 | 1.83 | S504S |
| T1528C | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | L510L |
| C1539T | C | C | C | 1 | 0.92 | Y531Y |
| A1683G | A | A | A | 1 | 0.92 | P561P |
| T1687C | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | L563L |
| C1721T | C | C | C | 1 | 0.92 | S574F |
| T1731G | T | T | T | 3 | 2.75 | P577P |
| T1732A | T | T | T | 1 | 0.92 | Y578N |
| C1901T | C | C | C | 1 | 0.92 | S634F |
AA: Asian–American lineage, As: Asian lineage, Af: African lineage
Table 3.
HPV16 E2 gene variations and amino acid substitutions
| HPV16 E2 nucleotide variation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant site | AA | As | Af | Number of variation samples | Variation frequency | Amino acid change | Structural domain |
| (n = 91) | (%) | ||||||
| C1901T | C | C | C | 1 | 1.10 | L4F | transcriptional activation domain |
| G1964A | G | A | G | 27 | 29.67 | D25N | |
| A2074G | A | A | A | 2 | 2.20 | T61T | |
| A2091C | A | A | A | 1 | 1.10 | N67T | |
| G2129A | G | G | G | 2 | 2.20 | E80K | |
| G2204A | G | G | G | 5 | 5.49 | A105T | |
| C2295A | A | A | A | 34 | 37.36 | T135K | |
| G2315A | G | G | G | 1 | 1.10 | E142D | |
| T2341C | T | T | T | 2 | 2.20 | G150G | |
| G2369T | G | G | G | 1 | 1.10 | V160F | |
| G2385A | A | A | A | 29 | 31.87 | R165Q | |
| T2410G | T | T | T | 13 | 14.29 | D173E | |
| G2504A | G | G | G | 1 | 1.10 | V205I | Hinge region |
| C2511T | C | C | C | 1 | 1.10 | S207F | |
| T2520C | T | C | T | 22 | 24.18 | I210T | |
| C2546T/A | T | T | T | 70 | 76.92 | P219S/T | |
| G2585A | A | A | A | 19 | 20.88 | E232K | |
| A2587C | A | A | A | 1 | 1.10 | E232K | |
| T2660C | T | C | T | 17 | 18.68 | L257L | |
| T2703G | T | T | T | 1 | 1.10 | F271V | |
| C2820A | A | A | A | 25 | 27.47 | T310K | DNA binding domain |
| C2923A | A | A | A | 4 | 4.40 | D344E | |
| C2934T | C | C | C | 1 | 1.10 | S348F | |
| T2956C | T | T | T | 1 | 1.10 | T355T | |
| T2983C | T | T | T | 9 | 9.89 | S364S | |
AA: Asian–American lineage, As: Asian lineage, Af: African lineage
Among the 165 HPV16 positive samples, 109 samples with HPV16 E1 variation and 48 sites with nucleotide variation were included, including 19 missense variations and 29 synonymous variations. The sample numbers of the HPV16 E1 nucleotide variation sites shown in Table 2 above for more than one missense variation are T98C, A117C, A189C, G299A, T557C, T658A, T779C, A978G, A1068C, G1473A. Variation sites and mutation frequency are shown in the Table 2. The most common nucleotide variation sites for HPV16 E1 were A189C (18/109, 16.5%), T57C (31/109, 28.4%), A978G (35/109, 32.1%), and G1473A (30/109, 27.5%). Among the 109 mutated samples, 29 sites with synonymous variations were found, including nt (nucleotide)105 (T–C) (1/109), nt195 (G–A) (3/109), nt252 (G–A) (1/109), nt256 (C–T) (1/109), nt288 (T–C) (1/109), nt519 (T–C) (1/109), nt531 (A–T) (1/109), nt583 (T–C) (1/109), nt600 (T–C) (2/109), nt651 (G–A) (62/109), nt723 (T–C) (3/109), nt939 (T–C) (1/109), nt945 (A–G) (1/109), nt969 (A–G) (1/109), nt1177 (C–T) (1/109), nt1294 (A–C) (5/109), nt1369 (T–C) (5/109), nt1374 (T–G) (1/109), nt1380 (A–G) (1/109), nt1390 (T–C) (15/109), nt1437 (T–C) (2/109), nt1479 (T–C) (1/109), nt1480 (C–T) (28/109), nt1512 (T–G) (2/109), nt1528 (T–C) (1/109), nt1539 (C–T) (1/109), nt1683 (A–G) (1/109), nt1687 (T–C) (1/109), and nt1731 (T–G) (3/109). In addition, there was a 63-base insertion sequence between nt510 and 511 in 32 samples (32/109, 29.4%).
Among the 165 HPV16 positive samples, 91 samples with HPV16 E2 variation and 25 sites with nucleotide variation were selected, including 20 missense variations and five synonymous variations. The sample numbers of HPV16 E2 nucleotide variation sites shown in Table 3 above are for those with more than one missense variation in the transactivation domain of HPV16 E2: G1964A (27/91), G2129A (2/91), G2204A (5/91), C2295A (34/91), G2385A (29/91), T2410G (13/91). Amino acids were, respectively, converted from aspartic acid to asparagine (D25N), glutamic acid to lysine (E80K), alanine to threonine (A105T), threonine to lysine (T135K), arginine to glutamine (R165Q), and aspartic acid to glutamic acid (D173E). The variants of T2520C (22/91), C2546T (41/91), C2564A (29/91) and G2585A (19/91) are located in the hinge region of HPV16 E2, with amino acids converted from isoleucine to threonine (I210T), proline to serine/threonine (P219S/T), and glutamic acid to lysine (E232K), respectively. The variants of C2820A (25/91) and C2923A (4/91) are located in the DNA binding domain of HPV16 E2, with the amino acids converted from threonine to lysine (T310K) and aspartic acid to glutamic acid (D344E), respectively. One sample each had variations at C1901T, A2091C, G2315A, G2369T, G2504A, C2511T, A2587C, T2703G, and C2934T. The amino acid changes were leucine to phenylalanine (L4F), aspartic acid to threonine (N67T), glutamic acid to aspartic acid (E142D), valine to phenylalanine (V160F), valine to isoleucine (V205I), serine to phenylalanine (S207F), glutamic acid to lysine (E232K), phenylalanine to valine (F271V), and serine to phenylalanine (S348F). The most common nucleotide variation sites for HPV16 E2 were G196A (27/91, 29.7%), C2295A (34/91, 37.4%), G2385A (29/91, 31.9%), C2546T (41/91, 45.1%), and C2564A (29/91, 31.9%). Among the 91 mutated samples of HPV16 E2, the sites of synonymous variation were NT 2074 (A–G) (2/91), NT 2341 (T–C) (2/91), NT 2660 (T–C) (17/91), NT 2956 (T–C) (1/91) and NT 2983 (T–C) (9/91).
Phylogenetic tree analysis of nucleotide sequence of HPV16 E1 and E2
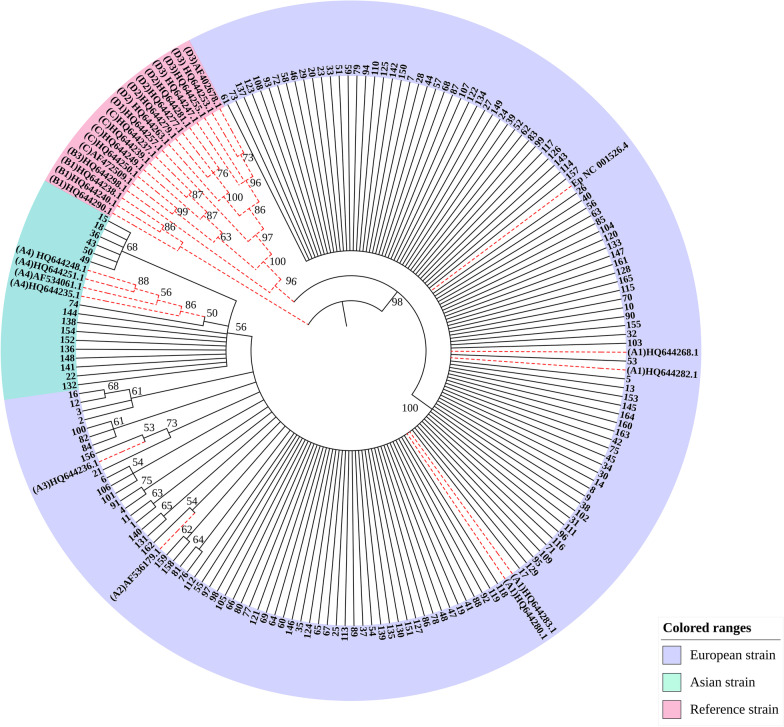
The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the N-J (neighbor-joining) method, the bootstrap method (1000 replications), and the Kimura two-parameter model. A bootstrap value > 50% indicates credibility, and a bootstrap value > 70% indicates high credibility. The nodes with bootstrap value < 50% were hidden in the evolutionary tree diagram in Fig. 1. From the phylogenetic tree results, 149 samples were European strains and 16 were Asian strains. No African or North American/Asian strains were found. The variations in European strain samples 6, 101, and 106 were shown to be all associated with the A117C variation by constructing a phylogenetic tree analysis of the nucleotide sequence of the HPV16 variant. The variations in samples 15, 18, 36, 43, 49, and 50 were all associated with the T2410G variation and all were Asian strains.
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic tree analysis of HPV16 E1 and E2 genes
Genetic variation of genomic HPV16 E1 in case and control groups
Samples with pathological information were counted, including 66 cases in normal group and 50 cases in cervical cancer group. All listed in the Table 4 are misspelled variations. There were 9 variations in the normal group and 11 variations in the cancer group. The variation of two sites showed that there was significant difference between the case group and the control group (P < 0.05). They are A978G(P = 0.047) and G1473A(P < 0.001), The amino acid changes were I326M and M491I, respectively. The E1 protein is a viral replication protein conserved in papillomaviruses, and plays roles in inducing the DNA damage response and disturbing the normal cell cycle, depending on its DNA binding and ATPase/helicase domains [20]. The difference between the case group and the control group can further explain that the variations at these two sites may promote the expression of replication protein E1, thus reducing the host cell defense capacity, and finally leading to the occurrence and development of cervical cancer.
Table 4.
Genetic variation of genomic HPV16 E1 in case and control groups
| Structural domain | Control groups (n = 66) | Case (n = 50) | P-values | Amino acid change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of variation samples | Variation frequency (%) | Number of variation samples | Variation frequency (%) | |||
| T98C | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 4.0 | 0.101 | I33T |
| A117C | 1 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.382 | E39D |
| A189C | 3 | 4.5 | 7 | 14.0 | 0.072 | E63D |
| G299A | 1 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.382 | G100E |
| T557C | 6 | 9.1 | 8 | 16.0 | 0.258 | I186T |
| T779C | 1 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.382 | L260S |
| A978G | 14 | 21.2 | 19 | 38.0 | 0.047 | I326M |
| A1030G | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 2.0 | 0.249 | T344A |
| A1068C | 3 | 4.5 | 6 | 12.0 | 0.137 | E356D |
| G1171T | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 2.0 | 0.249 | A391S |
| G1473A | 7 | 10.6 | 22 | 44.0 | < 0.001 | M491I |
| C568T | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 2.0 | 0.249 | P190S |
| A844T | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 2.0 | 0.249 | K282* |
| C1901G | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 2.0 | 0.249 | S634C |
| C1907A | 1 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.382 | P636Q |
Genetic variation of genomic HPV16 E2 in case and control groups
Table 5 shows the HPV16 E2 gene variation in normal group and cervical cancer group. All listed in the Table 5 are missense variations. There were 13 variations in the normal group and 16 variations in the cancer group. The variation of some sites showed that there was significant difference between the case group and the control group (P < 0.05). HPV16 E2 variations located at site G1964A (P = 0.017), C2295A (P = 0.009) and G2385A (P = 0.004) in the transactivation domain, The amino acid changes were D25N, T135K and R165Q, respectively. The sites T2520C (P = 0.002), C2546T (P < 0.001) and G2585A (P = 0.009) in hinge region, with corresponding amino acid changes of I210T, P219S and E232K, respectively. The sites C2820A (P = 0.002), C2873T (P = 0.044) and C2923A (P = 0.001) in DNA binding domain, the amino acid changes were T310K, H328Y and D344E. Since the E1 protein binds to the trans-activation domain of the E2 protein and co-localizes at the start site of transcription, it co-regulates viral transcription [21, 22], The variation of hinge region and DNA binding domain will affect the binding of E2 protein to LCR and inhibit the expression of E6 and E7 protein [23].
Table 5.
Genetic variation of genomic HPV16 E2 in case and control groups
| Structural domain | Variant site | Control groups (n = 66) | Case (n = 50) | P-values | Amino acid change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of variation samples | Variation frequency (%) | Number of variation samples | Variation frequency (%) | ||||
| Transcriptional activation domain | G1964A | 10 | 15.2 | 17 | 34.0 | 0.017 | D25N |
| G2204A | 2 | 3.0 | 2 | 4.0 | 0.777 | A105T | |
| C2295A | 11 | 16.7 | 19 | 38.0 | 0.009 | T135K | |
| G2315A | 1 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.382 | E142D | |
| G2385A | 7 | 10.6 | 16 | 32.0 | 0.004 | R165Q | |
| T2394A | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 2.0 | 0.249 | I168Y | |
| T2410G | 5 | 7.6 | 7 | 14.0 | 0.261 | D173E | |
| Hinge region | T2520C | 7 | 10.6 | 17 | 34.0 | 0.002 | I210T |
| C2546T | 17 | 25.8 | 36 | 72.0 | < 0.001 | P219S | |
| G2585A | 8 | 12.1 | 16 | 32.0 | 0.009 | E232K | |
| G2621C | 1 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.382 | E244Q | |
| A2636C | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 2.0 | 0.249 | N249H | |
| T2672C | 3 | 4.5 | 4 | 8.0 | 0.439 | S261P | |
| T2703G | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 4.0 | 0.101 | F271V | |
| DNA binding domain | C2820A | 8 | 12.1 | 18 | 36.0 | 0.002 | T310K |
| C2873T | 0 | 0.0 | 3 | 6.0 | 0.044 | H328Y | |
| C2923A | 1 | 1.5 | 10 | 20.0 | 0.001 | D344E | |
| C2934G | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 4.0 | 0.101 | S348C | |
Discussion
Some nucleotide variations in HPV16 affect amino acid changes and may also affect protein expression, thus, affecting the development of cervical cancer. Most studies on HPV nucleotide polymorphism have focused on E6 and E7, and variation of E6 and E7 can affect the occurrence and development of cervical cancer [7]. Variations that destroy the ORF(open reading frame) of HPV16 E1 or E2 lead to a further increase in the immortalization potential of human keratinocytes [16]. There is a 63-base insertion sequence between nt510 and 511 of HPV16 E1, and this mutant is associated with viral oncogenic activity and viral integration [24]. Variation of T310K in the HPV16 E2 DNA binding domain may alter cellular transcription factors, where the E2 protein interacts with LCR, resulting in enhanced expression of E6 and E7 proteins [25]. E232K is a linked variation in the E2 hinge region of HPV 16 AS that enhances dose-dependent inhibition of LCR (Long control region) activity and may affect the potential of the virus to cause cancer [26].
Of the 165 samples with HPV16 infection analyzed in Xinjiang, 149 samples were European strains and 16 samples were Asian strains; no African or North American/Asian strains were found. Nucleotide variation of HPV16 E1 occurred in 109 samples with 48 variation sites, and the amino acids of 19 samples were changed. The most common nucleotide variation sites were A189C (18/109, 16.5%), T57C (31/109, 28.4%), A978G (35/109, 32.1%), and G1473A (30/109, 27.5%). The amino acid changes were E63D, I186T, I326M, and M491I, respectively. Sequence analysis of HPV16 E2 revealed that nucleotide variations occurred in 91 samples with 25 variation sites, of which 20 sites caused amino acid changes. The most common nucleotide variation sites of HPV16 E2 were G1964A (27/91, 29.7%), C2295A (34/91, 37.4%), G2385A (29/91, 31.9%), C2546T (41/91, 45.1%), and C2564A (29/91, 31.9%), with corresponding amino acid changes of D25N, T135K, R165Q and P219S/T, respectively. Two variants, C–T and C–A, occur in the nucleotide sequence nt2545. The variation in three samples was associated with the A117C (E39D) variation and in six samples was associated with the T2410G (D173E) variation. The nucleotide variations at sites G195A (3/109, 2.75%), G252A (1/109, 0.92%), A351C (1/109, 0.92%), T377C (1/109, 0.92%), T379C (1/109, 0.92%), T519C (1/109, 0.92%), C568T (1/109, 0.92%), T600C (2/109, 1.83%), T784A (1/109, 0.92%), A844T (1/109, 0.92%), T939C (1/109, 0.92%), A945G (1/109, 0.92%), A969G (1/109, 0.92%), and A1380G (1/109, 0.92%) have not been reported. HPV16 E2 variations located at site A2091C (1/91,1.10%) in the transactivation domain, G2129A (2/91,2.20%), G2204A (5/91,5.49%), G2369T (1/91,1.10%), A2587C (1/91, 1.10%), and T2956C in the DNA-binding domain (1/91, 1.10%) have not been reported, and there may be synergistic variations in G1964A, C2295A, G2385A, T2410G, T2520C, C2546T/A, G2585A, T2660C, and C2820A. The variation of some sites showed that there was significant difference between the case group and the control group (P < 0.05).In our research, the variation of two sites in E1 showed that there was significant difference between the case group and the control group (P < 0.05). They are A978G (P = 0.047) and G1473A (P < 0.001), The amino acid changes were I326M and M491I, respectively. HPV16 E2 variations located at site G1964A (P = 0.017), C2295A (P = 0.009) and G2385A (P = 0.004) in the transactivation domain, The amino acid changes were D25N, T135K and R165Q, respectively. The sites T2520C (P = 0.002), C2546T (P < 0.001) and G2585A (P = 0.009) in hinge region, with corresponding amino acid changes of I210T, P219S and E232K, respectively. The sites C2820A (P = 0.002), C2873T (P = 0.044) and C2923A (P = 0.001) in DNA binding domain, the amino acid changes were T310K, H328Y and D344E.These base variations will lead to amino acid variations, which may affect the expression of proteins. In the future, we will study the role of HPV16E1 and E2 variants in the occurrence and development of cervical cancer based on experiments studying cell function.
Conclusion
From the phylogenetic tree results, 149 samples were of the European variant and 16 samples were of Asian variant type. No African or North American/Asian variant types were found.
Materials and methods
Collection of samples
A total of 165 HPV16 positive samples were collected from exfoliated cervical cells of women with cervical lesions at Yili Friendship Hospital, Kashi People's Hospital and Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region People's Hospital; informed consent was obtained from all patients. None of the patients had a history of long-term residence abroad. The samples were stored at − 80 °C.
DNA extraction and PCR amplification of samples
DNA extraction was carried out using a genomic DNA extraction kit (Shanghai Sangon Bio-logical Engineering Technology and Services Company, Shanghai, China), and the extracted DNA was stored at – 20 °C. A 1 µl DNA sample was mass examined and its concentration estimated by 1% agarose electrophoresis; it was then diluted to a working concentration of 10–20 ng/µl. Samples without significant DNA bands were not diluted. The reaction mixture (20 µl) included 1 × HotStarTaq buffer, 2.0 mM Mg2+, 0.2 mM dNTP, 0.2 µM of each primer, 1 U HotStarTaq polymerase (Qiagen Inc.) and 1 µl template DNA. The cycling program was 95 °C for 5 min; 30 cycles × (94 °C for 45 s, 50 °C for 45 s, 7 °C for 1 min); 72 °C for 5 min; 4 °C to finish. The PCR product could be stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C. PCR primer information is shown in Table 1.
Sequencing
Sequencing was performed by Shanghai Tianhao Technology Co., Ltd., and the PCR product was purified by SAP (Promega) and EXO I (Epicentre): 0.5 U SAP and 4 U Exo I were added to 8 µl PCR products. The mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 60 min, followed by incubation at 75 °C for 15 min. Finally, the BIG-DYE Terminator V3.1 cycle sequencing kit from ABI Co. was used for sample sequencing on a DNA analyzer (ABI3130XL) after purification with alcohol. The sequencing primers were: E-1R: 5′-ACTGCAACCACCCCCACT-3′, E-2R: 5′-ATCCATTCTGGCGTGTCTCC-3′, E-3F: 5′-TCATGGGGAATGGTTGTGTT-3′, E-4F: 5′-GGTGATTGGAAGCAAATTGTTATG-3′, E-5R: 5′-CCCGCATGAACTTCCCATAC-3′, E-6F: 5′-GAAGCATCAGTAACTGTGGTAGAGG-3′, as shown in Table 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of HPV16 variants
The sequencing results were analyzed for single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) using the Polyphred software, compared to the European standard prototype (GenBank: NC_001526.2) and compared to other typical HPV variants: HQ644283.1 (A1), HQ644268.1 (A1), HQ644280.1 (A1), HQ644282.1 (A1), AF536179.1 (A2), HQ644236.1 (A3), HQ644248.1 (A4), HQ644251.1 (A4), AF534061.1 (A4), HQ644235.1 (A4), HQ644240.1 (B1), HQ644290.1 (B1), HQ644238.1 (B1), HQ644298.1 (B3), HQ644237.1 (C), HQ644239.1 (C), HQ644249.1 (C), HQ644250.1 (C), AF472509.1 (C), HQ644257.1 (D1), HQ644279.1 (D2), HQ644281.1 (D2), HQ644263.1 (D2), HQ644277.1 (D2), HQ644247.1 (D3), HQ644253.1 (D3), HQ644255.1 (D3), AF402678.1 (D3). The evolutionary tree was constructed using MEGA7.
Statistical analysis
The frequency of each mutation in the HPV16 E1 and E2 genes was determined by direct enumeration. A chi-square test was performed to determine the association between HPV16 E1, E2 variants and cervical cancer. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 17. P-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Yili Friendship Hospital, Kashi People's Hospital and Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region People's Hospital for the samples.
Authors' contributions
ZP designed the study. LW and FW carried out the molecular genetic studies, participated in the genetic analysis and wrote the manuscript. SF and CZ carried out specimen collection and DNA extraction. XZ carried out HPV16 identification. HL, DL and RS participated in experimental design and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers: 82060518, U1503125), International Science and Technology Collaboration Projector of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps (grant numbers 2019BC007).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the NCBI GenBank repository,GenBankID:MZ151424/MZ151425.[link:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/MZ151424, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/MZ151425].
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the ethics committees of the First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University. (Approval Number: KJ2020-051-01, date:2020.3.28). And informed consent was obtained from all patients for our research.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Luyue Wang, Fang Wang and Shaowei Fu have contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
Luyue Wang, Email: 1476735045@qq.com.
Fang Wang, Email: 2419337671@qq.com.
Shaowei Fu, Email: 541631656@qq.com.
Chunhe Zhang, Email: 1134650061@qq.com.
Xiangyi Zhe, Email: 342480821@qq.com.
Hongtao Li, Email: 1152443029@qq.com.
Dongmei Li, Email: lidong_abc@126.com.
Renfu Shao, Email: rshao@usc.edu.au.
Zemin Pan, Email: panteacher89@sina.com.
References
- 1.Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Arbyn M, Weiderpass E, Bruni L, de Sanjosé S, Saraiya M, Ferlay J, et al. Estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: a worldwide analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2020;8(2):e191–e203. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30482-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Di J, Rutherford S, Chu C. Review of the cervical cancer burden and population-based cervical cancer screening in China. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prevent. APJCP. 2015;16(17):7401–7407. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.17.7401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wang J, Tang D, Wang K, Wang J, Zhang Z, Chen Y, et al. HPV genotype prevalence and distribution during 2009–2018 in Xinjiang, China: baseline surveys prior to mass HPV vaccination. BMC Womens Health. 2019;19(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12905-019-0785-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brant AC, Menezes AN, Felix SP, Almeida LM, Moreira MAM: Preferential expression of a HPV genotype in invasive cervical carcinomas infected by multiple genotypes. Genomics 2020; 112(5). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 6.Cornet I, Gheit T, Franceschi S, Vignat J, Burk RD, Sylla BS, et al. Human papillomavirus type 16 genetic variants: phylogeny and classification based on E6 and LCR. J Virol. 2012;86(12):6855–6861. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00483-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhe X, Xin H, Pan Z, Jin F, Zheng W, Li H, et al. Genetic variations in E6, E7 and the long control region of human papillomavirus type 16 among patients with cervical lesions in Xinjiang. China Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:65. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0774-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pan Z, Song Y, Zhe X, Wang W, Zhu J, Zheng W, et al. Screening for HPV infection in exfoliated cervical cells of women from different ethnic groups in Yili, Xinjiang, China. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):3468. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39790-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Seedorf K, Oltersdorf T, Krämmer G, Röwekamp W. Identification of early proteins of the human papilloma viruses type 16 (HPV 16) and type 18 (HPV 18) in cervical carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1987;6(1):139–144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Amaro-Filho SM, Pereira Chaves CB, Felix SP, Basto DL, de Almeida LM, Moreira MAM. HPV DNA methylation at the early promoter and E1/E2 integrity: a comparison between HPV16, HPV18 and HPV45 in cervical cancer. Papillomavirus Res. (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 2018;5:172–179. doi: 10.1016/j.pvr.2018.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Melendy T, Sedman J, Stenlund A. Cellular factors required for papillomavirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1995;69(12):7857–7867. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.12.7857-7867.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McBride AA, Romanczuk H, Howley PM. The papillomavirus E2 regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(28):18411–18414. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)55073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.McBride AA. The papillomavirus E2 proteins. Virology. 2013;445(1–2):57–79. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.06.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Evans MR, James CD, Bristol ML, Nulton TJ, Wang X, Kaur N et al: Human Papillomavirus 16 E2 regulates keratinocyte gene expression relevant to cancer and the viral life cycle. J Virol. 2019; 93(4). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Filho SMA, Bertoni N, Brant AC, Vidal J, Felix SP, Cavalcanti SMB, et al. Methylation at 3'LCR of HPV16 can be affected by patient age and disruption of E1 or E2 genes. Virus Res. 2017;232:48–53. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2017.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tsakogiannis D, Ruether I, Kyriakopoulou Z, Pliaka V, Theoharopoulou A, Skordas V, et al. Sequence variation analysis of the E2 gene of human papilloma virus type 16 in cervical lesions from women in Greece. Adv Virol. 2012;157(5):825–832. doi: 10.1007/s00705-012-1236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bristol ML, Wang X, Smith NW, Son MP, Evans MR, Morgan IM: DNA Damage Reduces the Quality, but Not the Quantity of Human Papillomavirus 16 E1 and E2 DNA Replication. Viruses. 2016; 8(6). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Yao Y, Yan Z, Dai S, Li C, Yang L, Liu S, et al. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E1 Mutations Associated with Cervical Cancer in a Han Chinese Population. Int J Med Sci. 2019;16(7):1042–1049. doi: 10.7150/ijms.34279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dai S, Yao Y, Yan Z, Zhou Z, Shi L, Wang X, et al. The association of human papillomavirus type 16 E2 variations with cervical cancer in a Han Chinese population. Infect Genet Evol J Mol Epidemiol Evol Genet Infect Dis. 2018;64:241–248. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fradet-Turcotte A, Bergeron-Labrecque F, Moody CA, Lehoux M, Laimins LA, Archambault J. Nuclear accumulation of the Papillomavirus E1 helicase blocks S-phase progression and triggers an ATM-dependent DNA damage response. J Virol. 2011;85(17):8996–9012. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00542-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kasukawa H, Howley PM, Benson JD. A fifteen-amino-acid peptide inhibits human papillomavirus E1–E2 interaction and human papillomavirus DNA replication in vitro. J Virol. 1998;72(10):8166–8173. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.10.8166-8173.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lusky M, Hurwitz J, Seo YS. Cooperative assembly of the bovine papilloma virus E1 and E2 proteins on the replication origin requires an intact E2 binding site. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(21):15795–15803. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)82325-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Villa LL, Schlegel R. Differences in transformation activity between HPV-18 and HPV-16 map to the viral LCR-E6-E7 region. Virology. 1991;181(1):374–377. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90507-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sabol I, Matovina M, Gasperov NM, Grce M. Identification of a novel human papillomavirus type 16 E1 gene variant with potentially reduced oncogenicity. J Med Virol. 2008;80(12):2134–2140. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cheung JLK, Cheung T-H, Yu MY, Chan PKS. Virological characteristics of cervical cancers carrying pure episomal form of HPV16 genome. Gynecol Oncol. 2013;131(2):374–379. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2013.08.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hang D, Gao L, Sun M, Liu Y, Ke Y. Functional effects of sequence variations in the E6 and E2 genes of humanpapillomavirus 16 European and Asian variants. J Med Virol. 2014;86(4):618–626. doi: 10.1002/jmv.23792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the NCBI GenBank repository,GenBankID:MZ151424/MZ151425.[link:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/MZ151424, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/MZ151425].