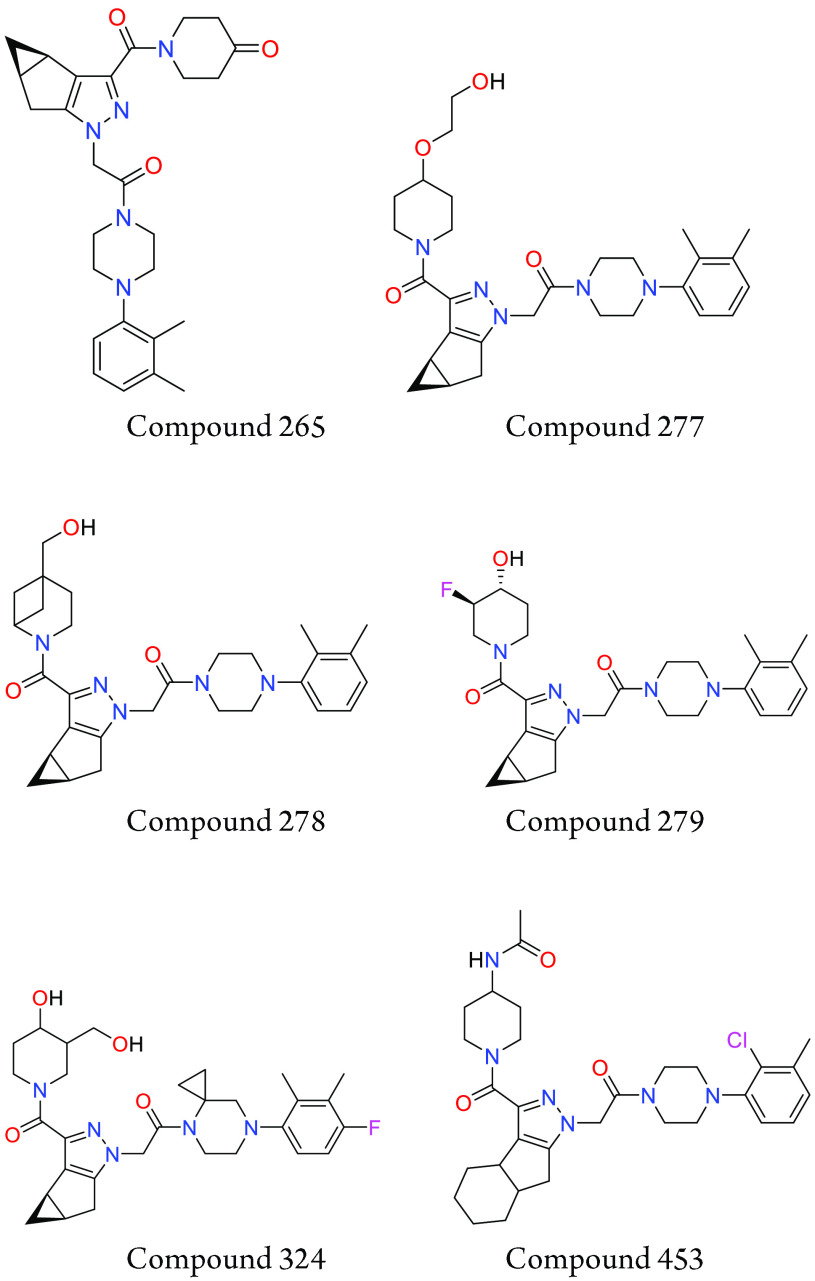
Important Compound Classes

Title
Novel Substituted Piperazine Amide Compounds as Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) Inhibitors
Patent Publication Number
WO 2020/112581 A1
Publication Date
June 4, 2020
Priority Application
US 62/772,357
Priority Date
November 28, 2018
Inventors
Clausen, D.; Chen, P.; Fradera, X.; Guo, L.; Han, Y.; He, S.; Huang, X.; Kozlowski, J.; Li, G.; Martinot, T. A.; Pasternak, A.; Verras, A.; Xiao, L.; Yu, W.; Zhang, R.; Ye, F.
Assignee Company
Merck, Sharp & Dohme Corp., USA
Disease Area
Cancer, viral infection, HCV infection, age-related cataracts, depression, neurodegenerative disorders, organ transplantation and autoimmune diseases
Biological Target
Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)
Summary
Tryptophan (Trp) is an essential amino acid required for the biosynthesis of proteins, niacin, and the neurotransmitter 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). The enzyme indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the degradation of l-tryptophan to N-formyl-kynurenine. IDO activity has an antiproliferative effect on many tumor cells.
It has been observed that HeLa cells cocultured with peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) acquire an immune-inhibitory phenotype through up-regulation of IDO activity. Several lines of evidence suggest that IDO is involved in induction of immune tolerance. Studies of mammalian pregnancy, tumor resistance, chronic infections, and autoimmune diseases have shown that cells expressing IDO can suppress T-cell responses and promote tolerance. High levels of IDO were observed in cells isolated from the synovia of arthritic joints. IDO inhibition can enhance the levels of virus-specific T-cells and, concomitantly, reduce the number of virally infected macrophages in a mouse model of HIV.
Considering the potential role of IDO in immunosuppression, tumor resistance, chronic infections, HIV infection, AIDS, autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis), immunologic tolerance, and prevention of fetal rejection in utero, therapeutic agents aimed at suppression of tryptophan degradation by inhibiting IDO activity are desirable. Inhibition of IDO may also be important treatment strategy for patients with depression.
The present application describes a series of novel substituted piperazine amide compounds as indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer, viral infection, HCV infection, age-related cataracts, depression, neurodegenerative disorders, organ transplantation, and autoimmune diseases. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
A = −O– and −CRgRg, wherein Rg is selected from H, halogen, OH and C1–6 alkyl, optionally substituted with 1–4 halogens;
Ra = H and C1–6 alkyl;
Rb = H, halogen, and C1–6 alkyl, optionally substituted with 1–4 halogens;
Rc = H, halogen, OH and C1–6 alkyl, optionally substituted with 1–4 halogens;
Rd = H, and C1–6 alkyl, optionally substituted with 1–4 halogens;
R1 and R2 = together with N to which they are attached form a 4–10 membered monocyclic, fused bicyclic, spiro bicyclic or bridged bicyclic heterocyclyl containing one N to which they are attached and 0–2 additional heteroatoms selected from N, S, and O, wherein heterocyclyl is optionally substituted with 1–4 substituents selected from halogen, OH, and C1–6 alkyl, optionally substituted with 1–4 substituents selected from halogen, OH, −O-C1–6 alkyl, NH2, −N(C1–6 alkyl)(C1–6 alkyl), −C(O)-NReRe, wherein Re is selected from H and C1–6 alkyl, and heterocyclyl;
R3 = C6−10 carbocyclyl and heterocyclyl, wherein carbocyclyl and heterocyclyl is optionally substituted with 1−4 substituents selected from halogen, C1–6 alkyl, optionally substituted with 1–4 halogens, −O-C1–6 alkyl, optionally substituted with 1–4 halogens, CN and C3–6 cycloalkyl, optionally substituted with C1–6 alkyl; and m = 1, 2 or 3.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The IDO1 cellular assay in HeLa cells with IFNγ was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit IDO1. The IDO1 IC50 (nM) are shown in the following table.
Biological Data
The table below shows representative
compounds were tested for IDO1 inhibition. The biological data obtained
from testing representative examples are listed in the following table.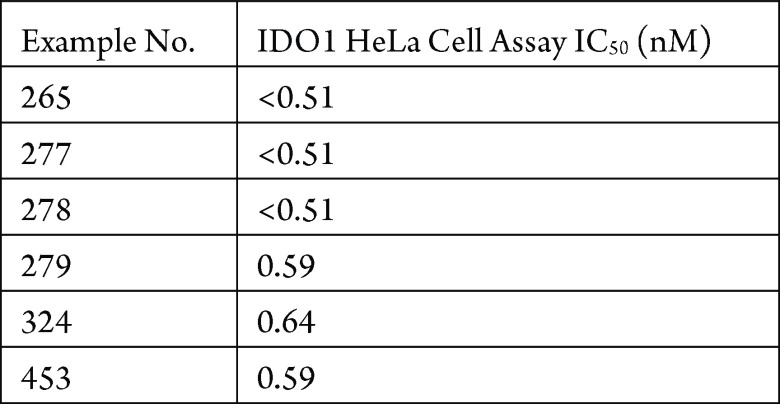
Claims
Total claims: 26
Compound claims: 19
Composition claims: 1
Method of treating claims: 5
Use of compound claims: 1
-
1.
Dolsak A.; Gobec S.; Sova M.. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 221, 107746.
-
2.
Singh R.; Salunke D. B.. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 211, 113071.
-
3.
Wells G.; Kennedy P. T.; Dahal L. N.. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 651687.
-
4.
Guo Y.; Liu Y.; Wu W.; Ling D.; Zhang Q.; Zhao P.; Hu X.. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121018.
-
5.
Chen S.; Tan J.; Zhang A.. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 110, 104815.
-
6.
Platten M.; Friedrich M.; Wainwright D. A.; Panitz V.; Opitz C. A.. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2021, 70, 57.
The author declares no competing financial interest.