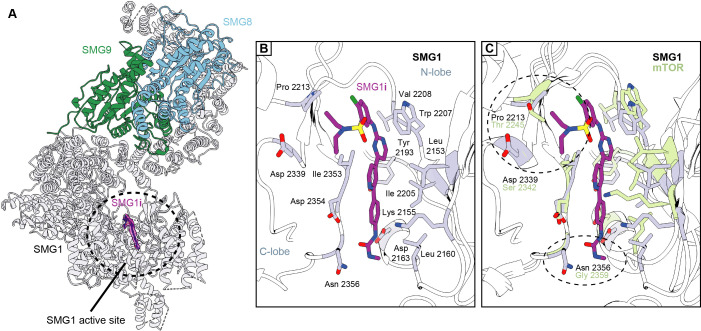
Figure 2. Structural basis for selective targeting of SMG1 by the SMG1 inhibitor.
(A) Model of the SMG1-8-9 kinase complex bound to SMG1i. SMG1 is in gray, SMG8 is in blue, and SMG9 is shown in green. SMG1i is shown as a magenta model overlaid with the isolated transparent density. Approximate location of the SMG1 active site is indicated by a black circle. (B) Key interactions of SMG1i with SMG1 active site residues. Important residues located in either the N- or the C-lobe of the SMG1 kinase domain are colored gray. Other parts of SMG1 are transparent and interactions of SMG1i with SMG1 backbone are not shown. (C) Superposition of SMG1i-bound SMG1 with the mTOR active site (PDB identifier: 4JSP) over the catalytic loops of both kinases. Key SMG1 residues indicated in (B) are shown alongside the respective mTOR residues colored in green. Regions possibly accounting for preferential interaction of SMG1i with SMG1 over mTOR are circled and the relevant residues are labeled.